Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
APUSHPeriod 5 Timelineof Major Events
Transféré par
GerardoTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
APUSHPeriod 5 Timelineof Major Events
Transféré par
GerardoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Period 5 Timeline of Major Ideas & Events (1844-1877)
Use Chapters 17-23 of American Pageant to complete the following chart. We will be debating the Varying Viewpoints
upon returning to class.
Key Concepts:
5.1: The United States became more connected with the world, pursued an expansionist foreign policy in the Western
Hemisphere, and emerged as the destination for many migrants from other countries.
5.2: Intensified by expansion and deepening regional divisions, debates over slavery and other economic, cultural, and
political issues led the nation into civil war.
5.3: The Union victory in the Civil War and the contested reconstruction of the South settled the issues of slavery and
secession, but left unresolved many questions about the power of the federal government and citizenship rights.
President: Event and Significance:
Congress Preemption Acts of the 1830s and 1840s
“Fifty-four Forty or Fight!” (Election of 1844)
Annexing Texas (1844, technically Tyler but how did it effect Polk?)
Samuel Morse invents Electric Telegraph (1844)
James K. Polk
Democrat Mexican-American War (1845-1848)
(1845-1849)
Wilmot Proviso (1846)
Elias Howe invents Sewing Machine (1846)
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (1848)
Free-Soil Party (1848)
James K. Polk
Democrat
(1845-1849) California Gold Rush (1849)
Know-Nothing Party (American Party) Created (1849)
Clayton-Bulwer Treaty (1850)
Zachary Taylor
Whig
(1849-July 1850)
Compromise of 1850
Fugitive Slave Law (1850)
Millard Fillmore
Underground Railroad
Whig
(July 1850-1853)
Uncle Tom’s Cabin (1852)
Gadsden Purchase (1853)
Republican Party created (1854)
Ostend Manifesto (1854)
Kansas-Nebraska Act (1854)
“Bleeding Kansas” (1855-56)
Franklin Pierce
Democrat
(1853-1857)
Caning of Senator Sumner (1856)
Panic of 1857
Impending Crisis of the South (1857)
Lecompton Constitution (1857)
Dred Scott v. Sandford (1857)
Lincoln-Douglas Debates (1858)
John Brown’s Raid at Harpers Ferry (1859)
Election of 1860
James Buchanan
Democrat Formation of the Confederate States of America (February 1861)
(1857-1861)
Crittenden Compromise (1861)
Fort Sumter (April 12, 1861)
Lincoln’s Use of Executive Power
Union Wartime Advantages
Abraham Lincoln
Republican
(1861- 1865)
Confederacy Wartime Advantages
Confederate Problems
Morrill Tariff Act (1861)
Homestead Act (1862)
Morrill Land Grant Act (1862)
Pacific Railway Act (1862)
First Battle of Bull Run (July 1861)
Abraham Lincoln
Republican
(1861- 1865)
Trent Affair (1861)
Peninsula Campaign (March 1862)
Monitor vs. Merrimac (March 1862)
Second Battle of Bull Run (August 1862)
Grant’s Capture of New Orleans (April 1862)
Antietam (September 1862)
Fredericksburg (December 1862)
Confiscation Acts (1861-1862)
Emancipation Proclamation (January 1863)
Proclamation of Amnesty and Reconstruction (1863)
Abraham Lincoln
Republican
(1861- 1865) Massachusetts 54th Regiment
Battle of Vicksburg (May-July 1863)
Battle of Gettysburg (July 1863)
New York Draft Riots (July 1863)
Wade-Davis Bill (1864)
Sherman’s March to the Sea (1864-65)
Freedmen’s Bureau created ( March 1865)
Abraham Lincoln Surrender at Appomattox (April 9, 1865)
Republican
(1861- 1865)
Assassination of Lincoln (April 14, 1865)
13th Amendment (1865)
Johnson’s Reconstruction Policy (1865)
Southern Governments of 1865
Andrew Johnson Black Codes
Democratic
(1865-1869)
Johnson’s Vetoes (1866)
Civil Rights Act of 1866
14th Amendment (1866; ratified 1868)
Report of the Join Committee (1866)
Andrew Johnson
Democratic Reconstruction Acts of 1867
(1865-1869)
Tenure of Office Act (1867)
15th Amendment (1869; ratified 1870)
Civil Rights Act of 1875
Building Black Communities
Ulysses S. Grant Sharecropping
Republican
(1869-1877)
Compromise of 1877
