Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Using The CONVAL Software For The Petrochemical Plant Control Valve Checking Case Study
Transféré par
chem_taTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Using The CONVAL Software For The Petrochemical Plant Control Valve Checking Case Study
Transféré par
chem_taDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Advances in Engineering Mechanics and Materials
Using the CONVAL® software for the
petrochemical plant control valves checking.
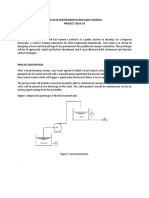
Case study
C. Patrascioiu, G. Stamatescu, C. Lazar
To obtaining the optimum control valve parameters,
Abstract — In the paper there are presented the researches Siemers defines seven steps of the control valve design [6]. In
into field of the CONVAL® software using to control valve this operation, the Conval® software is used to select the better
checking. There are presented the main facilities of the control valve for the input conditions and with the graphical
CONVAL® software, including the description of the used support to analyze the inherent and the work characteristics.
functions. The CONVAL® software has been used to plant Another problem solved by the CONVAL® software is the
refinery control valves checking. The results have been estimation of the static controllability index, there is
validated 87 % of the investigated control valves. implemented in 8th version of the software.
The paper presents the author’s researches in the field of the
Keywords — control, control valve, CONVAL software, industrial control valves simulation. The control valves that
refinery. have been investigated belong to the Romanian refinery plant.
The investigation has been focused to verify the control valves
I. INTRODUCTION in the new operating conditions.
The control valves are the most important control elements
of the control systems. A detailed presentation is showed in
specializes literature [1, 2]. A new component of the control II. THE CONVAL® SOFTWARE
valves is represented by the software for the control valve In 1985, a team of experienced engineers from the fields of
design. instrumentation and control, chemical processes and machine
The CONVAL® software, developed by the Ruhr University building, as well as various other branches of industry, joined
of Bochum, is used to simulate or design of the control valve forces with software development experts. At the end of a
[3]. The structure of this software contains the following development phase lasting four years, they were able to
elements [4]: present the first results - christened CONVAL® 1.0 - at
a) A thermodynamic database; INTERKAMA '89 [7].
b) A mathematical model of the control valve; The CONVAL ® software is destined to design or checking
c) An industrial control valve database. the chemical plant elements, such as: pipes, heat exchangers,
pumps, valves and control valves. Each component of the
The CONVAL ® software has been used to design the previous list may be activated using a specific command. To
control valves in many industrial applications. For example, activate the control valves design / check, the user will activate
Siemers describes the priorities concerning of the control the Control Valve command.
valves as follow: safety and reliability, control quality, This program is based on:
environmental aspects, trouble-free life cycles and lowest cost − IEC 60534 2 1-3 standard to calculate liquid flow rate;
[5]. The first element of the control valve design is the − VDMA 24422 standard to calculate the sound level;
geometry of the plant s pipes. A good knowledge of a pipe − IEC 60534 8-3 and IEC 60534 8-4 standard to
pressure and drop pressure and in the same time the calculate the gas flow rate.
knowledge of the characteristics of the pumps is necessary.
The main window of the Control Valve CONVAL ® menu is
presented in figure 1. The structure menu if the Control Valve
window is follow:
C. Patrascioiu is with the Petroleum-Gas University of Ploiesti, Romania.
He is now with the Automatics, Computers & Electronic Department.
a) Medium – the menu used to data specification of the
(e-mail: cpatrascioiu@upg-ploiesti.ro). fluid that circulates into control valve;
G.Stamatescu is with the Politehnica University of Bucharesti, Romania. b) Pipeline – the menu associated to pipes data, upstream
He is now with the Automatics and Industrial Informatics Department. and downstream of the control valve;
(e-mail: grigore.stamatescu@upb.ro).
C. Lazar was with FIWA Company, Sibiu, Romania. He is branch
c) Control valve – the configuration menu of the design
manager of the Romanian branch. (e-mail: office.ro@fiwagroup.com). control valve parameters;
ISBN: 978-1-61804-241-5 285
Advances in Engineering Mechanics and Materials
d) Noise calculation – the configuration menu of the fluid
flow noise calculation.
Fig 1 The Control Valve CONVAL ® window.
All four Control Valve menus are the most used and for this
reason there will be detailed in the next sections. The user may define three operating points: first point
is associated to minim flow rate, the second defines the
nominal flow rate and the last point is represents the
A. The Medium menu
maximum flow rate.
