Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
02-2 Equipment Modeling PDF
Transféré par
Ana Belén Albán TapiaTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
02-2 Equipment Modeling PDF
Transféré par
Ana Belén Albán TapiaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
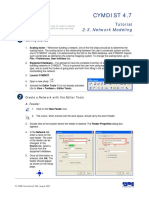
CYMDIST 4.
7
Tutorial
2-2. Equipment Modeling
This tutorial provides a guideline on how to create
equipments with the CYMDIST tools.
Modeling equipments is the first step in modeling a system. This tutorial provides examples on how to input the
data for a variety of equipment. The equipment database can be found in the Equipment menu of CYMDIST.
n General
1. Every equipment dialog box has a common layout. On its left-hand
side is the list of Equipment IDs already that exist in the database.
Click on any one of them to see its parameters displayed on the
right-hand side of the dialog box.
2. Type a string of the ID in the Filter field so the program finds the
closest match of the Equipment ID you are looking for.
3. To create a new Equipment ID, click on New and the Equipment ID
dialog box will appear in which you can enter the ID of the new
equipment.
4. You can also use the Remove and Rename buttons to
remove/rename existing equipments. First select in the list the
equipment to be removed or renamed before clicking on the
appropriate button.
o Create a Source
1. Go to Equipment > Source.
The dialog box opens where
you can create new sources
and enter its appropriate data
values. These data include the
capacity used to flag overload,
the nominal and desired
voltage, the source’s
configuration and the source
equivalent impedance.
2. If the source equivalent
impedance is not available, you
can use one of the two
calculation methods by clicking
on the Calculate button.
© CYME International T&D, August 2007
CYMDIST 4.7 Tutorial – Equipment Modeling Page 2
Calculation Method no. 1
The first calculation method implies that you know the
short-circuit power. Click on the Calculate button next
to the option Short-circuit MVA known. You enter
the data in the dialog box that is displayed.
Calculation Method no. 2
The second calculation method calculates the
equivalent impedance from the sum of the impedance
of the substation transformer(s) and the transmission
network.
• Click on the Calculate button next to the Source
Details known option and enter the primary
impedance or the short-circuit power.
• Click on the Transfo connection button to
enter the substation branches’ information
(such as primary/secondary protective device
and the transformer).
With the data entered, CYMDIST calculates
the equivalent impedance.
p Create a Transformer
1. Go to Equipment >
Transformer in the menu. You
have here two options: the
Two-winding Transformer
and the Three-winding
Transformer.
2. Fill in the ratings of the
transformer, its impedances,
type and connection. Should
there be any grounding
impedance, they should be
entered accordingly too.
3. If the transformer has a LTC,
select the LTC tab, check the
Load Tap Changer option and
enter the data.
© CYME International T&D, August 2007
CYMDIST 4.7 Tutorial – Equipment Modeling Page 3
q Create a Machine (Motor, Generator)
1. To create a generator, go to Equipment > Generator. There are three types of generators
available: Synchronous, Induction, and Electronically Coupled.
To create motors, go to Equipment > Motor. There are two types of motors: Induction and
Synchronous.
2. Fill in the ratings of the unit, its impedances and connection.
3. If the impedance of the generating unit is not known, you can get an estimation by using the
Estimation Function via the Estimate button. Select the most appropriate fields and CYMDIST will
estimate the impedance of the machine with the use of typical impedance curves.
r Create a Protective Device
CYMDIST has several protective
devices from the Equipment menu:
Fuse, LVCB, Recloser, Relay,
Sectionalizer, Switch and Breaker.
The dialog box is similar for all
above protective devices where you
can enter:
1. The device’s ratings
2. The reliability parameters
(should you wish to have
precise information for the
reliability assessment)
3. the operating mode, and
4. the exact device type from
CYMTCC.
s Create Other Equipment
By accessing the Equipment menu, you can create other equipments such as Shunt/Series Capacitors,
Shunt/Series Reactors, and Harmonic devices.
© CYME International T&D, August 2007
CYMDIST 4.7 Tutorial – Equipment Modeling Page 4
t Create a Line
It is suggested to have an inventory of conductors and spacing conductors prior to the building of
overhead lines and cables. This will facilitate their creation as you will be asked to select from the
conductor inventory in the overhead line and cable dialog boxes. The steps to successfully create a
line/cable are outlined below.
1. Create conductors
The first step towards creating a line or a cable is to have conductors.
(a) Go to Equipment >
Conductor to access the
conductor database.
