Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Suggested Topics Table For Edexcel Gcse Maths Paper 2 and Paper 3 Higher June 2017
Transféré par
api-3304579940 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
217 vues1 pageTitre original
suggested-topics-table-for-edexcel-gcse-maths-paper-2-and-paper-3-higher-june-2017
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
217 vues1 pageSuggested Topics Table For Edexcel Gcse Maths Paper 2 and Paper 3 Higher June 2017
Transféré par
api-330457994Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
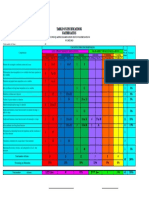
Suggested
Topics for Edexcel GCSE Maths Paper 2 and Paper 3 Higher June 2017
Number Algebra Ratio, Proportion and Rates of Change
BIDMAS (brackets) Forming expressions, formulae and equations (then solving) Ratio and proportion problems
2
Interpret calculator displays Substitution (v = u + at; s = ut + ½at ; v2 = u2 + 2as) Comparing quantities as a ratio and division of a quantity as a
Error intervals Gradient, mid-point and distance between two coordinates ratio
Converting metric units
Compare fractions, decimals and percentages Simplify algebraic indices
Solve proportion problems
Fractions and ratio problems Expand single and double brackets
Best buy problems
Recurring decimal to fraction (prove) nth term of a linear sequence
Scale drawings
Reverse fraction of an amount Linear equations (including variable on both sides)
Express one quantity as the percentage of another
Powers and roots Drawing graphs of linear functions
Percentage change
Multiples, factors, LCM and HCF Finding the equation of a line
Simple and compound interest and financial maths
Adding, subtracting, multiplying and diving fractions (problem) The equation of a tangent (to circle)
Compare lengths, area, volume
Writing in standard form and calculating with standard form Linear simultaneous equations (and graphically)
Speed, density, pressure
(calculator) Factorise single bracket
Upper and lower bounds (including calculations) Factorising quadratic expressions including where a > 1 Direct proportion
Simplify and manipulate surds Quadratic equations (including when needs re-arrangement) Non-standard real life graphs
Reciprocal real-life graphs
Recognise Fibonacci and quadratic sequences
Geometry and Measures Gradient of graphs
nth term of a quadratic sequence
Geometrical problems, alternate / corresponding angles and Distance-time and velocity-time graphs
angles in polygons Geometric Sequences
Perimeter and area of a triangle, parallelogram, and trapezium Drawing quadratic graphs Area under a graph
Area of a triangle using Area = ½absin C Rearranging Formulae (including when subject appears twice /
Perimeter of composite shapes factorising) Probability
Represent linear inequalities on number line and graphically Product rule
Circumference and area of a circle, arc length and perimeter
and area of a sector Solve linear inequalities and represent on number line and Relative frequency
Calculations using exact Pi graphically Sampling and unbiased samples
Represent quadratic inequalities graphically
Properties of 3D Shapes and plans and elevations Venn diagrams
Solving quadratic inequalities
Surface area and volume of prisms, pyramids, cones (not Frequency trees
volume) and spheres The Quadratic Formula
Probability trees for both independent events and conditional
Draw and identify transformations and combinations of Completing the square and turning points probability
transformations Draw and recognise reciprocal and cubic graphs
Pythagoras' Theorem (problem or in 3D, with trigonometry)
The equation of a circle (and graphical solution with linear Statistics
Trigonometric ratios (SOH CAH TOA), including in 3D equation simultaneously) Comparing data on statistical diagrams, including time series
Standard constructions using a compass (including triangles) Graphs of exponential functions and growth and decay graphs
Loci Graphical solution to equations (possibly quadratic) Mean from a discrete and grouped frequency table
Bearings Composite and inverse functions Constructing and interpreting a boxplot
Congruency and congruent triangles General iterative processes Drawing a CF graph and interpreting
Scale factors and similarity Algebraic fractions Comparing distributions; median and IQR (cumulative
frequency graph / box plots)
Circle Theorems Graphs of trigonometric functions Histograms
Sine Rule Translations and reflections of a graph and their functions
Cosine Rule (find angle)
Vectors
Based on the questions in Edexcel GCSE Maths Paper 1 Higher (examined Thursday 25 May), we have identified topics that have not yet been assessed and are likely to come up in Paper 2 and Paper 3.