In the Medium menu there are disposable five functions, as
follow: 4) Fluid operating data is the function used to calculate
1) The Calculation header function has a obligatory the fluid density (ρ1) and the vapour pressure (pv1), all
character, there being destined to file specification properties being calculated in the upstream conditions.
(Identifier) and to name the control valve in the P&ID The calculus is made using the equilibrium equations
(Tag No.). and thermodynamic data of the CONVAL data base. If
2) The Medium Selection State function specifies the fluid the user has better values, there may replace the
that circulates by the control valve. In this function calculated values.
exists the sub-function Medium, there is used to select 5) The Viscosity and laminar flow function is used to
the thermodynamic properties at thermodynamic data determine the correction factor FR. This factor is
base. The State sub-function specifies the liquid or calculated using the viscosity value and the Reynolds
vapor fluid state. criterion. Viscosity is calculated with IEC 60534
3) In the Operating data function, the user must specify standard. If the flow regime is turbulent, Re >100000,
next information: the correction factor will be FR = 1.
a) The calculated variable (Calculation), a variable
selected from the list: demand flow module Kv/Cv;
mass flow rate qm; upstream pressure p1; B. Pipeline menu
downstream pressure p2. The Pipeline menu contains the functions used to specify the
b) The operating point characteristics. These pipes constructive characteristics. The functions are following:
characteristics are dependent by the selected 1) The Influence of fittings function specifies the
calculated variable. If the selected calculated is connection mode of the control valve to upstream and
Kv/Cv, the operating point characteristics will be: downstream pipe. The user may set the control valve
t1 – the upstream temperature; nominal diameter with same pipe diameter. If this
p1 – the upstream pressure; situation is not possible, the user must specify the
p2 – the downstream pressure; following date:
qm or qv – the mass or volume flow rate. a) Flow coefficient of fittings;
ISBN: 978-1-61804-241-5 286
Advances in Engineering Mechanics and Materials
b) Piping geometric factor, defined by the relation frequency, Sound velocity, Power loss, Mechanical
[6] stream power.
−0.5
∑ K i CV 3) The Spectrum function is used to select the
Fp = 1 + ;
specifications of the spectral frequencies generated by
N 2 d 2 the control valve.
c) Valve modifier for fittings.
III. PETROCHEMICAL CONTROL VALVES CHECKING
2) The Pipe downstream of valve function is used to Technical sustainability check of a refinery plant consists in
specify the pipe material and the pipe diameter. The measurement systems checking, controller tuning and control
CONVAL program has a data base which contains valves checking. In this paper have been checked the control
the pipe design information. valves of a plant of catalytic reformer factory.
To check the control valves have been used the initial
design data, an example being presented in table 1. These
C. Control valve menu primary data contain:
The Control Valve menu is dedicated to select the − The name of the control valve system TAG;
calculated control valve from the produces data base. The − Information about the chemical composition of the
Control valve menu has four functions, as follow: stream;
1) The Valve Selection function is used to select: − Specific gravity of the fluid;
a) Valve manufacturer; − Temperature of the fluid;
b) Series of control valve; − The input pressure of the valve;
c) Valve selection. − The output pressure of the valve;
− The flow rate of the stream;
2) The Valve data function sets the user option of the next
− The type of the control valve.
specifications:
a) Size and pressure class: Metric or ANSI.
There have been analyzed 38 control valves of the plant. In
b) Valve type, as follow: Globe valve, Rotary plug
table 2 there is presented a partial list of the results obtained
valve, Butterfly valve, Ball valve, Ball valve,
Axial valve, Angle seat valve, Continuous globe by using the CONVAL® software for the FV-001 control
valve, Diaphragm valve etc. valve. The properties associated to the operating control valve
c) Trim type: Parabolic plug, V-port plug, Cage are calculated for 25, 50, 75 and 100% of the stroke
trim, Multihole plug and Seat-guided contoured displacement. The relative stroke displacement s/s100 is
plug. identical with the test values. The flow module Kv has values
d) Flow direction inside the control valve: FTO between 11 and 237 m3/h, the higher value being higher than
(fluid open), FTC (fluid close). the maximal value of the input data (125 m3/h). In all
e) Basic characteristic of valve (intrinsic situations (25, 50, 75 and 100% of stroke) the stream flow is
characteristic): Equal percentage, Linear, non-critical. The fluid velocity increases up to 3.1 m/s, value
Modified and On/Off. that is acceptable for the higher flow rate that passes in the
control valve. The noise of the control valve is 50 dB for the
normal flow rate and the maximum noise value is 55 dB, value
D. Noise Calculation menu
that is in admissible domain.
