Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Grading Scales Web PDF
Transféré par
Danielle Sangalang0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
307 vues2 pagesTitre original
Grading_Scales_web.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
307 vues2 pagesGrading Scales Web PDF
Transféré par
Danielle SangalangDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
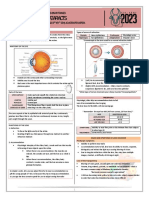
GRADING SCALES
www.brienholdenvision.org
1. VERY SLIGHT 2. SLIGHT 3. MODERATE 4. SEVERE
BULBAR
REDNESS
LIMBAL
REDNESS
LID REDNESS
(area 2)
LID ROUGHNESS:
WHITE LIGHT
REFLEX
(areas 1, 2)
LID ROUGHNESS:
FLUORESCEIN
(area 2)
CORNEAL
STAINING:
TYPE
CORNEAL
STAINING:
DEPTH
CORNEAL
STAINING:
EXTENT
(area 5)
CONJUNCTIVAL
STAINING
© Copyright Brien Holden Vision Institute 2011
GRADING SCALES
www.brienholdenvision.org
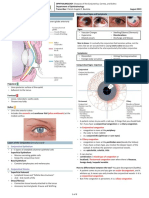
APPLICATION OF GRADING SCALES CORNEAL STAINING GRADES
• Patient management is based on how much the normal ocular • Staining assessed immediately after single instillation of fluorescein
appearance has changed. using cobalt blue light and wratten 12 (yellow) filter over the slit lamp
• In general, a rating of slight (grade 2) or less is considered within objective.
normal limits (except staining). • The cornea is divided into five areas. The type, extent and depth of
• A change of one grade or more at follow up visits is considered staining are graded in each area.
clinically significant.
Type
1 Micropunctate
PALPEBRAL CONJUNCTIVAL GRADES 2 Macropunctate
3 Coalescent macropunctate
• The palpebral conjunctiva is divided into
4 Patch
five areas to grade redness and roughness.
• Areas 1, 2 and 3 are most relevant in
contact lens wear.
Extent Description Depth Description*
1 ≤5% 1 Superficial epithelium
2 6-15% 2 Deep epithelium, delayed stromal glow
3 16-30% 3 Immediate localized stromal glow
ADVERSE EFFECTS WITH CONTACT LENSES 4 >30% 4 Immediate diffuse stromal glow
CLPC CONTACT LENS PAPILLARY CONJUNCTIVITIS * Based on penetration of fluorescein and slit lamp optic section
Inflammation of the upper palpebral conjunctiva
EROSION
Signs
Full thickness epithelial loss over a discrete area
• Redness
• Enlarged papillae Signs
• Excess mucus • No stromal inflammation
Symptoms • Immediate spread of fluorescein into stroma
• Itchiness Symptoms
• Mucus strands • Can be painful
• Lens mislocation • Photophobia
• Intolerance to lenses • Lacrimation
INFILTRATES
CLPU CONTACT LENS PERIPHERAL ULCER
Accumulation of inflammatory cells in corneal sub-epithelial stroma.
Inset: high magnification view Round, full thickness epithelial loss with inflamed base, typically in the
corneal periphery which results in a scar. Insets: with fluorescein, scar
Signs
• Whitish opacity (focal) or grey haze Signs
(diffuse) • Unilateral, “white spot”
• Usually confined to 2-3mm from limbus • Localized redness
• Localized redness • Infiltrates
Symptoms • Post healing scar
• Asymptomatic or scratchy, foreign body Symptoms
sensation • Varies from foreign body sensation to pain
• Redness, tearing and photophobia • Lacrimation and photophobia may occur
possible
INFECTED ULCER
CLARE CONTACT LENS ACUTE RED EYE Full thickness epithelial loss with stromal necrosis and inflammation, typi-
An acute corneal inflammatory episode associated with sleeping in soft cally central or paracentral
contact lenses Signs
Signs • Intense redness
• Unilateral • “White patch” (raised edges)
• Intense redness • Infiltrates
• Infiltrates • Epithelial and stromal loss
• No epithelial break • Anterior chamber flare
Symptoms • Conjunctival and lid edema
• Wakes with irritation or pain Symptoms
• Photophobia • Pain, photophobia
• Lacrimation • Redness, mucoid discharge
• VA (if over pupil)
POLYMEGETHISM
1. VERY SLIGHT 2. SLIGHT 3. MODERATE 4. SEVERE
VASCULARIZATION STROMAL STRIAE and FOLDS MICROCYSTS and VACUOLES
Vessel One striae = 5% edema Located in epithelium.