Please note that the topics already assessed in Paper 1 could be assessed again, so use our list with that in mind when planning your revision. Do not focus all your revision time on these topics alone.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Practiced Paper 1H, 2H and 3H SkillsDocument1 pagePracticed Paper 1H, 2H and 3H SkillsTahmid SiraziPas encore d'évaluation
- Advance Information June 2022: GCSE Mathematics (8300)Document21 pagesAdvance Information June 2022: GCSE Mathematics (8300)safaPas encore d'évaluation
- Math SyllabusDocument2 pagesMath SyllabusYana Rico100% (1)
- Checklist c1Document3 pagesChecklist c1Arwa HamdiPas encore d'évaluation
- A Level Pure Maths Pure Topic ChecklistDocument2 pagesA Level Pure Maths Pure Topic ChecklistMahbub RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Afda Vocab Cards 2016Document141 pagesAfda Vocab Cards 2016Anderson Nascimento100% (1)
- Gcse Maths Essential RevisionDocument1 pageGcse Maths Essential RevisionHaider KarrarPas encore d'évaluation
- article_careers360_20240129080611Document7 pagesarticle_careers360_20240129080611Devara MithilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Comprehensive Revision Planner-Final (Both)Document8 pagesComprehensive Revision Planner-Final (Both)Naman HemrajaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Alg 2 Vocab Cards 2016Document150 pagesAlg 2 Vocab Cards 2016hshahahshsPas encore d'évaluation
- Alg 2 Vocab Cards 2016Document154 pagesAlg 2 Vocab Cards 2016Hatice A. GürhanoğluPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths KS5Document4 pagesMaths KS5georgia.cuzucPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebra, Functions, and Data Analysis Vocab CardsDocument143 pagesAlgebra, Functions, and Data Analysis Vocab CardsHatice A. GürhanoğluPas encore d'évaluation
- GCSE Maths Revision ChecklistDocument3 pagesGCSE Maths Revision Checklistsahib kainthPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision Checklist HigherDocument3 pagesRevision Checklist HigherMr Twum. Yep that’s mePas encore d'évaluation
- KS3 Maths Now Scheme of Work Year 8Document6 pagesKS3 Maths Now Scheme of Work Year 8Mahamed AbusnenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Santos, John Albert M. - Cee2 Activity No.3Document2 pagesSantos, John Albert M. - Cee2 Activity No.3John Albert SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Basic Math For AlgebraDocument72 pages1 Basic Math For AlgebraNilam Doctor100% (5)
- Ratios and ScaleDocument6 pagesRatios and ScaleNilam DoctorPas encore d'évaluation
- MYP Mathematics Framework: Numerical and Abstract Reasoning Thinking With Models Spatial Reasoning Reasoning With DataDocument3 pagesMYP Mathematics Framework: Numerical and Abstract Reasoning Thinking With Models Spatial Reasoning Reasoning With DataKarthikeya ShukklaPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic Lists - HigherDocument1 pageTopic Lists - HigherMinnie WhitingPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Plan Year 7Document1 pageCourse Plan Year 7Oladele FamesoPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Map 7mathDocument5 pagesCurriculum Map 7mathapi-485606042Pas encore d'évaluation
- Year 7Document8 pagesYear 7woyePas encore d'évaluation
- Form2 MathematicsDocument4 pagesForm2 MathematicsMichael HarrilalPas encore d'évaluation
- NDA Syllabus and BooklistDocument7 pagesNDA Syllabus and BooklistPriyanshu UpadhyayPas encore d'évaluation
- NDA Syllabus and BooklistDocument7 pagesNDA Syllabus and BooklistPriyanshu UpadhyayPas encore d'évaluation
- Alg 1 Vocab Cards 2016Document110 pagesAlg 1 Vocab Cards 2016Hatice A. GürhanoğluPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Map S.Y 2019 - 2020: St. Francis Xavier Academy of Kapatagan IncDocument7 pagesCurriculum Map S.Y 2019 - 2020: St. Francis Xavier Academy of Kapatagan Incjoan niniPas encore d'évaluation