The Noise Calculation menu contains three functions for the
control valve noise calculation. The functions implemented in The CONVAl® software calculates the work characteristic
this menu are: of the control valve, figure 2. This characteristic is typical for
1) Noise prediction data function is used to select: the control valve characterized by Equal percentage inherent
a) Calculation standard – The standard used to characteristic. The operating point of the control valve is a
calculate the noise generated by liquid flow: very good choice because the operating point is s/s100=0.76,
VDMA 24422(1979-05), IEC 60534-8-4(1994- there represents that the operating point is into linear variation
05), IEC 60534-8-4(2005-08). of the characteristic.
b) Low noise design is a special function used to
select the control valve with the minimum sound
level.
2) The Minor noise prediction data is a function which
specifies the following data: Pressure ratio,
Acoustical efficiency factor, Ring frequency, Peak
ISBN: 978-1-61804-241-5 287
Advances in Engineering Mechanics and Materials
Table 1 Initial data about the control valves
Q
1 Control
Specific T P1 P2 [m3/h]
Fluid TAG Stream 2 valve
gravity [°C] [bar] [bar] [Nm3/h]
3 type
[kg/h]
1
Naphtha to V1 Normal 0.690 40 4.47 4.00 125 Fisher ET
Heptane FV-001 1 FTC
Maxim 0.690 40 5.70 4.00 165
1
FV- Naphtha to V1 Normal 0.690 40 9.80 4.00 20 Fisher ET
Heptane 1 FTC
002A Maxim 0.690 40 9.80 4.00 45
1
FV-005- Naphtha Normal 0.690 38 69.01 4.00 20 Fisher ET
Octane pass 1 1 FTC
1 Maxim 0.690 38 69.01 4.00 40
1
FV-005- Naphtha Normal 0.690 38 69.01 4.00 20 Fisher ET
Octane pass 2 1 FTC
2 Maxim 0.690 38 69.01 4.00 40
1
FV-005- Naphtha Normal 0.690 38 69.01 4.00 20 Fisher ET
Octane pass 3 1 FTC
3 Maxim 0.690 38 69.01 4.00 40
1
FV-005- Naphtha Normal 0.690 38 69.01 4.00 20 Fisher ET
Octane pass 4 1 FTC
4 Maxim 0.690 38 69.01 4.00 40
2
Comb gas to H1 Normal 0.700 35 2.50 1.00 1540 Fisher
Methane FV-006 2 EZ
Maxim 0.700 35 3.00 1.00 2000
1
FV- Naphtha from Normal 0.735 40 70.01 4.00 25 Fisher
Heptane 1
006A P1A Maxim 0.735 40 70.01 4.00 25 EZ
®
Table 2 Selected results obtained with CONVAL software
CONVAL® by F.I.R.S.T. Version 8.0 (Build 8.0.4)
Control valve: 001 1/29/2014 1:57:19 PM
Calculation header
Identifier FV-001
Characteristics values table
Caption Unit 25% 50% 75% 100%
s/s100 % 25.0 50.0 75.01 100.0
t1 °C 40.0 40.0 40.0 40.0
p1 bar(a) 4.47 4.47 4.47 4.47
p2 bar(a) 4.0 4.0 4.0 4.0
Kv m³/h 11.02 39.06 119.4 237.0
qv m³/h 9.247 32.78 100.2 198.9
qm kg/h 6,1... .0 21,8... .0 66,8... .0 132,7... .0
Type of flow - Non-critical Non-critical Non-critical Non-critical
va - 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
pv1 bar(a) 0.1191 0.1191 0.1191 0.11...
ρ1 kg/m³ 667.4 667.4 667.4 667.4
LpAe dB(A) 20.0 34.4 48.0 55.35
u1 m/s 0.1454 0.5152 1.574 3.126
ISBN: 978-1-61804-241-5 288
Advances in Engineering Mechanics and Materials
Fig 2 The flow characteristic of the FV-001 control valve. Fig 3 The characteristics of the associate parameters of the
FV-001 control valve.
Figure 3 represents the following parameters:
− Sound pressure level LpAe; Table 3 presents a comparison between the control valve
− The recovery factor for valves installed without fittings specification and the simulation CONVAL results. The
attached, value can be found in the flow coefficient numerical results analysis has four components: the nominal
tables, xF [6]; flow Kvs, the valve open, the flow velocity and the sound
− Rated liquid pressure recovery factor FL2, Kc, xFz. pressure level.