(b) Fill in the conductor data in
the General tab. Once
completed, click OK. The
Reliability Parameters
block can be ignored
should reliability
assessment not be an
analysis to perform. If it is,
consult the Reliability
Analysis tutorial (Part 12)
or the Reference manual.
(c) For the exercise, click on New and create a new
conductor. Call it: A_NEW_CONDUCTOR.
(d) Enter the data as shown to the right.
(e) Click OK to save and exit.
2. Create a spacing table
(a) Go to Equipment > Spacing Table OH-Line.
(b) If you have information on the GMD and the average
height, enter them directly.
However, if such information is not available, you can
make use of the GMD calculation function. A reference
point is selected by the user; and, based on this
reference point, the position of the conductors and the
neutral is to be determined and entered in CYMDIST
for the GMD and average height calculation.
In our example, the GMD and average height values
are not known. We designate the point where the pole
touches the ground as the reference point, and define
the distance of the conductors according to such
reference.
© CYME International T&D, August 2007
CYMDIST 4.7 Tutorial – Equipment Modeling Page 5
(c) Click New and create a
new spacing called
A_NEW_SPACING. Enter
the positions of the
conductor as shown here
below and click on GMD
Calculation to get the
GMD and average height
values.
(d) Click OK to exit.
3. Create a line
(a) Go to Equipment > Overhead Line.
(b) The balanced type uses the same conductor for all
phases, whereas the unbalanced type uses
different conductors for each of the three phases.
(c) The phase and neutral
conductor drop-down
menu lists all conductors
created in the conductor
database, and likewise the
spacing drop-down menu
lists all spacing created in
the database. Click on
New and create a new line
called A_NEW_OH.
(d) Choose the conductor
created earlier,
A_NEW_CONDUCTOR,
for phase and neutral.
(e) Select A_NEW_SPACING
for the spacing.
(f) Once all is selected, click on Calculate to have the equivalent impedance of the line.
(g) Click OK to exit.
© CYME International T&D, August 2007
CYMDIST 4.7 Tutorial – Equipment Modeling Page 6
u Create a Cable
1. Go to Equipment > Cable to access the cable database.
2. You can enter the parameters in the General tab of the cable if known.
If the latter are not known, click on the Calculate button to have CYMDIST calculate the equivalent
impedances by selecting the cable type and entering the cable information such as conductor
(Please refer to section 7.1) in the Cable Impedance Calculator dialog box.
3. As an example, create a new cable by clicking on the New
button and called it A_NEW_CABLE. Click OK.
4. The information to fill in the General tab fields are unknown,
hence click on Calculate.
5. Enter the cable information as
follows:
• multi-wire concentric neutral,
• 3-phase circuit with Dab = 2,
Dbc = 2 and Dac = 4,
• PVC insulation with 1in of
diameter over insulation,
• The conductor type for
phase and neutral is the one
created in 7.1, which is
A_NEW_CONDUCTOR,
• The number of concentric
wires is 3.
6. When completed, click on
Calculate to have the
impedances calculated and
click OK to exit.
© CYME International T&D, August 2007
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Vibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisD'EverandVibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- Quick Guide On Cdegs CRDocument28 pagesQuick Guide On Cdegs CRGilberto MejíaPas encore d'évaluation
- CDEGS Quick Guide PDFDocument28 pagesCDEGS Quick Guide PDFrian0201Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arc-Flash Hazard Calculation DistriviewSoftwareDocument2 pagesArc-Flash Hazard Calculation DistriviewSoftwareCesar CuyubambaPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 Voltage Drop Short CircuitDocument3 pages04 Voltage Drop Short CircuitAna Belén Albán TapiaPas encore d'évaluation
- StormCAD QuickStart PDFDocument62 pagesStormCAD QuickStart PDFPedro JaraPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A FBD?: Moment UtilityDocument22 pagesWhat Is A FBD?: Moment UtilitySantiago MolinaPas encore d'évaluation