- CAT Syllabus For MBA/IIM Preparation 2017: Topics Sub-TopicsDocument2 pagesCAT Syllabus For MBA/IIM Preparation 2017: Topics Sub-TopicsYugant RajPas encore d'évaluation
- New CRSDocument15 pagesNew CRSohdonna1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cur Map Sample 2Document3 pagesCur Map Sample 2GIL tabilingPas encore d'évaluation
- Every Topic On The Maths GCSE: Revision Checklist (Higher)Document2 pagesEvery Topic On The Maths GCSE: Revision Checklist (Higher)thomjeffPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 7.2 - Algebra I (Expressions and Equations)Document6 pagesUnit 7.2 - Algebra I (Expressions and Equations)guanajuato_christopherPas encore d'évaluation
- JEE Advanced 2018 Mathematics Crash Course - MathonGoDocument1 pageJEE Advanced 2018 Mathematics Crash Course - MathonGoNameet JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 7 2 Quarter Syllabus 2020-2021: Numbers Geometry Shapes and Measurements Unit 5: AnglesDocument1 pageClass 7 2 Quarter Syllabus 2020-2021: Numbers Geometry Shapes and Measurements Unit 5: AnglesAhmad AdnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Edexcel Further Pure Mathematics Term 1 GFSDocument1 pageEdexcel Further Pure Mathematics Term 1 GFSMohammed Aayan PathanPas encore d'évaluation
- SubjectPlanningTemplate - 2020 Grade 7 Maths With Resources AddedDocument4 pagesSubjectPlanningTemplate - 2020 Grade 7 Maths With Resources AddedpeterPas encore d'évaluation
- AS Maths Pure ChecklistDocument2 pagesAS Maths Pure Checklististvan.szaboPas encore d'évaluation
- Square Roots: Problem 1 of 6Document6 pagesSquare Roots: Problem 1 of 6Nilam DoctorPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Area Form 1 Form 2 Form 3Document1 pageLearning Area Form 1 Form 2 Form 3devinahPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus Expert TOCDocument10 pagesCalculus Expert TOCAnaLuManolePas encore d'évaluation
- U017 Edexcel GCSE Maths Chart P2Document1 pageU017 Edexcel GCSE Maths Chart P2al-gazPas encore d'évaluation
- Sat MathDocument1 pageSat Mathbaojia chenPas encore d'évaluation
- UoBS Mathematics Curriculum Outline 2023Document6 pagesUoBS Mathematics Curriculum Outline 2023Ummul BaneenPas encore d'évaluation
- Percentages: Problem 1 of 6Document6 pagesPercentages: Problem 1 of 6Nilam DoctorPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Quarter - Curriculum Map - Math 8Document6 pages1st Quarter - Curriculum Map - Math 8Grace Perez0% (2)
- TABLE OF SPECIFICATIONS FOR SECOND QUARTER EXAM IN MATH 8Document1 pageTABLE OF SPECIFICATIONS FOR SECOND QUARTER EXAM IN MATH 8Oscar EscaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Key Topics Edexcel Higher Paper 3Document4 pagesKey Topics Edexcel Higher Paper 3Ege IscanPas encore d'évaluation
- IIM CAT SYLLABUS COVERS ALGEBRA, QUANT, DI, LR AND VERBALDocument1 pageIIM CAT SYLLABUS COVERS ALGEBRA, QUANT, DI, LR AND VERBALamithbaluPas encore d'évaluation
- Pure Maths Guide - Welcome ChapterDocument10 pagesPure Maths Guide - Welcome ChapterLove of Maths100% (1)
- Algebra 2 - Patterns and Relationships Can Be Represented Numerically, Graphically, Symbolically, and VerballyDocument6 pagesAlgebra 2 - Patterns and Relationships Can Be Represented Numerically, Graphically, Symbolically, and VerballyKANPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 8 Math CurriculumDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Math CurriculumNamory DOSSOPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Progression Map AlgebraDocument2 pages6 Progression Map AlgebraSarah LilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Higher Revision ChecklistDocument1 pageHigher Revision ChecklistJones JonnyPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledapi-63318741Pas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledapi-63318741Pas encore d'évaluation
- IM Unit OverviewDocument1 pageIM Unit OverviewAheedam MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Subtracting Real NumbersDocument6 pagesSubtracting Real NumbersNilam DoctorPas encore d'évaluation
