Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Physics Note
Transféré par
Ben Man Jun0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
46 vues12 pagesPhysical quantities that cannot be defined quantities derived by combining base quantities hat has only magnitud hat has both magnitude and direction hat can be corrected, if the errors are known. Absolute errors refer to the smallest reading that can be measured by an instrument hapter.
Description originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
XLSX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentPhysical quantities that cannot be defined quantities derived by combining base quantities hat has only magnitud hat has both magnitude and direction hat can be corrected, if the errors are known. Absolute errors refer to the smallest reading that can be measured by an instrument hapter.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme XLSX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
46 vues12 pagesPhysics Note
Transféré par
Ben Man JunPhysical quantities that cannot be defined quantities derived by combining base quantities hat has only magnitud hat has both magnitude and direction hat can be corrected, if the errors are known. Absolute errors refer to the smallest reading that can be measured by an instrument hapter.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme XLSX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 12
PHYSICS Chapter 1
Words Definition
Physical Quantities A quantity that is measureable
Base Quantities Physical quantities that cannot be defined
quantities
Derived Quantities Physical quantities derived by combining b
Scalar Quantities Physical quantities that has only magnitud
Vector Quantities Physical quantities that has both magnitu
Consistency (Precision) The degree of uniformity of the measure
Accuracy The degree of how close a measurement i
Sensitivity The ability to detect small changes in me
Deviation The difference between the measured va
the average value
Systematic Error Cumulative errors that can be corrected,
Random Error Arises from unpredictable variation that
error every time the experiment is repea
Zero Error Arises when a not-in-used measuring inst
from zero
Parallax Error An error which the observer's eyes are n
to the scale
Absolute Error Refer to the smallest reading that can be
instrument
hapter 1
Definition
easureable
hat cannot be defined in term of other physical
erived by combining base quantities
hat has only magnitude
hat has both magnitude and direction
rmity of the measurements
close a measurement is from the actual value
t small changes in measuring physical quantities
ween the measured value and its mean value or
hat can be corrected, if the errors are known
ctable variation that may produce a different
e experiment is repeated
-used measuring instrument does not start
observer's eyes are not in a line perpendicular
t reading that can be measured by an
PHYSICS Chapter 2
Words Statement & Defi
Linear Motion Motion in a straight line
Kinematics The study of the motion of an object with
acting on it
Dynamics The study of the motion of an object and
Distance The total length of the path travelled
Displacement The distance travelled in a specific direc
Speed The rate of change in distance
Velocity The rate of change in displacement
Acceleration The rate of change in velocity
Deceleration The rate of decrease in speed in a specif
Uniform Speed Speed that remains the same in magnitud
direction
Uniform Velocity Velocity that remains the same in magnitu
Non-uniform Velocity (a)the direction of motion changes or the
(b)the magnitude of its velocity changes
Zero Acceleration An object moving at a constant velocity, t
direction of its velocity remain unchanged
Constant Acceleration Velocity increases at a uniform rate
Inertia The tendency of an object to resist chan
Momentum The product of its mass and velocity
Principle of conservation of The total momentum of a system is const
momentum ( PCM ) acts on the system
Collision The total momentum of the objects befo
(Based on PCM) after the collision
Explosion The sum of the momentum remains at zer
(Based on PCM)
Elastic Collision (a)Two objects collide and move apart aft
(b)Momentum is conserved
(c)Total energy is conserved
(d)Kinetic energy is conserved
Inelastic Collision (a)Two objects combine and stop, or move
after a collision
(b)Momentum is conserved
(c)Total energy is conserved
(d)Kinetic energy is not conserved
(e)The total kinetic energy after the coll
kinetic energy before the collision
Concepts of momentum (a)Momentum to the left = Momentum to