extension One fold = 8% edema Identified by side
beyond trans- (each additional striae showing brightness.
lucent limbal or fold indicates 1% reversed
zone more edema) Microcysts
is recorded
(mm) Vacuoles
unreversed
Record number observed Record number observed
© Copyright Brien Holden Vision Institute 2011
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Grading ScaleDocument2 pagesGrading ScaleFelipe SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- AutomatedPerimetry 2006Document208 pagesAutomatedPerimetry 2006David ToddPas encore d'évaluation
- Octopus PerimetryDocument59 pagesOctopus PerimetryPrashob Mohan100% (1)
- Visual Field Interpretation - EyeSuite - PeriTrend PDFDocument2 pagesVisual Field Interpretation - EyeSuite - PeriTrend PDFmdmmm100% (1)
- Grading Scale 2017 PDFDocument2 pagesGrading Scale 2017 PDFAlibek ZhumanazarovPas encore d'évaluation
- OPTHA 1.1 ANATOMY OF THE EYEBALL - Dr. CapuchinoDocument4 pagesOPTHA 1.1 ANATOMY OF THE EYEBALL - Dr. CapuchinoPatricia ManaliliPas encore d'évaluation
- Cornea 4Document27 pagesCornea 4Rana AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of The EyeballDocument3 pagesAnatomy of The EyeballMary Joy OamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture1-Human Eye SystemDocument29 pagesLecture1-Human Eye SystemPrajakta KhobragadePas encore d'évaluation
- Corneal Opacity 2Document16 pagesCorneal Opacity 2Ansif KPas encore d'évaluation
- Lens and Cataract - Dr. Angbue-Te (2023)Document4 pagesLens and Cataract - Dr. Angbue-Te (2023)Patricia ManaliliPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 Physical Assessment OsmaDocument29 pages9 Physical Assessment OsmaKate ChavezPas encore d'évaluation
- FL Stain1 (25265)Document22 pagesFL Stain1 (25265)Dr Anchal GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Apexogenesis Maintains Pulp Vitality for Root DevelopmentDocument1 pageApexogenesis Maintains Pulp Vitality for Root DevelopmentShalini BhardwajPas encore d'évaluation
- Sitesdefaultfilesstatic10131-Reedy Chandra Reedy Chandra Part 1 Minerals Rocks PDFDocument14 pagesSitesdefaultfilesstatic10131-Reedy Chandra Reedy Chandra Part 1 Minerals Rocks PDFFrancis AsiagtewenPas encore d'évaluation
- Histopathology of Dental Caries Zones and StagesDocument7 pagesHistopathology of Dental Caries Zones and StagesJOHN HAROLD CABRADILLAPas encore d'évaluation
- Hazy Vision Causes and Eye ExamDocument13 pagesHazy Vision Causes and Eye ExamPrincess Noreen SavellanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Shanz - PEDIA II 2.01 NEWDocument8 pagesShanz - PEDIA II 2.01 NEWPetrina XuPas encore d'évaluation
- Derma MegatableDocument21 pagesDerma MegatableCoy NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Skin Checklist ProcedureDocument6 pagesSkin Checklist ProcedureKristine Angie RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Observing Microorganisms Through a MicroscopeDocument20 pagesObserving Microorganisms Through a MicroscopeYousef DosouqiPas encore d'évaluation
- Retinal DetachmentDocument1 pageRetinal DetachmentMohannad AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Introduction To Corneal DiseaseDocument10 pages01 Introduction To Corneal DiseaseTrang Nguyễn ThuỳPas encore d'évaluation
- Corneal Ulcer - Modern PDFDocument90 pagesCorneal Ulcer - Modern PDFAnnasaheb PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- Optics and RefractionDocument12 pagesOptics and RefractionOscar Daniel MendezPas encore d'évaluation
- Retinal Detachment 1Document20 pagesRetinal Detachment 1Pd HariniPas encore d'évaluation
- 9893 Alcon Grading Scales 4pp - 0 PDFDocument4 pages9893 Alcon Grading Scales 4pp - 0 PDFDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- LeprosyDocument22 pagesLeprosyvisweswar030406Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dermatology Revision E6.5 'Document35 pagesDermatology Revision E6.5 'Riya SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ophtha ReviewerDocument3 pagesOphtha ReviewerToni Sy EncinaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Meas SpraysDocument60 pagesMeas Spraysnejmiddin boughattasPas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases of the Conjunctiva, Cornea, and Sclera SummaryDocument8 pagesDiseases of the Conjunctiva, Cornea, and Sclera SummaryNoreenPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Epithelial and Bowman's Layer LesionsDocument13 pages02 Epithelial and Bowman's Layer LesionsTrang Nguyễn ThuỳPas encore d'évaluation
