Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Transféré par
maherkamelTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Transféré par
maherkamelDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
NPTEL Syllabus
Probability and Statistics - Video
course
COURSE OUTLINE
NPTEL
Algebra of sets, introduction to probability, random variables,
probability distributions, moments, moment generating function,
Markov and Chebyshev inequalities, special discrete and
continuous distributions, function of a random variable, joint http://nptel.iitm.ac.in
distributions, bivariate normal distribution, transformation of
random vectors, central limit theorem, sampling distributions,
point estimation, unbiasedness, consistency, method of
moments and maximum likelihood estimation, confidence
Mathematics
intervals for parameters in one sample and two sample
problems from normal populations, testing of hypotheses,
Neyman-Pearson lemma, tests for one sample and two sample
problems for normal populations. Pre-requisites:
COURSE DETAIL Set Theory and Calculus
Module Topic/s Lectures Additional Reading:
No.
1. Modern Mathematical
Statistics by E.J.
1 Algebra of Sets: sets and classes, limit 2 Dudewicz & S.N. Mishra
of a sequence of sets, rings, sigma-
rings, fields, sigma-fields, monotone 2. Introduction to the
classes. Theory of Statistics by
A.M. Mood, F.A. Graybill
and D.C. Boes
2 Probability: Classical, relative 4
frequency and axiomatic definitions of Hyperlinks:
probability, addition rule and conditional
probability, multiplication rule, total none
probability, Bayes’ Theorem and
independence, problems.
Coordinators:
Prof. Somesh Kumar
3 Random Variables: Discrete, 3 Department of MathematicsIIT
continuous and mixed random Kharagpur
variables, probability mass, probability
density and cumulative distribution
functions, mathematical expectation,
moments, probability and moment
generating function, median and
quantiles, Markov inequality,
Chebyshev’s inequality, problems.
4 Special Distributions: Discrete 7
uniform, binomial, geometric, negative
binomial, hypergeometric, Poisson,
continuous uniform, exponential,
gamma, Weibull, Pareto, beta, normal,
lognormal, inverse Gaussian, Cauchy,
d o u b l e exponential distributions,
reliability and hazard rate, reliability of
series and parallel systems, problems.
5 Function of a random variable, 1
problems.
Joint Distributions: Joint, marginal
6 and conditional distributions, product 4
moments, correlation and regression,
independence of random variables,
bivariate normal distribution, problems.
7 Transformations: functions of random 1
vectors, distributions of order statistics,
distributions of sums of random
variables, problems.
8 Sampling Distributions: The Central 2
Limit Theorem, distributions of the
sample mean and the sample variance
for a normal population, Chi-Square, t
and F distributions, problems.
9 Descriptive Statistics: Graphical 2
representation, measures of locations
and variability.
10 Estimation: Unbiasedness, 6
consistency, the method of moments
and the method of maximum likelihood
estimation, confidence intervals for
parameters in one sample and two
sample problems of normal populations,
confidence intervals for proportions,
problems.
11 Testing of Hypotheses: Null and 8
alternative hypotheses, the critical and
acceptance regions, two types of error,
power of the test, the most powerful test
and Neyman-Pearson Fundamental
Lemma, tests for one sample and two
sample problems for normal
populations, tests for proportions, Chi-
square goodness of fit test and its
applications, problems.
References:
1. An Introduction to Probability and Statistics by V.K.
Rohatgi & A.K. Md. E. Saleh.
2. Introduction to Probability and Statistics by J.S. Milton &
J.C. Arnold.
3. Introduction to Probability Theory and Statistical Inference
by H.J. Larson.
4. Introduction to Probability and Statistics for Engineers and
Scientists by S.M. Ross
5. A First Course in Probability by S.M. Ross
6. Probability and Statistics in Engineering by W.W. Hines,
D.C. Montgomery, D.M. Gpldsman & C.M. Borror
7. Lectures in Probability by M. Kac (for example on
independent events)
8. C.K. Wong (1972) A note on mutually independent
events. Annals of Statistics, V. 26, 27.(for example on
independent events).
