Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
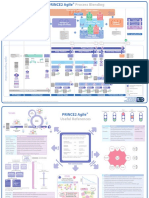
Prince2 Processes
Transféré par
nitind_kTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Prince2 Processes
Transféré par
nitind_kDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
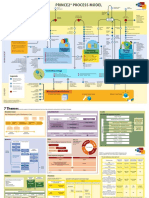
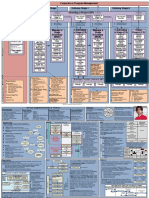
The 7 Processes Processes and Activities
Key Themes Techniques
(The step-wise progression through project lifecycle) Used* Used
Starting Up a Project (SU)
Starting Up a Project (SU) Appoint the Executive & the Project Manager
There must be a basic business requirement that triggers a project. Capture previous lessons •Business Case
•Product-
•Organization
The question ‘Do we have a worthwhile and viable project’? needs to
be answered. This process seeks to clarify this question and sets up
Design and appoint the Project Mgt team
Prepare the outline Business Case •Quality
based
planning Quick Reference Guide
*All the Themes apply to each process to one degree or another. We are simply listing the Themes which have the ‘strongest’ link.
•Risk
an organization structure in readiness to manage the project throughout its life. Select the project approach and assemble •Plans
The main outputs are the Project Brief and a plan for the first stage (Initiation the Project Brief
stage). Plan the Initiation stage
Directing a Project (DP)
Directing a Project (DP) Authorize initiation •Business Case
This process is aimed at the ‘directing’ level of management, that is the Project Authorize the project •Progress N/A
Board. It enables them to be accountable for the project’s success Authorize a Stage or Exception Plan •Risk
by making key decisions and exercising overall control while delegating day-to- Give ad hoc direction •Change
day management of the project to the Project Manager. Authorize project closure
Initiating a Project (IP)
Initiating a Project (IP) Prepare the Risk Mgt Strategy •Business Case
A project needs planning and setting up properly. IP plans the project Prepare the Configuration Mgt Strategy •Organization •Product-
at high level and sets up all the strategies and controls. The main document
for the project is created - this is called the Project Initiation Documentation, or
Prepare the Quality Mgt Strategy
Prepare the Communication Mgt Strategy
•Risk
•Plans
based
planning The 7 Principles
‘PID’. The PID forms the basis of a ‘contract’ between the Project Board and Set up the project controls •Quality •Quality (the guiding obligations)
the Project Manager and acts as a base document against which they can •Progress review
Create the Project Plan
assess progress, issues and ongoing viability questions. •Change PRINCE2® is principles-based.
Refine the Business Case
The principles are the basis of what defines a PRINCE2® project.
Assemble the Project Initiation Documentation
Principles facilitate good use of PRINCE2® by ensuring
Controlling a Stage (CS) Controlling a Stage (CS)
the method is not applied in an over-prescriptive way
Once a decision has been made to proceed with work, and the or in name only, but applied in a way that is sufficient
Authorize a Work Package •Business Case
appropriate resources have been committed, the project management team to contribute to project success.
Review Work Package status •Progress •Quality
must be focussed on delivering within the tolerances laid down. Receive completed Work Packages •Risk review If a project does not adhere to these 7 principles,
This process describes the work of the Project Manager in handling the Review the stage status •Change
day-to-day management of the project. Stage progress is monitored and any •Quality it is NOT being managed using PRINCE2®:
Report highlights
issues and risks captured and acted upon. It has close ties with the MP Capture and examine issues and risks
process which covers the development of the project’s products. Escalate issues and risks *Continued business justification*
Take corrective action
*Learn from experience*
Managing Product Delivery (MP) Managing Product Delivery (MP) •Plans •Product- *Defined roles and responsibilities*
This process allows a ‘controlled break’ between the Project Manager, Team Accept a Work Package •Risk based
Manager and the creation/provision of the products. The creation and quality Execute a Work Package •Change
•Progress
planning
•Quality
*Manage by stages*
checking and subsequent progress reporting of the specialist products related Deliver a Work Package
to each Work Package takes place in this process.