- SafeGrid Reference ManualDocument16 pagesSafeGrid Reference Manualrajarao1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- DOC0010691 - Idirect Remote Commissioning ProcedureDocument8 pagesDOC0010691 - Idirect Remote Commissioning Procedurerowinsitum4676Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ee 324 L Simulation Laboratory: Electrical Engineering Department, National Institute of Technology Calicut Year 2004Document5 pagesEe 324 L Simulation Laboratory: Electrical Engineering Department, National Institute of Technology Calicut Year 2004bubo28Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To ACD Version 12 NMR SoftwareDocument13 pagesIntroduction To ACD Version 12 NMR Softwarepatel_smitPas encore d'évaluation
- Essentials: Experiment No. 1 Introduction To NI MultisimDocument6 pagesEssentials: Experiment No. 1 Introduction To NI MultisimBiancaVillenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lunar RF Quick Installation ManualDocument24 pagesLunar RF Quick Installation Manualanand shekhawat100% (1)
- Getting Started in IAB (061-120)Document60 pagesGetting Started in IAB (061-120)Anh Kha Võ DânPas encore d'évaluation
- PC Software ManualDocument29 pagesPC Software ManualEndang Zenal MuttaqinPas encore d'évaluation
- Connect Strain Gages To A Data Acquisition (DAQ) Device - National InstrumentsDocument6 pagesConnect Strain Gages To A Data Acquisition (DAQ) Device - National InstrumentsLuigi ChulimPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual MelshortDocument120 pagesManual MelshortEnrique León Salva100% (1)
- Tools V2 Quick Start Guide: DatacolorDocument46 pagesTools V2 Quick Start Guide: DatacolorKazi ShorifPas encore d'évaluation
- VLAN Diagnostic Tools GuideDocument48 pagesVLAN Diagnostic Tools Guidejmgon20Pas encore d'évaluation
- Caesar IIDocument26 pagesCaesar IIasokkPas encore d'évaluation
- MtE-205 EPD LAB 03Document7 pagesMtE-205 EPD LAB 03Syed Suleman Ayub - Section-BPas encore d'évaluation
- DSC ManualDocument78 pagesDSC ManualLuis MurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.2.2.6 Frame For Rotor Temperature Alarm Value SetupDocument51 pages3.2.2.6 Frame For Rotor Temperature Alarm Value SetupClip nhungcaunoihayPas encore d'évaluation
- Help Manual PDFDocument19 pagesHelp Manual PDFRamanathanPas encore d'évaluation
- ICC Modbus Master Tool User's ManualDocument21 pagesICC Modbus Master Tool User's Manualalexwongks6118Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Line Differential ProtectionDocument6 pages1 Line Differential ProtectionJuan David RamírezPas encore d'évaluation
- Live Load Dispersion GeneratorDocument9 pagesLive Load Dispersion Generator2202199122Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab - 2 Handout-ELEC 201Document11 pagesLab - 2 Handout-ELEC 201AmroKashtPas encore d'évaluation
- Battery Testing System User Manual: Version: 1.0, Using BTS 7.5.XDocument79 pagesBattery Testing System User Manual: Version: 1.0, Using BTS 7.5.XICC KINSHASA TVPas encore d'évaluation
- Overcurrent Protection: 1 Import ProjectDocument14 pagesOvercurrent Protection: 1 Import ProjectJuan David RamírezPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial: Distribution Load FlowDocument9 pagesTutorial: Distribution Load FlowDavid Yungan GonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- Enron Modbus For Flow Devices: Easy GuideDocument12 pagesEnron Modbus For Flow Devices: Easy GuideSau VoPas encore d'évaluation
- Multisim Tutorial & Assignment May2019 AmendedDocument15 pagesMultisim Tutorial & Assignment May2019 AmendedShan PinPas encore d'évaluation
- BM Panelboard JA NADocument12 pagesBM Panelboard JA NAshoaibPas encore d'évaluation
- C Users Administrator AppData Local Temp hhAAD5Document42 pagesC Users Administrator AppData Local Temp hhAAD5bal krishna dubeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethernet: A Direct Link Network With Media Access ControlDocument14 pagesEthernet: A Direct Link Network With Media Access ControlJuani PollaviniPas encore d'évaluation
