Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
PTR 3480 PDF
Transféré par
RAVIKIRAN BARDETitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
PTR 3480 PDF
Transféré par
RAVIKIRAN BARDEDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Product Test Report PTR-3480
Swagelok Company Ver 02
29495 F.A. Lennon Drive December 2018
Solon, Ohio 44139 U.S.A. Page 1 of 7
TITLE
Fugitive Emissions and Seat Leakage Performance Type Test of Swagelok® VB05 Block and
Bleed Process Interface Valves Witnessed by a Third Party
PRODUCT TESTED
Valve
Series Description Test Pressure Test Qty.
Single ball/needle process interface valve ANSI Class 1500 1
VB05
3/8 in. (9.5 mm) bore size (DN 15) ANSI Class 2500 1
PURPOSE
The valve assemblies were tested under laboratory test conditions to observe fugitive emissions
and seat seal performance when tested according to MESC SPE 77/300, Procedure and
Technical Specification for Type Acceptance Testing (TAT) of Industrial Valves.
TEST CONDITIONS
Original test date: August 2013
Test Media:
• Helium (Fugitive Emissions Tests)
• Nitrogen (Seat Seal Tests)
Test Pressures: As specified according to each test
Test Temperatures:
• Room Temperature Tests: 70°F (20°C)
• Elevated Temperature Tests: 250°F (121°C)
• Low Temperature Tests: –58°F (–50°C)
Fugitive Emissions Leakage Acceptance Criterion: Tightness Class B
Seat Leakage Acceptance Criteria:
• Ambient and Elevated Temperatures:
o Ball valve: ISO 5208 Rate A
o Needle valve: ISO 5208 Rate B
• Low Temperature:
o Ball valve:1.5 mL/min × (valve DN size)
o Needle valve: 4.8 mL/min × (valve DN size)
TEST METHOD
The test conditions and test method were as outlined in MESC SPE 77/300. This test protocol
subjects the test valve to a series of mechanical and thermal cycles over the full range of the
test valve temperature rating. The test valve is tested for seat leakage at various pressures and
tested for static and dynamic fugitive emissions at rated pressure.
2018 Swagelok Company
Product Test Report PTR-3480
Swagelok Company Ver 02
29495 F.A. Lennon Drive December 2018
Solon, Ohio 44139 U.S.A. Page 2 of 7
According to MESC SPE 77/300, Section C.1, testing an ASME Class 2500 valve qualifies that
pressure class only, while a Class 1500 valve classifies both Class 1500 and Class 900. Thus,
Class 2500 and Class 1500 valve were both tested.
Figure 1 shows the thermal and mechanical profile required for the testing procedure as
specified.
Test Preparation and Initial Cycling
1. The test valves were placed into glove boxes that were equipped to supply pressurized
nitrogen and helium to the test valves. Bubble cups were used for seat leak detection,
consisting of 6 mm tubing placed in water to a depth of 5 mm, as specified. A helium leak
detector with a sniffer probe was used for fugitive emissions testing.
2. Three thermocouples were installed on the test valves: one on the outside surface, one
inside the valve near the ball valve seat, and one on the needle valve bonnet.
3. The test valve end screws were wrapped with adhesive foil tape to facilitate fugitive
emissions testing of the valve end screw body seals. The tape contained a hole near the
top of the end screw to allow insertion of the sniffer probe to determine the helium leak rate
of the end screw body seals.
4. The test valves were pressurized to their Cold Working Pressure (CWP) with nitrogen and
the ball and needle valves were cycled 100 times:
a. Class 2500 valve CWP: 6250 psig (430 bar)
b. Class 1500 valve CWP: 3750 psig (258 bar)
5. The test pressure was vented.
2018 Swagelok Company
Product Test Report PTR-3480
Swagelok Company Ver 02
29495 F.A. Lennon Drive December 2018
Solon, Ohio 44139 U.S.A. Page 3 of 7
Initial Ambient Temperature Test
1. A test pressure of 29 psig (2.0 bar) of nitrogen was applied, and the ball and needle valves
were closed and tested for seat leakage for 5 minutes. The test pressure was vented.