Table 3 Example of the results obtained by using the CONVAL software
Specifications The simulation CONVAL results
TAG Q Kvs Observation
1 Valve Flow
[m3/h] Nominal Lp
2 Open velocity
[Nm3/h] flow [dB(A)]
3 [%] [m/s]
[kg/h] [m3/h]
1
FV-001 125 237.0 63.8 1.99 50.9 Acceptable
1
FV-002A 20 21.0 36.9 3.50 75.7 Acceptable
1
FV-005-1 20 21.0 24.9 2.81 54.7 Acceptable
1
FV-005-2 20 21.0 24.9 2.81 54.7 Acceptable
1
FV-005-3 20 21.0 60.3 2.81 54.7 Acceptable
1
FV-005-4 20 21.0 60.3 2.81 54.7 Acceptable
2
FV-006 1540 13.7 10.0 0.01 20.0 Acceptable
1
FV-006A 25 1.3 100.0 3.71 55.3 Non-acceptable
For example, at the input data presented in table 1 there
have been validated 7 control valves. For these control valves, IV. CONCLUSION
the nominal flow is greater than the input flow rate, the valve The paper presents the facilities of the CONVAL® software
open is less than 60 %, the liquid flow velocity is less than 4 for the control valve checking. researches into field of the
m/s and the sound pressure level is less than 75 dB(A). using to. The main facilities of the CONVAL® software are
The analyzed plant has are 38 control valve, each control classified in Medium menu, Pipeline menu, Control valve
valve being checked with CONVAl® software. For five of the menu and Noise calculation menu. The CONVAL® software
analyzed control valves, the flow module value is less than the has been used to check the plant refinery control valves. The
nominal flow rate value, there do not assure a gut function of results have been validated 87 % of the investigated control
the control valve. valves.
ISBN: 978-1-61804-241-5 289
Advances in Engineering Mechanics and Materials
REFERENCES
[1] Fliegen J., Grutesen L., Industrial Process Control Valve, Corporate
Media GmbH, D-80992 Munich, Germany, 2007.
[2] * * * CONTROL VALVE HANDBOOK - Fourth Edition, Fisher
Controls International LLC 2005.
[3] Siemers H., Control valve design aspects for critical applications in
petrochemical plants – part I, Valve World, 2004.
[4] Plant design and control valve selection under increasing cost and time
pressure - Part I, Valve World, 2005.
[5] Hinssen H., Controllability Index: the effective CONVAL 8.0
approaches to optimize your valve configuration, Valve World, 2009.
[6] Siemers H., Control valve design aspects for critical applications in
petrochemical plants – part II, Valve World, 2004.
[7] http://www.firstgmbh.com/main.php?page=cv9_prod
ISBN: 978-1-61804-241-5 290
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Instrument Technology: Telemetering and Automatic ControlD'EverandInstrument Technology: Telemetering and Automatic ControlPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Control for Sheet-Metal Stamping: Process Modeling, Controller Design and Shop-Floor ImplementationD'EverandProcess Control for Sheet-Metal Stamping: Process Modeling, Controller Design and Shop-Floor ImplementationPas encore d'évaluation
- HIL Testing MPDDocument4 pagesHIL Testing MPDMichael ChandraPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Control System For Crude Oil Plant - A Case StudyDocument5 pagesAdvanced Control System For Crude Oil Plant - A Case Studyquercitron_7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chempute Software - Instrument Engineering CalculationsDocument4 pagesChempute Software - Instrument Engineering CalculationsSulis Tiyo100% (1)
- CVAP Software For Check Valve Performance Prediction Conditon Monitoring Maintenance Optimization & Root Cause Failure Evaluation 2Document30 pagesCVAP Software For Check Valve Performance Prediction Conditon Monitoring Maintenance Optimization & Root Cause Failure Evaluation 2EnformablePas encore d'évaluation
- PHD Research Plannin2Document7 pagesPHD Research Plannin2CharlesPas encore d'évaluation
- 17 MPC - Distillation - Column PDFDocument15 pages17 MPC - Distillation - Column PDFneiljain421Pas encore d'évaluation