(b)Momentum upwards = Momentum down
(c)Momentum forwards = Momentum back
Force The resistant of change to its state of m
Balanced Force When the force acting on an object are b
other out
Unbalanced Force / Resultant When the force acting on an object are n
Force a net force acting on it
Impulse Change in momentum
Impulsive Force (a)The rate of change of momentum
(b)Longer period of time → Impulsive for
(c)Shorter period of time → Impulsive fo
Gravitational Force The pull of gravity or the earth's gravita
Free Fall The falling of an object with only force o
Acceleration due to gravity Objects dropped under the influence of t
( 10 m/s ) constant acceleration
Gravitational Field The region around the earth in which an o
towards the centre of the earth
Gravitational Field Strength The gravitational force which acts on a m
( 10 N/kg )
Weight The gravitational force acting on the obje
Mass The amount of matter in the object
Force in Equilibrium (a)When an object is in equilibrium, the r
is zero
(b)The object will either be
→ at rest
→ moving with constant velocity
hapter 2
Statement & Definition
tion of an object without considering the force
tion of an object and the force acting on it
the path travelled
ed in a specific direction
n distance
n displacement
n velocity
e in speed in a specified direction
the same in magnitude regardless of its
s the same in magnitude and direction
motion changes or the motion is not linear
its velocity changes
a constant velocity, that is, the magnitude and
city remain unchanged
t a uniform rate
object to resist change to its state of motion
mass and velocity
m of a system is constant, if no external force
m of the objects before a collision equals that
entum remains at zero after an explosion
de and move apart after a collision
onserved
conserved
bine and stop, or move together with a common
onserved
not conserved
energy after the collision is less than the total
fore the collision
left = Momentum to the right
ds = Momentum downwards
rds = Momentum backwards
ange to its state of motion or move in the object
ng on an object are balanced, they cancel each
ng on an object are not balanced, there must be
ge of momentum
time → Impulsive force decreases
f time → Impulsive force increases
r the earth's gravitational force
ect with only force of gravity
der the influence of the pull of gravity with
he earth in which an object experiences a force
of the earth
rce which acts on a mass of 1 kilogram
rce acting on the object
er in the object
s in equilibrium, the resultant force acting on it
ther be
ant velocity
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Staelin, David H - Electromagnetics and Applications-Massachusetts Institute of Technology (2011)Document443 pagesStaelin, David H - Electromagnetics and Applications-Massachusetts Institute of Technology (2011)Marlon Recarte100% (2)
- Portfolio 2: Semester 1, 2015/2016Document10 pagesPortfolio 2: Semester 1, 2015/2016Ben Man JunPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyroid CarcinomaDocument13 pagesThyroid CarcinomaBen Man JunPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet - Week 6: InstructionDocument3 pagesWorksheet - Week 6: InstructionBen Man JunPas encore d'évaluation
- UPM-CALC/SEM1/2015-16/CEL2106 MEDIC/PORTFOLIO 2 Scholarship ApplicationDocument10 pagesUPM-CALC/SEM1/2015-16/CEL2106 MEDIC/PORTFOLIO 2 Scholarship ApplicationBen Man JunPas encore d'évaluation
- Abdominal X-ray Findings & Interpretation GuideDocument37 pagesAbdominal X-ray Findings & Interpretation GuideBen Man JunPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine EmergenciesDocument22 pagesEndocrine EmergenciesBen Man JunPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Pain AnestDocument45 pagesComplete Pain AnestBen Man JunPas encore d'évaluation
- Some Extra NotesDocument13 pagesSome Extra NotesBen Man JunPas encore d'évaluation
- Instability of The ShoulderDocument20 pagesInstability of The ShoulderBen Man Jun100% (1)
- Question 2 - PsoriasisDocument6 pagesQuestion 2 - PsoriasisBen Man JunPas encore d'évaluation
- COX-2 Inhibitors: Examples Parecoxib (Dynastat) Celecoxib (Celebrex) Etoricoxib (Arcoxia)Document31 pagesCOX-2 Inhibitors: Examples Parecoxib (Dynastat) Celecoxib (Celebrex) Etoricoxib (Arcoxia)Ben Man JunPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychiatric Case Write Up on Brief Psychotic DisorderDocument10 pagesPsychiatric Case Write Up on Brief Psychotic DisorderBen Man JunPas encore d'évaluation
- Advance Trauma Life Support (ATLS)Document47 pagesAdvance Trauma Life Support (ATLS)Ben Man Jun100% (2)