2. Step 1 was repeated with a test pressure of 35 % of CWP.
3. Step 1 was repeated with a test pressure of 70 % of CWP.
4. Step 1 was repeated with a test pressure of 110 % of CWP.
5. The test pressure was vented and the test valves were pressurized with helium at a test
pressure of 110 % of CWP.
6. The test pressure was maintained for 15 minutes, then the test pressure was reduced to
100 % of CWP.
7. The ball and needle valves were cycled 25 times. During the 25th cycle, each valve stem
was sniffed for dynamic fugitive emissions leakage by placing the sniffer probe within 3 mm
of the valve stem, as specified.
8. Each valve stem was sniffed for static fugitive emissions leakage.
9. The test valve end screw and needle bonnet body seals were sniffed for static fugitive
emissions leakage.
10. The test pressure was vented and the test valves pressurized with nitrogen to 100 % of
CWP. The ball and needle valves were closed and tested for seat leakage for 5 minutes.
11. The test pressure was vented.
Elevated Temperature Test
1. The test valve bodies were wrapped with heat tape and the temperature slowly increased
until the valve interior temperature reached 250°F (121°C). The heating was controlled so
that the difference between the test valve body surface and internal temperature did not
exceed 20°C (36°F).
2. A test pressure of 29 psig (2.0 bar) nitrogen was applied, and the ball and needle valves
were closed and tested for seat leakage for 5 minutes. The test pressure was vented.
3. Step 2 was repeated with a test pressure of 33 % of the valve elevated temperature working
pressure (WP).
4. Step 2 was repeated with a test pressure of 66 % of WP.
5. Step 2 was repeated with a test pressure of 100 % of WP.
6. The test pressure was vented and the test valves pressurized with helium at a test pressure
of 100 % of WP.
7. The test pressure was maintained for 15 minutes.
8. The ball and needle valves were cycled 25 times. During the 25th cycle, each valve stem
was sniffed for dynamic fugitive emissions leakage.
9. Each valve stem was sniffed for static fugitive emissions leakage.
10. The test valve end screw and needle bonnet body seals were sniffed for static fugitive
emissions leakage.
11. The test pressure was vented and the valve pressurized with nitrogen to 100 % of CWP.
The ball and needle valves were closed and tested for seat leakage test for 5 minutes.
12. The test pressure was vented and the valves allowed to return to ambient temperature
without any forced cooling.
2018 Swagelok Company
Product Test Report PTR-3480
Swagelok Company Ver 02
29495 F.A. Lennon Drive December 2018
Solon, Ohio 44139 U.S.A. Page 4 of 7
Low-Temperature Test
1. The test valves were placed into an insulated container. A controlled flow of vaporized liquid
nitrogen was directed into the container to cool the test valves to –58°F (–50°C). The
cooling was controlled so that the difference between the test valve body surface and
internal temperatures did not exceed 20°C (36°F).
2. The test steps from the Initial Ambient Temperature Test were repeated at low temperature.
3. The test valves were allowed to return to ambient temperature without any forced heating.
Final Ambient Temperature Test
1. A test pressure of 29 psig (2.0 bar) nitrogen was applied, and the ball and needle valves
were closed and tested for seat leakage for 5 minutes. The test pressure was vented.
2. The above step was repeated with a test pressure of 102 psig (7.0 bar).
3. The above step was repeated with the test valve CWP as the test pressure.
Anti-Static Test
The electrical resistance between each test valve body and each valve stem was measured with
an ohmmeter.
TEST RESULTS
All testing was witnessed by an independent third party.
