Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
SIM Combination Circuits
Transféré par
Irwansyah RamadhaniCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SIM Combination Circuits
Transféré par
Irwansyah RamadhaniDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Physics 12 Computer Simulation: Combination Circuits
Names: ____________________________, _________________________________
Computer Simulation: Combination Circuits
Open the PHET simulation Circuit Construction Kit. In
this experiment you will be using a simulation to explore
the relationships between current, voltage, and power in
series and parallel circuits: KIRCHOFF’S LAWS
Objectives:
• to verify Kirchoff’s Voltage Law and Current Law
• to determine the effects on total resistance and power by adding or removing resistors in series
• to determine the effects on total resistance and power by adding or removing resistors in parallel
Description
Open the Circuit Construction Kit software from the computer, or download it from the Phet website.
Select the Load option, and open the files named Series Circuit, Parallel Circuit, or Combination Circuit;
they should resemble the diagrams shown below. Voltmeters and ammeters can be added to take
measurements on each circuit element.
Series Circuits Parallel Circuits Combination Circuits
Switches can be used to Switches can be used to bypass a light Switches can be used to bypass a
bypass a light bulb, or bulb, or include it in the parallel section light bulb, or include it in either the
include it in the series parallel or series section
section
revision 1.7 Page #1 © Farenholtz
Physics 12 Computer Simulation: Combination Circuits
Data Collection and Analysis: Effect of Resistors in Series (simulation file: Series Circuits.cck)
1. Use the switches to have all three bulbs active in series. Draw the circuit diagram below including
the resistance of each bulb.
2. Record the voltage and current through each item, then calculate the power loss in each bulb.
Voltage (battery):_______ Current (battery):_______
• Bulb #1: Voltage :_______ Current:_______ Power: _________
• Bulb #2: Voltage :_______ Current:_______ Power: _________
• Bulb #3: Voltage :_______ Current:_______ Power: _________
Total Power loss in all bulbs: _______________
Check: total power using values for the battery. (P = IV)
3. Remove one of the bulbs from your series circuit (use the switches!). Record the voltage and current
through the battery, and calculate the power loss in all the active bulbs.
Voltage (battery):_______ Current (battery):_______
• Bulb #1: Voltage :_______ Current:_______ Power: _________
• Bulb #2: Voltage :_______ Current:_______ Power: _________
Total Power in all bulbs: _______________
Check: total power using values for the battery (P = IV)
revision 1.7 Page #2 © Farenholtz
Physics 12 Computer Simulation: Combination Circuits
Experiment with the simulation using the switches to bypass individual bulbs.
A. What is the effect of adding another resistor in series on the total resistance of the circuit?
________________________________________________________________________________
supporting calculation:
B. What is the effect of adding another resistor in series on the total power loss in the circuit?
________________________________________________________________________________
supporting calculation:
C. What is the effect of adding another resistor in series on the current in one of the other resistors?
________________________________________________________________________________
supporting calculation:
D. What is the effect of adding another resistor in series on the voltage in one of the other resistors?
________________________________________________________________________________
supporting calculation:
revision 1.7 Page #3 © Farenholtz
Physics 12 Computer Simulation: Combination Circuits
Data Collection and Analysis: Effect of Resistors in Parallel (simulation file: Parallel Circuits.cck)
Use the switches to have all three bulbs active in parallel; the forth bulb in series will always be on.
Draw the circuit diagram below including the resistance of each bulb.
1. Record the voltage and current through each item, then calculate the power loss in each bulb.
Voltage (battery):_______ Current (battery):_______
• Bulb #1: Voltage :_______ Current:_______ Power: _________
• Bulb #2: Voltage :_______ Current:_______ Power: _________
• Bulb #3: Voltage :_______ Current:_______ Power: _________
• Bulb #4: Voltage :_______ Current:_______ Power: _________
Total Power loss in all bulbs: _______________
Check: Total power using values for the battery, minus the power loss in the one bulb in series. (P = IV)
2. Remove one of the bulbs from your parallel circuit (use the switches!) Record the voltage and current
through each active bulb, then calculate the power loss in all the active bulbs.
Voltage (battery):_______ Current (battery):_______
• Bulb #1: Voltage :_______ Current:_______ Power: _________
• Bulb #2: Voltage :_______ Current:_______ Power: _________
Total Power loss in all bulbs: _______________
Check: total power using values for the battery (P = IV)
revision 1.7 Page #4 © Farenholtz
Physics 12 Computer Simulation: Combination Circuits
Experiment with the simulation using the switches to bypass individual bulbs.
A. What is the effect of adding another resistor in parallel on the total resistance of the circuit?
________________________________________________________________________________
supporting calculation:
B. What is the effect of adding another resistor in parallel on the total power loss in the circuit?
________________________________________________________________________________
supporting calculation:
C. What is the effect of adding another resistor in parallel on the current in one of the other resistors?
________________________________________________________________________________
supporting calculation:
D. What is the effect of adding another resistor in parallel on the voltage in one of the other resistors?
________________________________________________________________________________
supporting calculation:
revision 1.7 Page #5 © Farenholtz
Physics 12 Computer Simulation: Combination Circuits
Data Collection and Analysis: Kirchoff’s Laws (simulation file: Parallel Circuits.cck)
1. Use the switches to have all six bulbs active. Draw the circuit diagram below including the resistance of
each bulb. Calculate the total resistance of the entire circuit when all of the bulbs are active, using the
resistance equations for series and parallel resistors.
