Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
2008 H2 JC1 CT - Paper 2 (Core)
Transféré par
Chiu Chai HaoDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
2008 H2 JC1 CT - Paper 2 (Core)
Transféré par
Chiu Chai HaoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Civics Group Index Number Name (use BLOCK LETTERS)
ST. ANDREW’S JUNIOR COLLEGE
2008 JC1 Common Test
H2 BIOLOGY 9747/2
Paper 2: Core
Thursday 26 Jun 2008 2 hours
Additional Materials: Answer Paper
Cover Sheet for Section B
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
Do not open this booklet until you are told to do so.
Write your name, civics group and index number on all the work you hand in.
Write in dark blue or black pen.
You may use a soft pencil for any diagram, graph or rough working.
Do not use staples, paper clips, highlighters, glue or correction fluid.
Section A (Structured Questions)
Answer all seven questions.
Write your answers in the spaces provided on the question paper.
Section B (Essay Questions)
Choose one of the two questions.
Write your answers on the separate answer paper provided. For Examiner’s Use
All working for numerical answers must be shown. Section A
1 /15
INFORMATION TO CANDIDATES
2 /10
At the end of the examination,
3
1. Attach Section B answers to the cover sheet provided. /10
2. Enter the number of the Section B questions you have answered on the 4 /13
cover sheet.
5 /10
The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or
6
part question. /10
7 /12
Total
/80
This document consists of 21 printed pages.
[Turn over
2
Section A
Answer all questions.
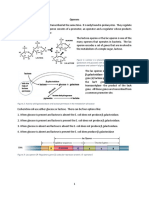
1 Peptic cells from the lining of mammalian stomach secrete the enzyme precursor
pepsinogen. Some of these cells were isolated and maintained in a culture solution
containing radioactively labeled amino acids. Samples of the cells were taken at
regular intervals and prepared for electron microscopy. The following figure shows a
drawing from an electron micrograph of a peptic cell. The time taken, in minutes, for
radioactivity to be detected in the various cell organelles viewed under the electron
microscope is shown on the right of the drawing.
(a) (i) Name the organelles labeled A to D.
A
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
B
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
C
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
D …………………………………………………………………………………………….[2]
(ii) Explain the detection at different times in the organelles labeled B and D.
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
3
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………………..….
[3]
(iii) Describe how the material in the organelles labeled A passes out of the cell.
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………………..….
[1]
(iv) Explain why large numbers of the organelle labeled E are required in cells
synthesizing and secreting proteins.
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………………..….
[2]
Cells can alter the lipid composition of their membranes as an adjustment to
changing temperature. For example, in winter wheat, the ratio of unsaturated
phospholipids to saturated phospholipids begins to change during autumn.
(b) (i) State how the ratio of unsaturated phospholipids to saturated phospholipids
will change during autumn.
………………………………………………………………………………….………….…
[½]
(ii) Explain how this change of ratio is advantageous for winter wheat.
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
4
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….…..…[2½]
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
5
(c) Cholesterol is a lipid found in the cell membranes of all animal tissues. It is either
synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum, or derived from the diet, in which case it is
delivered by the bloodstream in low-density lipoproteins. The following figure shows
the location and structure of cholesterol.
hydroxyl group
steroid ring
(i) With reference to membrane structure, suggest how cholesterol is held in the
membrane.
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
…………………………………………………………………..…………………….………
[2]
(ii) Explain the importance of cholesterol in cell membranes.
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
…………………………………………………………………..…………………….………
[2]
[Q1 Total: 15]
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
6
2 Thermus aquaticus is a bacteria which thrives in hot springs. A serine protease
found in these bacteria is found to have two disulphide bonds at amino acids
positions Cys69-Cys99 and Cys163-194. Three mutants of this serine protease were
prepared in which the disulphide bonds Cys69-Cys99, Cys163-Cys194 and both of
these disulphide bonds, respectively, were disrupted by replacing Cys residues with
Ser residues.
The table below summarises the results of the experiment when enzyme activity and
stability for the wild type and 3 mutant serine proteases were investigated.
Serine Disulphide bond Disulphide bond Enzyme Time taken for half of
Protease Cys69-Cys99 Cys163-Cys194 activity at total enzyme to
40°C / % denature at 90°C / min
Wild type No change No change 100 45
Mutant 1 Disrupted No change 68 40
Mutant 2 No change Disrupted 6 10
Mutant 3 Disrupted Disrupted 3 10
(a) (i) Explain why disulphide bonds are disrupted when the 2 two cysteine residues
are replaced with two serine residues in amino acid at positions 69 and 99 of the
polypeptide chain?