Table 1: Class 1500—Valve Initial Ambient Test Results
Test Acceptance Criteria
Pressure
Test Description psig (bar) Ball Valve Needle Valve Test Result
Seat test 29 (2.0) Pass
Seat test 1313 (90.4) 0 mL/ min 1.2 mL/ min Pass
Seat Test 2625 (180) Pass
Seat Test 4125 (284) Pass
Dynamic Fugitive
1.7 × 10–5 std cm3/s 1.1 × 10–5 std cm3/s Pass
Emissions (Stems)
Static Fugitive 3750 (258) 1.7 × 10–5 std cm3/s 1.1 × 10–5 std cm3/s Pass
Emissions (Stems)
Static Fugitive
Emissions 4.2 × 10–6 std cm3/s 3.2 × 10–6 std cm3/s Pass
(Body Seals)
Seat Test 3750 (258) 0 mL/ min 1.2 mL/ min Pass
2018 Swagelok Company
Product Test Report PTR-3480
Swagelok Company Ver 02
29495 F.A. Lennon Drive December 2018
Solon, Ohio 44139 U.S.A. Page 5 of 7
Table 2: Class 1500—Valve Elevated Temperature Test Results
Test Acceptance Criteria
Pressure
Test Description psig (bar) Ball Valve Needle Valve Test Result
Seat test 29 (2.0) Pass
Seat test 1165 (80.2) Pass
0 mL/ min 1.2 mL/ min
Seat Test 2330 (160) Pass
Seat Test 3530 (243) Pass
Dynamic Fugitive
1.7 × 10 –5 std cm3/s 1.1 × 10 –5 std cm3/s Pass
Emissions (Stems)
Static Fugitive 3530 (243) 1.7 × 10 –5 std cm3/s 1.1 × 10 –5 std cm3/s Pass
Emissions (Stems)
Static Fugitive
Emissions 4.2 × 10–6 std cm3/s 3.2 × 10–6 std cm3/s Pass
(Body Seals)
Seat Test 3530 (243) 0 mL/ min 1.2 mL/ min Pass
Table 3: Class 1500—Valve Low-Temperature Test Results
Test Acceptance Criteria
Pressure
Test Description psig (bar) Ball Valve Needle Valve Test Result
Seat test 29 (2.0) Pass
Seat test 1313 (90.4) Pass
22.5 mL/ min 72 mL/ min
Seat Test 2625 (180) Pass
Seat Test 4125 (284) Pass
Dynamic Fugitive
1.7 × 10 –5 std cm3/s 1.1 × 10 –5 std cm3/s Pass (1)
Emissions (Stems)
Static Fugitive 3750 (258) 1.7 × 10 –5 std cm3/s 1.1 × 10 –5 std cm3/s Pass
Emissions (Stems)
Static Fugitive
Emissions 4.2 × 10–6 std cm3/s 3.2 × 10–6 std cm3/s Pass
(Body Seals)
Seat Test 3750 (258) 22.5 mL/ min 72 mL/ min Pass
Note 1: After a packing adjustment, as permitted by the test specification, the needle valve passed the test.
Table 4: Class—1500 Valve Final Ambient Temperature and Anti-Static Test Results
Test Acceptance Criteria
Test Pressure Acceptance
Description psig (bar) Ball Valve Needle Valve Criteria
Seat test 29 (2.0) Pass
Seat test 102 (7.0) 0 mL/ min 1.2 mL/ min Pass
Seat Test 3750 (258) Pass
Anti-Static Test N/A 10 ohms 10 ohms Pass
2018 Swagelok Company
Product Test Report PTR-3480
Swagelok Company Ver 02
29495 F.A. Lennon Drive December 2018
Solon, Ohio 44139 U.S.A. Page 6 of 7
Table 5: Class 2500—Valve Initial Ambient Test Results
Test Acceptance Criteria
Pressure
Test Description psig (bar) Ball Valve Needle Valve Test Result
Seat test 29 (2.0) Pass
Seat test 2188 (150) Pass
0 mL/ min 1.2 mL/ min
Seat Test 4375 (301) Pass
Seat Test 6875 (473) Pass
Dynamic Fugitive
