Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Tugas 7
Transféré par
The Legend AtlanticTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Tugas 7
Transféré par
The Legend AtlanticDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
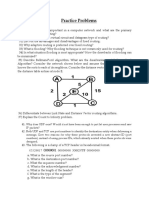
Exercises
1. Which fields of the IP header change from router to router?
2. Calculate the HLEN value if the total length is 1200 bytes, 1176 of which is data
from the upper layer.
3. Table 7.3 lists the MTUs for many different protocols. The MTUs range from 296
to 65,535. What would be the advantages of having a large MTU? What would be
the advantages of having a small MTU?
4. Given a fragmented datagram with an offset of 120, how can you determine the
first and last byte number?
5. An IP datagram must go through router 128.46.10.5. There are no other restrictions
on the routers to be visited. Draw the IP options with their values.
6. What is the maximum number of routers that can be recorded if the timestamp
option has a flag value of 1? Why?
7. Can the value of the header length in an IP packet be less than 5? When is it
exactly 5?
8. The value of HLEN in an IP datagram is 7. How many option bytes are present?
9. The size of the option field of an IP datagram is 20 bytes. What is the value of
HLEN? What is the value in binary?
10. The value of the total length field in an IP datagram is 36 and the value of the
header length field is 5. How many bytes of data is the packet carrying?
11. A datagram is carrying 1024 bytes of data. If there is no option information, what
is the value of the header length field? What is the value of the total length field?
12. A host is sending 100 datagrams to another host. If the identification number of the
first datagram is 1024, what is the identification number of the last?
13. An IP datagram arrives with fragmentation offset of 0 and an M bit (more fragment
bit) of 0. Is this a first fragment, middle fragment, or last fragment?
14. An IP fragment has arrived with an offset value of 100. How many bytes of data
were originally sent by the source before the data in this fragment?
15. An IP datagram has arrived with the following information in the header (in hexadecimal):
45 00 00 54 00 03 00 00 20 06 00 00 7C 4E 03 02 B4 0E 0F 02
a. Are there any options?
b. Is the packet fragmented?
c. What is the size of the data?
d. Is a checksum used?
e. How many more routers can the packet travel to?
f. What is the identification number of the packet?
g. What is the type of service?
16. In a datagram, the M bit is zero, the value of HLEN is 5, the value of total length is
200, and the offset value is 200. What is the number of the first byte and number of
the last byte in this datagram? Is this the last fragment, the first fragment, or a middle
fragment?
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Socket ProgrammingDocument1 pageSocket ProgrammingBuddhika GamagePas encore d'évaluation
- Questions: Tutorial Questions: Week 03 For Lecture 2: IP ProtocolsDocument2 pagesQuestions: Tutorial Questions: Week 03 For Lecture 2: IP ProtocolsDoan Tue TamPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet I: Exercise/review Questions On Introduction SectionDocument4 pagesWorksheet I: Exercise/review Questions On Introduction SectionAbraham GadissaPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Layer: Internet Protocol: Solutions To Review Questions and ExercisesDocument6 pagesNetwork Layer: Internet Protocol: Solutions To Review Questions and ExercisesMohammed MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Net331 Sheet 7Document4 pagesNet331 Sheet 7অন্তরা পাত্রPas encore d'évaluation
- HW10 SolDocument3 pagesHW10 SolTài LâmPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercises PDFDocument6 pagesExercises PDFMinh QuangPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesMultiple-Choice QuestionsmahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Forouzan Sol 20Document4 pagesForouzan Sol 20Anurag UpadhyayPas encore d'évaluation
- Student - ECTE992 - T2 - Solutions - For - L2 - IP Protocols PDFDocument4 pagesStudent - ECTE992 - T2 - Solutions - For - L2 - IP Protocols PDFDoan Tue TamPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Network Assignment 2Document2 pagesComputer Network Assignment 2vikash kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireshark Lab 4aDocument14 pagesWireshark Lab 4aTruonganh BaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 ExercisesDocument4 pagesChapter 8 ExercisesarrgantenPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Problems For Computer ComunicationsDocument3 pagesSample Problems For Computer ComunicationsFakrul HanifPas encore d'évaluation
