Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Kaur Misra 2019 PDF
Transféré par
Prabhjot AwasthiTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Kaur Misra 2019 PDF
Transféré par
Prabhjot AwasthiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
A JOURNAL OF COMPOSITION THEORY ISSN : 0731-6755
A Methodical Review on Network
Traffic Monitoring & Analysis Tools
Prabhjot Kaur1, Neeti Misra2
1
Department of Computer Science
2
Department of Management Studies
Uttaranchal University
Dehradun, India
Email address: {info.prabh, neeti.cm}@gmail.com
Abstract - Network traffic monitoring is observation of defined by [6] proposed an approach called k-ary
the inflow and outflow of traffic moving in-across the sketch which is a modified version of sketch data
network. The continuous monitoring is required for structure usages a lesser amount of memory, and has
various purposes such as intrusion detection, congestion constant per-record etc. to summarize traffic at
control, traffic redirection, network management and
various levels and then forecast them using
many more. There are varieties of Network traffic
monitoring tools used for these purposes. This paper
autoregressive moving averages model etc. to
reviews the network traffic monitoring and analysis determine significant forecast errors. Some of the
tools, along with the pros and cons of each tool are examples of network traffic monitoring and analysis
highlighted. This paper can help the prospective tools are: wireshark, TCPDump, snort, bro, Xplico
researchers in selection of respective tool based on etc. These are the sniffing tools and some of them
particular network scenario. also help in intrusion prevention. There is wide
variety of upcoming network sniffing tools.
Keyword Network traffic, tools, monitoring FlowScan is a network flow analysis and
visualization tool that is used for network traffic
I. INTRODUCTION report generation as well. Iris is a network traffic
Network traffic is defined as something arisen from analysis technique that can help the investigators in
the redirection flow from Origin to Destination [1]. iterative investigation of intrusions.
Network traffic monitoring is observation of the
A typical network traffic monitoring tool
inflow and outflow of traffic moving in-across the
displays the decoded data in atleast three parts as
network. Network traffic analysis is the technique of
stated by Shimonski: Summary: This displays
extracting the features from the traffic to understand
information regarding protocol details, traffic/packet
its behaviour. Various patterns are generated while its
capture time, and the source and destination
analysis to conclude meaningful judgments. Network
addresses; Detail: This displays information
traffic is analysed to detect anomaly [2] [3].
regarding complete layer, sub-layer details; Hex: The
Anomalies are unfamiliar plus important deviations
data is stored in hexadecimal format [7]. The
in a network traffic levels straddling across several
captured packet is dissected to obtain even the
links [4]. A subspace method usually applied to the
smallest available therein [8]. This paper carefully
flow traffic is used to count the number of feature
reviews the network monitoring and analysis tools
occurrences for features such as number of packets,
widely in use these days. This paper also explicitly
byte count of multivariate time series etc. to detecting
shows the new tools which can be encapsulated with
anomalies such as network outrage, flash crowds,
existing tools to upgrade the performance. Further
worm propagation etc. This technique provided a
section in this paper reviews the existing network
threshold to determine the anomaly at the initial
monitoring tools along with the pros and cons of each
phase as defined by [1].
tool.
[5] Barford have performed traffic analysis using
signals study to detect four categories of attacks on II. NETWORK TRAFFIC MONITORING TOOLS
collected SNMP traffic using wavelet filters as
Volume XII Issue IX SEPTEMBER 2019 Page No: 1964
A JOURNAL OF COMPOSITION THEORY ISSN : 0731-6755
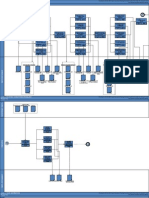
There are numerous network traffic collection and Iris, Bro are to name a few [9][10] [3]. Fig. 1 displays
monitoring tools available these days. Some of these different types of network monitoring tools discussed
include: wireshark, TcpDump, NfDump, PcapWT, further in this section.
Xplico, NetworkMinor, NetIntercept, Snort, PyFlag ,
Fig. 1. Network Traffic Monitoring Tools
Wireshark: This is the most widespread network password of the account holders whose network
traffic analyzer. It has the capability to implement traffic data is being captured [12]. It is also
real time capturing of network traffic in libpcap inefficient in handling large voluminous data.