•Quality review *Manage by exception*
*Focus on products*
Managing a Stage Boundary (SB) Managing a Stage Boundary (SB)
Plan the next stage
•Business Case
*Tailor to suit the project environment*
This process enables the Project Board to be provided with sufficient •Organization
Update the Project Plan •Product-
•Risk
information by the Project Manager so that it can review the success of the Update the Business Case based
•Plans
current stage, approve the next Stage Plan (or Exception Plan), review the planning
Report stage end •Progress
updated Project Plan and Business Case and confirm continued business Produce an Exception Plan •Quality
justification and acceptability of the risks.
Closing a Project (CP)
Closing a Project (CP) Prepare planned closure
•Business Case
•Risk
One of the defining features of a project is that it is finite – that is it has a start Prepare premature closure •Change Project Management Ltd
and an end. Just as SU and IP ensure a controlled start to the project, this Hand over products •Progress N/A
•Quality West Wing, Briggs House
process ensures a controlled end. The final product is accepted, handed over Evaluate the project
26 Commercial Road
to the customer and the project’s performance is evaluated. Recommend project closure
Poole, Dorset, BH14 OJR
PRINCE2® is a registered trademark of AXELOS Limited. Tel: +44 1202 73 63 73
The Swirl Logo™ is a trademark of AXELOS Limited. HO0304_2v1 June 2015 e-mail: info@spoce.com
© SPOCE Project Management Ltd 2010-15
Created by Richard Lampitt of SPOCE Project Management Ltd
web: www.spoce.com
Elements, Organization, Risk and Business Case diagrams and some text portions are
© 2009 AXELOS Limited. Reproduced under license from AXELOS Limited. Feedback please to: richard@spoce.com
The 7 Themes Change Theme
Every project should have a procedure to capture and manage issues and changes. The following
Plans Theme
PRINCE2® suggests 3 levels of plan: Project, Stage and Team levels. Progress controls allow the
(the project management aspects to apply) diagram shows a typical procedure covering the capturing, examining, deciding and implementing of project management team to monitor progress, compare achievement with the baselined
PRINCE2® contains 7 themes which are the aspects of project management which should issues. PRINCE2® has a procedure which follows this path. Without such a procedure, a project can (approved) plan, review plans and options against future situations, detect problems, initiate
be continuously applied in order to ensure a project is to be managed effectively and become unresponsive to its stakeholders and quickly drift out of control, where unconsidered corrective action, authorise further work and capture lessons based on actual performance.
professionally. The 7 themes are addressed in this section, as well as a little changes for example are implemented, causing the project’s scope to creep and subsequently Tolerance is a key control for the different management levels over what amount of deviation from
guidance on tailoring. increase the project timescale and cost. Change control should be backed up by a configuration the agreed plan is allowed before the plan is considered to be out of control. Most PRINCE2®
management procedure. An effective change control procedure will help to assess the impact of controls are ‘event-driven’, including the decision making ones. Highlight Reports and Checkpoint
Organization Theme issues on the project’s objectives and which issues should/should not be approved. Reports are ‘time-driven’ controls, so called because they are required at timely intervals, e.g. every
PRINCE2® offers an organization structure 2 weeks or every month. Stages are used for control purposes.
Decide and Implement
with defined roles and responsibilities which Identify and
Capture/ Examine Approve by
engages with the primary stakeholders of propose Technical Stages
assess impact (escalate if taking PID
business, user and supplier. This ensures options
priority & on project’s beyond necessary Specification
there is clear accountability for each level of to address
severity objectives delegated corrective
management (Directing, Managing and issue Design
authority) action
Delivering) within the project. Build
A Communication Management Strategy
Configuration management will ensure all the products being created/updated during the project Test
should be produced which defines the
bi-directional flow of information required to are uniquely identified, version controlled, tracked and protected, and any changes made to the Implement
be sent/received by the project and include products are carried out in a controlled manner, ensuring the change is tracked and old versions are End-Stage
Assessments
any ‘external’ stakeholders. Without an never discarded. Why a product had changed can be answered by an effective configuration (Project Board
effective project management team structure management system. Decision Points)
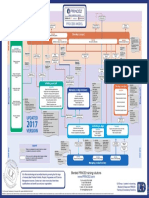
and a strategy for effective communication, Management Stages
a project is likely to fail. The project management team and communication strategy should be Risk Theme
reviewed and updated, typically at each stage end, to ensure it remains effective throughout the In PRINCE2® there are two types of stages – ‘management’ and ‘technical’. Management
Project management must control and contain any stages are partitions of the project with management decision points. Each stage is reviewed by the
project.
