Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Cascade Refrigeration
Transféré par
Adriel JohnDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Cascade Refrigeration
Transféré par
Adriel JohnDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
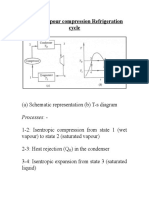
Cascade Refrigeration Cycle
This is a system that has 2 or more refrigeration cycles operating in series.
Cascade cycle is used where a very wide range of temperature between T L and
TH is required. As shown the figure, the condenser for the low temperature refrigerator is
used as the evaporator for the high temperature refrigerator.
Cascading improves the COP of a refrigeration cycle. Moreover, the refrigerants
can be selected to have reasonable evaporator and condenser pressures in the two or
more temperature ranges.
The two cycles are connected through the heat exchanger in the middle, which
serves as evaporator for cycle X and condenser for cycle Y. For the analysis of the
whole cascaded cycle:
Let: mX = mass flow rate of refrigerant in cycle X
mY = mass flow rate of refrigerant in cycle Y
The refrigeration capacity of the cycle, Q A
QA = mY (h1 - h4)
The heat rejected by the cycle, QR
QR = mX (h6 - h7)
The total input work in the cycle, W T
WT = WY + WX
W T = mY (h2 - h1) + mX (h6 - h5)
The coefficient of performance of the cycle, COP
𝑄 𝑚𝑌 (ℎ1 −ℎ4 )
𝐶𝑂𝑃 = 𝑊𝐴 = 𝑚
𝑇 𝑌 (ℎ2 −ℎ1 ) + 𝑚𝑋 (ℎ6 −ℎ5 )
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 2.theory: High Temperature Reservoir, TDocument4 pages2.theory: High Temperature Reservoir, TAman RedhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vapour Power Cycle Module 1Document59 pagesVapour Power Cycle Module 1ajaitkmPas encore d'évaluation
- Refrigeration CycleDocument32 pagesRefrigeration CycleAbdalla Faris100% (1)
- Exp 2Document3 pagesExp 2megfwfdkjPas encore d'évaluation
- Rankine Power and VCR Cycles PDFDocument9 pagesRankine Power and VCR Cycles PDFthienPas encore d'évaluation
- Literature ReviewDocument7 pagesLiterature ReviewNikylePas encore d'évaluation
- Rankine Cycle PDFDocument41 pagesRankine Cycle PDFAlmeghalawy83% (12)
- Analysis of Steam Power Plants - OB 2010Document57 pagesAnalysis of Steam Power Plants - OB 2010A_dotunPas encore d'évaluation
- Rankine and Carnot NumericalsDocument59 pagesRankine and Carnot NumericalsBhargav PrajwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 2 Vapor Compression CycleDocument18 pagesActivity 2 Vapor Compression CycleMahonyPas encore d'évaluation
- MM311 LAB 3 FinalDocument7 pagesMM311 LAB 3 FinaldipanshilPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec18 Reading WassgrenDocument6 pagesLec18 Reading WassgrenRupal ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Standard Vapor Compression Refrigeration CycleDocument11 pagesStandard Vapor Compression Refrigeration CyclejjPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied ThermodynamicsDocument48 pagesApplied Thermodynamicsdavesh jadonPas encore d'évaluation
- Cooling Tower TTTTDocument4 pagesCooling Tower TTTTمحمد المريسيPas encore d'évaluation
- Vapour Compression RefrigerationDocument38 pagesVapour Compression RefrigerationArvind75% (4)
- Unit - 4 Vapour Power Cycles: H T L PDocument14 pagesUnit - 4 Vapour Power Cycles: H T L PMukesh MystPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamics EquationsDocument11 pagesThermodynamics EquationsDilene DuarcadasPas encore d'évaluation
- PH Number 1Document40 pagesPH Number 1DhduPas encore d'évaluation
- Cop CalcDocument15 pagesCop CalcashwinsrvPas encore d'évaluation
- Carnot CycleDocument26 pagesCarnot CycleNafisa AnikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Engineering Lectures1Document120 pagesThermal Engineering Lectures1romasokyPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 2nd Law MAR PDFDocument14 pages4 2nd Law MAR PDFFarisPas encore d'évaluation
- Rankine Power Generation Cycle: Net NetDocument6 pagesRankine Power Generation Cycle: Net NetDofrt SlimobPas encore d'évaluation