(packet capture) format. Like many other tools it can
scrutinize, inspect and dissect packets data and TcpDump: The origin of tcpdump dates back in
perform analysis. It is compatible with multiple 1990‘s at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
platforms including Windows, Linux variants etc. This is a typical packet sniffer and analyser that work
This captures the network traffic in the form of in command line. It examines and provides output of
packets and stores them on to packet buffer for later the incoming/outgoing packets in the network. It
examination and analysis [7]. It has many filters displays the packet contents such as timestamp of the
predefined filters such as: Wireshark Capture Filter, packet, protocol used, source address and destination
Wireshark Protocol Filters etc. and alongwith one can hosts and ports etc. TCPDump uses CUI for better
create new filters as per requirement [11]. The user user-system interaction and preinstalled on Kali
can make sure that the incoming network traffic Linux [11]. It is used primarily when mode of
passes through these filters before getting stored into operation to be used is promiscuous [12][13]. One of
packet buffer. [8] Besides network traffic monitoring the application areas of tcpdump include in firewall
this tool also helps to analyse the traffic to determine construction e.g. for McAfee and Juniper deploy
the security concerns in the network. Another feature tcpdump in their toolset to easily debug or report a
of this tool is the ability to display interaction among problem [7]. TCPdump is reaches to the data faster in
OSI layers i.e. which layer of OSI model interacts comparison to wireshark tool [8].
with which other layer. It provides filters to look into
One of the limitations of Tcpdump is its
port numbers in layer 4 and IP address in layer 3 of
inefficiency to handle large packet traces. Tcpdump
OSI model. The traffic related to conversation can be
writes each captured data or packet to the terminal by
stored and searched based on keyword wherever
displaying the minimal information including the
required. The list of endpoints from a security zone
type of packet e.g. tcp, udp, icmp etc. In order to
can be determined using its end point correlation tool
increase the display of information on the output
to graphically display the end points which is easy to
terminal a special tag named verbose ‗-v‘ can be
visualize and understand [11].
used by increasing it upto three times as ‗-vvv‘. It
One of the limitations of wireshark if can even capture data from the lowest stream line.
installed in the open environment is password One of the main drawbacks of tcpdump is its inability
leakage i.e. it clearly displays the username and to translate the application layer data [8].
Volume XII Issue IX SEPTEMBER 2019 Page No: 1965
A JOURNAL OF COMPOSITION THEORY ISSN : 0731-6755
Xplico: It is a kind of sniffing tool that captures [23]. The pros of PyFlag is its ability to examine
network traffic, manipulated in forms by normalizing nested data/file structure and to recursively examine
it to be used by manipulators [14]. This tool is data at several levels.
primarily used to extract audio sessions from a
stream [15]. It is used to reconstruct the data NfDump: The origin of Nfdump dates back to late
generated from other network traffic collector tools 1990‘s. This tool helps to collect packet information
such as wireshark, tcpdump etc. [16]. It can extract such as IP address etc. as it passes through the nodes
webpages from the web data, similarly, specific data in the network. This tool provides command line
extraction i.e. images, audio from web data. Xplico is interface to the user in synonym to tcpdump [24].
by default available with Linux Kali distribution This tool displays the output on command line
which is best suited for penetration testing [17]. interface.
One of the limitations in Xplico is the access One of the limitations of NfDump is its
time to access hard disk drive in while extracting data performance issue in large data. However, a case
in real time [18]. On account of pros is its ability to study shows that its response time is better than
support multi-user environment. It can also support MySQL‘s response time [25]. The pros of this tool
cloud NFAT. are the ability to provide fast statistics of network
flow. Also this tool acts as backbone to many other
Snort: It is a network sniffing tool capable of higher end sniffing tools such as NfSen which is used
detecting intrusion in the network. It also provides to track hosts and automatic alerting [24].
network and system intrusion prevention
mechanisms. It can perform packet logging and real- PcapWT: The origin of PcapWT dates back to year
time traffic analysis. Likewise wireshark it also 2014. One of the pros of this tool is its ability to work
captures the network traffic data in libpcap format. on voluminous data. A recent case study showed that
This format can further be converted into other it is hundred times faster than tcpdump [26]. It can
formats for further analysis [19]. The snort work performs packet inspections using wavelet tree data
somewhat similar to tcpdump and differs in the fact structure on long arrays of packet data which
that the former does packet payload inspection [20]. otherwise has an extensive processing time with
traditional tools.
One of the limitations of snort is that it does
not lookup host names or port names while running One of the limitations of PcapWT is that it
as it quickly focuses on maximum packet collection does not support fine granule filtering operation. This
[20]. The pros of snort includes its capability to filter tool works even better in comparison to other tools
the packets based on specific category such as even when the traffic complexity on the network
protocol type that primarily makes use of Berkeley increases.
Packet Filter (BPF) commands [19].
