Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
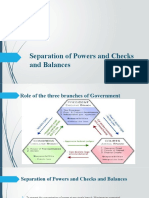
Definition of Checks and Balances
Transféré par
Jen DeeDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Definition of Checks and Balances
Transféré par
Jen DeeDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Definition of Checks and Balances
Noun
1. A system in which various divisions of an organization have powers that affect or
control other divisions, so that no division becomes too powerful, or to minimize
error.
2. Limits placed on all branches of government by giving each branch a right to void
or amend the actions of another branch.
3. Each branch exercises certain powers that can be checked by the powers
given to the other two branches.
The president (head of the executive branch) serves as commander in
chief of the military forces, but Congress (legislative branch) appropriates
funds for the military and votes to declare war. In addition, the Senate
must ratify any peace treaties.
Congress has the power of the purse, as it controls the money used to
fund any executive actions.
Within the legislative branch, each house of Congress serves as a check
on possible abuses of power by the other. Both the House of
Representatives and the Senate have to pass a bill in the same form for it
to become law.
Veto power. Once Congress has passed a bill, the president has the
power to veto that bill. In turn, Congress can override a regular
presidential veto by a two-thirds vote of both houses.
The Supreme Court and other judicial branch can declare laws or
presidential actions unconstitutional, in a process known as judicial
review.
In turn, the president checks the judiciary through the power of
appointment of justices.
By passing amendments to the Constitution, Congress can effectively
check the decisions of the Supreme Court.
Congress (considered the branch of government closest to the people)
can impeach both members of the executive and judicial branches.
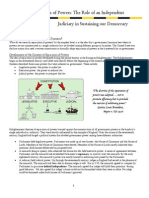
CHECKS AND BALANCES
The ends of government are better achieved if the system of checks and balances
will be observed.
Under the system of checks and balances, one department is given certain powers
by which it may definitely restrain the others from exceeding constitutional
authority. It may object or resist any encroachment upon its authority, or it may
question, if necessary any act or acts which unlawfully interferes with its sphere of
jurisdiction and authority. (Suarez, 2005).
The following are illustrations where there are checks and balances:
1. The lawmaking power of the Congress is checked by the President through its
veto power, which in turn maybe overturn by the legislature
2. The Congress may refuse to give its concurrence to an amnesty proclaimed
by the President and the Senate to a treaty he has concluded
3. The President may nullify a conviction in a criminal case by pardoning the
offender
4. The Congress may limit the jurisdiction of the Supreme Court and that of
inferior courts and even abolish the latter tribunals
5. The Judiciary in general has the power to declare invalid an act done by the
Congress, the President and his subordinates, or the Constitutional
Commissions.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Definition of Separation of PowerDocument4 pagesDefinition of Separation of PowerraymondkuPas encore d'évaluation
- Seven Basic Principles of The ConstitutionDocument6 pagesSeven Basic Principles of The ConstitutionMichael ManuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Separation of PowerDocument3 pagesSeparation of Powerjunior_chsPas encore d'évaluation
- The Separation of Power and Check and Balance - 1Document2 pagesThe Separation of Power and Check and Balance - 1Amir HameedPas encore d'évaluation
- Significant Principles and Rules of The State and Powers of The StateDocument4 pagesSignificant Principles and Rules of The State and Powers of The StateCindy Melford MarbellaPas encore d'évaluation
- 9.systems of Check and BalancesDocument3 pages9.systems of Check and BalancesAmee MemonPas encore d'évaluation
- Branches of Government (Week Five Report Manuscript)Document13 pagesBranches of Government (Week Five Report Manuscript)Ailah Jale CogolloPas encore d'évaluation