- 3-4 Management Hand BurnsDocument43 pages3-4 Management Hand BurnsProfesseur Christian DumontierPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of Oral Lesion: A. Anggun Mauliana PutriDocument42 pagesClassification of Oral Lesion: A. Anggun Mauliana PutripriskayoviPas encore d'évaluation
- Microscopy Techniques and Staining MethodsDocument2 pagesMicroscopy Techniques and Staining MethodsLuiciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Opthalmology Visuals New PDF-1Document100 pagesOpthalmology Visuals New PDF-1singh0% (1)
- Clin Bacteriology Lec - Roles of MicrosDocument2 pagesClin Bacteriology Lec - Roles of MicrosnikkiPas encore d'évaluation
- Vision: - Carlene S. Solidum, MD, DPPSDocument98 pagesVision: - Carlene S. Solidum, MD, DPPSJimell ObradorPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification Criteria For SLE PDFDocument4 pagesClassification Criteria For SLE PDFCocea MihaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lens: Anatomy, Pathology, and Mechanisms of Toxicity Lens DevelopmentDocument6 pagesLens: Anatomy, Pathology, and Mechanisms of Toxicity Lens DevelopmentAmit GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ophthalmology: Almendrala-Molina, Jorja Post Graduate InternDocument65 pagesOphthalmology: Almendrala-Molina, Jorja Post Graduate InternJajaAlmendralaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ophthalmology Instruments CollegeDocument26 pagesOphthalmology Instruments CollegeLavpreetPas encore d'évaluation
- The Slit Lamp ExamDocument30 pagesThe Slit Lamp Examrapid73Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of The Eye - Dr. Lim-Cecilio (2022)Document3 pagesAnatomy of The Eye - Dr. Lim-Cecilio (2022)Patricia ManaliliPas encore d'évaluation
- Para311 Laboratory: Lesson 2: MicroscopeDocument6 pagesPara311 Laboratory: Lesson 2: MicroscopeMarinel GaniaPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Lids and Lashes 2016Document13 pages10 Lids and Lashes 2016willemlrouxPas encore d'évaluation
- Paint Fiilm DefectsDocument33 pagesPaint Fiilm DefectsGAURAV AHUJAPas encore d'évaluation
- Primary Open Angle GlauDocument21 pagesPrimary Open Angle GlauwildaPas encore d'évaluation
- KeratoconusssDocument15 pagesKeratoconusssnurfatminsari almaidinPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 - FOREV - Less3 - PASS - SP PDFDocument46 pages03 - FOREV - Less3 - PASS - SP PDFAndriArdianPutraPas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases of CorneaDocument170 pagesDiseases of CorneaLavanya MadabushiPas encore d'évaluation
- Educational Moments: What You Need To KnowDocument4 pagesEducational Moments: What You Need To KnowRaeesah MehmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic Eruption TreatmentDocument4 pagesEctopic Eruption TreatmentDr-Basel RehawiPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic SuturingDocument4 pagesBasic SuturingMian SimporiosPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Fluorescence MicrosDocument28 pages4 Fluorescence MicrosSneakyRiderPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 PDFDocument62 pages3 PDFDiwakesh C BPas encore d'évaluation
- MicroPara LAB - M1Document3 pagesMicroPara LAB - M1Gianna LingadPas encore d'évaluation
- DISORDERS of The EYE and EARDocument8 pagesDISORDERS of The EYE and EARAnna Carmela P. MelendezPas encore d'évaluation
- Dermatology Revision E6.5 @theboggusdocDocument36 pagesDermatology Revision E6.5 @theboggusdockhushi koliPas encore d'évaluation
- Corneal Injury Leads To Discovery: A Case Study On Asymptomatic AmblyopiaDocument1 pageCorneal Injury Leads To Discovery: A Case Study On Asymptomatic AmblyopiaDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Horner's Syndrome As A Complication of Thyroidectomy: Report of A CaseDocument3 pagesHorner's Syndrome As A Complication of Thyroidectomy: Report of A CaseDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Volume 6, Issue 1 - 1Document10 pagesVolume 6, Issue 1 - 1Danielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Conclusions Background: Vision Development & RehabilitationDocument13 pagesConclusions Background: Vision Development & RehabilitationDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Acquired Infantile Horner Syndrome and Spontaneous Internal Carotid Artery Dissection: A Case Report and Review of LiteratureDocument10 pagesAcquired Infantile Horner Syndrome and Spontaneous Internal Carotid Artery Dissection: A Case Report and Review of LiteratureDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Horner's Syndrome During Spindle Cell Lipoma of The Neck - A CaseDocument4 pagesHorner's Syndrome During Spindle Cell Lipoma of The Neck - A CaseDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Characteristics of Exodeviated Patients With Accomodative Esotropia and Hyperopia Without StrabismusDocument5 pagesClinical Characteristics of Exodeviated Patients With Accomodative Esotropia and Hyperopia Without StrabismusDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Orthok Case Reviews in Ophthalmology 2eDocument2 pagesOrthok Case Reviews in Ophthalmology 2eDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Myopic Changes in A Climber After Taking Acetazolamide and The Use of Corrective Lenses To Temporize Symptoms: A Case Report From Mount KilimanjaroDocument4 pagesMyopic Changes in A Climber After Taking Acetazolamide and The Use of Corrective Lenses To Temporize Symptoms: A Case Report From Mount KilimanjaroDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- First Rib Fracture and Horner 'S Syndrome Due To A Motor Vehicle Collision: A Case ReportDocument5 pagesFirst Rib Fracture and Horner 'S Syndrome Due To A Motor Vehicle Collision: A Case ReportDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Slit Lamp Skills: How To Adjust The Lighting To See Stuff!Document45 pagesAdvanced Slit Lamp Skills: How To Adjust The Lighting To See Stuff!Danielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 Contact Lens Parameter Guide: Innovative Eyecare To Meet Your Patients' NeedsDocument4 pages2020 Contact Lens Parameter Guide: Innovative Eyecare To Meet Your Patients' NeedsDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- A Course in Low Vision Practice: P 5 - Magnification and MagnifiersDocument6 pagesA Course in Low Vision Practice: P 5 - Magnification and MagnifiersDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Alternating Horner Syndrome: Case Report and Review of The LiteratureDocument4 pagesAlternating Horner Syndrome: Case Report and Review of The LiteratureDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Horner's Syndrome After Carotid Artery Stenting:: Case ReportDocument5 pagesHorner's Syndrome After Carotid Artery Stenting:: Case ReportDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Horner's Syndrome Due To A Large Schwannoma of The Cervical Sympathetic Chain: Report of CaseDocument4 pagesHorner's Syndrome Due To A Large Schwannoma of The Cervical Sympathetic Chain: Report of CaseDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Optometry Primary Eye CareDocument3 pagesClinical Optometry Primary Eye CareDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Horners Syndrome Resulting From Agenesis of The Internal Carotid Artery: Report of A Third CaseDocument2 pagesHorners Syndrome Resulting From Agenesis of The Internal Carotid Artery: Report of A Third CaseDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- RPG Series Ophthalmology Buster PDFDocument299 pagesRPG Series Ophthalmology Buster PDFDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review of Ocular Genetics and Inherited Eye Diseases: SD MathebulaDocument12 pagesA Review of Ocular Genetics and Inherited Eye Diseases: SD Mathebulalavinia diaPas encore d'évaluation
- 09 OpticsDocument10 pages09 OpticsRena AdachiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Other Amsler ChartsFINALDocument20 pagesThe Other Amsler ChartsFINALDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Opht PDFDocument99 pagesOpht PDFDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometrical and Visual OpticsDocument382 pagesGeometrical and Visual OpticsWaleedAhmad100% (5)
- Infant ReflexesDocument14 pagesInfant ReflexesJohn Agana AyamgaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bino - Lec - Midterm Exam - Yellow - PadDocument11 pagesBino - Lec - Midterm Exam - Yellow - PadDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Orthoptics - Fiona Rowe - 146Document6 pagesClinical Orthoptics - Fiona Rowe - 146Danielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Binocular Vision & Orthoptics - Bruce Evans - 17Document3 pagesBinocular Vision & Orthoptics - Bruce Evans - 17Danielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment of Binocular Vision IssuesDocument3 pagesAssessment of Binocular Vision IssuesDanielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Best Aid To Ophthalmology - Pramod TK - 318Document3 pagesBest Aid To Ophthalmology - Pramod TK - 318Danielle SangalangPas encore d'évaluation