- Home Agent (HA) :: Chapter - 1 1. What Is TTL in IP Header?Document9 pagesHome Agent (HA) :: Chapter - 1 1. What Is TTL in IP Header?Group ThreePas encore d'évaluation
- Work SheetDocument21 pagesWork SheetAbraham GadissaPas encore d'évaluation
- Logical Addreessing CNDocument100 pagesLogical Addreessing CNRohan singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1Document9 pagesLecture 1Abraham GadissaPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Layer: Internet Protocol: Stephen KimDocument48 pagesNetwork Layer: Internet Protocol: Stephen Kimnishasaiyed2304Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-3 - IPv4 and IPv6 - 5 PDFDocument45 pagesUnit-3 - IPv4 and IPv6 - 5 PDFsingh_arun7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 4 Udp + Lab 5 IpDocument11 pagesLab 4 Udp + Lab 5 IpLê Hoàng ChínhPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesPractice ProblemsPRAGASM PROGPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution: What Is The IP Address of Your Computer?Document6 pagesSolution: What Is The IP Address of Your Computer?Trần Nhật HuyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 4 IPDocument5 pagesLab 4 IPAnonymous VuWxWThPas encore d'évaluation
- 2024 03 11 0.6122554500679145Document9 pages2024 03 11 0.6122554500679145adgjmap1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Network Layer Protocols: Arp, Ipv4, Icmp, Ipv6, and Icmpv6: Review QuestionsDocument4 pagesNetwork Layer Protocols: Arp, Ipv4, Icmp, Ipv6, and Icmpv6: Review QuestionsRizqi FajrilPas encore d'évaluation
- Bui NhuiDocument2 666 pagesBui NhuiHải Đăng HàPas encore d'évaluation
- Nguyen Tien Dat - IpDocument5 pagesNguyen Tien Dat - IpĐạt NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- Internet Protocol Version 4Document5 pagesInternet Protocol Version 4AartiPas encore d'évaluation
- HCIA Routing and Switching MOCK TestDocument6 pagesHCIA Routing and Switching MOCK TestAuto 888Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1akttripathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Final SolDocument7 pagesFinal SolTài Lâm100% (4)
- Internetworking and IPDocument34 pagesInternetworking and IPRakshanda SavarnyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 18fall Csci368 Quiz SampleDocument3 pages18fall Csci368 Quiz SampleMahamad AliPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.7 Ipv4 Datagram: Presented By: Shubhangi DesaiDocument23 pages6.7 Ipv4 Datagram: Presented By: Shubhangi DesaiShubhangiPas encore d'évaluation
- IPv4 - IPv4 Header - IPv4 Header Format - Gate VidyalayDocument15 pagesIPv4 - IPv4 Header - IPv4 Header Format - Gate VidyalaySakshi TapasePas encore d'évaluation
- Tcp/Ip Protocol Suite Forth EditionDocument45 pagesTcp/Ip Protocol Suite Forth EditionFirhan FPas encore d'évaluation
- Names of student: -Nguyễn Tiến Đức -Trần Hoàng Đăng Khoa Class: 16DTCLC1 Subject: Computer NetworkingDocument17 pagesNames of student: -Nguyễn Tiến Đức -Trần Hoàng Đăng Khoa Class: 16DTCLC1 Subject: Computer NetworkingAnonymous EAPWaVHfYp100% (1)
- Navdeep, IPv4 Header FormatDocument11 pagesNavdeep, IPv4 Header Formatkaransharma17200Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd Term2011 SolvedDocument3 pages2nd Term2011 Solvedhj43usPas encore d'évaluation
- Ipv6 AddressDocument51 pagesIpv6 AddressWeb TestPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems TCP and UDPDocument2 pagesProblems TCP and UDPamit_coolbuddy20Pas encore d'évaluation
- CN 2nd Unit MCQ 200Document28 pagesCN 2nd Unit MCQ 200Mohanaprakash EcePas encore d'évaluation
- Document 2Document5 pagesDocument 2Souvik DebnathPas encore d'évaluation
- 06-Wireshark IP Solution July 22Document6 pages06-Wireshark IP Solution July 22Waqas JavedPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 3 W SolDocument13 pagesAssignment 3 W SolHamas RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Slide Network LayerDocument41 pagesLecture Slide Network LayerMuhibbullah MuhibPas encore d'évaluation
- Provides Application To Application DeliveryDocument7 pagesProvides Application To Application DeliveryAqib SheraziPas encore d'évaluation
- VersionDocument5 pagesVersionJoLiAshPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Questions For MCADocument4 pagesPractice Questions For MCAmanisha bhandariPas encore d'évaluation
- IT Networking and Communication: MITS4004Document15 pagesIT Networking and Communication: MITS4004madan GairePas encore d'évaluation
- Anmlab 67 5451074084 5451074092Document9 pagesAnmlab 67 5451074084 5451074092Quoc Vuong HoangPas encore d'évaluation