- WEPGF092 ManuscriptDocument5 pagesWEPGF092 ManuscriptRustryPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Process Control - From A PID Loop Up To Refinery-Wide OptimizationDocument15 pagesAdvanced Process Control - From A PID Loop Up To Refinery-Wide OptimizationVuongTrinhPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Valve Design Aspects For Critical Applications in Petrochemical Plants - Part 1 Valve World 2004 Part I PDFDocument6 pagesControl Valve Design Aspects For Critical Applications in Petrochemical Plants - Part 1 Valve World 2004 Part I PDFonizuka-t2263Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ibp1169 11 PDFDocument11 pagesIbp1169 11 PDFRaiBernardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Samson: Control Valve Design Aspects For Critical Applications in Petrochemical PlantsDocument20 pagesSamson: Control Valve Design Aspects For Critical Applications in Petrochemical PlantsdharmendrabholePas encore d'évaluation
- Control Valves - Modeling and SimulationDocument7 pagesControl Valves - Modeling and SimulationErick Renzo Hidalgo OrtegaPas encore d'évaluation
- AIChE The Most Beneficial Technical ChemE SkillsDocument49 pagesAIChE The Most Beneficial Technical ChemE SkillsSubhradip BhattacharjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Testing and Evaluating Electronic Gas Measurement Flow ComputersDocument6 pagesTesting and Evaluating Electronic Gas Measurement Flow ComputersAhmed RamadanPas encore d'évaluation
- Modeling Water Supply System Control System Algorithms: SciencedirectDocument10 pagesModeling Water Supply System Control System Algorithms: SciencedirectKheav KimlengPas encore d'évaluation
- Selecting A Pipeline Leak Detection SystemDocument7 pagesSelecting A Pipeline Leak Detection SystemGalo AyalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Online Monitoring and Control of Flow Rate in Oil Pipelines TransportationDocument8 pagesOnline Monitoring and Control of Flow Rate in Oil Pipelines TransportationCeeta IndustriesPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Prerequisites To Establishing An Environmental Monitoring PlanDocument8 pages3 Prerequisites To Establishing An Environmental Monitoring PlanCatrinescu OanaPas encore d'évaluation
- PositionerDocument2 pagesPositionerystevePas encore d'évaluation
- Industrial Process Control ValvesDocument36 pagesIndustrial Process Control Valvesffown100% (1)
- 2015 Controlof Propylene Propane Distillation Processusing Unisim DesignDocument7 pages2015 Controlof Propylene Propane Distillation Processusing Unisim DesignMohsenPas encore d'évaluation
- A4 SPEC Surge Control Dynamics FIV AIV Station2014 PDFDocument4 pagesA4 SPEC Surge Control Dynamics FIV AIV Station2014 PDFJose BijoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Standard HVAC Control SystemsDocument127 pagesStandard HVAC Control Systemsdash_caddiesPas encore d'évaluation
- A4 SPEC Surge Control Dynamics FIV AIV Station2014Document4 pagesA4 SPEC Surge Control Dynamics FIV AIV Station2014Kroya HunPas encore d'évaluation
- Temperature Optimization of A Naphtha Splitter UnitDocument10 pagesTemperature Optimization of A Naphtha Splitter UnitSalma TajPas encore d'évaluation
- PFinal IME 8310-2020-10 PDFDocument3 pagesPFinal IME 8310-2020-10 PDFHarold A NaranjoPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Past, and Future Present,: ControlDocument8 pagesProcess Past, and Future Present,: ControlBorislav GeorgievPas encore d'évaluation
- Smart Valve Flow ConditionersDocument4 pagesSmart Valve Flow ConditionersMuzammil HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Hardwarex: Hardware ArticleDocument18 pagesHardwarex: Hardware ArticlekaisengPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Standards and Specifications Measurement of Hydrocarbon Liquids Rev01Document10 pagesProject Standards and Specifications Measurement of Hydrocarbon Liquids Rev01Ibnu JunifanPas encore d'évaluation
- (Advances in Industrial Control) Victor M. Alfaro, Ramon Vilanova (Auth.) - Model-Reference Robust Tuning of PID Controllers-Springer International Publishing (2016)Document202 pages(Advances in Industrial Control) Victor M. Alfaro, Ramon Vilanova (Auth.) - Model-Reference Robust Tuning of PID Controllers-Springer International Publishing (2016)raul rasconPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Process Control Technology Implementation in Ammonia PlantDocument5 pagesAdvanced Process Control Technology Implementation in Ammonia PlantSSR4 XlxlPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Performance Qualification Protocol For Autoclave - Pharmaceutical Guidelines 2Document12 pagesProcess Performance Qualification Protocol For Autoclave - Pharmaceutical Guidelines 2MykolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction and Analysis of PID, Fuzzy and Predictive Controllers in Flow SystemDocument7 pagesConstruction and Analysis of PID, Fuzzy and Predictive Controllers in Flow SystemLuigi FreirePas encore d'évaluation