- Refrigeration Comp. LinkedDocument6 pagesRefrigeration Comp. LinkedDin TescoPas encore d'évaluation
- 9621572Document6 pages9621572aliscribd46Pas encore d'évaluation
- Air ConditioningDocument20 pagesAir ConditioningJohanne Franz Calacday100% (1)
- Performance Analysis of 404a/508b Cascade Refrigeration Cycle For Low TemperatureDocument7 pagesPerformance Analysis of 404a/508b Cascade Refrigeration Cycle For Low TemperaturewbpeterPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Power PlantDocument99 pagesThermal Power PlantVishal Patel100% (3)
- Refrigeration SystemDocument30 pagesRefrigeration SystemMay Jade Genzola EsparesPas encore d'évaluation
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument263 pagesRefrigeration and Air ConditioningAjeet Verma92% (12)
- Carnot Vapour Compression Refrigeration Cycle: (A) Schematic Representation (B) T-S DiagramDocument6 pagesCarnot Vapour Compression Refrigeration Cycle: (A) Schematic Representation (B) T-S DiagramdhruvPas encore d'évaluation
- Refrigeracion y Bombas de CalorDocument58 pagesRefrigeracion y Bombas de CalorAnonymous GOKse1EaPPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.4 Heat Ex ChangersDocument7 pages4.4 Heat Ex Changersmukesh kaushikPas encore d'évaluation
- Innovative Vapor CompressionDocument13 pagesInnovative Vapor CompressionCj MoLanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Innovative Vapor-CompressionDocument13 pagesInnovative Vapor-CompressionCj MoLanoPas encore d'évaluation
- 251 2nd Law MARDocument14 pages251 2nd Law MARAdiela Syuhada RoslanPas encore d'évaluation
- Intermediate Thermodynamics Cycles: Heat-Engine CycleDocument7 pagesIntermediate Thermodynamics Cycles: Heat-Engine Cycleabdul_rehman_124Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 8Document20 pagesLecture 8Bradee DoodeePas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment of Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument30 pagesExperiment of Refrigeration and Air ConditioningNitin KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 351 Chap1 Refrigeration Intro 2014Document24 pages351 Chap1 Refrigeration Intro 2014Faiz AmeeriPas encore d'évaluation
- IV. Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument48 pagesIV. Second Law of ThermodynamicsBORASCA EZEKIELPas encore d'évaluation
- Abhas PoewerDocument6 pagesAbhas PoewerPranay IndurkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Two - Part 2: Air Cycle Refrigeration SystemsDocument58 pagesChapter Two - Part 2: Air Cycle Refrigeration SystemshermelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Juice HeatersDocument3 pagesJuice HeatersqqyukiPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Heat Exchanger Equations and Calculations: Perry'sDocument1 pageBasic Heat Exchanger Equations and Calculations: Perry'sPrathap VuyyuruPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyclic Process Second Law EnginesDocument18 pagesCyclic Process Second Law EnginesM Khaidiz RafiPas encore d'évaluation
- J. Gas CyclesDocument8 pagesJ. Gas CyclesdaphcosiPas encore d'évaluation
- Figure 1. Rankine Cycle PV and Ts DiagramDocument3 pagesFigure 1. Rankine Cycle PV and Ts DiagramM-a MarayagPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT-4 Part-1Document65 pagesUNIT-4 Part-1harish9Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cycle EfficiencyDocument17 pagesCycle Efficiencyrashm006ranjanPas encore d'évaluation
- RefrigerationDocument163 pagesRefrigerationali105Pas encore d'évaluation
- Me204 March 29 2023Document40 pagesMe204 March 29 2023naverfallPas encore d'évaluation
- Worked Problems in Heat, Thermodynamics and Kinetic Theory for Physics Students: The Commonwealth and International Library: Physics DivisionD'EverandWorked Problems in Heat, Thermodynamics and Kinetic Theory for Physics Students: The Commonwealth and International Library: Physics DivisionÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (3)