NetworkMiner: The origin of NetworkMiner dates
PyFlag: The origin of PyFlag dates back in year back to year 2007. This is network forensic analysis
2007 by a team at Australian Department of Defence tool that helps in packet sniffing and incident
and then released under GPL. Along with network response in case of threat is detected [27]. It can
traffic monitoring, this provides an advance network identify ports, mapping, geo IP identification, audio
forensic framework for intrusion detection [21] extraction from VoIP calls etc.
which in contrary was designed as database driven
One of the limitations of this tool is its
analysis tool for digital forensic. Its implementation
performance degradation in active network traffic
schemes are used by various areas including
sniffing. One of the case study shows that this tool
reconstruction of webpages and mail analysis etc.
can be combined other applications to manage and
[22].
process the semantic information efficiently [14].
One of the limitations found by Farrell is in
the database schema and source file organization
Volume XII Issue IX SEPTEMBER 2019 Page No: 1966
A JOURNAL OF COMPOSITION THEORY ISSN : 0731-6755
NetIntercept: The origin of NetIntercept dates back that can act as the basis for future research scope and
to year 2007. This is network monitoring and analysis can help the prospective researcher in selection of a
tool deployed at the interface of the network [28]. It particular tool for their study area.
comes encapsulated with hardware to be ready for
deployment. This tool provides deep packet REFERENCES
inspection and analysis at decent speed. [1] A. Lakhina, K. Papagiannaki, M. Crovella, C. Diot, E. D.
Kolaczyk, and N. Taft, ―Structural Analysis of Network
One of the limitations of this tool is its high Traffic Flows,‖ in SIGMETRICS ’04/Performance ’04
cost incurred in deep packet inception and analysis Proceedings of the joint international conference on
Measurement and modeling of computer systems, 2004,
[29]. The pro of NetIntercept is its user friendly vol. 6, pp. 61–72.
interface that enables ease of access in performing
[2] A. Chahuhan, M. Chand, and P. Kaur, ―Retroactive
complex tasks. It helps in parsing IPv6 traffic along Analysis Of Denial Of Service‖ in Conference on Recent
with audio sniffing [30]. Innovations in Emerging Technology & Science, 2018,
pp. 337–340.
III. CONCLUSION [3] P. Kaur, P. Chaudhary, and A. Bijalwan, ―Network
Traffic Classification Using Multiclass Classifier,‖
This paper carefully examines the tools and Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. - Springer, vol. 905, pp. 208–
217, 2018.
techniques used for network traffic monitoring and
analysis used by network administrators, researchers [4] A. Lakhina, M. Crovella, and C. Diot, ―Diagnosing
and scientists. Each tool differs from other tools by Network-Wide Traffic Anomalies,‖ 2004.
significant feature and functionality which is [5] P. Barford, J. Kline, D. Plonka, and A. Ron, ―A Signal
included in this paper. Like, one of the best features Analysis of Network Traffic Anomalies,‖ in Proceeding
IMW ’02 Proceedings of the 2nd ACM SIGCOMM
of wireshark is ease of creation of new filters as per Workshop on Internet measurment, 2002, pp. 71–82.
user requirement while tcpdump writes commands to
do new activity. Wireshark, NetIntercept uses GUI [6] B. Krishnamurthy, S. Sen, Y. Zhang, F. Park, and Y.
Chen, ―Sketch-based Change Detection : Methods ,
whereas TCPdump, Nfdump uses CUI interface. The Evaluation , and Applications,‖ in In Internet
CUI capability enables tcpdump to quickly jump to Measurement Conference, IMC’03, 2003.
the data and debug/report the problem. Since
[7] R. Shimonski, ―About Wireshark,‖ in The Wireshark
TCPdump is used only when mode of operation to be Field Guide, 2013, pp. 1–15.
used is promiscuous while Xplico on the other hand
[8] C. Sanders and J. Smith, ―Packet Analysis 13,‖ in
supports multi-user environment but limiting the Applied Network Security Monitoring Collection,
factor of HD. The capability of packet payload Detection, and Analysis, 2014, pp. 341–384.
inspection makes snort a better choice than tcpdump,
[9] E. S. Pilli, R. C. Joshi, and R. Niyogi, ―Network
while snort does not collect information of host name forensic frameworks: Survey and research challenges,‖
and port names which is the usual activity routine for Digit. Investig., vol. 7, no. 1–2, pp. 14–27, 2010.
tcpdump. PcapWT tool is efficient in handling [10] P. Kaur, A. Bijalwan, R. C. Joshi, and A. Awasthi,
voluminous data along with better speed in analysing ―Network Forensic Process Model and Framework : An
Alternative Scenario,‖ Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput., vol.
