Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
416 Blueprint Reading For Welders Course Description
Transféré par
Kathiravan MDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
416 Blueprint Reading For Welders Course Description
Transféré par
Kathiravan MDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
WELDING
Blueprint Reading for Welders
Course 416: Blueprint Reading for Welders
Covers basic shop math and measurement skills. Explains how to read, use, and make blueprints. Discusses various welds, weld
joints, and weld symbols. Explains advanced shop math and measurement skills.
TPC Training is accredited by IACET to offer 0.6 CEU for this program.
Lesson 1: Shop Math and Measurement Lesson 4: Welds and Weld Joints
Topics Topics
Fractions; Common Fractions; Reducing Common Fractions; Improper Basic Weld Joints; Butt Joint; Lap Joint; Tee Joint; Corner Joint; Edge
Fractions; Mixed Numbers; Calculations Involving Common Fractions; Joint; Weld Types; Groove Welds; Fillet Welds; Plug and Slot Welds; Spot
Shortcuts for Working with Common Fractions; Decimal Fractions; and Seam Welds; Stud Welds; Surface Welds; Backing Welds; Welding
Calculations Involving Decimal Fractions; Converting Common Fractions Positions and Locations
to Decimal Fractions; Converting Decimal Fractions to Common Fractions;
Standard Rules and Tape Measures; Reading a Rule or Tape Measure; Objectives
Using a Calculator • Identify and describe the five basic weld joints.
• Define the following terms: bead, stringer bead, weave bead,
Objectives base metal, filler metal, root pass, hot pass, fill pass, cap,
• Define and identify common fractions and decimal fractions. hardfacing.
• Define the term equivalent fraction. • Identify and describe the basic weld types.
• Perform calculations using common fractions and decimal • Name the basic welding positions and give advantages of the flat
fractions. position.
• Convert between common fractions and decimal fractions.
• Read and perform measurements using a standard rule or tape Lesson 5: Welding Symbols
measure. Topics
• Explain the use of calculators in welding Structure of Welding Symbols; Reference Line; Arrow; Weld Symbol;
Dimensions; Special Symbols; Tail; Reading Welding Symbols
Lesson 2: Introduction to Blueprints
Topics Objectives
Purpose of Blueprints; Types of Blueprints; Making Blueprints; Parts of a • Identify which side of a structure a weld is to be made from.
Blueprint; Body; Title Block; Bill of Material; Revision Block; Zoning; • Identify the kind of chamfer to be cut on a joint to be welded, and
Security; Care and Handling of Blueprints which part is to be chamfered.
• State the required dimensions of a weld.
Objectives • Identify the contour required on a finished weld.
• Explain the importance of information on blueprints. • State how a weld contour is to be finished.
• Explain the differences between assembly drawings and detail • Differentiate between welds that are to be made at the site of
drawings. final assembly and welds that are to be made before the parts are
• Describe methods used to create and reproduce blueprints. shipped to the site.
• Define and describe parts of a blueprint.
• Identify elements located within the title block of a detail drawing. Lesson 6: Advanced Shop Math and Measurement
• List methods of care and security of blueprints. Topics
Squares and Square Roots; Angles; Triangles; Circles; Linear
Lesson 3: Lines and Views on Blueprints Measurement; Calipers; Slide Calipers; Vernier Calipers; Micrometer
Topics Calipers; Angular Measurement; Metric Measurement
Lines Used on a Blueprint; Views on a Blueprint; Perspective; Orthographic
Projections; Oblique Projections; Isometric Projections; Other Views; Objectives
Selecting Views; Sketching • Explain the concepts of squares and square roots of numbers.
• Define the following kinds of angles: zero degree, acute, straight,
Objectives right, and obtuse.
• Identify the standard lines used on blueprints. • State the Pythagorean Theorem and explain its usefulness.
• Explain the meaning and applications of standard lines on • Define the following terms related to circles: radius, diameter, arc,
blueprints. and circumference.
• Identify common views used on a blueprint. • Give the equations for finding a circle’s circumference and area if
• Name the advantages and disadvantages of various projection you know its radius.
types. • Explain the use of the following measuring tools: calipers,
• Explain the concept of visualization. micrometers, and protractors.
• Demonstrate how to convert measurements from inches to
millimeters and from millimeters to inches.
