Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Dec 1
Transféré par
Jessica PerfinianTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Dec 1
Transféré par
Jessica PerfinianDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Amines
R-NH2
Basic compounds
Polar compounds
1° & 2° amines can form H bonding
3° amines cannot form H bonding
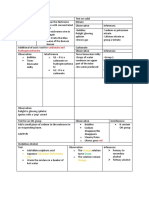
Color Reaction Test
NINHYDRIN TEST
Principle: Detection of free amino acids.
Decarboxylation of alpha-amino acids producing
CO2 and Ammonia.
AMINO ACIDS Result:
Building blocks of proteins Free amino acids – purple
Proline/ Hydroxyproline – yellow
BIURET TEST
Principle: Detection of peptide linkages
Reagents: Copper Sulfate & NaOH
Peptide Bonds Result: Purple/ violet solution
Linkage between amino acids
Dipeptides, Oligopeptides & Polypeptides BY HEAT
Principle: Heat disrupts the Hydrogen bonds and
hydrophobic interactions between “R” groups.
Heat destroys the structure of proteins.
Result: White precipitate
BY STRONG ACIDS
Polarity of Amino acids: Principle: Splits salt linkages by ionizing the –COOH
Depends on the R/ side chain group.
Classified: Results:
o Nonpolar AA Conc. Nitric acid – cloudy white precipitate
o Polar AA Conc. Sulfuric acid – brown solution w/ white
Neutral precipitate
Acidic
Basic ACIDITY AND BASICITY:
GLYCINE - NEUTRAL
PROTEINS ARGININE - BASIC
Contains Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen (C, HISTIDINE - BASIC
H, O, N) ALANINE - NEUTRAL
Made up of polymers of amino acids (basic unit) LYSINE - BASIC
Gelatin and Albumin ASPARTIC ACID – ACIDIC
Physical Properties
Solubility in water:
↑ MW amines – Insoluble/ Slightly soluble
↓ MW amines – Soluble
Alanine is insoluble to water
Solubility of Amines in aq. Acids
Formation of water soluble salts
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Preparing A Standards-Based Curriculum Map:: From Streamlining To Unpacking and AlignmentDocument75 pagesPreparing A Standards-Based Curriculum Map:: From Streamlining To Unpacking and AlignmentJc PelayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Deactivition of Nitrile PDFDocument9 pagesDeactivition of Nitrile PDFMonique PadovanPas encore d'évaluation
- Flame TestDocument2 pagesFlame Testfreedom5345Pas encore d'évaluation
- Disolusi Q & ADocument5 pagesDisolusi Q & AAlhara YuwandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Solubility of Liquids in LiquidsDocument33 pagesSolubility of Liquids in LiquidsYuppie Raj67% (3)
- MSDS Poly Aluminium PDFDocument6 pagesMSDS Poly Aluminium PDFAnida MauludinaPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEMISTRYDocument12 pagesCHEMISTRYDAYAL S PRIYANPas encore d'évaluation
- Acid BaseDocument17 pagesAcid BaseNia LisnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of DiureticsDocument34 pagesAnalysis of DiureticsMourya Sai100% (1)
- Water Conditioning IndustrialDocument27 pagesWater Conditioning IndustrialAdrianio LozhadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Naugard 445 Stabilizer: TechnicalDocument2 pagesNaugard 445 Stabilizer: TechnicalNguyen HongPas encore d'évaluation
- C4-Based Processes 8-01-11Document18 pagesC4-Based Processes 8-01-11Sistine Maquiling Cobcoban100% (1)
- Physical Properties of SolutionsDocument67 pagesPhysical Properties of SolutionsFABIO DE LIMAPas encore d'évaluation
- Physico - Chemical Analysis of Bawadi Water Sources and Distribution PointsDocument9 pagesPhysico - Chemical Analysis of Bawadi Water Sources and Distribution Pointsyeay_mePas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 6 Science Revision NotesDocument29 pagesGrade 6 Science Revision Notesd4rky100% (8)
- Edexcel Chemistry Unit 2 Revision NotesDocument10 pagesEdexcel Chemistry Unit 2 Revision NotesMohammad Izaz MahmudPas encore d'évaluation
- Nanotechnology-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Nanobiotechnol (2009) 5:17 - 33 DOI 10.1007/s12030-009-9028-2Document17 pagesNanotechnology-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Nanobiotechnol (2009) 5:17 - 33 DOI 10.1007/s12030-009-9028-2Manjunath Reddy SantimreddigariPas encore d'évaluation
- Selco Dipotassium Glycyrrhizinate Leaflet - KinetikDocument2 pagesSelco Dipotassium Glycyrrhizinate Leaflet - KinetikTruong Thi Thuy TrangPas encore d'évaluation
- Desifratacion (Sec 20) Gpsa Engineering Data BookDocument48 pagesDesifratacion (Sec 20) Gpsa Engineering Data Bookpol100% (1)
- Activity 7 Post-LabDocument7 pagesActivity 7 Post-LabNur-Zhiana MuhiddiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Alkaloids-Unit 2Document19 pagesAlkaloids-Unit 2Gayatri SisodiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Theories of SolutionsDocument280 pagesTheories of SolutionsRambabu PonnalaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Boiler Water ChemistryDocument14 pagesA Boiler Water ChemistryMuhammad MusharrafPas encore d'évaluation
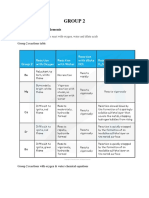
- Group 2Document19 pagesGroup 2Muhammad KalimPas encore d'évaluation
- Hunter NashDocument6 pagesHunter NashKrishanu SahaPas encore d'évaluation
- PPT41Document9 pagesPPT41Smruti PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- 9701 w07 QP 4cxDocument16 pages9701 w07 QP 4cxSyedFaizanAliPas encore d'évaluation
- Annex A: Measurement of ESDD and NSDD A.1. IntroductionDocument5 pagesAnnex A: Measurement of ESDD and NSDD A.1. IntroductionsamPas encore d'évaluation
- Caoh2 3rd EdDocument9 pagesCaoh2 3rd Edcano96Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Principles of Chemistry 19Document196 pages1 Principles of Chemistry 19LaziPas encore d'évaluation