- School DemographicsDocument3 pagesSchool Demographicsapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Goal 8 Reflective AnalysisDocument2 pagesGoal 8 Reflective Analysisapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kelli Stiltz ResumeDocument2 pagesKelli Stiltz Resumeapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Goal 4 Reflective AnalysisDocument2 pagesGoal 4 Reflective Analysisapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Goal 6 Reflective AnalysisDocument2 pagesGoal 6 Reflective Analysisapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Goal 5 Reflective AnalysisDocument2 pagesGoal 5 Reflective Analysisapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Goal 1 Reflective AnalysisDocument3 pagesGoal 1 Reflective Analysisapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Goal 7 Reflective AnalysisDocument2 pagesGoal 7 Reflective Analysisapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Goal 2 Reflective AnalysisDocument2 pagesGoal 2 Reflective Analysisapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- How The Mat Impacted My TeachingDocument3 pagesHow The Mat Impacted My Teachingapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Integers Math GuideDocument2 pagesIntegers Math Guideapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Goal 3 Reflective AnalysisDocument2 pagesGoal 3 Reflective Analysisapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Intelligence Quiz: Logic Smart Body SmartDocument20 pagesMultiple Intelligence Quiz: Logic Smart Body Smartapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mi Fractions Decimals Percents Choice BoardDocument1 pageMi Fractions Decimals Percents Choice Boardapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Integers Pre-TestDocument2 pagesIntegers Pre-Testapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Integers Guided NotesDocument2 pagesIntegers Guided Notesapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sa of A Sphere Orange Discovery ActivityDocument3 pagesSa of A Sphere Orange Discovery Activityapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Integers Math GuideDocument2 pagesIntegers Math Guideapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sa of Spheres NotesDocument1 pageSa of Spheres Notesapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hands On Dividing Fractions Anchor ChartDocument1 pageHands On Dividing Fractions Anchor Chartapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Goal 10 Reflective AnalysisDocument2 pagesGoal 10 Reflective Analysisapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Back To School PennantDocument1 pageBack To School Pennantapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- ccss7 2017-2018 Curriculum NightDocument14 pagesccss7 2017-2018 Curriculum Nightapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Goal 9 Reflective AnalysisDocument2 pagesGoal 9 Reflective Analysisapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- T Charts 2016Document2 pagesT Charts 2016api-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Goal 11 Reflective AnalysisDocument2 pagesGoal 11 Reflective Analysisapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Category Exceeds 4 Meets 3 Approaches 2 Emergent 1: Required ElementsDocument1 pageCategory Exceeds 4 Meets 3 Approaches 2 Emergent 1: Required Elementsapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Parent Letter and HWDocument2 pagesParent Letter and HWapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Application Get To Know YouDocument2 pagesApplication Get To Know Youapi-330457994Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2019 Course CatalogDocument31 pages2019 Course CatalogDeepen SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- IEQ CompleteDocument19 pagesIEQ Completeharshal patilPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotary Twin Scew Brochure UK HRDocument20 pagesRotary Twin Scew Brochure UK HRNguyễn Hữu DũngPas encore d'évaluation