uncertain events (risks) if a project is to achieve its Project Board who approve them one at a time (at an end stage assessment). Stages are
objectives. This included both threats and summarised in the following diagram. Management stages equate to commitment of resources and
Business Case Theme opportunities. Details about risks have to be
Implement Identify authority to spend and only run in sequence. Technical stages are groups of specialist skills/activities
regularly revisited and reconsidered, -Context required to create the specialist products and can run in parallel. A Management stage can have one
The business justification is the reason for the project. Without it no project should start. If the -Risks
as a minimum at each stage end. The management or more technical stages within it and a technical stage can span one or more management stages.
business justification disappears once the project is underway, the project should be stopped
or changed. The business justification is documented in the Business Case and supports the ongoing of risk is a continuous To show the true workload and related costs, plans should include the effort of creating and
decision-making regarding (continued) justification. The Business Case contains: Reasons, Business procedure shown by the adjacent diagram. updating all the relevant products, not just the specialist products but management products as
A Risk Management Strategy should be Communicate well, e.g. Highlight Reports, End Stage Reports etc.
Options, Benefits/Dis-benefits, Key Risks, Costs, Timescales and Investment Appraisal.
produced based on the project’s context.
The Business Case should be at the centre of any impact assessment of issues and risks and if the Each identified risk should be assessed for
impact is too great, the Executive may choose to stop the project, or not authorize implementation probability/impact and its proximity, then Products (Management & Specialist)
of a request for change. The Business Case drives the decision-making processes throughout the appropriate risk mitigation responses should be Plan A product is an input or output of the project, whether tangible or intangible. In PRINCE2® there are
planned and implemented with suitable risk Assess
project. The benefits will be defined by the Senior User(s), who will be held to account by Corporate -Estimate two types of product – ‘management’ and ‘specialist’. Management products are the products that
or Programme Management for providing evidence that those benefits have been realized. The -Evaluate
owners assigned to manage each risk. The are produced/updated to assist with the ‘managing’ of the project. The following is a list of the main
Business Case should show the right balance of costs, benefits/dis-benefits and risks. The following communication of risks should be carried out in PRINCE2® management products which have outline descriptions in ‘Appendix A’ of the PRINCE2®
diagram shows where, in a PRINCE2® project, the Business Case is developed, maintained & verified parallel with all other steps. manual:
and when confirmation of the realization of benefits is likely to happen.