data in comparison to tcpdump. These individual 624, pp. 493–502, 2018.
tools when combined with other tools enhance the
features and performance. Like, the integration of [11] C. Chapman, ―Using Wireshark and TCP dump to
visualize traffic,‖ in Network Performance and Security,
snort, NetIntercept or NetDetector can be helpful in 2016, pp. 195–225.
intrusion detection. One of the main drawbacks of
[12] F. Fuentes and D. C. Kar, ―ETHEREAL VS .
tcpdump tool is its inability to understand and TCPDUMP : A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON
translate the application layer data. One of problems PACKET SNIFFING TOOLS FOR EDUCATIONAL
related to these tools is false positives. The lesser the PURPOSE *,‖ J. Comput. Sci. Coll., pp. 169–176, 2005.
false positive rate the better the network traffic tool. [13] P. Arlos and M. Fiedler, ―A Comparison of
The comparison is done between the tools to Measurement Accuracy for DAG , Tcpdump and
Windump A Comparison of Measurement Accuracy for,‖
understand the edge of one tool over the other. The in COST279 TD, 2016, no. August, pp. 1–23.
drawbacks of the existing tools are also highlighted
[14] R. Hunt and S. Zeadally, ―Network Forensics : An
Volume XII Issue IX SEPTEMBER 2019 Page No: 1967
A JOURNAL OF COMPOSITION THEORY ISSN : 0731-6755
Analysis of,‖ Computer (Long. Beach. Calif)., vol. 45, [30] E. Casey, ―Network traffic as a source of evidence :
no. 12, pp. 36–43, 2012. tool strengths , weaknesses , and future needs,‖ Digit.
Investig., vol. 1, pp. 28–43, 2004.
[15] N. Grant and J. W. ShawII, ―A Brief Introduction,‖ in
Unified Communications Forensics Anatomy of Common
UC Attacks, 2014, pp. 1–14.
[16] R. McRee, ―Xplico: Internet Traffic Decoder. Network
Forensic Analysis Tool (NFAT),‖ ISSA J. |, no. June, pp.
37–40, 2011.
[17] ―Kali Linux Bug Tracker: Xplico,‖ 2013. [Online].
Available:http://bugs.kali.org/view.php?id=61.
[Accessed: 10-Jun-2019].
[18] ―Xplico,‖ 2019. [Online]. Available:
https://www.xplico.org/about. [Accessed: 10-Jun-2019].
[19] M. Roesch, ―SNORT — LIGHT WEIGHT INTRUSION
Snort – Lightweight Intrusion Detection for Networks,‖ in
Proceedings of LISA ’99: 13th Systems Administration
Conference, 1999, pp. 228–238.
[20] H. Koike and K. Ohno, ―SnortView : Visualization
System of Snort Logs,‖ in Proceedings of the 2004 ACM
workshop on Visualization and data mining for computer
security, 2004, pp. 143–147.
[21] M. I. Cohen, ―PyFlag – An advanced network forensic
framework,‖ Digit. Investig., vol. 5, pp. 112–120, 2008.
[22] A. Byrski, W. Stryjewski, and B. Czechowicz,
―Adaptation of PyFlag to Efficient Analysis of Seized
Computer Data Storage,‖ J. Digit. Forensics, Secur. Law,
vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 49–62, 2010.
[23] P. F. Farrell, ―A framework for automated digital
forensic reporting,‖ 2009.
[24] P. Haag, ―Watch your Flows with NfSen and
NFDUMP,‖ 2005.
[25] R. Hofstede, A. Sperotto, T. Fioreze, and A. Pras, ―The
Network Data Handling War : MySQL vs . NfDump,‖
Networked Serv. Appl. - Eng. Control Manag. EUNICE
2010. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci., vol. 6164, pp. 167–176,
2010.
[26] Y.-H. Kim, R. Konow, D. Dujovne, T. Turletti, W.
Dabbous, and G. Navarro, ―PcapWT : An Efficient
Packet Extraction Tool for Large Volume Network
Traces,‖ Comput. NETWORKS, 2014.
[27] ―NetworkMiner,‖ 2007. [Online]. Available:
https://www.netresec.com/?page=networkminer.
[Accessed: 11-Jun-2019].
[28] Michele Mjordan, ―NIKSUN NetIntercept,‖ NIKSUN
Inc., 2010. [Online]. Available:
https://www.securitywizardry.com/index.php/products/fo
rensic-solutions/network-forensic-tools/niksun-
netintercept.
