Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Biotechnology - Igcse Biology
Transféré par
TheStar0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
96 vues4 pagesbiotechnology for igcse biology
Titre original
Biotechnology - igcse biology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentbiotechnology for igcse biology
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
96 vues4 pagesBiotechnology - Igcse Biology
Transféré par
TheStarbiotechnology for igcse biology
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
20.
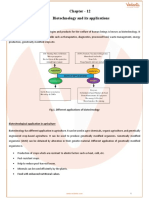
1) Biotechnology and genetic engineering
Biotechnology is the application of biological organisms,
systems or processes to manufacturing and service
industries.
Genetic engineering involves the transfer of genes from
one organism to (usually) an unrelated species.
Both processes often make use of bacteria because of their
ability to make complex molecules (eg. proteins) and their
rapid reproduction rate.
Bacteria are useful in biotechnology and genetic engineering
because they can be grown and manipulated without raising
ethical concerns.
They have a genetic code that is the same as all other
organisms, so genes from other animals or plants can be
successfully transferred into bacterial DNA.
Bacterial DNA is in the form of a circular strand and also
small circular pieces called plasmids.
Scientists have developed techniques to cut open these
plasmids and insert sections of DNA from other organisms
into them.
When the bacterium divides, the DNA in the modified
plasmid is copied, including the ‘foreign’ DNA.
This may contain a gene to make a particular protein such as
insulin, which can be extracted and used as a medicine to treat
diabetes.
20.2) Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering: is changing the genetic material of an
organism by removing, changing or inserting individual genes.
Examples of genetic engineering:
The insertion of human genes into bacteria to produce
human insulin.
The insertion of genes into crop plants to confer resistance
to herbicides and insect pests.
The insertion of genes into crop plants to provide additional
vitamins.
Bacterial production of a human protein such as insulin:
1. Isolation of the DNA making up a human gene using
restriction enzymes, forming sticky ends.
2. Cutting of bacterial plasmid DNA with the same RE, forming
complementary sticky ends.
3. Insertion of human DNA into bacterial plasmid DNA using
ligase enzymes to form a recombinant plasmid.
4. Insertion of plasmid into bacteria.
5. Replication of bacteria containing recombinant plasmid
which make human protein as they express the gene.
Restriction enzymes cut DNA at specific sites, rather than
just in random places along the DNA molecule. Eg. between
the A and the T in the sequence GAA-TTC.
ligase enzymes join pieces of DNA together at specific
sites.
The plasmids are said the be vectors that carry the human
DNA into the bacteria and the techniques are sometimes
called gene-splicing.
The bacteria are cultured in special vessels called
fermenters and the insulin that they produce can be
extracted from the culture medium and purified for use in
treating diabetes.
Golden rice:
Advantages
Produces beta carotene which is needed by humans in order
to make vitamin A.
Used in areas where vitamin A deficiency is common, so it
can help prevent night blindness.
Disadvantages
beta carotene levels in golden rice may not be high enough
to make a difference.
there are fears that it will cross-breed with and contaminate
wild rice.
there are concerns that food from GM plants might harm
people.
seed for GM plants can be expensive.
Soya and Maize:
Disadvantages
Can contain pesticide residues or substances that causes
allergies (allergens).
Herbicide-resistant crops:
Disadvantages
The potential development of herbicide-resistant weeds.
Loss of biodiversity because fewer weeds survive – resulting in
reduced food and shelter for animals.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Biotechnology and Genetic EngineeringDocument4 pagesBiotechnology and Genetic EngineeringArianz GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 2.5 - Genetic-Engineering (General Biology II)Document34 pagesCHAPTER 2.5 - Genetic-Engineering (General Biology II)Queen Iris Angeline CrisostomoPas encore d'évaluation
- 13 Gmo PDFDocument14 pages13 Gmo PDFKenneth AustriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9 BiotechnologyDocument21 pagesChapter 9 BiotechnologyAtiya FalakPas encore d'évaluation
- The Process of Genetic Engineering PDFDocument7 pagesThe Process of Genetic Engineering PDFprimalPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 5 Lesson 11Document6 pagesModule 5 Lesson 11John eric CatayongPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology Karnatakapuc 110709070353 Phpapp01Document11 pagesBiotechnology Karnatakapuc 110709070353 Phpapp01Lovryan Tadena AmilingPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic Engineering and BiotechnologyDocument34 pagesGenetic Engineering and BiotechnologyCristy Jean ApdianPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic Modification: DNA A, T, G, and CDocument4 pagesGenetic Modification: DNA A, T, G, and CAbubakar Siddiq RaminPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA Recombination and DNA TechnologyDocument8 pagesDNA Recombination and DNA TechnologyJhun Lerry TayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument6 pagesPlant Recombinant DNA TechnologyPaula FranciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocument8 pagesBiotechnology and Its ApplicationsS SURAJPas encore d'évaluation
- BiotechnologyDocument81 pagesBiotechnologyYvonne Dulay BarrozoPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic EngineeringDocument8 pagesGenetic EngineeringWynne Cassandra JoverPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is genetic-WPS OfficeDocument16 pagesWhat Is genetic-WPS OfficeShamoon HaroonPas encore d'évaluation
