Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
5 Waves Answers
Transféré par
Noor Ulain NabeelaCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
5 Waves Answers
Transféré par
Noor Ulain NabeelaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
P1, Chapter 5
Answers Marks
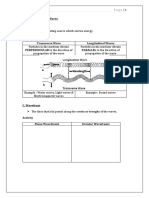
1 a Diagram must show direction of wave travel. 2
Diagram must show direction of vibration perpendicular to direction of
wave travel.
b Diagram must show direction of wave travel. 2
Diagram must show direction of vibration parallel to direction of wave
travel.
2 A amplitude 3 4
B frequency 4
C wave speed 1
D wavelength 2
3 A It is a virtual image. 1
4 a refraction 1
b Diagram B 1
5 Diffraction, when the gap is of the same order of magnitude as the 2
wavelength.
6 Similarity: They can both be reflected, refracted, diffracted. 2
Difference: Light waves are much faster /sound waves are much
slower OR light waves are transverse/sound waves are longitudinal.
7 v = f × λ so 256 × 1.3 = 333 m/s 2
8 a i Any example using a mirror/water or a shiny smooth surface. 1
ii Any example of an echo. 1
iii Any example using a lens, e.g. spectacles, cameras. 1
iv Any example of hearing a sound around a corner. 1
b b The wavelength of light is very small, so diffraction only occurs
when light passes through a very narrow gap. 2
OR
The wavelength of light is very small, so the diffraction effect is very
small.
9 Wave speed = frequency wavelength 3
speed
Frequency = wavelength
New AQA GCSE Science © Nelson Thornes Ltd 2011 1
P1, Chapter 5
Answers Marks
300 000 000 m/s
Frequency =
1500 m
Frequency = 200 000 Hz
10 There is a clear, balanced and detailed description of how the wave form 5-6
would change including increased amplitude and frequency. The answer
shows almost faultless spelling, punctuation and grammar. It is coherent
and in an organised, logical sequence. It contains a range of appropriate or
relevant specialist terms used accurately.
There is a description of at least one of the ways in which the wave form 3-4
would change. There are some errors in spelling, punctuation and
grammar. The answer has some structure and organisation. The use of
specialist terms has been attempted, but not always accurately.
There is a brief description of at least one way in which the wave form
would change, which has little clarity and detail. The spelling, punctuation 1-2
and grammar are very weak. The answer is poorly organised with almost
no specialist terms and/or their use demonstrating a general lack of
understanding of their meaning.
No relevant content. 0
Examples of physics points made in the response:
• louder sound means larger amplitude
• so height of crests increases
• depth of troughs increases
• speed is constant
• higher pitch means higher frequency
• so wavelength becomes smaller
• crests are closer together.
New AQA GCSE Science © Nelson Thornes Ltd 2011 2
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Chapter 5Document12 pagesChapter 5Noor Ulain NabeelaPas encore d'évaluation
- F5 WavesDocument29 pagesF5 WavesThayabaran MunusamyPas encore d'évaluation
- G Refle Fract Conv Ion Of: Eneral Ction of Ion of Li Erging Le Light AnDocument80 pagesG Refle Fract Conv Ion Of: Eneral Ction of Ion of Li Erging Le Light Anqaz xswPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.1 WaveDocument13 pages5.1 WaveMazni HanisahPas encore d'évaluation
- WavesDocument11 pagesWavesdilsharakaviPas encore d'évaluation
- kggy640lXqskFWtfhgdi PDFDocument38 pageskggy640lXqskFWtfhgdi PDFArsinno Azain LeoninnPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.1 General Properties of WavesDocument5 pages3.1 General Properties of WavesAyana AkjolovaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 - WavesDocument12 pagesUnit 3 - WavesT. Christabel VijithaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2 02 - Wave Properties - PPTX - AutoRecoveredDocument9 pagesLecture 2 02 - Wave Properties - PPTX - AutoRecoveredAisyah KiswantohPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.4 Refraction of WavesDocument16 pages5.4 Refraction of WavesNurlailie Md JamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 Worksheet 5 Aurora High SchoolDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Worksheet 5 Aurora High SchoolシューゴPas encore d'évaluation