2. Calculate the total resistance of the circuit when all of the bulbs are active using Ohm’s Law and the
current flowing through the battery. How does your answer compare to that from step #2?
3. Use values from the simulation to verify Kirchoff’s current law for two junctions in the circuit. Show
all you work clearly below.
Junction 1 Junction 2
4. Use values from the simulation to verify Kirchoff’s voltage law for two different loops in the circuit.
Show all you work clearly below.
Loop 1 Loop 2
revision 1.7 Page #6 © Farenholtz
Physics 12 Computer Simulation: Combination Circuits
Experiment with the simulation using the switches to bypass individual bulbs.
A. What is the effect of adding another resistor in parallel on the total resistance of the circuit?
________________________________________________________________________________
supporting calculation:
B. What is the effect of adding another resistor in parallel on the total power loss in the circuit?
________________________________________________________________________________
supporting calculation:
C. What is the effect of adding another resistor in series on the current in one of the other resistors?
________________________________________________________________________________
supporting calculation:
D. What is the effect of adding another resistor in parallel on the voltage in one of the other resistors?
________________________________________________________________________________
supporting calculation:
revision 1.7 Page #7 © Farenholtz
Physics 12 Computer Simulation: Combination Circuits
Conclusion:
Summarize, in a brief paragraph, what relationships you have learned from this simulation. Be sure to
include a description of the relationships between the current and voltage in series and parallel circuits,
as well as how power consumption is effected when resistors are added in series and parallel.
revision 1.7 Page #8 © Farenholtz
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Manual: Installation, Operation & MaintenanceDocument86 pagesManual: Installation, Operation & MaintenanceNhân NgọcPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Railway Engineering 3Document31 pagesRailway Engineering 3Sheikh UbaidPas encore d'évaluation
- SP 1129Document25 pagesSP 1129Selva NizanthPas encore d'évaluation
- Carnauba WaxDocument5 pagesCarnauba WaxsimilcemalcemilPas encore d'évaluation
- The Global Commitment 2021 Progress ReportDocument39 pagesThe Global Commitment 2021 Progress ReportComunicarSe-ArchivoPas encore d'évaluation
- Circular Motion Lab For Physics 2016 SpringDocument1 pageCircular Motion Lab For Physics 2016 SpringIrwansyah Ramadhani100% (1)
- Experiment Hooke S LawDocument3 pagesExperiment Hooke S LawIrwansyah RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves On A StringDocument2 pagesWaves On A StringIrwansyah RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Input Students Data Grade 8B in Academic Year 2021Document1 pageInput Students Data Grade 8B in Academic Year 2021Irwansyah RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Balancing ActDocument3 pagesBalancing ActIrwansyah RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Investigating Specific Heat CapacityDocument1 pageInvestigating Specific Heat CapacityIrwansyah RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Each Group Looking For A Place To Take A Sample and Do Activities To Get SamplesDocument2 pagesEach Group Looking For A Place To Take A Sample and Do Activities To Get SamplesIrwansyah RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Each Group Looking For A Place To Take A Sample and Do Activities To Get SamplesDocument2 pagesEach Group Looking For A Place To Take A Sample and Do Activities To Get SamplesIrwansyah RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- (Total 1 Mark) : IB Questionbank Physics 1Document5 pages(Total 1 Mark) : IB Questionbank Physics 1Irwansyah RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves Virtual Lab en InglesDocument4 pagesWaves Virtual Lab en Inglesjuan0% (1)
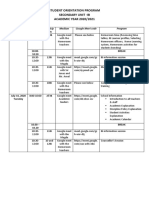
- Student Orientation Program Secondary 2020-2021Document2 pagesStudent Orientation Program Secondary 2020-2021Irwansyah RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Plan Grade 9 2020-2021Document5 pagesYearly Plan Grade 9 2020-2021Irwansyah RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- (Total 1 Mark) : IB Questionbank Physics 1Document5 pages(Total 1 Mark) : IB Questionbank Physics 1Irwansyah RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus: Cambridge IGCSE Physics 0625Document46 pagesSyllabus: Cambridge IGCSE Physics 0625christ MascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Semester 2 Plan Grade 9 2020-2021Document4 pagesSemester 2 Plan Grade 9 2020-2021Irwansyah RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Motion 2 QPDocument14 pagesMotion 2 QPUddin AimanPas encore d'évaluation