228 TPC
TRAINING P: 847.808.4000 • F: 847.808.4003 • www.tpctraining.com
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Technical Drawing SBADocument21 pagesTechnical Drawing SBATani B71% (7)
- GD&T - Training - Part 1Document310 pagesGD&T - Training - Part 1Kl100% (1)
- Screwcutting in the Lathe for Home Machinists: Reference Handbook for Both Imperial and Metric ProjectsD'EverandScrewcutting in the Lathe for Home Machinists: Reference Handbook for Both Imperial and Metric ProjectsPas encore d'évaluation
- 101 Reading Blueprints Course DescriptionDocument2 pages101 Reading Blueprints Course DescriptionAnonymous q9eCZHMuSPas encore d'évaluation
- Traditional Toolmaking: The Classic Treatise on Lapping, Threading, Precision Measurements, and General ToolmakingD'EverandTraditional Toolmaking: The Classic Treatise on Lapping, Threading, Precision Measurements, and General ToolmakingÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Basic Engineering Drawing PDFDocument192 pagesBasic Engineering Drawing PDFvrsafe100% (2)
- Validated TVL Smaw11 q3 M 6Document11 pagesValidated TVL Smaw11 q3 M 6tibo bursioPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction of Engineering DrawingDocument31 pagesIntroduction of Engineering DrawingSuvab KambojPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Engineering Drawing & Coordinate Systems in AutoCADDocument38 pagesFundamentals of Engineering Drawing & Coordinate Systems in AutoCADArya GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- FITTERDocument43 pagesFITTERsuchi987Pas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Drawing N2Document41 pagesEngineering Drawing N2Ofentse Racodi100% (3)
- WeldingDocument64 pagesWeldingLiyana100% (1)
- Reading Blueprints: FundamentalsDocument2 pagesReading Blueprints: FundamentalsJessie GoranPas encore d'évaluation
- Architecture Drafting Design SyllabusDocument24 pagesArchitecture Drafting Design SyllabusfcharafPas encore d'évaluation
- Threads and FastenersDocument25 pagesThreads and FastenersMuhammed UmarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 & 4 - DimensioningDocument75 pagesLecture 3 & 4 - DimensioningZeeshan AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Print Reading and Tolerances SyllabusDocument1 pagePrint Reading and Tolerances SyllabusrajuhaveriPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution MQCDocument16 pagesSolution MQCrushikesh yevalePas encore d'évaluation
- Core Skill ED CTSDocument11 pagesCore Skill ED CTSOsman AddawePas encore d'évaluation
- 5112Document3 pages5112goldencometPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry PDFDocument14 pagesGeometry PDFgladys manaliliPas encore d'évaluation
- 346 Tubing and Hose System Maintenance Course DescriptionDocument1 page346 Tubing and Hose System Maintenance Course DescriptionAnonymous q9eCZHMuSPas encore d'évaluation
- #4 Pengukuran Geometri 2: Metrologi Industri & Kontrol KualitasDocument87 pages#4 Pengukuran Geometri 2: Metrologi Industri & Kontrol KualitasChegg Cek akunPas encore d'évaluation
- Shape Features: Jamil AhmadDocument28 pagesShape Features: Jamil AhmadhandojoePas encore d'évaluation
- MCNC 71 Introduction To Machining and CNC Processes 4 1/2 Unit(s)Document6 pagesMCNC 71 Introduction To Machining and CNC Processes 4 1/2 Unit(s)taher ncirPas encore d'évaluation
- Mech Engg DrawingDocument6 pagesMech Engg Drawing22hubPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Engineering Drawing 0-0-3: Code: Credit: 03 L-T-PDocument1 pageMechanical Engineering Drawing 0-0-3: Code: Credit: 03 L-T-PAnanyaMaheshwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Threads FastenersDocument81 pagesThreads FastenersДмитрий РыбаковPas encore d'évaluation
- Trade Theory - Draughtsman-SyllabusDocument6 pagesTrade Theory - Draughtsman-SyllabusUmang SoniPas encore d'évaluation
- First Year Theory ITIDocument2 pagesFirst Year Theory ITImangla prasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank MQC Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3Document2 pagesQuestion Bank MQC Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3PrakharPas encore d'évaluation
- Strands and Standards: WoodworkingDocument7 pagesStrands and Standards: WoodworkingAlazar MekuriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Iv - Scaling and Dimensioning - 085621Document10 pagesChapter Iv - Scaling and Dimensioning - 085621Lessed DesselPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Engineering QuestionsDocument2 pagesBasic Engineering Questionsnguyen thi van dongPas encore d'évaluation