- AQA Physics P12 Summary AnswersDocument3 pagesAQA Physics P12 Summary AnswersjayakantharushanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1: WavesDocument8 pagesChapter 1: WavesWAN NOOR AZILAH BT WAN UMAR MoePas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 10 Physics LPDocument17 pagesGrade 10 Physics LPWilber TuryasiimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 18Document63 pagesChapter 18Arthur ParizPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 2 Key NotesDocument45 pagesPaper 2 Key NotesJEEVAN KATHIRESANPas encore d'évaluation
- C 09 Properties of Mechanical WavesDocument39 pagesC 09 Properties of Mechanical Waveszaliha a-voyiPas encore d'évaluation
- Gcse Physics: WavesDocument16 pagesGcse Physics: WavesThamiso GolwelwangPas encore d'évaluation
- WAVESDocument28 pagesWAVESAbdallah Soud AllyPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 3Document36 pagesPaper 3Orisa THANAJAROPas encore d'évaluation
- Wave OpticsDocument8 pagesWave OpticsFaruk Shaik (munna)Pas encore d'évaluation
- ME Sci 7 Q3 0902 SGDocument20 pagesME Sci 7 Q3 0902 SGSophia TorresPas encore d'évaluation
- 29 Waves-Wave CharacteristicsDocument9 pages29 Waves-Wave CharacteristicseltytanPas encore d'évaluation
- Wave Interactions: ObjectivesDocument8 pagesWave Interactions: ObjectivesKhim NavalPas encore d'évaluation
- Wave Characteristics 14163540Document59 pagesWave Characteristics 14163540roberto lizardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Wave PropertiesDocument122 pagesWave PropertiesHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Superposition Tutorial Solutions 2022Document41 pagesSuperposition Tutorial Solutions 2022Woh Jon LaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics ProblemsDocument4 pagesPhysics ProblemsQuazi Rafquat HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Option ADocument13 pagesOption AMartinPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves: Name - TeacherDocument47 pagesWaves: Name - TeachersaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Student Book Answers - Physics 1 Chapter 2Document5 pagesStudent Book Answers - Physics 1 Chapter 2Mhmd AlrashedPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer Key: Transparency 15-1 WorksheetDocument1 pageAnswer Key: Transparency 15-1 Worksheetsara motleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Phys HW20Document1 pagePhys HW20Adam LiangPas encore d'évaluation
- CfE Waves and Sound NOTES NAT 4 With Answers.Document26 pagesCfE Waves and Sound NOTES NAT 4 With Answers.Ross O'BrienPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 3Document4 pagesExperiment 3ammadm540Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wave Propagation in Shallow Water: Ert - C WDocument24 pagesWave Propagation in Shallow Water: Ert - C WMarco QuirozPas encore d'évaluation
- On Line Ripple Tank LabDocument5 pagesOn Line Ripple Tank LabWillie HuffPas encore d'évaluation
- 07 WavesDocument23 pages07 Wavesfisica2Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Waves SDocument47 pages6 Waves SNor ShuhadaPas encore d'évaluation
- 13-General Wave Properties-Waves-Cie o Level Physics-1-2Document20 pages13-General Wave Properties-Waves-Cie o Level Physics-1-2diyanooooooorPas encore d'évaluation
- 14 Waves and Sound Formula Sheets Getmarks AppDocument8 pages14 Waves and Sound Formula Sheets Getmarks Appanshm2119Pas encore d'évaluation
- Waves 3Document6 pagesWaves 3krichenkyandex.ruPas encore d'évaluation
- Obt751 - Analytical Methods and Instrumentation Lecture - 2Document28 pagesObt751 - Analytical Methods and Instrumentation Lecture - 2Jayashree Sathiyanarayanan100% (1)