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
…………………………………………………………………..…………………….………
[1]
(ii) With reference to the table above, explain which disulphide bond is more
important for catalytic activity and conformational stability of the serine protease in
Thermus aquaticus?
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
…………………………………………………………………..…………………….………
[2]
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
7
Collagen is the main structural protein in the human body. It strengthens the tendons
and supports the skin and internal organs. Bones and teeth are made by adding
mineral crystals to collagen. Collagen molecules are composed of three polypeptide
chains, wound together in a tight triple helix.
(b) (i) Explain why collagen is described as a fibrous protein.
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
…………………………………………………………………..…………………….………
[2]
(ii) Name the types of bonds in the collagen molecule that hold together:
the primary structure;
…………………………………………………………………..………………….………...
[½]
the secondary structure;
…………………………………………………………………..………………….………...
[½]
(iii) Describe the main features of collagen that contribute to its tensile strength.
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
8
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
…………………………………………………………………..…………………….………
[4]
[Q2 Total: 10]
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
9
3 The figure below shows the effect of increasing sucrose concentration on the
activity of sucrase. The rate was determined by measuring the amount of reducing
sugar produced in 15 minutes using a fixed amount of the enzyme.
(a) Explain the effect of increasing sucrose concentration on rate of reaction in
terms of enzyme action
(i) between 0 and 0.6 mol dm-3 sucrose concentration.
………………………………………………………………………….
………………………..
………………………………………………………………………….
………………………..
…………………………...………………………………………...…………………….…
[1½]
(ii) Between 0.6 and 0.8 mol dm-3 concentration.
………………………………………………………………………….
………………………..
………………………………………………………………………….
………………………..
…………………………...………………………………………...……………………….…
[1]
(iii) Above 0.8 mol dm-3 sucrose concentration.
………………………………………………………………………….
………………………..
………………………………………………………………………….
………………………..
…………………………...………………………………………...…………………….…
[1½]
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
10
A strain of the bacterium, Streptococcus pneumoniae, has been found. This strain
does not grow in the presence of the antibiotic vancomycin, but neither does it die.
This vancomycin tolerance is caused by a mutation of a gene coding for an enzyme
G.
(b) Explain briefly how a mutation of a gene coding for the enzyme G:
(i) may still result in the production of a functional enzyme.
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
…………………………………………………………………..…………………….………
[3]
(ii) may result in an enzyme with reduced activity.
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
…………………………………………………………………..…………………….………
[3]
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
11
[Q3 Total: 10]
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
12
4 The graph below shows how the amount of DNA per cell of Chrysanthemum
makinoi varies during periods A to E in the cell cycle
D
A B C E
(a) (i) Radioactive thymine was supplied to the cells of some growing
Chrysanthemum tissue. With reference to the graph, during which period (A to E) of
the cell cycle does radioactivity of the nuclei first increase? Explain your answer.
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
…………………………………………………………………..…………………….………
[3]
(ii) At anaphase of mitosis, sister chromatids separate to become individual
chromosomes. Identify the period (A to E) during which anaphase occurs. Explain
your answer.
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
…………………………………………………………………..…………………….………
[2]
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
13
The figure below shows the chromosomes from a cell of another plant species during
anaphase I.
(b) (i) State the haploid chromosome number of this species.
…………………………………………………………………..…………………….……..
[½ ]
(ii) At the time shown in the figure, this cell contained 8 picograms of DNA. How
much DNA would be present in each gamete produced from this cell?
…………………………………………………………………..……………………...…….
[½]
(iii) Explain why haploid cells need to be produced during a life cycle which includes
sexual reproduction and state what would happen otherwise.
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
…………………………………………………………………..………………………….…
[2]
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
14
(c) Using the table below, distinguish between chromatids and chromosomes.
Chromatids Chromosomes
[2]
(d) Outline the sources of genetic variation in a sexually reproducing population of
organisms.
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
…………………………………………………………………..…………………….………
[3]
[Q4 Total: 13]
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
15
5
Step 1: During research into the mechanism of DNA replication, bacteria were grown
for many generations in a medium containing only the ‘heavy’ isotope of nitrogen,
15
N. This resulted in all the DNA molecules containing only 15N. This is illustrated in
the figure below.
% DNA molecules
100
75
50
25
DNA containing 14 N only DNA containing 14 N/15 N DNA containing 15 N only
Step 2: These bacteria were then grown in a medium containing only “light’ nitrogen,
14
N. After the time taken for the DNA to replicate once, the DNA was analysed.
Step 3: The bacteria continued to grow in the ‘light’ nitrogen, 14N, medium until the
DNA had replicated once more. The DNA molecules were then analysed.