- C. Genetic Modification ObjectivesDocument9 pagesC. Genetic Modification ObjectivesFengyiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Plant BiotechnologyDocument39 pagesChapter 6 Plant BiotechnologyInuyashayahooPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio ApplicationsDocument4 pagesBio ApplicationskaiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Agricultural Uses of DNA TechnologyDocument5 pagesAgricultural Uses of DNA TechnologyAidy StarkPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Plant BiotechnologyDocument39 pagesChapter 6 Plant Biotechnologyshivabt07Pas encore d'évaluation
- TM-08 Genetically Modified Organisms (2016)Document33 pagesTM-08 Genetically Modified Organisms (2016)ZANUBA ULYA’ HAURA CELLIN 1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology and Its Applications Chapter - 12Document5 pagesBiotechnology and Its Applications Chapter - 12Mauz KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocument9 pagesBiotechnology and Its Applicationstamalbio7Pas encore d'évaluation
- © Ncert Not To Be Published: Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocument10 pages© Ncert Not To Be Published: Biotechnology and Its Applicationsaayushi24681438Pas encore d'évaluation
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocument20 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsMehul JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 12 CH 12 Bio - 221015 - 211431Document27 pagesClass 12 CH 12 Bio - 221015 - 211431Anant VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Review: Science, Medicine, and The FutureDocument4 pagesClinical Review: Science, Medicine, and The FuturemaryvemaxPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.5.9 Genetic EngineeringDocument44 pages2.5.9 Genetic EngineeringHanung PujanggaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Unit 5Document2 pagesBio Unit 5jaina4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Earth and Life Science - Q2 - Week4ADocument19 pagesEarth and Life Science - Q2 - Week4Adyevelyn19Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Seminar ON Genetic Engineering and Gene Cloning BY Ayinde Samson MATRIC NUMBER: 168859049 Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Ekiti State University. JUNE, 2021Document12 pagesA Seminar ON Genetic Engineering and Gene Cloning BY Ayinde Samson MATRIC NUMBER: 168859049 Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Ekiti State University. JUNE, 2021SamsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12. Xii Biotechnology and Its ApplicationDocument33 pagesChapter 12. Xii Biotechnology and Its ApplicationBeena PalPas encore d'évaluation
- MCB 311 & MCB 309 New VersionDocument69 pagesMCB 311 & MCB 309 New VersionChaos HadesPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic Engineering: Pages 286 - 289Document8 pagesGenetic Engineering: Pages 286 - 289Mohammad Ali QayyumPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering Summary PPT Igcse CaieDocument16 pagesBiotechnology and Genetic Engineering Summary PPT Igcse Caiearyan patelPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetically Modified OrganismsDocument17 pagesGenetically Modified Organismsrashid100% (2)
- Chapter 12Document6 pagesChapter 12a34146525Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bio 3Document3 pagesBio 3CameronPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd-Quarter General Biology 2 STEMDocument35 pages3rd-Quarter General Biology 2 STEMKassandra MariePas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology AND It Application: By: Dr. Anand ManiDocument7 pagesBiotechnology AND It Application: By: Dr. Anand Mani....Pas encore d'évaluation
- BIO-Chapter 20. BiotechDocument27 pagesBIO-Chapter 20. Biotechkathleen hoPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 4: Genetic Engineering and Its Applications in ReproductionDocument19 pagesWeek 4: Genetic Engineering and Its Applications in ReproductionDonna RemitarPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocument8 pagesBiotechnology and Its ApplicationsAzad SamiPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 CH 12Document4 pages12 CH 12Ring BabuPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic Engineering and Recombinant Dna: Lesson 1Document5 pagesGenetic Engineering and Recombinant Dna: Lesson 1Dexie MusaPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Biology ImpQ CH12 Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsDocument8 pages12 Biology ImpQ CH12 Biotechnology and Its ApplicationsSaiAbhijith100% (1)
- Recombinant DnaDocument52 pagesRecombinant DnaGian Carlo RoseroPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Techniques of Genetic EngineeringDocument10 pagesAssignment Techniques of Genetic EngineeringmariashekinahdPas encore d'évaluation
- Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument14 pagesRecombinant DNA TechnologyAnshika SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Biotechnology and Genetic EngineeringDocument14 pagesBiotechnology and Genetic EngineeringTanyaradzwa MugutaPas encore d'évaluation
- IAL Biology SB2 Answers 8CDocument5 pagesIAL Biology SB2 Answers 8CsalmaPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA Genetic EngineeringDocument72 pagesDNA Genetic EngineeringEmman Matthew GregorioPas encore d'évaluation
- WEEK 4 - Q2 - Earth and LifeDocument16 pagesWEEK 4 - Q2 - Earth and Lifenoreen lubindinoPas encore d'évaluation
- General Biology Week 1 Supplementary NotesDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology Week 1 Supplementary NotesMakspeyn del Valle - MoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic Engineering Part 3 and 4Document42 pagesGenetic Engineering Part 3 and 4KSHITIJ K GAUTAMPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 5 9-Genetic-EngineeringDocument42 pages2 5 9-Genetic-EngineeringsoffiahPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 10Document4 pagesScience 10Jaime Añora ParedesPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.3.1 Describe Mutation Definition and Types of MutationDocument28 pages5.3.1 Describe Mutation Definition and Types of MutationLee llPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproduction in Organisms MCQDocument5 pagesReproduction in Organisms MCQKartik Gaming 2.0Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1 Cell Structure and Organization: Structur e FunctionDocument14 pages2.1 Cell Structure and Organization: Structur e Functionwafa eliasPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant - WikipediaDocument148 pagesPlant - WikipediaBashiir NuurPas encore d'évaluation