- UNIT I - Wave OpticsDocument33 pagesUNIT I - Wave Opticsmirae kangPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 3: Wave Phenomena in The Ripple Tank: WavelengthDocument12 pagesLab 3: Wave Phenomena in The Ripple Tank: WavelengthAhmad ShaqeerPas encore d'évaluation
- Phys Int CC CH 12 - Waves and Energy Transfer - Answers PDFDocument7 pagesPhys Int CC CH 12 - Waves and Energy Transfer - Answers PDFPatrick Gerard SerandonPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Teaching Plan f5 2011Document9 pagesYearly Teaching Plan f5 2011zflankerPas encore d'évaluation
- Sonar Introduction 2012 Compressed PDFDocument11 pagesSonar Introduction 2012 Compressed PDFBrenno Moura MouraPas encore d'évaluation
- AQA Physics P12 Practice AnswersDocument2 pagesAQA Physics P12 Practice AnswersjayakantharushanPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Waves: A Strategic Intervention Material in Science Grade 7Document12 pagesElectromagnetic Waves: A Strategic Intervention Material in Science Grade 7DAVID JONH ACOSTAPas encore d'évaluation
- Country's Best Online Test PlatformDocument7 pagesCountry's Best Online Test PlatformTejas DhandaPas encore d'évaluation
- 14 Waves and Sound Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument6 pages14 Waves and Sound Formula Sheets QuizrrArjunPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves, Particles, Light and Matter in U4Document28 pagesWaves, Particles, Light and Matter in U4Kevin LEEPas encore d'évaluation
- 2023 IGCSE Chapter 14 Properties of WavesDocument19 pages2023 IGCSE Chapter 14 Properties of WavesHumalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Read Important Questions Class 12 Physics of Chapter 10Document39 pagesRead Important Questions Class 12 Physics of Chapter 10Mani RohitPas encore d'évaluation
- Light As An Electromagnetic WaveDocument30 pagesLight As An Electromagnetic WaveKit Augustine TantoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 10 Physics - 2021 - Term 3Document112 pagesGrade 10 Physics - 2021 - Term 3tsholofelomdhlanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ujian 1Document16 pagesUjian 1cikgusyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise 7: Tying A Well To A Seismic Line: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesExercise 7: Tying A Well To A Seismic Line: ObjectiveSadiq JalalPas encore d'évaluation
- The Fundamentals of Signal Transmission: Optical Fibre, Waveguides and Free SpaceD'EverandThe Fundamentals of Signal Transmission: Optical Fibre, Waveguides and Free SpacePas encore d'évaluation
- Year 11 GCSE Revision Guidance and Exam Booklet Solihull PDFDocument27 pagesYear 11 GCSE Revision Guidance and Exam Booklet Solihull PDFNoor Ulain Nabeela83% (6)
- Yellowstone Story and WorksheetDocument4 pagesYellowstone Story and WorksheetNoor Ulain Nabeela0% (1)
- Simple Machines Unit PacketDocument24 pagesSimple Machines Unit PacketNoor Ulain NabeelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet Electronic Configuration BC Science - AnsDocument2 pagesWorksheet Electronic Configuration BC Science - AnsNoor Ulain NabeelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Target Aqa Gcse Combined Science Grade 5 Physics Unit 6 Graph SkillsDocument8 pagesTarget Aqa Gcse Combined Science Grade 5 Physics Unit 6 Graph SkillsNoor Ulain NabeelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Year 7 and 8 Textbooks and Websites.96222304 PDFDocument4 pagesYear 7 and 8 Textbooks and Websites.96222304 PDFNoor Ulain Nabeela17% (6)
- CBSE Class 8 Science WorksheetDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 8 Science WorksheetNoor Ulain Nabeela100% (1)
- Forces, Centre of Gravity, Reactions and Stability - FINAL PDFDocument12 pagesForces, Centre of Gravity, Reactions and Stability - FINAL PDFNoor Ulain NabeelaPas encore d'évaluation
- 153D3F2BFF7CFF0729EB5088345643CEDocument10 pages153D3F2BFF7CFF0729EB5088345643CENoor Ulain NabeelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reducing The PressureDocument1 pageReducing The PressureNoor Ulain NabeelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rheology and Soil Mechanics RH Ologie Et M Canique Des Sols Symposium Grenoble April 1-8-1964 Symposium Grenoble 1er 8 Avril 1964 2Document519 pagesRheology and Soil Mechanics RH Ologie Et M Canique Des Sols Symposium Grenoble April 1-8-1964 Symposium Grenoble 1er 8 Avril 1964 2Jasmin AgriPas encore d'évaluation