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- America 8th Edition Tindall Test Bank PDFDocument80 pagesAmerica 8th Edition Tindall Test Bank PDFJohn Torres50% (2)
- Eric Foner - The Second Founding - How The Civil War and Reconstruction Remade The Constitution-W. W. Norton Company (2019)Document262 pagesEric Foner - The Second Founding - How The Civil War and Reconstruction Remade The Constitution-W. W. Norton Company (2019)Levente Vajda100% (1)
- White MansionsDocument80 pagesWhite MansionsSIMACOMAU100% (1)
- The Reconstruction Amendments: The Essential Documents, Volume 2D'EverandThe Reconstruction Amendments: The Essential Documents, Volume 2Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Was Life Like in Tudor London?Document4 pagesWhat Was Life Like in Tudor London?LucianPas encore d'évaluation
- Ebook PDF The Unfinished Nation A Concise History of The American People 8th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF The Unfinished Nation A Concise History of The American People 8th Edition PDFbrian.sheffield119100% (35)
- African American History Syllabus For BCC Fall 2015Document12 pagesAfrican American History Syllabus For BCC Fall 2015Beloved Community Center of Greensboro100% (2)
- U. S. History Presidents List: The Young Republic, 1788-1815Document11 pagesU. S. History Presidents List: The Young Republic, 1788-1815richsong1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ap U. S. History Presidents ListDocument7 pagesAp U. S. History Presidents Listlotus44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ap Us History Decades ReviewDocument12 pagesAp Us History Decades Reviewapi-595413521Pas encore d'évaluation
- Presidential OrganizerDocument7 pagesPresidential OrganizerSeth AdlerPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 5 Toward - IndependenceDocument28 pagesLesson 5 Toward - Independencefishertr1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 18 An Era of ReformDocument34 pagesLesson 18 An Era of Reformfishertr1100% (1)
- Key Events Battles of The American RevolutionDocument2 pagesKey Events Battles of The American Revolutionapi-263382165Pas encore d'évaluation
- MWBA +frontiersman+ +Viewing+GuideDocument5 pagesMWBA +frontiersman+ +Viewing+GuideMolly ChambersPas encore d'évaluation
- MWBA +frontiersman+ +Viewing+GuideDocument6 pagesMWBA +frontiersman+ +Viewing+GuideMolly ChambersPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 12 Foreign Affairs in The Young NationDocument28 pagesLesson 12 Foreign Affairs in The Young Nationfishertr1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 4 Life in The ColoniesDocument22 pagesLesson 4 Life in The Coloniesfishertr1Pas encore d'évaluation
- America The Story of Us QuestionsDocument2 pagesAmerica The Story of Us QuestionszoePas encore d'évaluation
- StudentnotesDocument4 pagesStudentnotesapi-264685275Pas encore d'évaluation
- Adrian Bryant - CH 12 The West Graphic OrganizerDocument2 pagesAdrian Bryant - CH 12 The West Graphic Organizerapi-512321475Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 24 Tensions in The WestDocument30 pagesLesson 24 Tensions in The Westfishertr1Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Social Reforms of The Antebellum EraDocument4 pages3 Social Reforms of The Antebellum Eraapi-294843376Pas encore d'évaluation
- World History Important DateDocument3 pagesWorld History Important DateHabib ManzerPas encore d'évaluation
- 20 Century: A Time For ChangesDocument2 pages20 Century: A Time For ChangesFlorcha CharpentierPas encore d'évaluation
- StudentnotesDocument5 pagesStudentnotesapi-264685275Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 The Rise of The Atlantic World Organizer GuideDocument2 pagesChapter 2 The Rise of The Atlantic World Organizer GuideoleymaPas encore d'évaluation
- MWBA All in 1Document6 pagesMWBA All in 1Molly ChambersPas encore d'évaluation