Quality Theme
Confirm Confirm Confirm PRINCE2® ensures the products A.1 Benefits Review Plan A.14 Lessons Log
benefit benefit benefit
will meet business expectations Project Product A.2 Business Case A.15 Lessons Report
and enable the desired benefits
Description A.3 Checkpoint Report A.16 Plan (Proj/Stage/Team/Exc’n)
Customer’s quality expectations/ A.4 Communication Mgmt Strategy A.17 Product Description
to be achieved. A set of activities acceptance criteria; quality tolerances
Pre-project Initiation Subsequent delivery stage(s) Final delivery stage Post-project are followed to ensure the final and acceptance methods
A.5 Configuration Item Records A.18 Product Status Account
stage product and its quality requirements/ A.6 Configuration Mgmt Strategy A.19 Project Brief
acceptance criteria, the scope of A.7 Daily Log A.20 Project Initiation Documentation
what the project will deliver and the Quality Management
A.8 End Project Report A.21 Project Product Description
Verify Verify Verify
outline detailed updated quality criteria for each product to be Strategy A.9 End Stage Report A.22 Quality Management Strategy
Business Case Business Case Business Case delivered within scope are clearly (Standards, responsibilities, A.10 Exception Report A.23 Quality Register
quality methods etc to be A.11 Highlight Report A.24 Risk Management Strategy
Develop Business Case Maintain Business Case understood. A Quality Management applied throughout project)
Strategy is developed to show how A.12 Issue Register A.25 Risk Register
The expected benefits are documented in the Business Case, but a Benefits Review Plan is A.13 Issue Report A.26 Work Package
created and used to show how, when and by whom a measurement of the project’s benefits the project will ensure the agreed
quality will be delivered. Sufficient Stage Plan Product Descriptions
can be made. Many benefits are not realized until after the project product has been in Quality method dates Part of Quality criteria Specialist products – these are unique to your project. They equate to the specialist work involved
operational use for some time, however some benefits may be realized during the project. quality controls are planned and
planned and Quality tolerances to create the physical end product (i.e. if a car was the end product of your project, the specialist
Benefit reviews both during and after the project are covered by the Benefits Review Plan. executed to make sure each product resources assigned to Quality methods
does indeed meet its specific quality each quality method Quality skills required products would be the designs, bonnet, boot, doors, wheels, engine etc which would have Product
The Benefits Review Plan will also contain details of how a measurement of the products Descriptions produced for them and of course the ‘final’ product itself – the car, which would be
performance will be made in operational life to see if there were any unexpected side-effects, requirements, as detailed in its
Product Description. A quality control described in the Project Product Description). They are the products (outputs) from the project
either positive or negative. For example, the product may have generated an unexpected which the business will use to generate the outcomes and consequential benefits. The benefits of
outcome and additional benefits, or may have underperformed against business expectations. technique covered by PRINCE2® is the Quality Register
‘quality review’, which is an effective the project should be mapped to the specialist products. If a product can not be mapped to a
Details of planned and
way of checking finished products, actuals of all quality benefit, then the question should be asked whether the product is required and is perhaps outside
Tailoring of PRINCE2® typically documents, where there is Cyclical methods/controls of the scope. The scope of a plan is shown by the products on the related product breakdown
Another element of PRINCE2® is ‘Tailoring to the project environment’. To get the most out of some subjectiveness and professional for each structure, backed up by the Product Descriptions. A principle of PRINCE2® is that a project should
PRINCE2®, you should tailor the method to suit the size, complexity and nature of your project. All mgt stage Update with results ‘focus on products’ and the quality of those products. The creation of Product Descriptions and
judgement is required. Once all products
the 7 process activities should be followed and the 7 principles applied, however Themes can be have been developed and all criteria Products created and quality checked as
inclusion of quality control activities within the relevant plan helps to achieve this. The end result is
adapted, for example roles can be combined, management products adapted to suit specific have been confirmed as being met, defined in each Work Package Project the delivery of products that are fit for purpose and capable of delivering the expected business
information requirements and reporting can be done verbally. Adapt the method to make the customer will give final acceptance closure benefits.
