Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
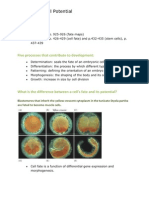
Cell Determination (EoG)
Transféré par
danialnero100%(1)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (1 vote)
23 vues1 pageIn an embryo a cell has the potential to generate many different cell types. During development cells generally lose this potential (or potency') this process by which cells become progressively restricted in their potency is referred to as determination. Determination is a multistep process, in which a cell is specified to a particular developmental pathway, and a more extended process of commitment.
Description originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentIn an embryo a cell has the potential to generate many different cell types. During development cells generally lose this potential (or potency') this process by which cells become progressively restricted in their potency is referred to as determination. Determination is a multistep process, in which a cell is specified to a particular developmental pathway, and a more extended process of commitment.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
100%(1)100% ont trouvé ce document utile (1 vote)
23 vues1 pageCell Determination (EoG)
Transféré par
danialneroIn an embryo a cell has the potential to generate many different cell types. During development cells generally lose this potential (or potency') this process by which cells become progressively restricted in their potency is referred to as determination. Determination is a multistep process, in which a cell is specified to a particular developmental pathway, and a more extended process of commitment.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
1 C e l l D e t er mi n at i on
Cell Determination established that cell fate specification in embryos can
involve both cell-autonomous mechanisms and induct-
A Chisholm ive signals from a cell's surroundings. Combinations
Copyright ß 2001 Academic Press of these influences result in progressive alterations in
doi: 10.1006/rwgn.2001.0170 the gene expression patterns of embryonic cells. The
later process of commitment is less well understood ±
Chisholm, A for example, why the determined state is stable and
Department of Biology, University of California, heritable, and why it is unstable in some situations.
Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA 95064, USA Cells can become undetermined in special circum-
stances. In amphibian limb regeneration, cells lose
their differentiated characteristics and form a `regen-
In an early embryo a cell has the potential to generate eration blastema,' which can generate all the tissues
many different cell types. During development cells of a mature limb. Certain cultured cell lines behave as
generally lose this potential (or `potency'), and be- if undetermined, such as the embryonic stem cells
come restricted to making one or a few cell types. (ES cells) used in generating transgenic mice. Germ-
This process by which cells become progressively line cells are also exceptional in that they retain the
restricted in their potency is referred to as determina- potency to generate an entire organism when they
tion. combine to form a zygote.
Determination of a cell or tissue is an operational The distinction between cell fate specification and
concept, and is analyzed by experiments in which the determination is exemplified by Drosophila genes
cell or tissue is isolated or placed in an abnormal known as selector genes. Genetic analysis in Dros-
environment. If the cell's fate does not change as a ophila identified homeotic mutants, in which the fates
result of the experiment, then the cell can be said to of certain body regions were altered. These homeotic
be determined with respect to that manipulation. mutants defined the homeobox-containing selector
However, it is possible that other experiments could genes, which function to specify region-specific cell
cause alterations in the cell's fate. Thus, a cell cannot fates. For example, cell fates in the third thoracic (T3)
be said to be absolutely `determined' but only deter- segment of Drosophila are specified by the homeobox
mined relative to experimental tests. Evidence that a gene Ultrabithorax (Ubx).
cell is not determined can also come from cell marking The specification of cells to the T3 identity occurs
(clonal analysis) experiments: if a marked cell gives during embryogenesis and involves the localized activ-
rise to multiple cell types in its progeny, then the ation of Ubx by transcription factors that are tran-
marked precursor can not have been determined to siently expressed in the embryo. Ubx expression is
make any one cell type. activated in the future T3 segment and then persists
From analyses of cell fate determination in many in these cells throughout development. If Ubx func-
organisms, the following general rules have emerged. tion is removed from cells later in development, they
First, determination is a gradual process, in which a lose their T3 identity and become transformed in fate,
cell's potency is progressively restricted during devel- indicating that Ubx activity is required continuously to
opment. Second, the `determined state' is heritable maintain the cells in their determined state. The stable
through somatic cell divisions, an example of `cellular activation of Ubx in T3 cells and its stable repression in
memory.' Third, determination is usually but not other cells involves chromatin-associated proteins
always irreversible; in some situations a cell can revert required for the maintenance of active and inactive
to an apparently undetermined state, or can `trans- states of gene expression. Thus, the stability of the
determine' to a different stable state. determined state may in part reflect stable patterns of
Although determination is a multistep process, two chromatin. In vertebrates, DNA methylation could
basic phases can be distinguished: an initial phase in provide an additional heritable mechanism for stable
which a cell is specified to a particular developmental patterns of gene expression.