- Mechatronic Design Solution For Fuel Level Monitoring Using Pressure Sensor PDFDocument8 pagesMechatronic Design Solution For Fuel Level Monitoring Using Pressure Sensor PDFJohn Renz M. CleofasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Systems Starting and TestingDocument4 pagesMechanical Systems Starting and Testingabdullah sahibPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Industrial Process Control - Text PDFDocument253 pagesPrinciples of Industrial Process Control - Text PDFMurali GangadharPas encore d'évaluation
- 26 Edad 90 Ec 0 BF 657Document15 pages26 Edad 90 Ec 0 BF 657Fatiha HAMDIPas encore d'évaluation
- Control PidDocument3 pagesControl PidfraichePas encore d'évaluation
- Taller 2 - Análisis de Criticidad Torre de Enfriamiento BACDocument11 pagesTaller 2 - Análisis de Criticidad Torre de Enfriamiento BACJuan David Sandoval HerreraPas encore d'évaluation
- MachinesDocument31 pagesMachinesmonse369Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kalsi Engineering, Inc.: The Leading AOV/MOV Software..Document37 pagesKalsi Engineering, Inc.: The Leading AOV/MOV Software..Ahmed KhairiPas encore d'évaluation
- Testing, Adjusting and Balancing SystemsDocument3 pagesTesting, Adjusting and Balancing SystemsZineddine ALICHEPas encore d'évaluation
- Darmouth College Design November 15, 2007 & Construction GuidelinesDocument6 pagesDarmouth College Design November 15, 2007 & Construction GuidelinesAhmed MostafaPas encore d'évaluation
- SPE-173759-MS Scale Modeling in ReservoirsDocument10 pagesSPE-173759-MS Scale Modeling in ReservoirsLawPas encore d'évaluation
- A Runtime Verification Framework For Control System SimulationDocument10 pagesA Runtime Verification Framework For Control System SimulationHesam SaeidiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Dependability Control Analysis: Applied To Centrifugal Pumps in A Oil Petrochemical PlantDocument9 pagesThe Dependability Control Analysis: Applied To Centrifugal Pumps in A Oil Petrochemical PlantNor El Houda KhanfriPas encore d'évaluation
- SONA COLLEGE LAB MANUAL FOR HYDRAULIC AND PNEUMATIC SYSTEMSDocument41 pagesSONA COLLEGE LAB MANUAL FOR HYDRAULIC AND PNEUMATIC SYSTEMSKanishk KannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Real-Time Embedded Control System For VTOL Aircrafts: Application To Stabilize A Quad-Rotor HelicopterDocument6 pagesReal-Time Embedded Control System For VTOL Aircrafts: Application To Stabilize A Quad-Rotor HelicopterasdssPas encore d'évaluation
- D S D S T C: Etection Ystem Esign of Ubsea REE OntrollerDocument8 pagesD S D S T C: Etection Ystem Esign of Ubsea REE OntrollerijcsesPas encore d'évaluation
- An Experimental Setup For The Study of Field-OrienDocument5 pagesAn Experimental Setup For The Study of Field-OrienAraujo AlvesPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Valve Fundamentals ExplainedDocument55 pagesControl Valve Fundamentals Explainedعبدالحميد عبدالغفار الدرديريPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Bottle FillingDocument41 pagesAutomatic Bottle FillingSanjana Singh100% (1)
- ApplicationofRCMforachipping AndsawingmillDocument25 pagesApplicationofRCMforachipping AndsawingmillflavianosamelPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Report: Study of Piping and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID), Distributed Control SystemsDocument32 pagesProject Report: Study of Piping and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID), Distributed Control SystemsrockynsitPas encore d'évaluation
- Hardware-In-The-Loop Testing of Marine Control System: Modeling, Identification and Control (MIC) October 2006Document21 pagesHardware-In-The-Loop Testing of Marine Control System: Modeling, Identification and Control (MIC) October 2006antony grandePas encore d'évaluation
- Static Analysis of Software: The Abstract InterpretationD'EverandStatic Analysis of Software: The Abstract InterpretationPas encore d'évaluation