- (Woodhead Publishing Series in Welding and Other Joining Technologies 6) H. Granjon-Fundamentals of Welding Metallurgy-Woodhead Publishing (1991)Document227 pages(Woodhead Publishing Series in Welding and Other Joining Technologies 6) H. Granjon-Fundamentals of Welding Metallurgy-Woodhead Publishing (1991)Luis Testa75% (4)
- Science 10 QUARTER 4 WEEK 2Document3 pagesScience 10 QUARTER 4 WEEK 2Shin LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Iso 10684Document26 pagesIso 10684Jay GaneshPas encore d'évaluation
- DMCR Protection Relay For Oil TransformerDocument8 pagesDMCR Protection Relay For Oil Transformerraul_bsuPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is The Ozone Layer and Where Is It Located?Document6 pagesWhat Is The Ozone Layer and Where Is It Located?JosePas encore d'évaluation
- Edec Standard: CoretronicDocument14 pagesEdec Standard: Coretronic彭以和Pas encore d'évaluation
- Solidstatephysics PDFDocument608 pagesSolidstatephysics PDFTomislav Octenjak100% (1)
- Why Kinetics Is Very Important in PharmacyDocument13 pagesWhy Kinetics Is Very Important in PharmacyRavi KantPas encore d'évaluation
- Pressure Cells Types, Working Principle and ApplicationsDocument20 pagesPressure Cells Types, Working Principle and ApplicationsEncardio RitePas encore d'évaluation
- ThermoDynamics Conversion Table PDFDocument1 pageThermoDynamics Conversion Table PDFCloie Chavez100% (1)
- 6 EntropyDocument18 pages6 EntropyRasel khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bolt ConnectionDocument98 pagesBolt ConnectiondanessatiriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vapor-Liquid Equilibria of Nonideal Solutions: Harrison C. Carlson, and Allan P. ColburnDocument10 pagesVapor-Liquid Equilibria of Nonideal Solutions: Harrison C. Carlson, and Allan P. ColburnAlfonso Dominguez GonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- MDSP SET O3Document26 pagesMDSP SET O3BrilliantJohnMalandacRubiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Powder Technology (POWDER TECHNOL)Document8 pagesPowder Technology (POWDER TECHNOL)Dappa DavidPas encore d'évaluation
- RV College of EngineeringDocument12 pagesRV College of EngineeringRahul ChandraPas encore d'évaluation
- PrimerTaller 2023-1Document12 pagesPrimerTaller 2023-1Juan PabloPas encore d'évaluation
- Equipos Mini Splits Comfortstar CSC1024CDDocument4 pagesEquipos Mini Splits Comfortstar CSC1024CDAguilar Joel100% (1)
- The HALO Range: Uv-Visible and Visible SpectrophotometersDocument9 pagesThe HALO Range: Uv-Visible and Visible Spectrophotometersrohmen042Pas encore d'évaluation
- Muk204e - Syllabus - Strength of Materials-IIDocument2 pagesMuk204e - Syllabus - Strength of Materials-IIAkif CengizPas encore d'évaluation
- Cold Rolled Steel StripDocument40 pagesCold Rolled Steel StripshelarsanjayPas encore d'évaluation
- FoglerDocument105 pagesFogleryvehuangPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Liofilizador BiobaseDocument14 pagesManual Liofilizador BiobaseAlejandro Palomino100% (3)
- FS 530-11 CI Single Convolution Air Actuator: Purchase Order Data Technical DataDocument1 pageFS 530-11 CI Single Convolution Air Actuator: Purchase Order Data Technical DataMichael AkhramovichPas encore d'évaluation
- Nanotechnologies and Nano Materials in Welding Production ReviewDocument5 pagesNanotechnologies and Nano Materials in Welding Production ReviewVIJAY KUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic: Concrete at Early AgeDocument33 pagesTopic: Concrete at Early AgechristianPas encore d'évaluation
- ORLENOIL Folder Przemyslowy en 2014Document45 pagesORLENOIL Folder Przemyslowy en 2014Handerson PanjaitanPas encore d'évaluation
- Potentiometry FinalDocument27 pagesPotentiometry FinalDeepak shahPas encore d'évaluation