- 0625 s16 Ms 42Document10 pages0625 s16 Ms 42Abdullah NaveedPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan Weekly Grade 9 New AY 2020-2021Document12 pagesLesson Plan Weekly Grade 9 New AY 2020-2021Irwansyah RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Untitled NotebookDocument8 pagesUntitled NotebookIrwansyah RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Forces 2 MSDocument3 pagesForces 2 MSIrwansyah RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Motion 1 QPDocument12 pagesMotion 1 QPpromaPas encore d'évaluation
- An Automatic Method of Direct Interpretation of Re PDFDocument15 pagesAn Automatic Method of Direct Interpretation of Re PDFIrwansyah RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Ib Physics ch2Document3 pagesIb Physics ch2Irwansyah RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade DescriptorsDocument36 pagesGrade DescriptorsMostafa DardirPas encore d'évaluation
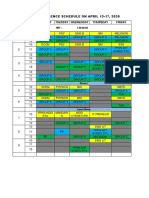
- Zoom Conference Schedule April 13-17, 2020Document1 pageZoom Conference Schedule April 13-17, 2020Irwansyah RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- 0625 s18 QP 12 PDFDocument16 pages0625 s18 QP 12 PDFIrwansyah RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationiSean1337Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ib Physics ch1Document1 pageIb Physics ch1Irwansyah RamadhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- 0625 w16 QP 23Document20 pages0625 w16 QP 23Oneil LewinPas encore d'évaluation
- BBB BCP-15W Cycling ComputerDocument2 pagesBBB BCP-15W Cycling ComputerDannyPas encore d'évaluation
- 63-2003 Local Water District Franchise and Income TaxDocument2 pages63-2003 Local Water District Franchise and Income Taxapi-247793055100% (1)
- Balzac GaitDocument7 pagesBalzac Gaithieratic_headPas encore d'évaluation
- Tzu Chi Medical Journal: Xiao-Jun Lin, I-Mei Lin, Sheng-Yu FanDocument5 pagesTzu Chi Medical Journal: Xiao-Jun Lin, I-Mei Lin, Sheng-Yu Fanperisici4_535458722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Clerical Exam Sample PaperDocument21 pagesClerical Exam Sample PaperSarbjit Singh100% (1)
- A Study On Financial Analysis of Tri Van Drum AirportDocument81 pagesA Study On Financial Analysis of Tri Van Drum AirportN.MUTHUKUMARAN100% (1)
- Cinnamon Streusel Muffin Recipe (Coffee Cake) - DDocument3 pagesCinnamon Streusel Muffin Recipe (Coffee Cake) - DBryce MitchellPas encore d'évaluation
- Processing and Characterization of Recycled Poly (Ethylene Terephthalate) BlendsDocument3 pagesProcessing and Characterization of Recycled Poly (Ethylene Terephthalate) BlendsJason WilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- FOOD PRESERVATION CHART FOR CANNING LOW-ACID & ACID FOODSDocument2 pagesFOOD PRESERVATION CHART FOR CANNING LOW-ACID & ACID FOODSjhPas encore d'évaluation
- The Enchanted ForestDocument3 pagesThe Enchanted ForestRichealle Vaniel Delicano SeverinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample/Pre-Board Paper 14 Class X Term 1 Exam Nov - Dec 2021 English Language and Literature (Code 184)Document5 pagesSample/Pre-Board Paper 14 Class X Term 1 Exam Nov - Dec 2021 English Language and Literature (Code 184)parmila raniPas encore d'évaluation
- Working Principle Iwind Wind TurbinesDocument25 pagesWorking Principle Iwind Wind TurbinesKarbonKalePas encore d'évaluation
- SAP Sales Order Store Returns (Intercompany)Document2 pagesSAP Sales Order Store Returns (Intercompany)Donny CorleonPas encore d'évaluation
- Columbus United Methodist Church: in This IssueDocument11 pagesColumbus United Methodist Church: in This IssueColumbusUMCPas encore d'évaluation
- MM 361: Advanced Manufacturing: InstructionsDocument3 pagesMM 361: Advanced Manufacturing: InstructionsSimLo Lulumani Ko'osiko Taloanimae'aPas encore d'évaluation
- Certification Shop Test 3Document13 pagesCertification Shop Test 3sanyam dhawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical Positivism of Glanville Williams and Ludwig WittgensteinDocument9 pagesAnalytical Positivism of Glanville Williams and Ludwig WittgensteinPrabhakaran KarthikeyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Normal Laboratory Study Values: DefinitionDocument6 pagesComplete Blood Count (CBC) Normal Laboratory Study Values: DefinitionGlare RhaynePas encore d'évaluation
- Ask Astrologer Report - Specific Answer To Major Concern of LifeDocument8 pagesAsk Astrologer Report - Specific Answer To Major Concern of LifecyberastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Bharat Heavy Electricals LimitedDocument19 pagesBharat Heavy Electricals LimitedChandreshDharDubeyPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF If I Break 15 Portia Moore CompressDocument61 pagesPDF If I Break 15 Portia Moore CompressAlbenis RodríguezPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOpolitics PDFDocument3 pagesBIOpolitics PDFalpar7377Pas encore d'évaluation
- Your First ProgramDocument7 pagesYour First ProgramJosephat MugumbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ihp MicroDocument13 pagesIhp MicroTejas HambirPas encore d'évaluation
- Pages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-6 - Gas PressureDocument1 pagePages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 22-6 - Gas Pressurelelon ongPas encore d'évaluation