- Separation of PowerDocument25 pagesSeparation of PowerKuber JaishiPas encore d'évaluation
- Check and BalanceDocument9 pagesCheck and Balancemodicam oloyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Branches of The Philippine Government: Separation of PowersDocument3 pagesBranches of The Philippine Government: Separation of PowersAl-zobair MacarayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Constitution I: 4. Separation of PowersDocument21 pagesConstitution I: 4. Separation of PowersMarco Ramon100% (1)
- Blending of PowersDocument1 pageBlending of PowersAnnie GulapanPas encore d'évaluation
- Blending of PowersDocument1 pageBlending of PowersAnnie GulapanPas encore d'évaluation
- Blog - Separation of Powers-3322394 - ThoughtCoDocument4 pagesBlog - Separation of Powers-3322394 - ThoughtCoAbhimanyu SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledChristian Catapang GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Check and BalancesDocument6 pagesCheck and BalancesmaricottaPas encore d'évaluation
- Consti 9 8 21Document4 pagesConsti 9 8 21AshPas encore d'évaluation
- Separation of PowersDocument4 pagesSeparation of PowersAbdullah BhattiPas encore d'évaluation
- Separation of Powers and Checks and BalancesDocument10 pagesSeparation of Powers and Checks and BalancesNuraya Shahrin Nisa 1722305Pas encore d'évaluation
- Blending of Powers Doctrine of Separation of PowersDocument1 pageBlending of Powers Doctrine of Separation of PowersIkkinPas encore d'évaluation
- Checks and Balances Blending of Powers Doctrine of Separation of PowersDocument1 pageChecks and Balances Blending of Powers Doctrine of Separation of PowerszeynPas encore d'évaluation
- Checks and Balances, Blending of Powers, Doctrine of Separation of PowersDocument1 pageChecks and Balances, Blending of Powers, Doctrine of Separation of PowersLizzy Way100% (3)
- Parliament and JudiciaryDocument4 pagesParliament and JudiciaryGauravPas encore d'évaluation
- Separation of PowersDocument16 pagesSeparation of PowersJawad ChathaPas encore d'évaluation
- Checks and BalancesDocument2 pagesChecks and BalancesClaudine ClaudioPas encore d'évaluation
- Constitutional Law 1aDocument7 pagesConstitutional Law 1aGrace NacionalPas encore d'évaluation
- UCSPDocument3 pagesUCSPFernandez, Nadine Kate T.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Task 2Document2 pagesPractical Task 2Zhuldyz ZhambylovaPas encore d'évaluation
- Consti 1 09012022Document7 pagesConsti 1 09012022Docefjord EncarnacionPas encore d'évaluation
- Consti 1 AssignmentDocument5 pagesConsti 1 AssignmentGrey LightPas encore d'évaluation
- And Is Supreme in Matters Falling Within Its Own Constitutionally Allocated SphereDocument2 pagesAnd Is Supreme in Matters Falling Within Its Own Constitutionally Allocated SphereMark Angelo CabilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of Separation of PowersDocument15 pagesTheory of Separation of PowersKaynat KatariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Doctrine of Separation of PowersDocument2 pagesDoctrine of Separation of PowersMary Anne TurianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Constitution of UsDocument14 pagesConstitution of UsAdan NiaziPas encore d'évaluation
- The Separation of Powers in The USDocument4 pagesThe Separation of Powers in The USoshantoridoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Separation of PowersDocument6 pagesSeparation of PowersBanni BanniPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit4masteryproject 2Document3 pagesUnit4masteryproject 2api-295725781100% (1)
- Pol Seperation of PowersDocument10 pagesPol Seperation of PowersSwatantraPandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar Paper About Executive PaperDocument12 pagesSeminar Paper About Executive PaperHedhili GriraPas encore d'évaluation
- Institution. by Functional Separation He Meant That An Executive Organ's Function Must BeDocument3 pagesInstitution. by Functional Separation He Meant That An Executive Organ's Function Must BeMitiku YibeltalPas encore d'évaluation