PRINCE2® work effectively for you and your projects. at project closure. Ultimate approval/acceptance at closure
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- PRINCE2 Cheat SheetDocument1 pagePRINCE2 Cheat Sheetetlaame82% (11)
- PRINCE2® Foundation (Study Notes)Document44 pagesPRINCE2® Foundation (Study Notes)bachir89% (9)
- Prince2 Agile Process Map PDFDocument2 pagesPrince2 Agile Process Map PDFSantiago Manuel Rios Lara100% (2)
- Prince2 Foundation Training Manual Frank PDFDocument20 pagesPrince2 Foundation Training Manual Frank PDFshahaab7860% (4)
- PRINCE2 Quick Reference GuideDocument2 pagesPRINCE2 Quick Reference Guidezigmoid100% (4)
- Prince2 Process ModelDocument2 pagesPrince2 Process Modeltoninillo91% (11)
- PRINCE2 Agile - AXELOSDocument4 pagesPRINCE2 Agile - AXELOSnamurame0% (4)
- PRINCE2 PRINCE2 Questions and AnswersDocument9 pagesPRINCE2 PRINCE2 Questions and AnswersMaroof Khatib67% (3)
- Learn PRINCE2 ThruQuestionsDocument82 pagesLearn PRINCE2 ThruQuestionsEdson Garcia de Freitas100% (1)
- The Official PRINCE2 Agile Accreditor Sample Examination Papers Terms of UseDocument24 pagesThe Official PRINCE2 Agile Accreditor Sample Examination Papers Terms of UseVishnu RajanPas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 eBOOK PDFDocument17 pagesPRINCE2 eBOOK PDFNIPASHU83% (6)
- Prince2 AnswersDocument5 pagesPrince2 AnswersbwsubbuPas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 Agile An Implementation Pocket Guide: Step-by-step advice for every project typeD'EverandPRINCE2 Agile An Implementation Pocket Guide: Step-by-step advice for every project typePas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction to PRINCE2: Managing and Directing Successful ProjectsD'EverandAn Introduction to PRINCE2: Managing and Directing Successful ProjectsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- PRINCE2 Practitioner Sample Paper v1.5Document59 pagesPRINCE2 Practitioner Sample Paper v1.5Rawe100% (1)
- MindMap For PRINCE2Document1 pageMindMap For PRINCE2muralidurai100% (3)
- Prince2 - Practitioner PapersDocument140 pagesPrince2 - Practitioner Paperspkdor200875% (12)
- PRINCE2 Practitioner Sample PaperDocument43 pagesPRINCE2 Practitioner Sample PaperAndre Kaiser67% (3)
- Prince2 Flash CardsDocument2 pagesPrince2 Flash Cardsgreenfinger2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Master The PRINCE2 Principles With PicturesDocument10 pagesMaster The PRINCE2 Principles With PicturesKnowledge TrainPas encore d'évaluation
- Prince2 Process Model v1.1 PDFDocument1 pagePrince2 Process Model v1.1 PDFdaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Prince 2 Practitioner ExamDocument16 pagesPrince 2 Practitioner ExamChy Buzzy50% (2)
- Prince2 - Foundation Exercise QuestionsDocument33 pagesPrince2 - Foundation Exercise QuestionsChiedu Oranye100% (3)
- PRINCE2 Agile Exam PreparationDocument4 pagesPRINCE2 Agile Exam Preparationsanja34Pas encore d'évaluation
- p2 Process Model 2017Document1 pagep2 Process Model 2017Miguel Fernandes0% (1)
- Prince2 - Practitioner PapersDocument140 pagesPrince2 - Practitioner Paperspkdor200875% (12)
- Master The PRINCE2 Themes With PicturesDocument11 pagesMaster The PRINCE2 Themes With PicturesKnowledge Train100% (1)
- PRINCE2 Foundation + Practitioner OutlineDocument2 pagesPRINCE2 Foundation + Practitioner Outlinespm9062100% (3)
- Prince2 Pass Prince2 Exams ContentsDocument15 pagesPrince2 Pass Prince2 Exams Contentsa_sarfaraz100% (1)
- PRINCE2 Primer - Introduction To PRINCE2Document7 pagesPRINCE2 Primer - Introduction To PRINCE2spm9062100% (1)
- PRINCE2 Foundation NotesDocument46 pagesPRINCE2 Foundation NotesBozzor100% (4)