- America Story of Us V-GuideDocument1 pageAmerica Story of Us V-Guideapi-256414698Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cfe2 T 2548234 Usa Information Powerpoint English Ver 5Document17 pagesCfe2 T 2548234 Usa Information Powerpoint English Ver 5Gaby KramerPas encore d'évaluation
- StudentnotesDocument5 pagesStudentnotesapi-264685275Pas encore d'évaluation
- Russian Revolution: Strikes Occurred in Russian Poland, Baltic Provinces, Transcaucasia and Bakut & OdessaDocument7 pagesRussian Revolution: Strikes Occurred in Russian Poland, Baltic Provinces, Transcaucasia and Bakut & OdessaAnamyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Periods PDFDocument3 pagesPeriods PDFSourabh AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- StudentnotesDocument7 pagesStudentnotesapi-264685275Pas encore d'évaluation
- New England ColoniesDocument6 pagesNew England ColoniesDennis PincayPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 2 SfisDocument7 pagesCH 2 Sfisapi-328008296Pas encore d'évaluation
- Final Project - Modern Age 1Document8 pagesFinal Project - Modern Age 1Maria MadrazoPas encore d'évaluation
- US SOL Review WorksheetsDocument69 pagesUS SOL Review Worksheetstack87Pas encore d'évaluation
- VocabularyDocument4 pagesVocabularyapi-264685275Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chaucer To ShakespeareDocument17 pagesChaucer To ShakespeareAbinaya RPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronology of Events in The History of EnglishDocument7 pagesChronology of Events in The History of Englishlb0336Pas encore d'évaluation
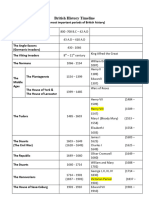
- Unit 2. British History TimelineDocument2 pagesUnit 2. British History Timeline21Nguyễn Đặng Hoàng My12A6NTTPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cold War 1945 The Cold War 1945 - 1991 1991Document13 pagesThe Cold War 1945 The Cold War 1945 - 1991 1991A Miguel Simão LealPas encore d'évaluation
- Renaissance: - 14th To The 17th Century - ItalyDocument69 pagesRenaissance: - 14th To The 17th Century - ItalySammelsPas encore d'évaluation
- Ap Us History Intensive Review GuideDocument73 pagesAp Us History Intensive Review GuideMaLik HaSeebPas encore d'évaluation
- Inventions and Discoveries in The Modern Age: Khryss Lin Deguit GE 5 - Science, Technology and Society (MWF 7:00-8:00AM)Document7 pagesInventions and Discoveries in The Modern Age: Khryss Lin Deguit GE 5 - Science, Technology and Society (MWF 7:00-8:00AM)Mae Ann Tomimbang MaglintePas encore d'évaluation
- StudentnotesDocument6 pagesStudentnotesapi-264685275Pas encore d'évaluation
- Manifest Destiny Vocabulary Power PointDocument21 pagesManifest Destiny Vocabulary Power PointlanePas encore d'évaluation
- Chaucer To Restoration PeriodDocument55 pagesChaucer To Restoration PeriodAbinaya RPas encore d'évaluation
- CPUSH Agenda For Unit 1.1: - "Compare The Spanish, French, Dutch, & British Colonies" NotesDocument35 pagesCPUSH Agenda For Unit 1.1: - "Compare The Spanish, French, Dutch, & British Colonies" Notesapi-294843376Pas encore d'évaluation
- ChronologyDocument55 pagesChronologyapi-296653915Pas encore d'évaluation
- The French RevolutionDocument33 pagesThe French RevolutionGowry KvsPas encore d'évaluation
- StudentnotesDocument5 pagesStudentnotesapi-264685275Pas encore d'évaluation
- Manifest DestinyDocument2 pagesManifest DestinyMark JacksonPas encore d'évaluation
- StudentnotesDocument6 pagesStudentnotesapi-264685275Pas encore d'évaluation
- PrehistoryDocument5 pagesPrehistoryMiriam MantasPas encore d'évaluation
- Rulers of Great BritainDocument3 pagesRulers of Great BritainflafsyPas encore d'évaluation
- 658-2003 - A Timeline of English PoetryDocument98 pages658-2003 - A Timeline of English PoetryjavedarifPas encore d'évaluation
- First Americans - Pre-Columbian: NotesDocument73 pagesFirst Americans - Pre-Columbian: NotesCaroline BrownPas encore d'évaluation
- Usi 6a D AmericanrevolutionDocument6 pagesUsi 6a D Americanrevolutionapi-327551303Pas encore d'évaluation
- Civil War DBQDocument10 pagesCivil War DBQKevin Earlie100% (1)
- Geography FactsDocument6 pagesGeography Factsvirgo_signnPas encore d'évaluation