pathway (`cell fate specification'), and a more extend-
ed process of commitment, in which the specification See also: 0421
is fixed and made largely irreversible. It is now well
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Potency, Commitment, GenomicDocument19 pagesPotency, Commitment, Genomicjohn cenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Determination and DifferentiationDocument19 pagesCell Determination and DifferentiationDrAbhilasha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Cytoplasm in Cell DifferentiationDocument7 pagesRole of Cytoplasm in Cell DifferentiationJ LALPas encore d'évaluation
- 06-Determination and DifferentiationDocument20 pages06-Determination and DifferentiationMu LokPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Fate Commitment and Determination Through Gene Regulation and SignalingDocument41 pagesCell Fate Commitment and Determination Through Gene Regulation and SignalingShampa SenPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 19 LodishDocument52 pagesChapter 19 LodishablucPas encore d'évaluation
- ISSCR WriteupDocument3 pagesISSCR Writeupachuthasaran@11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Lineage Mapping TechniquesDocument7 pagesCell Lineage Mapping TechniquesAmar Kant JhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Inv 13Document9 pagesInv 13mrojasf.1996Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Cell Cycle and Cell Division: Understanding How Cells Replicate Through Mitosis and MeiosisDocument17 pagesThe Cell Cycle and Cell Division: Understanding How Cells Replicate Through Mitosis and MeiosisMaricris GatdulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Development Q&ADocument6 pagesDevelopment Q&AKathleen AraújoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Interactions Guide FateDocument25 pagesCell Interactions Guide Fatekaladhar reddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Vishwakarma Et Al. - 2017 - The Need To Study, Mimic, and Target Stem Cell NicDocument11 pagesVishwakarma Et Al. - 2017 - The Need To Study, Mimic, and Target Stem Cell NicAnonymous 2JIHmobJlsPas encore d'évaluation
- Cancer Stem CellsDocument7 pagesCancer Stem Cellskadir2613Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reprogramming of Genome Function Through Epigenetic InheritanceDocument7 pagesReprogramming of Genome Function Through Epigenetic InheritanceElianePas encore d'évaluation
- Teacher: DR Gouri Course: Zoology Hons. 6 Sem Paper: Developmental BiologyDocument17 pagesTeacher: DR Gouri Course: Zoology Hons. 6 Sem Paper: Developmental BiologyApratim SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell我们毕业啦 - Cell Differentiation and Key FactorsDocument46 pagesCell我们毕业啦 - Cell Differentiation and Key Factorsthri zonartiPas encore d'évaluation
- Differential Gene Expression and DevelopmentDocument9 pagesDifferential Gene Expression and DevelopmentShaher Bano Mirza100% (1)
- Growth and Differentiation in HematopoiesisDocument9 pagesGrowth and Differentiation in HematopoiesisslxuPas encore d'évaluation
- (Visvader Et Al., 2016) Tissue-Specific Designs of Stem Cell HierarchiesDocument7 pages(Visvader Et Al., 2016) Tissue-Specific Designs of Stem Cell HierarchiesJulio dR AltavasPas encore d'évaluation
- Baghdad College of Medical Science (Human Biology)Document9 pagesBaghdad College of Medical Science (Human Biology)علي صلاح مهديPas encore d'évaluation
- Developmental BiologyDocument77 pagesDevelopmental Biologyshishir757678Pas encore d'évaluation
- All Sexual Organisms Begin As A Single CellDocument12 pagesAll Sexual Organisms Begin As A Single CellAFRIADMA AULIA PERDANAPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloning Human BeingsDocument312 pagesCloning Human BeingswalterkondorPas encore d'évaluation
- Trager 1963Document6 pagesTrager 1963IñigoGaitanSalvatellaPas encore d'évaluation
