Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
1 - Locom Notes Key
Transféré par
its id04Description originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1 - Locom Notes Key
Transféré par
its id04Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
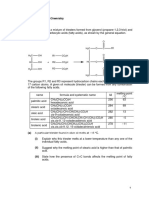
Writing Chemical Equations
A chemical equation is exactly what it says it is—an equality between the reactants (which are substances written
on the left side of the equation) and the products (which are substances written on the right side). An arrow
pointing to the right serves as the = sign it is read “yields”.
A. HOW TO WRITE A BALANCED EQUATION
(1) Write a correct formula for each of the reactants. Put a plus sign between the reactants to separate them.
Note: A plus sign means “added to” or “reacts with”.
(2) Draw a yield arrow
(3) Write a correct formula for each of the products, putting a plus sign between them also.
Note: On the product side, the plus sign means “as well as” or “in addition to”.
(4) Place a state symbol on every substance in the reaction.
(5) Balance the equation, putting coefficients where necessary
NOTE: Coefficients CANNOT be placed in the middle of a compound and subscripts CANNOT be
changed.
B. STATE SYMBOLS
There are four physical state symbols which are used immediately following substances whose
physical states are known or given.
(s) – solid, which is used for solids or precipitates
(l) – liquid, which is used only for “true” liquids
(g) – gas
(aq) – aqueous, which means dissolved in water, denoted within the word equation as “solution”.
C. SIMPLE GUIDELINES for writing state symbols when the state is not given or known:
(1) All pure metallic elements (except mercury) will be designated (s) unless the reaction indicates otherwise
(2) Water will be designated as (l) unless it is a combustion reaction or the vapor state is indicated; pure
bromine and pure mercury will be designated (l); organic substances (CHO compounds) which are listed as
“liquids” in the problem will be designated (l); anything which is “molten” or “melted” will be designated (l)
(3) Metallic oxides are always (s); non-metallic oxides are (g)
AQUEOUS
(4) Acids are designated (aq); soluble ionic compounds are designated (aq)
(5) If it is an element, check the big periodic table in the back of the room:
a. Red = gas b. Blue = liquid c. Black = solid
EXAMPLES:
1. When solid scandium (III) oxide is put in water, solid scandium (III) hydroxide forms.
2. Sodium reacts violently with water to produce sodium hydroxide solution and hydrogen gas.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- CHM131 - Chapter 1 - Atoms - Molecules Ions - Chemical EqDocument106 pagesCHM131 - Chapter 1 - Atoms - Molecules Ions - Chemical EqLeo PietroPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Notes of CH 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations - Class 10th ScienceDocument8 pagesNotes of CH 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations - Class 10th ScienceHarsh Pal 1918Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Science Cala A 2023.Document3 pagesScience Cala A 2023.Lamec ZambukoPas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Heavy Metal Contamination and Ecological Risk Assessment of Soils AroundDocument15 pagesHeavy Metal Contamination and Ecological Risk Assessment of Soils AroundJessica Patricia SitoePas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- ACS Practice Test 1Document10 pagesACS Practice Test 1drwams100% (2)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Chapter 3: Earth Materials Minerals and RocksDocument60 pagesChapter 3: Earth Materials Minerals and RocksKashish K BanslaPas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- 6.4 TextbookDocument4 pages6.4 TextbookJoshua AdetoroPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Jahn Teller DistortionDocument7 pagesJahn Teller DistortionBharath Reddy100% (1)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Earth Science Tarbuck 14th Edition Test BankDocument24 pagesEarth Science Tarbuck 14th Edition Test BankMichaelRobertskneda100% (27)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Zinc CitrateDocument1 pageZinc CitrateKasidit SornchaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Salt) Base) : Kantipur Engineering College Dhapakhel, LalitpurDocument3 pagesSalt) Base) : Kantipur Engineering College Dhapakhel, Lalitpursachin50% (2)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Types of Chemical Reactions Worksheet Writing Formulas: Ca CL Cacl Al So Al (So)Document5 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions Worksheet Writing Formulas: Ca CL Cacl Al So Al (So)Bayot KuhPas encore d'évaluation
- 0708 F3 Chem Notes 3Document8 pages0708 F3 Chem Notes 3Lee MeltyPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Suggested Answers Ting.5Document28 pagesSuggested Answers Ting.5engPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Electron Configurations of The Elements (Data Page) - WikipediaDocument25 pagesElectron Configurations of The Elements (Data Page) - WikipediaAlex OmungaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- E Brite - 23 11Document9 pagesE Brite - 23 11Usman ali CheemaPas encore d'évaluation
- Final PM IS 16240 - 10042023Document15 pagesFinal PM IS 16240 - 10042023exceltechconsultingPas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- First Name Last Name: 1st Midterm Exam Ian R. Gould CHEM 233, Fall 2007Document7 pagesFirst Name Last Name: 1st Midterm Exam Ian R. Gould CHEM 233, Fall 2007Armando Shehi SayhellotogoodbyePas encore d'évaluation
- Bab 12 - Nota A+Document7 pagesBab 12 - Nota A+Azemi AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrolysis of Silver SulphateDocument5 pagesElectrolysis of Silver SulphateJackson_de_Roz_6005100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- HCLDocument13 pagesHCLHussein AlkafajiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Objectives of HydrometallurgyDocument14 pagesObjectives of HydrometallurgyAnubhav ChandilPas encore d'évaluation
- D-70 Cupronickel Rev 06Document3 pagesD-70 Cupronickel Rev 06Luis Gustavo AndradePas encore d'évaluation
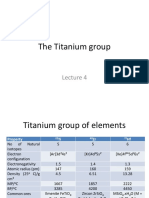
- Lecture 4 - Titanium GroupDocument31 pagesLecture 4 - Titanium Groupmalenya1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet C: Answers: Teaching Pack: The Electrolysis of Molten Zinc ChlorideDocument7 pagesWorksheet C: Answers: Teaching Pack: The Electrolysis of Molten Zinc ChlorideAstridPas encore d'évaluation
- 2016 A Level H2 Chemistry Paper 2 Answers Student Version PDFDocument11 pages2016 A Level H2 Chemistry Paper 2 Answers Student Version PDFIMEI: 355686052799688Pas encore d'évaluation
- United States Patent Office: Patented Nov. 13, 1956Document2 pagesUnited States Patent Office: Patented Nov. 13, 1956karmilaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Physical Science Quarter 3 Week 1: Not For SaleDocument8 pagesPhysical Science Quarter 3 Week 1: Not For SaleMurs H. AsbiPas encore d'évaluation
- Senior ChemistryDocument12 pagesSenior ChemistryDanny 341Pas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of AluminiumDocument2 pagesProperties of AluminiumAl Amin MustaffaPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)