1.7 × 10 –5 std cm3/s 1.1 × 10 –5 std cm3/s Pass
Emissions (Stems)
Static Fugitive 6250 (430) 1.7 × 10 –5 std cm3/s 1.1 × 10 –5 std cm3/s Pass
Emissions (Stems)
Static Fugitive
Emissions 4.2 × 10–6 std cm3/s 3.2 × 10–6 std cm3/s Pass
(Body Seals)
Seat Test 6250 (430) 0 mL/ min 1.2 mL/ min Pass
Table 6: Class 2500—Valve Elevated Temperature Test Results
Test Acceptance Criteria
Pressure Test
Test Description psig (bar) Ball Valve Needle Valve Result
Seat test 29 (2.0) Pass
Seat test 1940 (133) Pass
0 mL/ min 1.2 mL/ min
Seat Test 3881 (267) Pass
Seat Test 5880 (405) Pass
Dynamic Fugitive
1.7 × 10 –5 std cm3/s 1.1 × 10 –5 std cm3/s Pass
Emissions (Stems)
Static Fugitive 5880 (405) 1.7 × 10 –5 std cm3/s 1.1 × 10 –5 std cm3/s Pass
Emissions (Stems)
Static Fugitive
Emissions 4.2 × 10–6 std cm3/s 3.2 × 10–6 std cm3/s Pass
(Body Seals)
Seat Test 5880 (405) 0 mL/ min 1.2 mL/ min Pass
Table 7: Class 2500—Valve Low-Temperature Test Results
Test Acceptance Criteria
Pressure Test
Test Description psig (bar) Ball Valve Needle Valve Result
Seat test 29 (2.0) Pass
Seat test 2188 (150) Pass
22.5 mL/ min 72 mL/ min
Seat Test 4375 (301) Pass
Seat Test 6875 (473) Pass
Dynamic Fugitive
1.7 × 10 –5 std cm3/s 1.1 × 10 –5 std cm3/s Pass
Emissions (Stems)
Static Fugitive 6250 (430)
1.7 × 10 –5 std cm3/s 1.1 × 10 –5 std cm3/s Pass
Emissions (Stems)
Static Fugitive
Emissions 4.2 × 10–6 std cm3/s 3.2 × 10–6 std cm3/s Pass
(Body Seals)
Seat Test 6250 (430) 22.5 mL/ min 72 mL/ min Pass
2018 Swagelok Company
Product Test Report PTR-3480
Swagelok Company Ver 02
29495 F.A. Lennon Drive December 2018
Solon, Ohio 44139 U.S.A. Page 7 of 7
Table 8: Class 2500—Valve Final Ambient Temperature and Anti-Static Test Results
Test Acceptance Criteria
Pressure Test
Test Description psig (bar) Ball Valve Needle Valve Result
Seat test 29 (2.0) Pass
Seat test 102 (7.0) 0 mL/ min 1.2 mL/ min Pass
Seat Test 6250 (430) Pass
Anti-Static Test N/A 10 ohms 10 ohms Pass
The tests were conducted beyond the product’s recommended operating parameters and
do not modify the published product ratings.
These tests were performed to consider a specific set of conditions and should not be
considered valid outside those conditions. Swagelok Company makes no representation or
warranties regarding these selected conditions or the results attained there from. Laboratory
tests cannot duplicate the variety of actual operating conditions. Test results are not offered as
statistically significant. See the product catalog for technical data.
SAFE PRODUCT SELECTION
When selecting a product, the total system design must be considered to ensure safe, trouble-
free performance. Function, material compatibility, adequate ratings, proper installation,
operation, and maintenance are the responsibilities of the system designer and user.