- CSIR Unit 5@lifescience - BiotechDocument78 pagesCSIR Unit 5@lifescience - BiotechJigyasu bPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell FateDocument3 pagesCell FateNeha ThakranPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 01, Week 2Document11 pagesAssignment 01, Week 2padhiyararpitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Processes hand out '21Document3 pagesCell Processes hand out '21Amazing GreenPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Differentiation and Tissue MaintenanceDocument8 pagesCell Differentiation and Tissue MaintenanceAly R.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of Developmental BiologyDocument16 pagesBasics of Developmental BiologyhenviPas encore d'évaluation
- GB1 - W4 Module 2 1st QTR 1Document145 pagesGB1 - W4 Module 2 1st QTR 1AyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Fate and Cell PotentialDocument12 pagesCell Fate and Cell PotentialSavannah Simone PetrachenkoPas encore d'évaluation
- 0 BooksDocument20 pages0 Bookslaraib zahidPas encore d'évaluation
- State Phase Abbrevia Tion DescriptionDocument5 pagesState Phase Abbrevia Tion DescriptionMae Matias100% (1)
- Csir - Ugc (Net) : Life SciencesDocument24 pagesCsir - Ugc (Net) : Life SciencesVarshini KPas encore d'évaluation
- Aging and CorneaDocument4 pagesAging and CorneaRani AprianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics (Introduction)Document10 pagesGenetics (Introduction)Mielah RuthPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 6 Cell Cycle HAND OUTDocument10 pagesLesson 6 Cell Cycle HAND OUTAyera DicaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Autonomous Cell Specification by Cytoplasmic DeterminantsDocument9 pagesAutonomous Cell Specification by Cytoplasmic DeterminantsMoaz Fiaz80% (5)
- Cell Reproduction: How Does It Happen?Document63 pagesCell Reproduction: How Does It Happen?Gabriel NonanPas encore d'évaluation
- Vertebrate Embryonic Cleavage Pattern DeterminationDocument55 pagesVertebrate Embryonic Cleavage Pattern DeterminationtrivikramraoPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Development: Key ConcepDocument20 pagesAnimal Development: Key ConcepKelas A, Antika, 9040Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Cycle (Scitable)Document2 pagesCell Cycle (Scitable)LibrofiloPas encore d'évaluation
- Insights New111Document13 pagesInsights New111cassidy conchaPas encore d'évaluation
- Developmental Specification & DifferentiationDocument14 pagesDevelopmental Specification & DifferentiationDrAbhilasha SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- proliferation,Document10 pagesproliferation,micklemagdy50Pas encore d'évaluation
- CellsDocument5 pagesCellsoiu7hjjs100% (5)
- Pembelahan Embrio (Cleavage) S2 2017Document47 pagesPembelahan Embrio (Cleavage) S2 2017Desy NataliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Maintenance of Epigenetic Memory in Cloned Embryos: Ray K. NG J. B. GurdonDocument4 pagesMaintenance of Epigenetic Memory in Cloned Embryos: Ray K. NG J. B. GurdonShivam VinothPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Cycle: The Stages of Growth and DivisionDocument20 pagesCell Cycle: The Stages of Growth and DivisionUzma AdnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cellular InteractionsDocument15 pagesCellular InteractionsEva A ArzatePas encore d'évaluation
- Ryan E. DaveyDocument7 pagesRyan E. DaveyNeeraj KannaugiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Entwickslungmechanik: Developmental MechanismsDocument29 pagesEntwickslungmechanik: Developmental MechanismsAbhisekh ChhatarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Cycle Stages and Phases ExplainedDocument43 pagesCell Cycle Stages and Phases ExplainedMariam QaisPas encore d'évaluation
- ! Cellular and Epigenetic Drivers of Stem Cell Ageing 2018 Review PDFDocument17 pages! Cellular and Epigenetic Drivers of Stem Cell Ageing 2018 Review PDF畏Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cancer and cell cycle controlDocument12 pagesCancer and cell cycle controljayweinxPas encore d'évaluation