- The 1850sDocument44 pagesThe 1850sapi-32765348150% (2)
- Best British Inventions EverDocument4 pagesBest British Inventions EverMaya PmPas encore d'évaluation
- Andrew Jackson: Heroic Leader or Cold-hearted Ruler?D'EverandAndrew Jackson: Heroic Leader or Cold-hearted Ruler?Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Full Download Test Bank For Social Psychology 10th Editionby Elliot Aronson PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Social Psychology 10th Editionby Elliot Aronson PDF Full Chapterquantitycatboatukmgh100% (20)
- Apush DBQ ReconstructionDocument2 pagesApush DBQ ReconstructionBlake LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Civil War Thesis StatementDocument8 pagesCivil War Thesis Statementjmvnqiikd100% (2)
- Ial Civil Rights - Murphy - SearchableDocument190 pagesIal Civil Rights - Murphy - SearchableCafeNet GirnePas encore d'évaluation
- America's History - 6th Edition Volume 2 (Ch. 14-Ch. 18)Document55 pagesAmerica's History - 6th Edition Volume 2 (Ch. 14-Ch. 18)Anna MariePas encore d'évaluation
- A-A. Teacher's ManualDocument98 pagesA-A. Teacher's Manualaloriz66Pas encore d'évaluation
- Apush AssignmentsDocument10 pagesApush AssignmentsAlex SchmiraPas encore d'évaluation
- On The History of The KKKDocument5 pagesOn The History of The KKKKamil RizviPas encore d'évaluation
- 2024 Specimen Paper 1 Mark SchemeDocument50 pages2024 Specimen Paper 1 Mark Schemesaifsain49Pas encore d'évaluation
- Amber Kelsie - Blackened Debate at The End of The World - Project - Muse - 721920 PDFDocument9 pagesAmber Kelsie - Blackened Debate at The End of The World - Project - Muse - 721920 PDFdocbrown85Pas encore d'évaluation
- On The Nature of Slavery in The Plantation South: A Question of ConditionDocument12 pagesOn The Nature of Slavery in The Plantation South: A Question of ConditionAnthony Fotenos100% (1)
- Chapter 20-22 ApushDocument14 pagesChapter 20-22 Apushapi-235479305Pas encore d'évaluation
- 20 Gershwin-Scandal-Walk - Piano RollDocument6 pages20 Gershwin-Scandal-Walk - Piano RollsherlockwatsiPas encore d'évaluation
- History E-PortfolioDocument2 pagesHistory E-Portfolioapi-249991288Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Unfinished Nation A Concise History of The American People 10Th Edition Alan Brinkley All ChapterDocument67 pagesThe Unfinished Nation A Concise History of The American People 10Th Edition Alan Brinkley All Chapterlarry.watton486100% (7)
- Full Download Test Bank For Essentials of Sonography and Patient Care 2nd Edition Craig PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Essentials of Sonography and Patient Care 2nd Edition Craig PDF Full Chapteranalcitedonary46f2d100% (17)
- Racial Violence and Reconstruction Politics in Texas, 1867-1868Document24 pagesRacial Violence and Reconstruction Politics in Texas, 1867-1868sahicurnPas encore d'évaluation
- The Civil Rights MovementDocument4 pagesThe Civil Rights Movementsharon wanjikuPas encore d'évaluation
- Rumble Fish EssayDocument8 pagesRumble Fish Essayafibzdftzaltro100% (2)
- America A Narrative History Vol 2 10th Edition Shi Test BankDocument15 pagesAmerica A Narrative History Vol 2 10th Edition Shi Test Banktracyrosswbmjpykrnz100% (13)
- Anudaan Sahayata Karyabidhi 2072 Unofficial English TranslationDocument12 pagesAnudaan Sahayata Karyabidhi 2072 Unofficial English TranslationDinesh PoudelPas encore d'évaluation
- US History Exam Review2Document4 pagesUS History Exam Review2Brian GeisePas encore d'évaluation
- Dan Smoot Report 1963 Vol IXDocument446 pagesDan Smoot Report 1963 Vol IXHal ShurtleffPas encore d'évaluation
- US History EOC Study GuideDocument16 pagesUS History EOC Study GuideJalen ChaneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Women and Post-Conflict Reconstruction Issues & Sources, Birgitte Sorensen (1998)Document70 pagesWomen and Post-Conflict Reconstruction Issues & Sources, Birgitte Sorensen (1998)United Nations Research Institute for Social DevelopmentPas encore d'évaluation