9. Measure Theory by P. Halmos (for algebra of sets)
A joint venture by IISc and IITs, funded by MHRD, Govt of India http://nptel.iitm.ac.in
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Introduction To Six SigmaDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Six SigmaadysubagyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Inspection, Quality Control, and Assurance SHEET (1) : 6-If The Mean Value of The Measured Stress Was 15 KG/MMDocument1 pageInspection, Quality Control, and Assurance SHEET (1) : 6-If The Mean Value of The Measured Stress Was 15 KG/MMmaherkamelPas encore d'évaluation
- GE2022 TQM Notes 2 PDFDocument15 pagesGE2022 TQM Notes 2 PDFBalakumar MurugesanPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Assurance and Quality ControlDocument17 pagesQuality Assurance and Quality Controltraslie0% (1)
- PQ Unit-IiDocument6 pagesPQ Unit-IimaherkamelPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 QualityDocument26 pages8 QualitymaherkamelPas encore d'évaluation
- Beyond Taguchi's Concept of The Quality Loss Function: Atul Dev, Pankaj JhaDocument5 pagesBeyond Taguchi's Concept of The Quality Loss Function: Atul Dev, Pankaj JhamaherkamelPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9Document9 pagesChapter 9Rasha Abduldaiem ElmalikPas encore d'évaluation
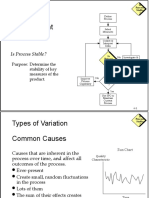
- The Quality Improvement Model: Is Process Capable?Document19 pagesThe Quality Improvement Model: Is Process Capable?maherkamelPas encore d'évaluation
- ISO History (Brief) and Basic FactsDocument9 pagesISO History (Brief) and Basic FactsmaherkamelPas encore d'évaluation
- Gage R&RDocument24 pagesGage R&ROMAR CECEÑASPas encore d'évaluation
- Acceptance SamplingDocument19 pagesAcceptance Samplingpm3dPas encore d'évaluation
- Attributes Data: Binomial and Poisson DataDocument31 pagesAttributes Data: Binomial and Poisson DatamaherkamelPas encore d'évaluation
- Acceptance SamplingDocument19 pagesAcceptance Samplingpm3dPas encore d'évaluation
- Forming 2 PDFDocument43 pagesForming 2 PDFNeoXana01Pas encore d'évaluation
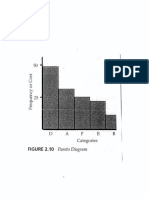
- Pareto and QualityDocument1 pagePareto and QualitymaherkamelPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of Defining ProcessesDocument18 pagesBasics of Defining Processesmaherkamel100% (1)
- Basics 1Document7 pagesBasics 1maherkamelPas encore d'évaluation
- HW 1Document2 pagesHW 1maherkamelPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Chart ConceptsDocument13 pagesBasic Chart ConceptsmaherkamelPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9Document9 pagesChapter 9Rasha Abduldaiem ElmalikPas encore d'évaluation
- HW3 ADocument2 pagesHW3 Ajambu99Pas encore d'évaluation
- Course 649Document2 pagesCourse 649jambu99Pas encore d'évaluation
- HW1 2Document2 pagesHW1 2maherkamelPas encore d'évaluation
- ChatterDocument9 pagesChattermaherkamelPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Lecture NotesDocument23 pagesQuality Lecture NotesmaherkamelPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics 2Document14 pagesMechanics 2maherkamelPas encore d'évaluation
- Me423 PDFDocument2 pagesMe423 PDFmaherkamelPas encore d'évaluation
- Me338 10Document2 pagesMe338 10maherkamelPas encore d'évaluation
- QM in Library PDFDocument25 pagesQM in Library PDFgaurav sharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Partially Directed Graphs and Conditional Random Fields: Sargur Srihari Srihari@cedar - Buffalo.eduDocument43 pagesPartially Directed Graphs and Conditional Random Fields: Sargur Srihari Srihari@cedar - Buffalo.eduSai SwaroopPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Basic StatisticsDocument86 pagesReview of Basic StatisticsWilliam DengPas encore d'évaluation