- NEET PPT Biology SyllabusDocument7 pagesNEET PPT Biology Syllabusjyotisharma20577Pas encore d'évaluation
- Malignant Phyllodes Tumor of Breast: Group 18Document16 pagesMalignant Phyllodes Tumor of Breast: Group 18Richard LivPas encore d'évaluation
- General ZoologyDocument736 pagesGeneral ZoologyShapnil Azam100% (1)
- DNA Replication 2014Document15 pagesDNA Replication 2014SATYANARAYANA RAO100% (1)
- Common Breeding Systems For Livestock ProductionDocument4 pagesCommon Breeding Systems For Livestock ProductionRica Mae EnvergaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Study GuideDocument207 pagesBiology Study GuideMaryClinton100% (2)
- Learning Module General Biology 1Document18 pagesLearning Module General Biology 1John Paull CuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ankita Sharma CrisprDocument41 pagesAnkita Sharma CrisprAnkita SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- B-Cell DevelopmentDocument85 pagesB-Cell Developmentعلي عايد عبدالشهيدPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 11: Reagent Manufacture: Guidelines For The Blood Transfusion ServicesDocument33 pagesChapter 11: Reagent Manufacture: Guidelines For The Blood Transfusion ServicesFuadPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Endocrinology Review Mcqs - Part 2: April 2020Document39 pagesPediatric Endocrinology Review Mcqs - Part 2: April 2020Bhagwani LohanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Revisiting The Stress Concept: Implications For Affective DisordersDocument10 pagesRevisiting The Stress Concept: Implications For Affective DisordersJefferson MorenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia PPT - KeyDocument16 pagesAnemia PPT - KeyAyman RehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 2 - EpitheliumDocument3 pagesQuiz 2 - EpitheliumstuffPas encore d'évaluation
- An Integer Linear Programming Solution For Domain Gene and Species Reconciliation ProblemDocument12 pagesAn Integer Linear Programming Solution For Domain Gene and Species Reconciliation Problemlei liPas encore d'évaluation
- Novel COVID-19 VaccineDocument25 pagesNovel COVID-19 VaccineJuan VidrioPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood (Anaphy)Document8 pagesBlood (Anaphy)CORONEL, SOPHIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Erythritol As SweetenerDocument9 pagesErythritol As SweetenerKishoPas encore d'évaluation
- Addiction: A Dysregulation of Satiety and Inflammatory ProcessesDocument27 pagesAddiction: A Dysregulation of Satiety and Inflammatory ProcessesAulas EspañolPas encore d'évaluation
- Skateboarders Study RevDocument2 pagesSkateboarders Study RevAnna YakutenokPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Kcet 2022 c4Document5 pagesBiology Kcet 2022 c4JohnsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology Mci One Liners MCQDocument21 pagesPathology Mci One Liners MCQadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Diego Alejandro Safian Carrillo QualificationsDocument3 pagesDiego Alejandro Safian Carrillo Qualificationsapi-615670705Pas encore d'évaluation
- L8 Peptide StructureDocument11 pagesL8 Peptide StructureCheng FuPas encore d'évaluation
- JMB 28 314 PDFDocument9 pagesJMB 28 314 PDFkenneth ogocPas encore d'évaluation
- Natural SelectionDocument7 pagesNatural SelectionDaniel BerryPas encore d'évaluation
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseD'EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (52)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldD'EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (597)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityD'EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsD'EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (6)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerD'EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (393)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomD'EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (216)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessD'Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (33)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceD'EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (517)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeD'EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifePas encore d'évaluation
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)D'EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (411)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceD'EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (18)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesD'EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (397)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedD'EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (11)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainD'EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (111)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionD'EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (812)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainD'EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (65)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorD'EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorPas encore d'évaluation
- Lymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthD'EverandLymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (13)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildD'EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (44)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindD'EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (93)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemD'EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (115)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsD'EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2083)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveD'EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (66)