Referenced Documents
MESC SPE 77/300, Procedure and Technical Specification for Type Acceptance Testing (TAT)
of Industrial Valves. Shell Global Solutions International B.V., The Netherlands
ISO 5208, Industrial Valves – Pressure Testing of Metallic Valves, International Organization for
Standardization, 1, ch. De la Voie-Creuse, Case postale 56, CH-1211 Geneva 20, Switzerland
Swagelok—TM Swagelok Company
2018 Swagelok Company
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Prevention of Valve Fugitive Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryD'EverandPrevention of Valve Fugitive Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryPas encore d'évaluation
- PTR-4068 Thermal Cycle Test of Stainless Steel Swagelok FKB Series Medium-Pressure Ball Valves 20ksiDocument3 pagesPTR-4068 Thermal Cycle Test of Stainless Steel Swagelok FKB Series Medium-Pressure Ball Valves 20ksiCricri CriPas encore d'évaluation
- Know Connectors - AmphenolDocument24 pagesKnow Connectors - AmphenolJohn Glowacki100% (3)
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGD'EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGPas encore d'évaluation
- Tubing Data ChartsDocument30 pagesTubing Data ChartsIvo NunesPas encore d'évaluation
- Contemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsD'EverandContemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsPas encore d'évaluation
- Sem 1 Brazing With Oxyacetylene WeldingDocument3 pagesSem 1 Brazing With Oxyacetylene WeldingKamarul Nizam100% (1)
- All-in-One Manual of Industrial Piping Practice and MaintenanceD'EverandAll-in-One Manual of Industrial Piping Practice and MaintenanceÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Handbok Fittings Eng Web-211217 PDFDocument72 pagesHandbok Fittings Eng Web-211217 PDFjoseocsilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 5 - Thermocouple Temperature Calibration (PRTS)Document7 pagesLab 5 - Thermocouple Temperature Calibration (PRTS)Slim ShaddysPas encore d'évaluation
- Spec. Number Suffixes: US Based On US Codes, ON For Onshore Projects, M&U Units Used: SI Metric and US Customary UnitsDocument30 pagesSpec. Number Suffixes: US Based On US Codes, ON For Onshore Projects, M&U Units Used: SI Metric and US Customary Unitsrahul100% (1)
- Escc Component Qualification - BrochureDocument11 pagesEscc Component Qualification - BrochurejsadachiPas encore d'évaluation
- Workmanship Manual: Revision RecordDocument20 pagesWorkmanship Manual: Revision Recordfrancisco lopez moyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3604 2Document17 pages3604 2Tiffany WilsonPas encore d'évaluation
- 7492 - Agile Test Summary Report TemplateDocument9 pages7492 - Agile Test Summary Report TemplateDaniel JosiahPas encore d'évaluation
- MS CRD 0007Document2 pagesMS CRD 0007cypPas encore d'évaluation
- KSC de 512 SM - Interim - M PDFDocument101 pagesKSC de 512 SM - Interim - M PDFramalingamPas encore d'évaluation
- MSDS SwakDocument4 pagesMSDS Swaktolkien9Pas encore d'évaluation
- Test Plan ForDocument17 pagesTest Plan ForAli HamzaPas encore d'évaluation
- An818 Rev-20 2Document5 pagesAn818 Rev-20 2Senthil KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensor Catalog 2018Document20 pagesSensor Catalog 2018Aníbal RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Format 4 Test PlansDocument2 pagesFormat 4 Test Plansapi-3710677Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dimensional Inspection Report: Sample Production Lot/BatchDocument1 pageDimensional Inspection Report: Sample Production Lot/BatchCristina TinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Material Test ReportDocument5 pagesMaterial Test ReportJuan Carlos Sua SuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Summary Report: Yes YesDocument2 pagesTest Summary Report: Yes YesNilotpal Shankar MitraPas encore d'évaluation
- RTD Tolerance Classes TBRTDTOL-0614Document4 pagesRTD Tolerance Classes TBRTDTOL-0614Anonymous zdCUbW8HfPas encore d'évaluation
- Agilent Temperature PDFDocument36 pagesAgilent Temperature PDFcnrk777Pas encore d'évaluation
- Stainless Steel Pressure Gauges Glycerin Filling InstructionsDocument1 pageStainless Steel Pressure Gauges Glycerin Filling InstructionsAfzal RiazPas encore d'évaluation