- Analog Circuit Simulation Using VirtuosoDocument17 pagesAnalog Circuit Simulation Using Virtuosohideeponhere@gmail.comPas encore d'évaluation
- TutorialDocument11 pagesTutorialEd SilPas encore d'évaluation
- MultiSim PDFDocument5 pagesMultiSim PDFjaya1816Pas encore d'évaluation
- CBex ManualDocument14 pagesCBex ManualMohammad TaherPas encore d'évaluation
- DCON Utility Pro User Manual: Version 2.0.1, February 2019Document49 pagesDCON Utility Pro User Manual: Version 2.0.1, February 2019harves100% (1)
- Lab 1: Schematic and Layout of A NAND Gate: Part B: ProcedureDocument43 pagesLab 1: Schematic and Layout of A NAND Gate: Part B: ProcedureademPas encore d'évaluation
- MultiSim 8 Quick StartDocument8 pagesMultiSim 8 Quick StartRahul SushruthPas encore d'évaluation
- HW1Document6 pagesHW1paulshuvaPas encore d'évaluation
- AC Simulation: August 2005Document24 pagesAC Simulation: August 2005Aichetou ElkhadarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ee433 Lab Appendix: Case Study Using Powerworld Simulator: Basic Menu FunctionsDocument15 pagesEe433 Lab Appendix: Case Study Using Powerworld Simulator: Basic Menu Functionssolo4000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Industrial Robot - Online Session NotesDocument21 pagesIndustrial Robot - Online Session NotesPrince SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- RTL8187 User ManualDocument21 pagesRTL8187 User ManualRodrigo IslasPas encore d'évaluation
- Segment Checker ManualDocument32 pagesSegment Checker ManualCarlos VidelaPas encore d'évaluation
- ICS52 - Introduction To Software Engineering Final Exam - Winter, 2002 Name: - Student IDDocument6 pagesICS52 - Introduction To Software Engineering Final Exam - Winter, 2002 Name: - Student IDSoo Lian KeiPas encore d'évaluation
- AllPlan Report Guidelines 2019 UpdatedDocument15 pagesAllPlan Report Guidelines 2019 UpdatednasyonellPas encore d'évaluation
- ECCE221 - Lab0 - Installation and Introduction To MULTISIMDocument20 pagesECCE221 - Lab0 - Installation and Introduction To MULTISIMsultanPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No.7: Aim: Design Differential Amplifier Software Used: AWR Design Environment 10 TheoryDocument12 pagesExperiment No.7: Aim: Design Differential Amplifier Software Used: AWR Design Environment 10 TheorySaurabh ChardePas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Large Displacement Analysis of A Cantilever Beam Using RADIOSS PDFDocument9 pages3 Large Displacement Analysis of A Cantilever Beam Using RADIOSS PDFSangharshBhustalimathPas encore d'évaluation
- Debugger M8051ewDocument41 pagesDebugger M8051ewcarver_uaPas encore d'évaluation
- 04,1 ZXUR 9000 GSM (V6.50.202) TroubleshootingDocument23 pages04,1 ZXUR 9000 GSM (V6.50.202) TroubleshootingmelisachewPas encore d'évaluation
- Quick Guide On CDEGS CRDocument28 pagesQuick Guide On CDEGS CRrian0201100% (1)
- Deep Belief Nets in C++ and CUDA C: Volume 3: Convolutional NetsD'EverandDeep Belief Nets in C++ and CUDA C: Volume 3: Convolutional NetsPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Differential Analysers: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationD'EverandDigital Differential Analysers: International Series of Monographs on Electronics and InstrumentationPas encore d'évaluation
- Cymdist 4.7: 7.1. Attaching MapsDocument3 pagesCymdist 4.7: 7.1. Attaching MapsAna Belén Albán TapiaPas encore d'évaluation
- 05-1 Load BalancingDocument2 pages05-1 Load BalancingAna Belén Albán TapiaPas encore d'évaluation
- 02-3 Network ModelingDocument11 pages02-3 Network ModelingAna Belén Albán TapiaPas encore d'évaluation
- 02-2 Equipment Modeling PDFDocument6 pages02-2 Equipment Modeling PDFAna Belén Albán TapiaPas encore d'évaluation
- 02-3 Network ModelingDocument11 pages02-3 Network ModelingAna Belén Albán TapiaPas encore d'évaluation
- 02-3 Network ModelingDocument11 pages02-3 Network ModelingAna Belén Albán TapiaPas encore d'évaluation