- Gotham City: A Study into the Darkness Reveals Dangers WithinDocument13 pagesGotham City: A Study into the Darkness Reveals Dangers WithinajPas encore d'évaluation
- Lathe - Trainer ScriptDocument20 pagesLathe - Trainer ScriptGulane, Patrick Eufran G.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Awakening The MindDocument21 pagesAwakening The MindhhhumPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypophosphatemic Rickets: Etiology, Clinical Features and TreatmentDocument6 pagesHypophosphatemic Rickets: Etiology, Clinical Features and TreatmentDeysi Blanco CohuoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sap ThufingteDocument10 pagesSap ThufingtehangsinfPas encore d'évaluation
- Sto - Cristo Proper Integrated School 1 Grading Grade 9 Science Table of SpecializationDocument2 pagesSto - Cristo Proper Integrated School 1 Grading Grade 9 Science Table of Specializationinah jessica valerianoPas encore d'évaluation
- PC3 The Sea PeopleDocument100 pagesPC3 The Sea PeoplePJ100% (4)
- 40 26Document3 pages40 26Maxi452Pas encore d'évaluation
- Space DynamicsDocument37 pagesSpace Dynamicspurushottam KashyapPas encore d'évaluation
- DNB Paper - IDocument7 pagesDNB Paper - Isushil chaudhari100% (7)
- Acuity Assessment in Obstetrical TriageDocument9 pagesAcuity Assessment in Obstetrical TriageFikriPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Arms S400 EXPDocument3 pagesAir Arms S400 EXPapi-3695814Pas encore d'évaluation
- CIRC 314-AN 178 INP EN EDENPROD 195309 v1Document34 pagesCIRC 314-AN 178 INP EN EDENPROD 195309 v1xloriki_100% (1)
- Lec9-Rock Cutting ToolsDocument35 pagesLec9-Rock Cutting ToolsAmraha NoorPas encore d'évaluation
- European GMP Annex 1 - 2008 Edition - 'Pmeasuring'Document3 pagesEuropean GMP Annex 1 - 2008 Edition - 'Pmeasuring'Khairul AnwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal BurnsDocument50 pagesThermal BurnsPooya WindyPas encore d'évaluation
- Seed SavingDocument21 pagesSeed SavingElectroPig Von FökkenGrüüven100% (2)
- Lesson 2 Socio Anthropological View of The SelfDocument12 pagesLesson 2 Socio Anthropological View of The SelfAilyn RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Patent for Fired Heater with Radiant and Convection SectionsDocument11 pagesPatent for Fired Heater with Radiant and Convection Sectionsxyz7890Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chain Surveying InstrumentsDocument5 pagesChain Surveying InstrumentsSachin RanaPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Week Heavy Slow Resistance Progression For Patellar TendinopathyDocument4 pages12 Week Heavy Slow Resistance Progression For Patellar TendinopathyHenrique Luís de CarvalhoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1010 PDS WLBP 170601-EN PDFDocument4 pages1010 PDS WLBP 170601-EN PDFIan WoodsPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 202: Di Fferential Equations: Course DescriptionDocument2 pagesMath 202: Di Fferential Equations: Course DescriptionNyannue FlomoPas encore d'évaluation
- Background of The Study Statement of ObjectivesDocument4 pagesBackground of The Study Statement of ObjectivesEudelyn MelchorPas encore d'évaluation
- IS 4991 (1968) - Criteria For Blast Resistant Design of Structures For Explosions Above Ground-TableDocument1 pageIS 4991 (1968) - Criteria For Blast Resistant Design of Structures For Explosions Above Ground-TableReniePas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Some Algal Filtrates and Chemical Inducers On Root-Rot Incidence of Faba BeanDocument7 pagesEffect of Some Algal Filtrates and Chemical Inducers On Root-Rot Incidence of Faba BeanJuniper PublishersPas encore d'évaluation
- Liquid Out, Temperature 25.5 °C Tube: M/gs P / WDocument7 pagesLiquid Out, Temperature 25.5 °C Tube: M/gs P / WGianra RadityaPas encore d'évaluation