- Constitutionalism MeaningDocument12 pagesConstitutionalism MeaningSARIKAPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 - Separation of Powers - Check and BalanceDocument13 pages4 - Separation of Powers - Check and BalanceBhuwan SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparative and Development NotesDocument28 pagesComparative and Development NotesMeena MalikPas encore d'évaluation
- Prelims Note 3Document11 pagesPrelims Note 3Chriscelle Ann PimentelPas encore d'évaluation
- Politics and GovernanceDocument7 pagesPolitics and GovernanceMarilyn BasaPas encore d'évaluation
- Legislative GODocument4 pagesLegislative GOGrant NaillingPas encore d'évaluation
- Separation of Powers: Dr. Sushma Sharma, Associate Professor, NLIU, BhopalDocument26 pagesSeparation of Powers: Dr. Sushma Sharma, Associate Professor, NLIU, BhopalEkansh AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- Separation of PowerDocument3 pagesSeparation of Power17PAD021- Shahrukh RayhanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Legislative Branch of USDocument3 pagesThe Legislative Branch of USSyeda Rida ZahraPas encore d'évaluation
- Viviana Tryfonopoulos DBQ TestDocument2 pagesViviana Tryfonopoulos DBQ TestViviana TryfonopoulosPas encore d'évaluation
- What Kind of Legal System Exists in The Philippines?Document3 pagesWhat Kind of Legal System Exists in The Philippines?YanilyAnnVldzPas encore d'évaluation
- A System of Checks and BalancesDocument4 pagesA System of Checks and Balancesregie odiamarPas encore d'évaluation
- Arms of GovernmentDocument2 pagesArms of GovernmentKagiso komanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Doctrine of Separation of PowersDocument10 pagesDoctrine of Separation of PowersBren Bernard PabloPas encore d'évaluation
- Legislative System UK-USADocument8 pagesLegislative System UK-USATatiana KabanovaPas encore d'évaluation
- The United States of America - A Presidential RepublicDocument3 pagesThe United States of America - A Presidential RepublicAni RukhadzePas encore d'évaluation
- Montesquieu's Theory of Separation of PowerDocument3 pagesMontesquieu's Theory of Separation of PowerHira KabirPas encore d'évaluation
- South Africa Essay PDFDocument19 pagesSouth Africa Essay PDFLia LBPas encore d'évaluation
- The Philippines Is A Democratic and Republican StateDocument5 pagesThe Philippines Is A Democratic and Republican StateKathleen A. Pascual100% (1)
- The Seven Pillars of Democracy: A US Constitution JourneyD'EverandThe Seven Pillars of Democracy: A US Constitution JourneyPas encore d'évaluation
- NAPOCOR v. ILETODocument1 pageNAPOCOR v. ILETOJen DeePas encore d'évaluation
- University of The East vs. Romeo A. JaderDocument1 pageUniversity of The East vs. Romeo A. JaderJen DeePas encore d'évaluation
- NATIONAL POWER CORPORATION vs. SALUDARESDocument6 pagesNATIONAL POWER CORPORATION vs. SALUDARESJen DeePas encore d'évaluation
- RODZSSEN SUPPLY CO. INC. vs. FAR EAST BANK & TRUST CO.Document1 pageRODZSSEN SUPPLY CO. INC. vs. FAR EAST BANK & TRUST CO.Jen DeePas encore d'évaluation
- Delsan Transport vs. C & A ConsortiumDocument2 pagesDelsan Transport vs. C & A ConsortiumJen DeePas encore d'évaluation
- Republic v. Lim GR No. 161656Document1 pageRepublic v. Lim GR No. 161656Jen DeePas encore d'évaluation
- Land Bank of The Philippines v. AMS Farming Corp. GR 174971Document23 pagesLand Bank of The Philippines v. AMS Farming Corp. GR 174971Jen DeePas encore d'évaluation
- Manosca vs. CaDocument2 pagesManosca vs. CaJen Dee100% (3)
- MIAA Vs Rodriguez - Eminent Domain - Just Compensation - DigestDocument2 pagesMIAA Vs Rodriguez - Eminent Domain - Just Compensation - DigestJen Dee100% (1)
- EPZA vs. DulayDocument1 pageEPZA vs. DulayJen DeePas encore d'évaluation
- Sumulong Vs GuerreroDocument2 pagesSumulong Vs GuerreroJen DeePas encore d'évaluation
- Sumulong Vs GuerreroDocument2 pagesSumulong Vs GuerreroJen DeePas encore d'évaluation
- REYES Vs NHADocument1 pageREYES Vs NHAJen DeePas encore d'évaluation
- National-Power-Corporation-vs-Hon-Aguirre-Paderanga-GR-No-155065-7-28-2005 - SCRIBDDocument1 pageNational-Power-Corporation-vs-Hon-Aguirre-Paderanga-GR-No-155065-7-28-2005 - SCRIBDJen DeePas encore d'évaluation
- EXECUTIVE SECRETARY v. FORERUNNER MULTI RESOURCESDocument3 pagesEXECUTIVE SECRETARY v. FORERUNNER MULTI RESOURCESJen DeePas encore d'évaluation