- RELEASE: A Model with Data to Predict Aerosol Rainout in Accidental ReleasesD'EverandRELEASE: A Model with Data to Predict Aerosol Rainout in Accidental ReleasesPas encore d'évaluation
- SIL Classification For Intelligent Motor Control Systems in Accordance With ATEX Directive - PCIC - 2007Document6 pagesSIL Classification For Intelligent Motor Control Systems in Accordance With ATEX Directive - PCIC - 2007chem_taPas encore d'évaluation
- Hazard Identification of ConstructionDocument29 pagesHazard Identification of ConstructionPintu Jaiswal100% (1)
- Two Flare Stacks in One Facility Make Sure To Consider Radiation From One Stack To The Other Stack SurfaceDocument2 pagesTwo Flare Stacks in One Facility Make Sure To Consider Radiation From One Stack To The Other Stack Surfacechem_taPas encore d'évaluation
- Alarm ManagementDocument5 pagesAlarm Managementchem_taPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Human ErrorDocument2 pagesTypes of Human ErrorPankaj PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- The Effect of Nitrogen Dilution On The Flammability Limits of Hydrogen Enriched Natural GasDocument26 pagesThe Effect of Nitrogen Dilution On The Flammability Limits of Hydrogen Enriched Natural Gaschem_taPas encore d'évaluation
- Ldarguide PDFDocument52 pagesLdarguide PDFzaxaderPas encore d'évaluation
- HSG Safety Con Strut IonDocument141 pagesHSG Safety Con Strut IonbelcaPas encore d'évaluation
- Instrucalc 5 1 User Manual 1 PDFDocument398 pagesInstrucalc 5 1 User Manual 1 PDFchem_taPas encore d'évaluation
- Dispersion Modeling of Accidental Release of Chlorine GasDocument6 pagesDispersion Modeling of Accidental Release of Chlorine Gaschem_taPas encore d'évaluation
- ETL Flame Arrester GuideDocument12 pagesETL Flame Arrester GuideaysegulPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting For Human Error Probability in SIL Verification WebsiteDocument20 pagesAccounting For Human Error Probability in SIL Verification Websites3dbwPas encore d'évaluation
- Consequenc Assessment Model For Incidents Involving Release From LNG CarrierDocument128 pagesConsequenc Assessment Model For Incidents Involving Release From LNG CarrierRichard HollidayPas encore d'évaluation
- BLast AnalsyisDocument146 pagesBLast AnalsyisSri DharPas encore d'évaluation
- A Framework For Ignition Probability of Flammable Gas Clouds - ICHEMEDocument12 pagesA Framework For Ignition Probability of Flammable Gas Clouds - ICHEMEchem_taPas encore d'évaluation
- Managing The Hazards of Flare Disposal SystemsDocument12 pagesManaging The Hazards of Flare Disposal Systemschem_taPas encore d'évaluation
- MistDocument6 pagesMistchem_taPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of Piping System Thermal Expansion For Process EngineersDocument14 pagesBasics of Piping System Thermal Expansion For Process EngineersGoce VasilevskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Reduce Pumping Cost Through Optimize Pipe Size PDFDocument2 pagesReduce Pumping Cost Through Optimize Pipe Size PDFchem_taPas encore d'évaluation
- Corrosion and Cathodic Protection in Underground Piping Systems EBAA PDFDocument3 pagesCorrosion and Cathodic Protection in Underground Piping Systems EBAA PDFChristian D. OrbePas encore d'évaluation
- Marplot PDFDocument211 pagesMarplot PDFJonathanMaxwellZerecedaNovoaPas encore d'évaluation
- Triple IR Flame Detector-SharpEye PDFDocument62 pagesTriple IR Flame Detector-SharpEye PDFchem_taPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Methods For Calculating Pressure Profiles of Explosive PDFDocument143 pagesReview of Methods For Calculating Pressure Profiles of Explosive PDFchem_taPas encore d'évaluation
- Polyethylene Production Technologies PDFDocument81 pagesPolyethylene Production Technologies PDFJelssy Huaringa Yupanqui100% (1)
- Correcting The Prediction by BST Model For The Blast Explosion PDFDocument8 pagesCorrecting The Prediction by BST Model For The Blast Explosion PDFchem_taPas encore d'évaluation
- Plantwide Review3Document32 pagesPlantwide Review3pavanchem61Pas encore d'évaluation
- Prac Rel Tools Refn ChemPltDocument9 pagesPrac Rel Tools Refn ChemPltpolancusPas encore d'évaluation