- (Project Name) Test Plan: (Document Version Number) Project Team: (Date)Document3 pages(Project Name) Test Plan: (Document Version Number) Project Team: (Date)periwinkle_radcliffePas encore d'évaluation
- R0607-Cm-Itr-08-606 321a PDFDocument13 pagesR0607-Cm-Itr-08-606 321a PDFShelton S S SheltonPas encore d'évaluation
- Master Soppd101 02Document23 pagesMaster Soppd101 02boimziiPas encore d'évaluation
- Visual Weld Inspection: Organizational IssuanceDocument7 pagesVisual Weld Inspection: Organizational IssuanceEdAlmPas encore d'évaluation
- Swagelok TighteningDocument4 pagesSwagelok TighteningiswantmachooPas encore d'évaluation
- MSFC-SPEC-3679 - Process Specification Welding Aerospace HardwareDocument102 pagesMSFC-SPEC-3679 - Process Specification Welding Aerospace HardwareXto PeregrinPas encore d'évaluation
- TUBE, UNS S31600/S31609, SMLS, AnnealedDocument2 pagesTUBE, UNS S31600/S31609, SMLS, AnnealedTuấn Dương QuốcPas encore d'évaluation
- Fit - Up and Visual Examination Report: Attachment Drawing Joint DetailDocument1 pageFit - Up and Visual Examination Report: Attachment Drawing Joint DetailMuhammad Fitransyah Syamsuar Putra100% (1)
- Process StructuresDocument38 pagesProcess StructuresPayalmba19Pas encore d'évaluation
- 380 1 PDFDocument7 pages380 1 PDFJimyTeránAgudeloPas encore d'évaluation
- 1000 Wog Ball ValveDocument1 page1000 Wog Ball ValveSandi AslanPas encore d'évaluation
- Certified Mill Test Report: S O L D T O S H I P T ODocument1 pageCertified Mill Test Report: S O L D T O S H I P T OMohamed RaafatPas encore d'évaluation
- Check Valve 6in HT 6YF4Document1 pageCheck Valve 6in HT 6YF4Juan Pablo Perdomo OrtizPas encore d'évaluation
- SwageloK MS 02 468Document20 pagesSwageloK MS 02 468meseicarmePas encore d'évaluation
- Pyromation Product Catalog Part Number Application GuideDocument8 pagesPyromation Product Catalog Part Number Application GuideSakahi SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kingsa FD90 Test Report Body Cote - UnlockedDocument35 pagesKingsa FD90 Test Report Body Cote - UnlockedsmartscsPas encore d'évaluation
- Section Subject: Shaybah CPF Expansion ProjectDocument21 pagesSection Subject: Shaybah CPF Expansion ProjectAdhie Waelacxh100% (1)
- Development and Application of Nickel Alloys in Aerospace Engineering PDFDocument9 pagesDevelopment and Application of Nickel Alloys in Aerospace Engineering PDFAditya Budi FauziPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Management System: Orrective Ction EportDocument2 pagesBusiness Management System: Orrective Ction EportBự BụngPas encore d'évaluation
- QMS Form TemplateDocument2 pagesQMS Form Templatebdumeng665Pas encore d'évaluation
- Form 400-3-1439 - Notification of Escape (NOE)Document3 pagesForm 400-3-1439 - Notification of Escape (NOE)Michel DisderoPas encore d'évaluation
- Red DN80 50 50936Document1 pageRed DN80 50 50936slimane AIT-IDIRPas encore d'évaluation
- Tubacex 10Document2 pagesTubacex 10Akash SinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lithika - 001Document1 pageLithika - 001Harkesh RajputPas encore d'évaluation
- LV-110120-110220 35-35112 3in ANSI 300Document12 pagesLV-110120-110220 35-35112 3in ANSI 300mggz_15Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ball Valve Passport 10x8 2500#Document43 pagesBall Valve Passport 10x8 2500#Alejandro RojasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mil STD 810C: Prepared By: Muhammad Abdullah Roll No: BAEM-F17-003Document6 pagesMil STD 810C: Prepared By: Muhammad Abdullah Roll No: BAEM-F17-003Muhammad Abdullah100% (1)
- ValveDocument6 pagesValvetharmarajuPas encore d'évaluation
- DPF VT1222 TyV 4.2.0. REV3Document37 pagesDPF VT1222 TyV 4.2.0. REV3Pavlo Fabres SierraltaPas encore d'évaluation
- Neway Gate 6 X 150 RFDocument6 pagesNeway Gate 6 X 150 RFcomercial 3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Vee-Lok CatalogueDocument1 pageVee-Lok CatalogueReza RhiPas encore d'évaluation
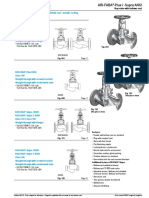
- Valve Range Strainer SupplierDocument8 pagesValve Range Strainer SupplierRAVIKIRAN BARDEPas encore d'évaluation