- Asymmetrical Cell: Submitted byDocument5 pagesAsymmetrical Cell: Submitted byJeffrey VictoryPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.1 Replication and Division of Nuclei and Cells-MinDocument3 pages5.1 Replication and Division of Nuclei and Cells-MinShean LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsD'EverandHuman Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Integration of MetabolismDocument10 pagesIntegration of MetabolismAditya NayakPas encore d'évaluation
- (Carte) Handbook of Meat ProcessingDocument604 pages(Carte) Handbook of Meat ProcessingddddddpPas encore d'évaluation
- BSCI 4001 Lesson 3: Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument40 pagesBSCI 4001 Lesson 3: Cell Structures and Their FunctionsGisselle100% (1)
- Bhatia LMRP PDFDocument200 pagesBhatia LMRP PDFshalialoo22100% (7)
- Car-T Cell 2 (7757)Document8 pagesCar-T Cell 2 (7757)Saradha PellatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Document 35Document17 pagesDocument 35Oyasor Ikhapo AnthonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical 3Document6 pagesPractical 3Wei YiPas encore d'évaluation
- BCR-ABL Cancer Protein Structure FunctionDocument3 pagesBCR-ABL Cancer Protein Structure FunctionEdric GabotPas encore d'évaluation
- Ono Et Al 2021 Frontiers in NeuroscienceDocument8 pagesOno Et Al 2021 Frontiers in NeuroscienceDaisuke OnoPas encore d'évaluation
- ErytropoiesisDocument23 pagesErytropoiesiswarda farooqPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction of Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument27 pagesIntroduction of Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDebora Intan D. LarashatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Antibiotics For Cancer Treatment: A Double-Edged SwordDocument15 pagesAntibiotics For Cancer Treatment: A Double-Edged SwordRushikesh G ParitPas encore d'évaluation
- Iron Man Poster - Science Behind The ExtremisDocument1 pageIron Man Poster - Science Behind The ExtremisNadya AmaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cells Introduction SHODocument5 pagesCells Introduction SHOshamshadPas encore d'évaluation
- General Types of Hormone Receptors:: Receptors Function and Signal TransductionDocument12 pagesGeneral Types of Hormone Receptors:: Receptors Function and Signal Transductionmamoun mufarraqPas encore d'évaluation
- CellDocument39 pagesCellMicah Hanna Mae CazenasPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunity To Microbes: Prof. Dr. Dr. Djoni Djunaedi, SPPD, KptiDocument24 pagesImmunity To Microbes: Prof. Dr. Dr. Djoni Djunaedi, SPPD, KptiArdea SafiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Metabolisme Sel Prof TriDocument29 pagesMetabolisme Sel Prof Trimanusia bergerakPas encore d'évaluation
- Chloroplast and Mitochondria OrganellesDocument9 pagesChloroplast and Mitochondria OrganellesBicolanoJan25% (4)
- Eukaryotes and MicroorganismsDocument10 pagesEukaryotes and MicroorganismsRIA MAEVE NGOPas encore d'évaluation
- ISBBhandoutDocument55 pagesISBBhandoutRed GillianPas encore d'évaluation
- Plasma Proteins and Immunoglobulins GuideDocument41 pagesPlasma Proteins and Immunoglobulins GuideTwinkle SalongaPas encore d'évaluation
- Struktur Dan Fungsi KromosomDocument32 pagesStruktur Dan Fungsi KromosomAniss MaharaniPas encore d'évaluation
- PATag RFPDocument23 pagesPATag RFPKapil BambardekarPas encore d'évaluation
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 4 Module 7 Mitosis and Meiosis 2Document21 pagesSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 4 Module 7 Mitosis and Meiosis 2James Aringo100% (1)
- Stem Cells in Regenerative MedicineDocument28 pagesStem Cells in Regenerative MedicineSumanta Kar100% (1)
- CHEM464 Metabolism: Basic ConceptsDocument9 pagesCHEM464 Metabolism: Basic ConceptsMohammad AadilPas encore d'évaluation
- Fcell 10 878350Document21 pagesFcell 10 878350Rofiqi RofiqPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Injury and Cell DeathDocument35 pagesCell Injury and Cell DeathMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S0169409X21002830 MainDocument31 pages1 s2.0 S0169409X21002830 MainRocio Angie Navarro SeguraPas encore d'évaluation