- Experiment No. 3 Applications of Bernoulli'S Equation - Computational LaboratoryDocument1 pageExperiment No. 3 Applications of Bernoulli'S Equation - Computational LaboratoryAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Turbines: Problem SetDocument5 pagesTurbines: Problem SetAdriel John67% (3)
- Planning: By: Engr. Marizen B. ContrerasDocument53 pagesPlanning: By: Engr. Marizen B. ContrerasAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Machine Elements 2 (Me18 Lec & Lab) Date: HOME EXERCISE - Bodies in Pure Rolling ContactDocument1 pageMachine Elements 2 (Me18 Lec & Lab) Date: HOME EXERCISE - Bodies in Pure Rolling ContactAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- GEARSDocument1 pageGEARSAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Machine Elements 2 (Lec & Lab) Mechanical Engineering DeptDocument1 pageMachine Elements 2 (Lec & Lab) Mechanical Engineering DeptAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Name: Section: Activity 3 Ericsson and Brayton Cycle (For LMS)Document3 pagesName: Section: Activity 3 Ericsson and Brayton Cycle (For LMS)Adriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Belts, Ropes and Chain: Flexible ConnectorsDocument3 pagesBelts, Ropes and Chain: Flexible ConnectorsAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Machine Elements 2 (Lec & Lab) Mechanical Engineering DeptDocument1 pageMachine Elements 2 (Lec & Lab) Mechanical Engineering DeptAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- ME18 Lec6 - Gear TrainsDocument28 pagesME18 Lec6 - Gear TrainsAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- CBA Activity 3.6 Yrs Moses and Aaron Meet With Pharaoh PDFDocument1 pageCBA Activity 3.6 Yrs Moses and Aaron Meet With Pharaoh PDFAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Moses and Aaron Meet With Pharaoh Story Guide PDFDocument1 pageMoses and Aaron Meet With Pharaoh Story Guide PDFAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- ME LabDocument28 pagesME LabAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Gear Train USEFUL FOMULAS AND RELATIONSHIPSDocument1 pageGear Train USEFUL FOMULAS AND RELATIONSHIPSAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Machine Elements 2 (Lec & Lab) Mechanical Engineering DeptDocument1 pageMachine Elements 2 (Lec & Lab) Mechanical Engineering DeptAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- The Passover Story Guide - 1Document1 pageThe Passover Story Guide - 1Adriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- God Sends Plagues On Egypt Story Guide Part 2Document1 pageGod Sends Plagues On Egypt Story Guide Part 2Adriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Turbines: Problem SetDocument5 pagesTurbines: Problem SetAdriel John67% (3)
- Pointers For ReviewDocument3 pagesPointers For ReviewAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- CBA Activity 3.6 Yrs Moses and Aaron Meet With Pharaoh PDFDocument1 pageCBA Activity 3.6 Yrs Moses and Aaron Meet With Pharaoh PDFAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Refrigerants Table-SI Unit PDFDocument31 pagesRefrigerants Table-SI Unit PDFAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- SharefaithDocument4 pagesSharefaithAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Handout 4 Losses of DC Generator and EfficiencyDocument13 pagesHandout 4 Losses of DC Generator and EfficiencyKhate ÜüPas encore d'évaluation
- MD StressesDocument34 pagesMD StressesAdriel John50% (2)
- Handout 3 Types of DC GeneratorsDocument11 pagesHandout 3 Types of DC GeneratorsAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Handout 3 Types of DC GeneratorsDocument11 pagesHandout 3 Types of DC GeneratorsAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Ece1: Electronic Devices and Circuits: Semiconductor BasicsDocument71 pagesEce1: Electronic Devices and Circuits: Semiconductor BasicsAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Instruction: Solve The Following ProblemsDocument1 pageInstruction: Solve The Following ProblemsAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Bible StoryDocument1 pageBible StoryAdriel JohnPas encore d'évaluation