- PRINCE2 Training Foundation & PractitionerDocument107 pagesPRINCE2 Training Foundation & PractitionerMonir Bhuiyan67% (6)
- PRINCE2 2017 Foundation SyllabusDocument5 pagesPRINCE2 2017 Foundation SyllabusMuhammad Khurram AfzalPas encore d'évaluation
- Prince2 Practitioner Exam TipsDocument16 pagesPrince2 Practitioner Exam Tipsamraoua80% (5)
- PRINCE2 Primer - Introduction To PRINCE2Document7 pagesPRINCE2 Primer - Introduction To PRINCE2spm9062100% (1)
- Prince2 Project Mandate TemplateDocument6 pagesPrince2 Project Mandate TemplateksolesiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Concise PRINCE2® - Principles and essential themes: Third editionD'EverandThe Concise PRINCE2® - Principles and essential themes: Third editionPas encore d'évaluation
- Master The PRINCE2 Processes With PicturesDocument12 pagesMaster The PRINCE2 Processes With PicturesKnowledge Train100% (2)
- PRINCE2 Methodology DiagramDocument1 pagePRINCE2 Methodology Diagramshaunbuk100% (2)
- Prince2 Themes EbookDocument16 pagesPrince2 Themes EbookRupoPas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 in One Thousand WordsDocument7 pagesPRINCE2 in One Thousand WordsSolomon Joseph100% (1)
- PRINCE2 Process MapDocument3 pagesPRINCE2 Process MapSreedhar Madur50% (2)
- PRINCE2 Training ManualDocument245 pagesPRINCE2 Training ManualFalak HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Management: Prince2Document13 pagesProject Management: Prince2Shreyo Chakraborty100% (3)
- Project Lifecycles and PRINCE2 20190403Document31 pagesProject Lifecycles and PRINCE2 20190403csharpplusPas encore d'évaluation
- Prince2 in 60 Minutes Flat v7.2Document59 pagesPrince2 in 60 Minutes Flat v7.2Reni Dimitrova100% (1)
- PRINCE2 2018 Masterclass: Foundation and PractitionerDocument26 pagesPRINCE2 2018 Masterclass: Foundation and Practitionerdeepen0% (1)
- PRINCE2 Practitioner Exam Candidate GuidanceDocument8 pagesPRINCE2 Practitioner Exam Candidate GuidanceJohn N. Constance100% (1)
- PRINCE2 OverviewDocument8 pagesPRINCE2 OverviewprojectingIT100% (1)
- AFA PRINCE2 Foundation QuestionsDocument5 pagesAFA PRINCE2 Foundation QuestionsmailmendPas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 Explained - Incl Prince2 Training & QualificationsDocument16 pagesPRINCE2 Explained - Incl Prince2 Training & QualificationsSteve TwinePas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 WallchartDocument1 pagePRINCE2 WallchartThomas GeorgiouPas encore d'évaluation
- Prince2 Practitioner Resource Book v3.5Document237 pagesPrince2 Practitioner Resource Book v3.5Luis Alberto Lamas LavinPas encore d'évaluation
- Prince2® Process Model: Directing A ProjectDocument2 pagesPrince2® Process Model: Directing A ProjectSam DesuzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Prince2 Agile BimDocument11 pagesPrince2 Agile Bimkurtling100% (1)
- PPM1310CL Practitioner Workbook-Trainer.r5.6 - DemoDocument0 pagePPM1310CL Practitioner Workbook-Trainer.r5.6 - Demopkdor2008Pas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 ThemesDocument11 pagesPRINCE2 ThemesRavi Arunachalam100% (1)
- Prince2 Foundation User Guide v1.6Document76 pagesPrince2 Foundation User Guide v1.6Marissa YaxleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Prince2 in 40 MinutesDocument18 pagesPrince2 in 40 Minutesকাউসারী নুর ফাতিন33% (3)
- P2 Process Model v3Document2 pagesP2 Process Model v3matteozamolo100% (1)
- PRINCE2 Agile Slides2Document132 pagesPRINCE2 Agile Slides2Seboka Matsoso100% (1)
- All About Prince2 With Useful ResourcesDocument4 pagesAll About Prince2 With Useful ResourcesSasaPas encore d'évaluation
- Prince2 User GuideDocument85 pagesPrince2 User GuideSamba-Diom BaPas encore d'évaluation