- Mec 231Document2 pagesMec 231Sanjog KarkiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2009 GDTDocument4 pages2009 GDTSreejith S NairPas encore d'évaluation
- Me TrologyDocument33 pagesMe TrologyIntan NurhaslindaPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering DrawingDocument11 pagesEngineering DrawingBrian MukaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Notice: Metalwork 6040 GCE O Level 2007Document7 pagesImportant Notice: Metalwork 6040 GCE O Level 2007mstudy123456Pas encore d'évaluation
- Phpy DX0 SeDocument8 pagesPhpy DX0 SeJoy OramaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Parametric Design: Sophomore Engineering Clinic IDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Parametric Design: Sophomore Engineering Clinic IMarsha MianPas encore d'évaluation
- m1 U4 Hole TappingDocument16 pagesm1 U4 Hole TappingViệt Đặng XuânPas encore d'évaluation
- PRLR14 - Machine Drawing CAD and Cost Estimation: Introduction, Conventions, Abbreviations and SymbolsDocument53 pagesPRLR14 - Machine Drawing CAD and Cost Estimation: Introduction, Conventions, Abbreviations and SymbolsKeshav GargPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual 1 - 3 PDFDocument16 pagesManual 1 - 3 PDFMaria MeharPas encore d'évaluation
- Hardware, Fasteners, Drills, and Thread RepairDocument14 pagesHardware, Fasteners, Drills, and Thread RepairfermelPas encore d'évaluation
- D1 - Mechanical Design GuidelinesDocument16 pagesD1 - Mechanical Design GuidelinesJubairAhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- 9X1 Shape 1 ObjectivesDocument1 page9X1 Shape 1 ObjectivesmrstuckePas encore d'évaluation
- Threads and FastenersDocument38 pagesThreads and FastenersNaveen KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- National Institute of Technology Warangal Department of Mechanical Engineering Warangal - 506 004Document50 pagesNational Institute of Technology Warangal Department of Mechanical Engineering Warangal - 506 004Venu Gopal AnnePas encore d'évaluation
- Furniture Design and Manufacturing (522) : EscriptionDocument8 pagesFurniture Design and Manufacturing (522) : EscriptionGeremu TilahunPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 M1 Orientation and IntroductionDocument39 pages01 M1 Orientation and Introductionpatrickreyeszecond2Pas encore d'évaluation
- LINES and LETTERINGDocument68 pagesLINES and LETTERINGShrutikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Creo - Flexible ModelingDocument8 pagesCreo - Flexible ModelingAmar DeepuPas encore d'évaluation
- Rebar Modeling in Revit: Keep It in Check: Ovidiu PaunescuDocument19 pagesRebar Modeling in Revit: Keep It in Check: Ovidiu PaunescuSohail ElwanPas encore d'évaluation
- GDNT 1Document24 pagesGDNT 1ganpath_ram@hotmail.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Metalwork Notes NEWDocument49 pagesMetalwork Notes NEWJudePas encore d'évaluation
- Camd Lab Manual17Document50 pagesCamd Lab Manual17Kavi ArasuPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuts and Bolts: DescriptionDocument9 pagesNuts and Bolts: Descriptionvignesh varmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Boilermaker Essential Skills Profile 2pgDocument2 pagesBoilermaker Essential Skills Profile 2pgAR RmsPas encore d'évaluation
- SkyscraperBanner2019 PDFDocument1 pageSkyscraperBanner2019 PDFKathiravan MPas encore d'évaluation
- New Doc 2019-01-18Document38 pagesNew Doc 2019-01-18Kathiravan MPas encore d'évaluation
- Compressor: Moocs - IitgDocument18 pagesCompressor: Moocs - IitgKathiravan MPas encore d'évaluation
- 28.13 OpkwDocument1 page28.13 OpkwKathiravan MPas encore d'évaluation
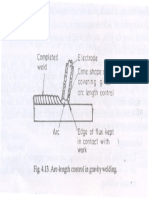
- Completed Weld Cone Shape of Flux Covering Gives Arc Length ControlDocument1 pageCompleted Weld Cone Shape of Flux Covering Gives Arc Length ControlKathiravan MPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Metal Arc WeldingDocument12 pagesGas Metal Arc WeldingKathiravan MPas encore d'évaluation
- History of WeldingDocument8 pagesHistory of WeldingKathiravan MPas encore d'évaluation
- 3a Electro Slag WeldingDocument66 pages3a Electro Slag WeldingKathiravan MPas encore d'évaluation
- RoboticDocument13 pagesRoboticKathiravan MPas encore d'évaluation
- Report: Establishment of "Welding Training School" For Students From Neighboring ITI at Toshiba JSW Chennai FactoryDocument3 pagesReport: Establishment of "Welding Training School" For Students From Neighboring ITI at Toshiba JSW Chennai FactoryKathiravan MPas encore d'évaluation