- Non Stochastic Volatility RevDocument29 pagesNon Stochastic Volatility RevLiza R. JaelPas encore d'évaluation
- 01homework ProblemsDocument2 pages01homework ProblemsEssouffleePas encore d'évaluation
- The Expectation Maximization AlgorithmDocument7 pagesThe Expectation Maximization AlgorithmChrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Forecasting MethodsDocument42 pagesForecasting Methodsryan cappas100% (1)
- StratifiedDocument17 pagesStratifiedrajeshaisdu009Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment ONE May 2023 With AnswerDocument6 pagesAssignment ONE May 2023 With AnswerTimothy CheungPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020quan Case2 (Solution)Document7 pages2020quan Case2 (Solution)Soham DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Section 9.5:: Versus: With 4 and 6Document23 pagesSection 9.5:: Versus: With 4 and 6hellomiketest_365886Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exam (Q) Set ADocument13 pagesExam (Q) Set Aflowerpot321100% (1)
- MANISH BHUSHAN - OPSCM ProjectDocument4 pagesMANISH BHUSHAN - OPSCM Projectankie27Pas encore d'évaluation
- The T TEST An IntroductionDocument5 pagesThe T TEST An IntroductionthishaniPas encore d'évaluation
- W1 Extra ReadingDocument62 pagesW1 Extra ReadingNguyễn Thanh NgọcPas encore d'évaluation
- Total Pages: 3: Apj Abdul Kalam Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesTotal Pages: 3: Apj Abdul Kalam Technological UniversityvoxovPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical Statistics - IDocument12 pagesMathematical Statistics - ISuresh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- On A Bivariate PoissonDocument11 pagesOn A Bivariate PoissonAsif ThottathilPas encore d'évaluation
- Regression WorksheetDocument2 pagesRegression WorksheetRocket FirePas encore d'évaluation
- Alajaji Chen2018 Book AnIntroductionToSingle UserInfDocument333 pagesAlajaji Chen2018 Book AnIntroductionToSingle UserInfSevy Tom ZoriuqPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter III. Discrete Probability DistributionDocument13 pagesChapter III. Discrete Probability DistributionMatthew MiradorPas encore d'évaluation
- A Further Study of Estimating AveragesDocument12 pagesA Further Study of Estimating Averagesliutianwei8848Pas encore d'évaluation
- Revista Romana Statistica Supliment 02 2020Document188 pagesRevista Romana Statistica Supliment 02 2020Mihaela Bidina100% (1)
- Supply Chain Key ConceptDocument68 pagesSupply Chain Key ConceptRAHUL DIXITPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypothesis TestingDocument19 pagesHypothesis TestingNei chimPas encore d'évaluation
- Case - Demand For Toffe IncDocument16 pagesCase - Demand For Toffe IncSaikat MukherjeeePas encore d'évaluation
- Statistical Analysis With R - A Quick StartDocument47 pagesStatistical Analysis With R - A Quick StartPonlapat Yonglitthipagon100% (1)
- Chapter 9 One Sample Hypothesis TestingDocument25 pagesChapter 9 One Sample Hypothesis TestingLakhan Subhash TrivediPas encore d'évaluation
- SPANOVADocument16 pagesSPANOVACress Lorraine SorianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hoffmann - Linear Regression Analysis - Second EditionDocument285 pagesHoffmann - Linear Regression Analysis - Second Editionslatercl100% (1)
- Arch GarchDocument28 pagesArch GarchsergioPas encore d'évaluation