- Metabolic Abnormalities On ECGDocument15 pagesMetabolic Abnormalities On ECGBen Man JunPas encore d'évaluation
- Metabolic Abnormalities On ECGDocument15 pagesMetabolic Abnormalities On ECGBen Man JunPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow HandkerchiefDocument7 pagesThe Yellow HandkerchiefBen Man JunPas encore d'évaluation
- CopdDocument11 pagesCopdBen Man Jun50% (2)
- FeverDocument15 pagesFeverBen Man JunPas encore d'évaluation
- Resume Faizal B Marta at Mustafha For NDT and Welding InspectionDocument5 pagesResume Faizal B Marta at Mustafha For NDT and Welding InspectionBen Man JunPas encore d'évaluation
- COPD - PDFDocument10 pagesCOPD - PDFBen Man JunPas encore d'évaluation
- Sos Mdcat Test Session - 2020Document9 pagesSos Mdcat Test Session - 2020MobiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2016 Aakash Anthe Junior Sample Paper Class10Document16 pages2016 Aakash Anthe Junior Sample Paper Class10ats edu100% (1)
- Haven, Quantum Social ScienceDocument306 pagesHaven, Quantum Social ScienceMichael H. HejaziPas encore d'évaluation
- 6PH04 01 Que 20120307 PDFDocument24 pages6PH04 01 Que 20120307 PDFannikaPas encore d'évaluation
- FMDC Past Papers PDFDocument21 pagesFMDC Past Papers PDFduniya t v100% (1)
- Cie Igcse Physics Chapter 1 2023 OnwDocument24 pagesCie Igcse Physics Chapter 1 2023 OnwZeinab ElkholyPas encore d'évaluation
- Law of Conservation of Linear MomentumDocument2 pagesLaw of Conservation of Linear MomentumAnurag MalikPas encore d'évaluation
- ME2213 Boundary Layer Theory SolutionsDocument36 pagesME2213 Boundary Layer Theory SolutionsAhmed Zawad ShovonPas encore d'évaluation
- Continuum MechanicsDocument10 pagesContinuum Mechanicschristophe100% (1)
- Kinematicsof Particles - Rectilinear Motion: KinematicsDocument98 pagesKinematicsof Particles - Rectilinear Motion: KinematicsVinoth RajaguruPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade: 11 Semester: First Semester: Culminating Performance StandardDocument4 pagesGrade: 11 Semester: First Semester: Culminating Performance Standardnorielle oberioPas encore d'évaluation
- Wind Turbine Blade Analysis Using The Blade Element Momentum MethodDocument21 pagesWind Turbine Blade Analysis Using The Blade Element Momentum MethodcsmistryPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 9 12Document179 pagesPhysics 9 12Qulb e AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- (1 Mark) : MarkschemeDocument29 pages(1 Mark) : MarkschemeAbdulaziz HalabiPas encore d'évaluation
- JR - Inter Physics Model Paper 2Document2 pagesJR - Inter Physics Model Paper 2angadibalajithkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Qualifier Study Guide: Office 221 Department of Physics, Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL 32308Document17 pagesQualifier Study Guide: Office 221 Department of Physics, Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL 32308Hussein AlghoulPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus Lecture NotesDocument122 pagesCalculus Lecture Notesdaniel_bashir808Pas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 4Document28 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 4qalanis100% (3)
- Science9 Q4 M4Document16 pagesScience9 Q4 M4Chergaets AndresPas encore d'évaluation
- Aerodynamic Theory: A General Review of ProgressDocument417 pagesAerodynamic Theory: A General Review of ProgressEvagelos MamiosPas encore d'évaluation
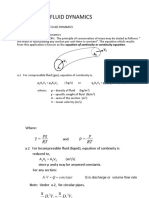
- Part I Fundamentals of Fluid DynamicsDocument42 pagesPart I Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamicsmike100% (1)
- IndiGo PhysicsDocument9 pagesIndiGo PhysicsAryaman ParmarPas encore d'évaluation
- 大连学校物理动量知识Document33 pages大连学校物理动量知识leoPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 10 For DemoDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 10 For DemoSylvs Enong100% (2)
- Ch4 Kinetics of Systems of ParticlesDocument9 pagesCh4 Kinetics of Systems of ParticlesGian MorenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 2D Relativity and Quantum Mechanics Homework SolutionsDocument6 pagesPhysics 2D Relativity and Quantum Mechanics Homework SolutionsMuzamil ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Physics - 20.7Document35 pagesApplied Physics - 20.7AJESH MPas encore d'évaluation
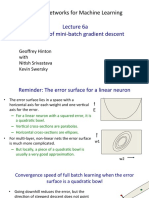
- Neural Networks For Machine Learning: Lecture 6a Overview of Mini - Batch Gradient DescentDocument31 pagesNeural Networks For Machine Learning: Lecture 6a Overview of Mini - Batch Gradient DescentMario PeñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Olympiad 2010 PDFDocument2 pagesPhysics Olympiad 2010 PDFSayeed Mohammed100% (2)