Step 4: The bacteria was allowed to grow in the ‘light’ nitrogen, 14N, medium for
another round of DNA replication.
(a) (i) Complete the bar chart below to indicate the expected results of the
composition of these DNA molecules after Step 4.
% DNA molecules
100
75
50
25
DNA containing 14 N only
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) DNA containing 14 N/15 N DNA containing 15
N only
Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
16
[2]
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
17
The following shows simple diagrams of DNA molecules, indicating the nitrogen
content of each.
(ii) With reference to the above diagrams, select the letter or letters which best
represent the resulting bacterial DNA from Step 2 and 3.
Step 2 ...…………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
Step 3 .……………………………………………………………………………….……....
[1]
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
18
The figure below illustrates the binding of an enzyme to a DNA double helix during
DNA replication.
(b) (i) Explain how the binding of this enzyme to the double helix cause changes to
both their original structures.
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
…………………………………………………………………..…………………….………
[2]
(ii) Both regions X and Y are helical in nature, yet they are different in their
structural makeup. Briefly explain this statement.
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
…………………………………………………………………..…………………….………
[2]
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
19
On a planet in a distant galaxy, the organisms have evolved such that they have 6
rather than 4 different bases in their DNA, with a base composition: 24.5% U, 19% V,
25.2% W, 7.4% X, 18.8% Y and 7% Z; and they have 30 naturally occurring amino
acids instead of 20.
(c) (i) With reference to the information given above, deduce the DNA structure of
the extra-galactic organisms.
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
…………………………………………………………………..…………………….………
[2]
(ii) State, with a reason, the minimum number of nucleotides that code for an amino
acid.
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
…………………………………………………………………..…………………….………
[1]
[Q5 Total: 10]
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
20
6 The figure below shows the structure of influenza virus. Influenza virus is a
member of the Orthomyxoviridae family of viruses and comprise two genera:
influenza A and B viruses, and influenza C virus. Influenza A, B and C viruses are
distinguished on the basis of their internal nucleoprotein and matrix proteins which
are specific for each viral type.
(a) State the nature of the genetic material found in the influenza virus.
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
………………………………………………………………………………….
………………..
…………………………………………………………………..……………………….……
[1]
(b) Name structure P and Q. Explain their roles in the success of influenza virus life
cycle.
Structure P …………………..
Role…………………………………………………………….…………………………….…
…………………………………………………………………..……………………..……
[1½]
Structure Q …………………..
Role…………………………………………………………….…………………………….…
…………………………………………………………………..……………………..……
[1½]
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
21
(c) The highly pathogenic avian flu subtype H5N1 is currently the world’s largest
pandemic threat. Billions of dollars are being pumped into the research of H5N1 and
other subtypes in preparation for an imminent influenza pandemic. New vaccines
need to be created constantly to combat these viruses. Explain why this is so.
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….………..
[4]
(d) Describe the two different mechanisms by which enveloped viruses penetrate
host cells.
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
…………………………………………………………………..……………………..…...…
[2]
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
22
[Q6 Total: 10]
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
23
7 The figure below is an electron micrograph of an organism isolated from the gut of
a human.
(a) (i) With reference to the figure, state 2 distinguishing features which show that
this organism is a bacterium.
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
…………………………………………………………………..……………………..…...…
[2]
(ii) Using the table below, state 2 structural differences between the chromosome
of a bacterium and a human cell.
Bacterium Human cell
[2]
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
24
A study of the bacterium’s chromosome showed that it possessed a lac operon to
allow the bacterium to metabolise lactose. The structure of the lac operon is shown
below:
Operator Structural genes
Promoter
P lacI lacZ lacY lacA
Promoter
(b) Bacterium is grown on a medium of lactose and glucose. On the axes below,
draw a graph showing how the amount of β -galactosidase in the bacterium is
affected after all glucose has been utilized.
[2]
Amount of β -galactosidase
0
Time
All glucose utilized
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
25
The graph below shows the growth of bacteria in the presence of glucose and
lactose.
Concentration/ M
Cell count /%
B
C
Legend for graphs:
A A = lactose
B = glucose
C = bacteria
Time/ min
Part I II III
(c) Describe and explain the three parts of graph C.
Part I:
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
…………………………………………………………………..……………………..…...…
[2]
Part II:
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
…………………………………………………………………..……………………..…...…
[2]
Part III:
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
26
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….
…………..
…………………………………………………………………..……………………..…...…
[2]
[Q7 Total: 12]
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
27
Section B
Answer one of the questions.
Your answers should be illustrated by large, clearly labelled diagrams, where
appropriate.
Your answers must be in continuous prose, where appropriate.