- ASME B16.10 RF/BWE Valve Face To Face Dimension Ball/GGC/PlugDocument1 pageASME B16.10 RF/BWE Valve Face To Face Dimension Ball/GGC/PlugRAVIKIRAN BARDEPas encore d'évaluation
- F316L Austenitic Stainless Steel: Related SpecificationsDocument2 pagesF316L Austenitic Stainless Steel: Related SpecificationsRAVIKIRAN BARDEPas encore d'évaluation
- ASME B16.11 Socket Weld End Dimensions: Adelaide Brisbane PerthDocument1 pageASME B16.11 Socket Weld End Dimensions: Adelaide Brisbane PerthRAVIKIRAN BARDEPas encore d'évaluation
- Ansi B16 Valve Face To Face Dimensions: Ball Valves Ball ValvesDocument3 pagesAnsi B16 Valve Face To Face Dimensions: Ball Valves Ball ValvesRAVIKIRAN BARDEPas encore d'évaluation
- Bill of Material - Globe Valve - Model 3000Document1 pageBill of Material - Globe Valve - Model 3000RAVIKIRAN BARDEPas encore d'évaluation
- API 600 - TrimDocument3 pagesAPI 600 - TrimRAVIKIRAN BARDEPas encore d'évaluation
- Bellow Seal Valve: Energy Environment Solutions For Sustainable GrowthDocument2 pagesBellow Seal Valve: Energy Environment Solutions For Sustainable GrowthRAVIKIRAN BARDEPas encore d'évaluation
- Bill of Material - Globe Valve - Model 3000Document1 pageBill of Material - Globe Valve - Model 3000RAVIKIRAN BARDEPas encore d'évaluation
- Ex Protection PDFDocument41 pagesEx Protection PDFSiddharth Sahu100% (1)
- Fluid FlowDocument11 pagesFluid FlowRAVIKIRAN BARDEPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 PDFDocument12 pages2 PDFRAVIKIRAN BARDEPas encore d'évaluation
- Cable Tray Price ListDocument54 pagesCable Tray Price ListSunil WadekarPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrodynamics: Naveen Mathew Nathan S. 10/1/2019Document2 pagesHydrodynamics: Naveen Mathew Nathan S. 10/1/2019SNaveenMathewPas encore d'évaluation
- Kennol Touring 15W-40 enDocument1 pageKennol Touring 15W-40 enjunaa AlbayatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mixing Analysis in A Tank Stirred With Ekato Intermig ImpellersDocument13 pagesMixing Analysis in A Tank Stirred With Ekato Intermig ImpellersBheemannaChandur100% (1)
- Section Properties and CapacitiesDocument19 pagesSection Properties and CapacitiesRufus ChengPas encore d'évaluation
- EC Drive - EC PlusDocument21 pagesEC Drive - EC PlusMohammed FarhanPas encore d'évaluation
- 3b. Column Base Plate Ce134p Escruz LRFDDocument17 pages3b. Column Base Plate Ce134p Escruz LRFDjohn devonPas encore d'évaluation
- 2mark and 16markDocument8 pages2mark and 16markGowri ShankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Fluid Thermal Systems 4th Edition by Janna ISBN Solution ManualDocument36 pagesDesign of Fluid Thermal Systems 4th Edition by Janna ISBN Solution Manualsteven100% (21)
- Car Dynamics Using Quarter Model and Passive Suspension, PDFDocument9 pagesCar Dynamics Using Quarter Model and Passive Suspension, PDFwelsya100% (1)
- DAILY Maintenance Checklist: Qt/Elect/MiscDocument2 pagesDAILY Maintenance Checklist: Qt/Elect/MiscAli KammouniPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 5 States of Matter Solution Guide Sem1 2019Document3 pagesTutorial 5 States of Matter Solution Guide Sem1 2019Myeisha WilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Proposed Utilities Piping & Fittings of Soaps & Cometics PlantDocument1 pageProposed Utilities Piping & Fittings of Soaps & Cometics PlantLuigi Andrew MercadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Preliminary Welding Procedure Specification (PWPS)Document2 pagesPreliminary Welding Procedure Specification (PWPS)Maneesh0% (1)
- Bsc/Msci Examination: PHY-304 Physical DynamicsDocument8 pagesBsc/Msci Examination: PHY-304 Physical DynamicsRoy VeseyPas encore d'évaluation
- LR Mate 200id Series - 187Document2 pagesLR Mate 200id Series - 187Kevin ScogginsPas encore d'évaluation
- DC09-311A 240kW ATSDocument4 pagesDC09-311A 240kW ATSJulio SullaymePas encore d'évaluation
- Operating Manual SV 550Document14 pagesOperating Manual SV 550juan manuel sierra solisPas encore d'évaluation
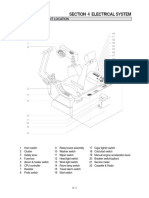
- Section 4 Electrical System: Group 1 Component LocationDocument2 pagesSection 4 Electrical System: Group 1 Component LocationSONPas encore d'évaluation