- Exec. Secretary vs. Forerunner Multi Resources - Civil Procedure Man NiDocument2 pagesExec. Secretary vs. Forerunner Multi Resources - Civil Procedure Man NiJen DeePas encore d'évaluation
- Major Concerns On Equity and EqualityDocument9 pagesMajor Concerns On Equity and EqualityEarlithaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gold - Line - Tours - Inc. - v. - Heirs - of - LacsaDocument9 pagesGold - Line - Tours - Inc. - v. - Heirs - of - LacsamimimilkteaPas encore d'évaluation
- KKK Arkansas 1920sDocument21 pagesKKK Arkansas 1920sPuneet BakshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Submitted By: Mr. Alfie G. Rellon (FB and Messenger) (AMA OED Student) (Agrsaudi: Username in The Site)Document12 pagesSubmitted By: Mr. Alfie G. Rellon (FB and Messenger) (AMA OED Student) (Agrsaudi: Username in The Site)Kaxy PHPas encore d'évaluation
- Right To HealthDocument9 pagesRight To HealthPriya SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kopirati Do 461 Strane KnjigeDocument592 pagesKopirati Do 461 Strane KnjigeLakić Todor100% (1)
- UnpublishedDocument19 pagesUnpublishedScribd Government DocsPas encore d'évaluation
- Election Commission of PakistanDocument13 pagesElection Commission of PakistanAdnan GhafoorPas encore d'évaluation
- 19 Aratea vs. ComelecDocument45 pages19 Aratea vs. ComelecbillietotPas encore d'évaluation
- Issues About Academic FreedomDocument4 pagesIssues About Academic FreedomNenita Lara MaglasangPas encore d'évaluation
- G.R. No. 198356 SUPAPO VS SPS. ROBERTODocument1 pageG.R. No. 198356 SUPAPO VS SPS. ROBERTOamareia yapPas encore d'évaluation
- Statcon Digests For August 15Document20 pagesStatcon Digests For August 15Jassy BustamantePas encore d'évaluation
- Watch The Documentary and Answer The Questions. Carefully and Write Thorough, Detailed Answers. Each Question Is Worth 3 Points!Document5 pagesWatch The Documentary and Answer The Questions. Carefully and Write Thorough, Detailed Answers. Each Question Is Worth 3 Points!Kayn Baringer100% (1)
- 2016-Grounds of AppealDocument2 pages2016-Grounds of Appealwasim ul ghani khanPas encore d'évaluation
- ESPIRITU Vs Municipality of PozzorubioDocument2 pagesESPIRITU Vs Municipality of PozzorubioGean Pearl Pao Icao100% (3)
- Manila 1945 KWLDocument3 pagesManila 1945 KWLJairah Faith CammayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Political Party (CSE 1307)Document3 pagesPolitical Party (CSE 1307)dhakaeurekaPas encore d'évaluation
- Beige Scrapbook Art and History PresentationDocument33 pagesBeige Scrapbook Art and History PresentationjheyzaletaPas encore d'évaluation
- CBL of Liga NG Barangay NG PilipinasDocument28 pagesCBL of Liga NG Barangay NG Pilipinasroy rubaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pimentel V Exec. Sec DigestDocument2 pagesPimentel V Exec. Sec DigestPeperonii100% (3)
- World War II Lesson 2 HomefrontDocument15 pagesWorld War II Lesson 2 Homefrontapi-242847854Pas encore d'évaluation
- ArevaloDocument1 pageArevaloFeliciano Mondigo IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To International Humanitarian Law and IHL Moot in Asia Pacific RegionDocument156 pagesIntroduction To International Humanitarian Law and IHL Moot in Asia Pacific Regionrdesgagne2002100% (1)
- A Critical AnalysisDocument5 pagesA Critical AnalysisSana Gul100% (1)
- Indian RAW Kao Plan in BalochistanDocument9 pagesIndian RAW Kao Plan in BalochistanSpy FJ0% (1)
- Local Government Units Reviewer MidtermsDocument10 pagesLocal Government Units Reviewer Midtermsdianne rosalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Public Administration System of United Kingdom and Its ReformsDocument8 pagesPublic Administration System of United Kingdom and Its ReformsAarush SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Labour Co-Operatives in India PDFDocument9 pagesLabour Co-Operatives in India PDFTapesh Awasthi0% (1)
- Bosch Supplier Code of ConductDocument3 pagesBosch Supplier Code of ConductSenthil_KPas encore d'évaluation
- Ermita-Malate Hotel and Motel Operators v. City of ManilaDocument15 pagesErmita-Malate Hotel and Motel Operators v. City of ManilaOceane AdolfoPas encore d'évaluation