- Nguyễn Trâm Anh LAB5 IPDocument12 pagesNguyễn Trâm Anh LAB5 IPngiahuy1004Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2010 Tutorial8 SolutionsDocument3 pages2010 Tutorial8 Solutionsjante5000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ipv4 Internet Protocol (Ip)Document6 pagesIpv4 Internet Protocol (Ip)sunnys45Pas encore d'évaluation
- IPv4 HeaderDocument18 pagesIPv4 Headerjsk244807Pas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesD'EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesPas encore d'évaluation
- IPv4 Subnetting for Beginners: Your Complete Guide to Master IP Subnetting in 4 Simple Steps: Computer Networking, #1D'EverandIPv4 Subnetting for Beginners: Your Complete Guide to Master IP Subnetting in 4 Simple Steps: Computer Networking, #1Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Networking BasicsDocument60 pagesNetworking BasicsShubhra Pahwa GoelPas encore d'évaluation
- Access Control List: ACL'sDocument31 pagesAccess Control List: ACL'sTolosa TafesePas encore d'évaluation
- CN - MID-1 - Quiz PaperDocument2 pagesCN - MID-1 - Quiz PaperAmbica AnnavarapuPas encore d'évaluation
- MTCNA Certified Training and Exam in Karachi, PakistanDocument6 pagesMTCNA Certified Training and Exam in Karachi, PakistanMuhammad ShoaibPas encore d'évaluation
- RRAS TutorialDocument10 pagesRRAS TutorialruletriplexPas encore d'évaluation
- Huawei AirEngine 8760-X1-PRO Access Point DatasheetDocument15 pagesHuawei AirEngine 8760-X1-PRO Access Point Datasheetsabry KhalilPas encore d'évaluation
- F5 Profile TypesDocument2 pagesF5 Profile TypeszayalaksmePas encore d'évaluation
- XML Signature Syntax and ProcessingDocument53 pagesXML Signature Syntax and ProcessingHelen GrayPas encore d'évaluation
- May.08 07226-1-Final: Intel Cantiga-GMDocument62 pagesMay.08 07226-1-Final: Intel Cantiga-GMAnubys 365Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ip SpoofingDocument14 pagesIp Spoofingvikram kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- ASNT Ultra Sonic TestingDocument98 pagesASNT Ultra Sonic TestingKiran NikatePas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas 1 Pertemuan 6 1811510211 Dani Tri MujiantoDocument5 pagesTugas 1 Pertemuan 6 1811510211 Dani Tri MujiantoDani Tri MujiantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 11 PPT OSPFDocument84 pagesChapter 11 PPT OSPFhappy girl100% (2)
- ATM Adaptation LayerDocument33 pagesATM Adaptation LayerMubeen TajPas encore d'évaluation
- Syrotech Sy Gpon 1110 Wdaont Wont Optical Network UnitDocument6 pagesSyrotech Sy Gpon 1110 Wdaont Wont Optical Network UnitAbhay BaruahPas encore d'évaluation
- Pl1000e CatDocument1 pagePl1000e CatOmar Lorenzo Gonzalez MeloPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Experiments On Packet Tracer Module 1Document24 pagesNetwork Experiments On Packet Tracer Module 1anon_452653639Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco Notes 2Document6 pagesCisco Notes 2La PyaePas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument1 343 pagesUntitledamiral AïgoPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless Tips and Tricks For Routeros V6: Mum South Africa 2013 Johannesburg Uldis Cernevskis MikrotikDocument80 pagesWireless Tips and Tricks For Routeros V6: Mum South Africa 2013 Johannesburg Uldis Cernevskis Mikrotikh1934698Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ascent™ Control Module (ACM) : Technical DatasheetDocument3 pagesAscent™ Control Module (ACM) : Technical Datasheetvntung100% (1)
- ADB - PRG F4202N - A4 - DatasheetDocument2 pagesADB - PRG F4202N - A4 - DatasheetThanh NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- LTE F BandsDocument50 pagesLTE F BandsRajithRannPas encore d'évaluation
- EWAN PTAct 2 1 7Document3 pagesEWAN PTAct 2 1 7Lekan Mulana0% (1)
- Link Dahsyat Mei 2021Document2 pagesLink Dahsyat Mei 2021Hadi SuagungPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 7 (DHCP)Document2 pagesLesson 7 (DHCP)Jeff LacasandilePas encore d'évaluation
- Wi-Fi WPS Test Plan Wi-Fi AllianceDocument48 pagesWi-Fi WPS Test Plan Wi-Fi AllianceMarco LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Wireshark Lab: TCP: Approach, 6 Ed., J.F. Kurose and K.W. RossDocument12 pagesWireshark Lab: TCP: Approach, 6 Ed., J.F. Kurose and K.W. RossMaria Eduarda RosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Implementation of MPLS L3VPN Using GNS3: Akshay, Pooja AhlawatDocument5 pagesImplementation of MPLS L3VPN Using GNS3: Akshay, Pooja AhlawatYogesh KhollamPas encore d'évaluation
- Qos 6dscp ValDocument2 pagesQos 6dscp ValMarcos TokunagaPas encore d'évaluation