- 02-2 Equipment Modeling PDFDocument6 pages02-2 Equipment Modeling PDFAna Belén Albán TapiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework1 AlbanDocument3 pagesHomework1 AlbanAna Belén Albán TapiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document2 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.bala muruganPas encore d'évaluation
- Liebert CRV Row Based Cooling System Design Manual 00Document208 pagesLiebert CRV Row Based Cooling System Design Manual 00Oscar Orlando CuervoPas encore d'évaluation
- FilterFanDocument2 pagesFilterFanPhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- HygroclipDocument6 pagesHygroclipilic.dragan73370Pas encore d'évaluation
- Huawei Smart PV Solution Anti-PID Module Application Guide 01 - (20151219)Document18 pagesHuawei Smart PV Solution Anti-PID Module Application Guide 01 - (20151219)Jaime Andres Herrera RestrepoPas encore d'évaluation
- Kenmore FridgeDocument80 pagesKenmore FridgelarryPas encore d'évaluation
- Outdoor - Units - MOU 12HDN1 - MOUB 36HDN1 R220075500920 - MOUB 48HDN1 R220075700690 - MOUD 60HDN1 R - MOUA 60HRDN1Document48 pagesOutdoor - Units - MOU 12HDN1 - MOUB 36HDN1 R220075500920 - MOUB 48HDN1 R220075700690 - MOUD 60HDN1 R - MOUA 60HRDN1Muhidin KozicaPas encore d'évaluation
- PTG Chapter 15 Asal PhysicsDocument10 pagesPTG Chapter 15 Asal Physicszzrnwdzpsmhs951003Pas encore d'évaluation
- AIM-4SL Hardware Manual: Revision Date: 02 AUG 2010Document51 pagesAIM-4SL Hardware Manual: Revision Date: 02 AUG 2010Sholahuddin100% (1)
- Powerpress ANDRITZDocument4 pagesPowerpress ANDRITZCesar LapaPas encore d'évaluation
- C0008310 CLM PDFDocument588 pagesC0008310 CLM PDFjobyPas encore d'évaluation
- Weil Mclain Radiant HeatDocument112 pagesWeil Mclain Radiant HeatBen Sharp100% (1)
- DSE4520 MKII User Manual PDFDocument41 pagesDSE4520 MKII User Manual PDFDonovan van der Sandt100% (2)
- CRAFTER 2,0D TDI CR 4motion Achleitner-CKUB-2 (2EX-2FX) 2.0 (2012-2017)Document5 pagesCRAFTER 2,0D TDI CR 4motion Achleitner-CKUB-2 (2EX-2FX) 2.0 (2012-2017)Matias Martinez100% (1)
- SHIMANO 105 Caliper Brake: Black / SilverDocument1 pageSHIMANO 105 Caliper Brake: Black / SilverGaudencio LingamenPas encore d'évaluation
- High-Side Power Distribution Switch With Enable and Flag AP2820Document19 pagesHigh-Side Power Distribution Switch With Enable and Flag AP2820SangaPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Digital VLSI Design (ECE 521) (Makeup) PDFDocument2 pagesAdvanced Digital VLSI Design (ECE 521) (Makeup) PDFRahul PinnamaneniPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Analysis of Rotary Car Parking System: M.Raghupathi, C.Velmurugan, K.Elavarasan, Dr.A.PremkumarDocument6 pagesDesign Analysis of Rotary Car Parking System: M.Raghupathi, C.Velmurugan, K.Elavarasan, Dr.A.PremkumarJuan SantiagoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sewing Machine TypesDocument6 pagesSewing Machine TypesJuan Alas Ronaldo AziongPas encore d'évaluation
- Mouse PDFDocument5 pagesMouse PDFjadhavbhavesh1131Pas encore d'évaluation
- SpellmanDocument204 pagesSpellmanSebastian Cruz CPas encore d'évaluation
- SIRIO - NEW Mighty Vector 4000 - ManualDocument8 pagesSIRIO - NEW Mighty Vector 4000 - ManualLeonardus Suryo SuhartoPas encore d'évaluation
- Installation Manual UB-5325 UB-5825: Electronic BoardDocument22 pagesInstallation Manual UB-5325 UB-5825: Electronic BoardIstimawan_BagusPas encore d'évaluation
- Spek ETS 2017-HighDocument1 pageSpek ETS 2017-HighValentino Budi PratamaPas encore d'évaluation
- TrioTC36H - Parts Manual (Ref)Document33 pagesTrioTC36H - Parts Manual (Ref)Carolina Váquiro Gamboa100% (1)
- SV-520/550 Instruction ManualDocument32 pagesSV-520/550 Instruction ManualLe DuPas encore d'évaluation
- Microprocessor Systems & Interfacing EEE-342: Comsats UniversityDocument16 pagesMicroprocessor Systems & Interfacing EEE-342: Comsats UniversityBilal HabibPas encore d'évaluation
- LFE Desicant Dryer ManualDocument12 pagesLFE Desicant Dryer ManualNaveen KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Yamato Z610, Z612 PARTS BOOK PDFDocument44 pagesYamato Z610, Z612 PARTS BOOK PDFIvan Ortiz López100% (1)
- Desmontaje Mando Final D155AX-6Document3 pagesDesmontaje Mando Final D155AX-6claudioPas encore d'évaluation