- Explosion Load Calculation For Building Design by Risk Based VS Consequence Based PDFDocument6 pagesExplosion Load Calculation For Building Design by Risk Based VS Consequence Based PDFchem_taPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculation of Blast Loads Structural Components - JRC EU PDFDocument58 pagesCalculation of Blast Loads Structural Components - JRC EU PDFjntbrobalo100% (2)
- Pompe Perkins 3340f261t PDFDocument2 pagesPompe Perkins 3340f261t PDFKamel BelhibaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nissan Skyline R34 Workshop Manual EnglishDocument401 pagesNissan Skyline R34 Workshop Manual Englishrecklessone0% (2)
- Mechanical and Natural VentilationDocument43 pagesMechanical and Natural VentilationSudhanshu Mandlik100% (1)
- Glycerol Production, Consumption, Prices, Characterization and New Trends in CombustionDocument19 pagesGlycerol Production, Consumption, Prices, Characterization and New Trends in CombustionmkamalzamanPas encore d'évaluation
- As-Built Drawing ListDocument14 pagesAs-Built Drawing Listsugeng wahyudi100% (1)
- Transistor and Thyristor (SCR) Replacement For 1336 Plus, Plus Ii, Force, Impact and REGEN DrivesDocument6 pagesTransistor and Thyristor (SCR) Replacement For 1336 Plus, Plus Ii, Force, Impact and REGEN DrivesgeniunetPas encore d'évaluation
- 2006, Piela Et Al, JECS, ImpedanceDocument13 pages2006, Piela Et Al, JECS, ImpedanceKaustubhPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 - Acid and Base TitrationDocument90 pages2 - Acid and Base TitrationEnin SofiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychrometric Chart ReadingDocument10 pagesPsychrometric Chart ReadingEzakiman OtanimPas encore d'évaluation
- DHA Anita MHA2 Paper2 Unit 3.1Document34 pagesDHA Anita MHA2 Paper2 Unit 3.1Priyan TripathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Winddevil ProductDocument2 pagesWinddevil Productavalladolid05Pas encore d'évaluation
- Inphorm Online: Click Here To AccessDocument10 pagesInphorm Online: Click Here To AccessconimecPas encore d'évaluation
- HMCDocument8 pagesHMCmahmoud nafiePas encore d'évaluation
- Air Compressor Presentation 1.1Document20 pagesAir Compressor Presentation 1.1ROBERTO FELIX RUEDASPas encore d'évaluation
- How Do Electric Cars Work - Electric Engines Explained - EDFDocument2 pagesHow Do Electric Cars Work - Electric Engines Explained - EDFrainceder100Pas encore d'évaluation
- He165 (A4)Document4 pagesHe165 (A4)KennethWilfredoVegaOviedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Toshiba 4550: Service Manual Service HandbookDocument499 pagesToshiba 4550: Service Manual Service Handbookصلاح هزاعPas encore d'évaluation
- Simon Dagher ProjectDocument114 pagesSimon Dagher ProjectSimon DagherPas encore d'évaluation
- Green Building Rating Systems ExplainedDocument42 pagesGreen Building Rating Systems ExplainedJake CerezoPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus: Certificate in Subsea EngineeringDocument6 pagesSyllabus: Certificate in Subsea EngineeringJerome LIKIBIPas encore d'évaluation
- Elec Engg Exit Exam 2018 (Part 9)Document10 pagesElec Engg Exit Exam 2018 (Part 9)Master JaguarPas encore d'évaluation
- Accident Radio Logic GOIANIADocument157 pagesAccident Radio Logic GOIANIACatalin CuraliucPas encore d'évaluation
- PHYSICSDocument3 pagesPHYSICSAndrew NibungcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Model TM-T24J TABLE TOP STEAM STERILIZER INSTRUNCTION MANUAL OF OPERATIONDocument9 pagesModel TM-T24J TABLE TOP STEAM STERILIZER INSTRUNCTION MANUAL OF OPERATIONhuguito320% (1)
- STW21NM50N MosfetDocument16 pagesSTW21NM50N MosfetrigowPas encore d'évaluation
- How Roller Coasters Work ARTICLEDocument6 pagesHow Roller Coasters Work ARTICLEmarie.tl.naarPas encore d'évaluation
- DXXXX-QSOP - Well Control Procedure For Non - Routine OperationsDocument6 pagesDXXXX-QSOP - Well Control Procedure For Non - Routine Operationsharry mulyafitPas encore d'évaluation
- Lista Precios Ahu Mas Accesorios Sinclair 2020Document80 pagesLista Precios Ahu Mas Accesorios Sinclair 2020Jonathan ArboledaPas encore d'évaluation
- Proforma 300 L Dye. Alibaba PDFDocument3 pagesProforma 300 L Dye. Alibaba PDFFer ChicoPas encore d'évaluation
- Type FL Low Profile NTC Temperature Sensor: AmphenolDocument3 pagesType FL Low Profile NTC Temperature Sensor: Amphenolmauricio alfonsoPas encore d'évaluation