[29] P. Venezia, ―NetIntercept 2.0,‖ 2003. [Online].
Available:
https://www.infoworld.com/article/2679039/netintercept-
2-0-delivers-deep-data-scrutiny-for-less.html. [Accessed:
14-Jun-2019].
Volume XII Issue IX SEPTEMBER 2019 Page No: 1968
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Ziad Masri - Reality Unveiled The Hidden KeyDocument172 pagesZiad Masri - Reality Unveiled The Hidden KeyAivlys93% (15)
- Chapter 4 Solutions To Exercises PDFDocument70 pagesChapter 4 Solutions To Exercises PDFWilly Rodríguez GuerreroPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Types of Emergency Shutdown and Emergency Isolation ValvesDocument4 pages3 Types of Emergency Shutdown and Emergency Isolation ValvesMateusz KonopnickiPas encore d'évaluation
- STS Cat-1Document490 pagesSTS Cat-1Sri AdityaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 01 Properties of SolutionDocument70 pagesChapter 01 Properties of SolutionYo Liang SikPas encore d'évaluation
- DBM PC SpecificationDocument11 pagesDBM PC SpecificationkesharinareshPas encore d'évaluation
- FM Testbank Ch08Document6 pagesFM Testbank Ch08David LarryPas encore d'évaluation
- Je Tire 006084Document7 pagesJe Tire 006084AmerPas encore d'évaluation
- Spring State Machine TransitionsDocument6 pagesSpring State Machine TransitionsGroza CristiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pfaff Hobbymatic 917 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualDocument88 pagesPfaff Hobbymatic 917 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualiliiexpugnansPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Lab Report-20bci7108Document22 pagesFinal Lab Report-20bci7108rupa sreePas encore d'évaluation
- (Pakget - PK) Maths MCQS Book (Pakget - PK)Document42 pages(Pakget - PK) Maths MCQS Book (Pakget - PK)Mohammad AshfaqPas encore d'évaluation
- Viking Bladder Tanks - enDocument11 pagesViking Bladder Tanks - enVINOD PAULPas encore d'évaluation
- Bearing FitsDocument9 pagesBearing Fitsm2110Pas encore d'évaluation
- FITEL Fusion Splicer Catalog PDFDocument25 pagesFITEL Fusion Splicer Catalog PDFAbdelilah CharboubPas encore d'évaluation
- VPLS Practice GuideDocument7 pagesVPLS Practice Guidedelgado08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Stoichiometry 1Document54 pagesSolution Stoichiometry 1Johncy MoradaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rational Algebraic Expressions: ObjectivesDocument11 pagesRational Algebraic Expressions: ObjectivesSonny ArgolidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineeringinterviewquestions Com RCC Structures Design Multiple Choice QuestionDocument87 pagesEngineeringinterviewquestions Com RCC Structures Design Multiple Choice QuestionRajeev BansalPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Interpolation Equation Formula Calculator PDFDocument3 pagesLinear Interpolation Equation Formula Calculator PDFMatthew HalePas encore d'évaluation
- ESM Upgrade To 72 PDFDocument46 pagesESM Upgrade To 72 PDFsantoshs2002848Pas encore d'évaluation
- LG Rp29fa40Document15 pagesLG Rp29fa40palomoqro100% (1)
- Ladblock PDFDocument542 pagesLadblock PDFrogernarvaezPas encore d'évaluation
- Alternator E1S13S A/4: Three-Phase Synchronous Alternator With Brushes and Compound - 4 PolesDocument7 pagesAlternator E1S13S A/4: Three-Phase Synchronous Alternator With Brushes and Compound - 4 PolesmasanmartinfPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecs448 Chapter 5a ArchDocument28 pagesEcs448 Chapter 5a Archdixn__Pas encore d'évaluation
- 04d Process Map Templates-V2.0 (PowerPiont)Document17 pages04d Process Map Templates-V2.0 (PowerPiont)Alfredo FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- About Ramfs Rootfs InitramfsDocument7 pagesAbout Ramfs Rootfs InitramfsNavaneethPas encore d'évaluation
- An Analysis of Stravinsky's Symphony of Psalms Focusing On Tonality and HarmonyDocument68 pagesAn Analysis of Stravinsky's Symphony of Psalms Focusing On Tonality and Harmonyr-c-a-d100% (2)
- SANS5847 - Flakiness Index of Course AggregatesDocument7 pagesSANS5847 - Flakiness Index of Course AggregatesAndrew MwindililaPas encore d'évaluation