- Subject Autumn Term Spring Term Summer Term ART (1 Hour Per Week)Document8 pagesSubject Autumn Term Spring Term Summer Term ART (1 Hour Per Week)nitind_kPas encore d'évaluation
- File 47049821 PDFDocument45 pagesFile 47049821 PDFnitind_kPas encore d'évaluation
- Adioma Powerpoint Slides Templates DarkDocument45 pagesAdioma Powerpoint Slides Templates Darknitind_kPas encore d'évaluation
- Scalable Capital ISA GuideDocument15 pagesScalable Capital ISA Guidenitind_kPas encore d'évaluation
- ATOC - Days Out GuideDocument2 pagesATOC - Days Out Guidenitind_kPas encore d'évaluation
- ISO 21500 Lean Construction PMBoK PDFDocument9 pagesISO 21500 Lean Construction PMBoK PDFBlazeifritPas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 Executive BriefingDocument1 pagePRINCE2 Executive Briefingspm9062Pas encore d'évaluation
- Business Relationship Management and The Nine ITIL® Guiding PrinciplesDocument7 pagesBusiness Relationship Management and The Nine ITIL® Guiding PrinciplesIvanei SousaPas encore d'évaluation
- Agile PM White Paper - Feb 11Document12 pagesAgile PM White Paper - Feb 11varsiva1827Pas encore d'évaluation
- Prince2 - Foundation Papers PDFDocument69 pagesPrince2 - Foundation Papers PDFHarktheDark100% (1)
- P050 Origins of Modern PM PDFDocument27 pagesP050 Origins of Modern PM PDFBogdanloePas encore d'évaluation
- PM Process MindmapsDocument13 pagesPM Process MindmapsShiblee Khalid AhmodPas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 2018 Masterclass: Foundation and PractitionerDocument26 pagesPRINCE2 2018 Masterclass: Foundation and Practitionerdeepen0% (1)
- Software Project ManagementDocument9 pagesSoftware Project ManagementSunnyArora0% (1)
- PRINCE2-Foundation - PRINCE2 Foundation Exam: Dumps - HTMLDocument43 pagesPRINCE2-Foundation - PRINCE2 Foundation Exam: Dumps - HTMLJawwad HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- "Phases of Project": Assignment - 1Document19 pages"Phases of Project": Assignment - 1Pardeep KapilPas encore d'évaluation
- Project and Project ManagementDocument9 pagesProject and Project ManagementdghettosmurfPas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2®2017 Process Model Detailed - Potifob - en - v4.0Document2 pagesPRINCE2®2017 Process Model Detailed - Potifob - en - v4.0Eric Desportes100% (1)
- PRINCE2 WallchartDocument1 pagePRINCE2 WallchartThomas GeorgiouPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Manager CV Example 2Document2 pagesProject Manager CV Example 2hegazymdPas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCE2 LeafletDocument2 pagesPRINCE2 Leafletgistme24Pas encore d'évaluation
- p2 Practitioner Exam Paper3Document9 pagesp2 Practitioner Exam Paper3krishnaheet100% (1)
- PRINCE2 Templates For Successful Project ManagementDocument4 pagesPRINCE2 Templates For Successful Project ManagementKarine RussellPas encore d'évaluation
- P2MM Self Assess PRINCE2Project v012Document22 pagesP2MM Self Assess PRINCE2Project v012Stéphane SmetsPas encore d'évaluation
- MBA Dissertation Example On ITILDocument19 pagesMBA Dissertation Example On ITILMBA DissertationPas encore d'évaluation
- Prince2 Lesson 06 PDFDocument65 pagesPrince2 Lesson 06 PDFrhuria@rediffmail.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Pad 409 - Introduction To Project ManagementDocument23 pagesPad 409 - Introduction To Project ManagementVerifiedsissysubs MistressPas encore d'évaluation
- 9S-BM522 Project ManagementDocument23 pages9S-BM522 Project ManagementRahul SarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.8 IP: Project Initiation Documentation (PID)Document1 page3.8 IP: Project Initiation Documentation (PID)damicogPas encore d'évaluation
- Prince2 FoundationDocument2 pagesPrince2 Foundationshiva_1912-1Pas encore d'évaluation