- Stability Analysis of Steel Storage Rack StructuresDocument6 pagesStability Analysis of Steel Storage Rack StructurescoolkaisyPas encore d'évaluation
- 2007 LC4 690 LC8 990 Diagnostic Measurements Failure CodesDocument49 pages2007 LC4 690 LC8 990 Diagnostic Measurements Failure Codeschili_s16Pas encore d'évaluation
- Restoration of The Contact Surface in The HLL-Riemann SolverDocument10 pagesRestoration of The Contact Surface in The HLL-Riemann SolverRafael HenriquePas encore d'évaluation
- Toyota North America New FeaturesDocument735 pagesToyota North America New FeaturesRobPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Puller Catalog - EUDocument20 pagesMechanical Puller Catalog - EUSergiSerranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ntu MethodDocument11 pagesNtu MethodPradyumna DhamangaonkarPas encore d'évaluation
- D-155 - 3 Cylinder Diesel Engine (01/75 - 12/85) 00 - Complete Machine 08-11 - Valve LeverDocument4 pagesD-155 - 3 Cylinder Diesel Engine (01/75 - 12/85) 00 - Complete Machine 08-11 - Valve LeverMANUALESPas encore d'évaluation
- Big Dutchman Stallklima Poultry Pig Climate Control Wall Fans enDocument6 pagesBig Dutchman Stallklima Poultry Pig Climate Control Wall Fans enNenad JovanovskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Shallow Foundations 2019 - MAK SlidesDocument90 pagesShallow Foundations 2019 - MAK SlidesOdiit StephenPas encore d'évaluation
- The Second Law of Thermodynamics: UNIT-3Document48 pagesThe Second Law of Thermodynamics: UNIT-319-810Anitha bhukyaPas encore d'évaluation
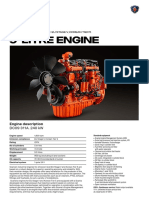
- Technical Data Sheet D245SDocument14 pagesTechnical Data Sheet D245SAslam Kamal AfdhalPas encore d'évaluation
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemD'EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemPas encore d'évaluation
- Workbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesD'EverandWorkbook to Accompany Maintenance & Reliability Best PracticesÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- Electrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70ED'EverandElectrical Safety Code Manual: A Plain Language Guide to National Electrical Code, OSHA and NFPA 70EÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (6)
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisD'EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Redefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesD'EverandRedefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsD'EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (11)
- Incidents That Define Process SafetyD'EverandIncidents That Define Process SafetyPas encore d'évaluation
- Fire Protection Engineering in Building DesignD'EverandFire Protection Engineering in Building DesignÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (5)
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsD'EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsPas encore d'évaluation
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersD'EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- What Went Wrong?: Case Histories of Process Plant Disasters and How They Could Have Been AvoidedD'EverandWhat Went Wrong?: Case Histories of Process Plant Disasters and How They Could Have Been AvoidedÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsD'EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeD'EverandThe Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (21)
- A Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesD'EverandA Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesD'EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (14)
- Healthy Buildings: How Indoor Spaces Drive Performance and ProductivityD'EverandHealthy Buildings: How Indoor Spaces Drive Performance and ProductivityÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Fire Fighting Pumping Systems at Industrial FacilitiesD'EverandFire Fighting Pumping Systems at Industrial FacilitiesÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyD'EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersD'EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (12)