- SKYRIM ULTIMATE 4.0.3 Mod ListDocument6 pagesSKYRIM ULTIMATE 4.0.3 Mod ListCrowMechanicsPas encore d'évaluation
- World Music LessonDocument2 pagesWorld Music Lessonapi-323143699Pas encore d'évaluation
- King Explicitly Invokes Aristotle's Theoretical Statements On Poetics. To Argue, As Does Chinua AchebeDocument20 pagesKing Explicitly Invokes Aristotle's Theoretical Statements On Poetics. To Argue, As Does Chinua AchebeSuhrab Khan JamaliPas encore d'évaluation
- DAGMAR Advertising Model ExplainedDocument11 pagesDAGMAR Advertising Model ExplainedAmit KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.2.7 Packet Tracer - Investigate NAT Operation - ILMDocument4 pages6.2.7 Packet Tracer - Investigate NAT Operation - ILMDaniel LemaPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidance Re Unknown Signature Image 23873Document1 pageGuidance Re Unknown Signature Image 23873Erick MoraPas encore d'évaluation
- An Urgent Rescue: A 2-3 Hour Adventure For Three To Four 2 Level CharactersDocument11 pagesAn Urgent Rescue: A 2-3 Hour Adventure For Three To Four 2 Level CharactersМаксим ДьяконенкоPas encore d'évaluation
- I Shall See Him by and by - Frank E. Graeff PDFDocument1 pageI Shall See Him by and by - Frank E. Graeff PDFEducational PurposesPas encore d'évaluation
- Russie T. Edaño 12-STEMDocument7 pagesRussie T. Edaño 12-STEMMer VinPas encore d'évaluation
- Zillion TV CorporationDocument1 pageZillion TV Corporationmdaniels1901Pas encore d'évaluation
- Artius BrochureDocument3 pagesArtius Brochure87krishan0% (1)
- Alice Falls Down Rabbit Hole and Explores WonderlandDocument3 pagesAlice Falls Down Rabbit Hole and Explores WonderlandAlina-Mihaela Vintila100% (1)
- Adventures in Middle Earth Loremasters Guide MapsDocument2 pagesAdventures in Middle Earth Loremasters Guide MapsRazor191183% (6)
- Mill Valley School District Art Department: Drawing Curriculum MapDocument20 pagesMill Valley School District Art Department: Drawing Curriculum MapMill ValleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ilmuguru - Org - Soal PAS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 8 Semester 1 Tahun 2020Document5 pagesIlmuguru - Org - Soal PAS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 8 Semester 1 Tahun 2020Rien BiPas encore d'évaluation
- Free PDF Priyanka ChopraDocument1 pageFree PDF Priyanka ChopraAmberPas encore d'évaluation
- Mintwallin BlackD ToolsDocument6 pagesMintwallin BlackD ToolsBone HigónPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Kings, Farmers and TownsDocument30 pages2 Kings, Farmers and TownsAnushka MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- MAPEH Summative Test ReviewDocument2 pagesMAPEH Summative Test ReviewJhackhie Mirasol CaliboPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 Nominative and VocativeDocument10 pagesLesson 1 Nominative and VocativeSeijuro HikoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cub & BulBulDocument9 pagesCub & BulBulProud Indian100% (1)
- TeclisDocument4 pagesTeclisCharlie BowenPas encore d'évaluation
- Gedung Kantor Gubernur Sulut PDFDocument7 pagesGedung Kantor Gubernur Sulut PDFNJ TVPas encore d'évaluation
- Gpsa Engineering Data Book Free PDFDocument2 pagesGpsa Engineering Data Book Free PDFBindu joglekar0% (1)
- Collection of Ielts Speaking Part 2Document12 pagesCollection of Ielts Speaking Part 2Hu MihiPas encore d'évaluation
- DH-IPC-HFW2431T-AS-S2: 4MP Lite IR Fixed-Focal Bullet Network CameraDocument3 pagesDH-IPC-HFW2431T-AS-S2: 4MP Lite IR Fixed-Focal Bullet Network CameraZelaya DudPas encore d'évaluation
- Opening Program Intramurals 2019 ScriptDocument2 pagesOpening Program Intramurals 2019 ScriptAnnamarie P. Balahadia Lpt100% (2)
- Star Wars Rebel Force 5 Trapped by Alex WheelerDocument103 pagesStar Wars Rebel Force 5 Trapped by Alex Wheelerrivjo toelh100% (1)
- Art and Politics in Our EpochDocument8 pagesArt and Politics in Our EpochspirospotPas encore d'évaluation
- Once Upon A Time in AmericaDocument11 pagesOnce Upon A Time in AmericaaliciarnoldPas encore d'évaluation