Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
3 2done
Transféré par
eperlaDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
3 2done
Transféré par
eperlaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
3.
2 Differentiability
Differentiability Implies Continuity
If f HxL has a derivative at x = a, then f HxL is continuous at x = a.
Intermediate Value Theorem for Derivatives
If a and b are any two x - values in an interval in which f is differentiable, then
f ¢ takes on every value between f ¢ HaL and f ¢ HbL
Left and Right Hand Derivatives
f Ha + hL - f HaL f Ha + hL - f HaL
lim - ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ and lim + ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
hÆ0 h hÆ0 h
Numerical Approximation for Derivatives, Symmetric Difference Quotient
f Ha + hL - f Ha - hL
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
2h
Reasons for derivative failure
"#### »x»
A. a corner, » x »
2 3
B. a cusp, x ÄÄ3ÄÄÄ C. a vertical tangent, x D. a discontinuity, ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
x
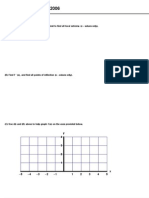
1. Find all points on the graph where the function is not differentiable. Determine why the function is
not differentiable at these points.
−4 −3 −2 −1 1 2 3 4 5
−1
−2
Not differentiable at the following values
x = -3 Æ Removable Discontinuity, x = -2 Æ Corner
x = -1 Æ Infinite Discontinuity, x = 0 Æ Jump Discontinuity
x = 1 Æ Vertical Tangent x = 2 Æ Corner
x = 3 Æ Corner x = 4 Æ Corner
x = 5 Æ Can ¢ t approach from the left
For problems 2 - 5, find the left and right hand derivatives to determine if the function is differentiable at
the given point.
2. f HxL = Px + 1T at x = 2 3. f HxL = sin x, x π 0 at x = 0
1, x = 0
f H2 + hL - f H2L f H0 + hL - f H0L
left - hand Æ lim - ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ left - hand Æ lim - ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
hÆ0 h hÆ0 h
2-3 sin h - 1 sin h -1
Æ lim - ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ = • and for the right - hand, Æ lim - ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ = lim - ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ + lim - ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
h h h h
f H2 + hL - f H2L
hÆ0 hÆ0 hÆ0 hÆ0
3-3
lim + ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ = lim + ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ = 0 = 1 + • Æ • and for the right - hand,
h h
f H0 + hL - f H0L
hÆ0 hÆ0
sin h - 1
so the function is not differentiable at x = 2 lim ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ = lim + ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
h Æ 0+ h h Æ 0 h
sin h -1
= lim + ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ + lim + ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ = 1 - • Æ -•
hÆ0 h hÆ0 h
so the function is not differentiable at x = 0
4. f HxL = » x - 2 » at x = 2 5. f HxL = x2 - 1, x £ 1 at x = 1
2 x - 1, x > 1
f H2 + hL - f H2L f H1 + hL - f H1L
left - hand Æ lim ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ left - hand Æ lim ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
h Æ 0- h h Æ 0- h
»2 + h - 2» -0 -h H1 + hL2 - 1 - H H 1L2 - 1 L
= lim - ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ = lim - ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ = -1 = lim - ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
hÆ0 h hÆ0 h hÆ0 h
f H2 + hL - f H2L h2 + 2 h
and for the right - hand Æ lim ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ = lim - ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ = 2
h Æ 0+ h h
»2 + h - 2» -0
hÆ0
h
= lim + ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ = lim + ÄÄÄÄÄÄ = 1 and for the right - hand Æ there is a jump
hÆ0 h hÆ0 h
so the function is not differentiable at x = 2 discontinuity at x = 1 , making lim = •
h Æ 0+
so the function is not differentiable at x = 1
For problems 6 and 7, find all values for which the function is differentiable
f HxL = ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ f HxL = log3 » x »
x3 + 1
6. 7.
x2 - 2 x - 3
H x + 1 L H x2 - x + 1 L
f HxL = ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ
Hx - 3L Hx + 1L
ÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄÄ Looking at the graph, there is an infinite
there is a removable discontiuity at disontinuity at x = 0 , so f HxL is differentiable
x = -1, and an infinite discontinuity at on the interval H -•, 0 L ‹ H 0, • L
x = 3, so f HxL is differentiable on the
interval H -• , -1 L ‹ H -1, 3 L ‹ H 3, • L
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Trig Products PostDocument1 pageTrig Products PosteperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Talent Application 2008Document2 pagesTalent Application 2008eperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Recommendation Request Form 2008Document2 pagesRecommendation Request Form 2008eperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Sum To Integral PostDocument1 pageSum To Integral PosteperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Sum To Integral DoneDocument2 pagesSum To Integral DoneeperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Trig Products DoneDocument1 pageTrig Products DoneeperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Trigonometric Substitution: X "################# A - X A Q X "################# A + X Q "################# X - A XDocument3 pagesTrigonometric Substitution: X "################# A - X A Q X "################# A + X Q "################# X - A XeperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Quadratic Expressions DoneDocument2 pagesQuadratic Expressions DoneeperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- FlashcardTest01-63d After CH 8Document1 pageFlashcardTest01-63d After CH 8eperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- FlashcardTest01-52solutions End of CH 6Document1 pageFlashcardTest01-52solutions End of CH 6eperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- FlashcardTest01-70dsolutions After TaylorDocument2 pagesFlashcardTest01-70dsolutions After TayloreperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- FlashcardTest01-60 During CH 7Document2 pagesFlashcardTest01-60 During CH 7eperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- FlashcardTest01-70d After TaylorDocument1 pageFlashcardTest01-70d After TayloreperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- FlashcardTest01-46bsolutions After CH 5Document2 pagesFlashcardTest01-46bsolutions After CH 5eperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Free Response Final 2006 NameDocument4 pagesFree Response Final 2006 NameeperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- FlashcardTest01-52 End of CH 6Document1 pageFlashcardTest01-52 End of CH 6eperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- FlashcardTest01 35Document1 pageFlashcardTest01 35eperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Final MC2006 DecemberDocument6 pagesFinal MC2006 DecembereperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 10 Test April 7, 2005 No Calculators NameDocument4 pagesChapter 10 Test April 7, 2005 No Calculators NameeperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- FlashcardTest01-46b After CH 5Document2 pagesFlashcardTest01-46b After CH 5eperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Final MC2006Document5 pagesFinal MC2006eperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Chapter 10 Test April 6, 2007 No Calculators NameDocument4 pagesChapter 10 Test April 6, 2007 No Calculators NameeperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Final FR2006 DecemberDocument4 pagesFinal FR2006 DecembereperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 10 Test April 4, 2006 No Calculators NameDocument4 pagesChapter 10 Test April 4, 2006 No Calculators NameeperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9 Test March 18, 2007 No Calculators NameDocument4 pagesChapter 9 Test March 18, 2007 No Calculators NameeperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9 Test March 18, 2005 No Calculators NameDocument4 pagesChapter 9 Test March 18, 2005 No Calculators NameeperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 10 Test No Calculators NameDocument3 pagesChapter 10 Test No Calculators NameeperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Chapter 10 Test April 8, 2004 No Calculators NameDocument4 pagesChapter 10 Test April 8, 2004 No Calculators NameeperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9 Test March 17, 2006 No Calculators NameDocument4 pagesChapter 9 Test March 17, 2006 No Calculators NameeperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9 Test March 22, 2004 No Calculators NameDocument1 pageChapter 9 Test March 22, 2004 No Calculators NameeperlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics-I: Code No: MA1501 Model Question Paper I B. Tech I Semester External ExaminationsDocument2 pagesMathematics-I: Code No: MA1501 Model Question Paper I B. Tech I Semester External ExaminationsKrish PavanPas encore d'évaluation
- A First Course in Differential Equations Solutions Odd Exercises PDFDocument62 pagesA First Course in Differential Equations Solutions Odd Exercises PDFFernandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 5 - DifferentiationDocument29 pagesLecture 5 - DifferentiationNabiha AzadPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Engineering Mathematics PDFDocument199 pagesAdvanced Engineering Mathematics PDFkrish garg83% (6)
- Differential Equation PDFDocument3 pagesDifferential Equation PDFhasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ma5252 SyllabusDocument2 pagesMa5252 SyllabusArmahPas encore d'évaluation
- Curve Tracing PDFDocument5 pagesCurve Tracing PDFStevenzel Eala EstellaPas encore d'évaluation
- DE ReportDocument25 pagesDE ReportGuenivere SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- B.E. EEE SyllabusDocument196 pagesB.E. EEE Syllabusrkar-7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fem 2Document26 pagesFem 2Venkitaraj K PPas encore d'évaluation
- HW04 - Ly Thierno Mouhamadou Samassa - D2021738Document2 pagesHW04 - Ly Thierno Mouhamadou Samassa - D2021738Thierno Samassa LyPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Title Instructor E Mail Office EL Office Hours ExtbookDocument2 pagesCourse Title Instructor E Mail Office EL Office Hours ExtbookKhairi Saleh100% (1)
- Infinite Series SandhamDocument7 pagesInfinite Series SandhamscionaPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 337 - Elementary Differential EquationsDocument32 pagesMath 337 - Elementary Differential EquationsmichaelPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 152 (Final) Formula Sheet Fall 2021Document2 pagesPhysics 152 (Final) Formula Sheet Fall 2021emily gPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set of Differential Equation PDFDocument72 pagesProblem Set of Differential Equation PDFVictor SinagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Problems On First Order First Degree Differential EquationsDocument4 pagesPractice Problems On First Order First Degree Differential EquationsAkshita PillaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Numerical Methods - Part1Document9 pagesNumerical Methods - Part1AlthafPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Differential EquationsDocument4 pagesTypes of Differential EquationsAbbas WarsiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bridge CourseDocument8 pagesBridge CourseDavidMaighlPas encore d'évaluation
- Ordinary Differential Equations NotesDocument95 pagesOrdinary Differential Equations Notespocolo1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- 9.2.1 To Determine The First Derivative ofDocument9 pages9.2.1 To Determine The First Derivative ofcygNemoPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus Math 305Document4 pagesSyllabus Math 305Nataly SusanaPas encore d'évaluation
- LaplaceDocument4 pagesLaplacebelleblackPas encore d'évaluation
- CO3 - Math 146Document85 pagesCO3 - Math 146Keith LizanPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Laplace Transform Problem Set 1Document2 pages1 Laplace Transform Problem Set 1Fearless HeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Partial DerivativesDocument117 pagesPartial DerivativesMitrabhanuPas encore d'évaluation
- Class Notes - CalculusDocument31 pagesClass Notes - CalculusRyan GilbertPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet (1) - Home Work: Q 8: Determine The Fourier Series Up To and Including The Third Harmonic For The FunctionDocument5 pagesSheet (1) - Home Work: Q 8: Determine The Fourier Series Up To and Including The Third Harmonic For The FunctionZayn AhmedPas encore d'évaluation