Your answers must be set out in sections (a), (b) etc., as indicated in the question.
8 (a) Compare and contrast DNA and RNA. [8]
(b) Describe how the information on mRNA is used to synthesize functional
polypeptides. [12]
[Total: 20]
9 (a) Describe in detail the lysogenic life cycle of a bacteriophage using a
named example. [10]
(b) Name the enzymes found in HIV and explain their importance in the
replication of the virus. [5]
(c) Explain how viruses damage host cells. [5]
[Total: 20]
SAJC/9747 H2 Biology Paper 2 (Core) Jc1 H2 Common Test 2008
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- (VCE Biology) 2017 Insight Unit 34 ExamDocument39 pages(VCE Biology) 2017 Insight Unit 34 ExamAyesha RiazPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- RI TYS Ans 2007-2019-CompressedDocument215 pagesRI TYS Ans 2007-2019-CompressedelgiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Operon Problems 1Document2 pagesOperon Problems 1Anwesha BosePas encore d'évaluation
- Gene Expression in ProkaryotesDocument43 pagesGene Expression in ProkaryotesravibiriPas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Subunidad SigmaDocument5 pagesSubunidad SigmaGeorgina HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Griffiths Introduction To Genetic Analysis 12th EditionDocument3 002 pagesGriffiths Introduction To Genetic Analysis 12th Editionmartin.kv4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Lac OperonDocument14 pagesLac Operonsony_arora10% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- 1603LEADERACHIEVERMLABCDEMAZA MAJOR TEST 65760 TEST PDF Fv16Si8njhDocument64 pages1603LEADERACHIEVERMLABCDEMAZA MAJOR TEST 65760 TEST PDF Fv16Si8njhGjgcdPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Lodish6e ch07Document8 pagesLodish6e ch07nPas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Soal Biosel PDFDocument7 pagesSoal Biosel PDFjessicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Gene Expression and RegulationDocument27 pagesGene Expression and RegulationgengkapakPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- USABO 18 Open Exam - Final Wo AnsDocument17 pagesUSABO 18 Open Exam - Final Wo AnsJ.Chang ChangPas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- SMK Matang Jaya Trial Term 3 2017 QPDocument8 pagesSMK Matang Jaya Trial Term 3 2017 QPViola Voon Li WeiPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Assignment Questions Biology Class: XII CHAPTER 1: Reproduction in OrganismDocument14 pagesAssignment Questions Biology Class: XII CHAPTER 1: Reproduction in Organismzach23628Pas encore d'évaluation
- Operons and Prokaryotic Gene Regulation08 NatEduDocument2 pagesOperons and Prokaryotic Gene Regulation08 NatEduSubhadip PalPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Biochemistry/Molecular Biology Review SheetDocument10 pagesBiochemistry/Molecular Biology Review Sheetcrzybboy09Pas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction To Genetic Analysis 11th Edition PDFDocument897 pagesAn Introduction To Genetic Analysis 11th Edition PDFAnonymous oVNAcvT83% (59)
- Catabolite RepressionDocument7 pagesCatabolite RepressionLucy SirinehPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- AP Biology Daily Lesson Plans PDFDocument24 pagesAP Biology Daily Lesson Plans PDFJayCesarPas encore d'évaluation
- Food-Chemistry 2011 128 773Document5 pagesFood-Chemistry 2011 128 773Brenda C RoldánPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- BiologyDocument495 pagesBiologyNCCA NCCAPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Super Notes by Seep PahujaDocument75 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance - Super Notes by Seep Pahujaaltashabts7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 5 Respiration, Internal Environment, Coordination and Gene TechnologyDocument55 pagesUnit 5 Respiration, Internal Environment, Coordination and Gene TechnologyMaha NaserPas encore d'évaluation
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Biological Science 2nd Canadian Edition PDF ScribdDocument41 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF Biological Science 2nd Canadian Edition PDF Scribdmatthew.weimar370100% (40)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Lac Operon PDFDocument3 pagesLac Operon PDFS NairPas encore d'évaluation
- ScanDocument32 pagesScanIka S NurroyaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzymes: Dennis Ivan Bravo, MDDocument10 pagesEnzymes: Dennis Ivan Bravo, MDcarlosPas encore d'évaluation
- IBO 2010 Korea Theory Paper 2Document73 pagesIBO 2010 Korea Theory Paper 2Bikash Ranjan RayPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- AP Q Chapter 4Document56 pagesAP Q Chapter 4Mahra AlketbiPas encore d'évaluation
- Repressible Operon System (Fig. 6.35)Document2 pagesRepressible Operon System (Fig. 6.35)Valar Mathei PadmanadhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)