Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Philippine Science High School - Bicol Region Campus
Transféré par
Neon Z0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
35 vues4 pagesTitre original
Course-Outline-for-Grade-9
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
35 vues4 pagesPhilippine Science High School - Bicol Region Campus
Transféré par
Neon ZDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Science and Technology
Philippine Science High School System
PHILIPPINE SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL – BICOL REGION CAMPUS
MATHEMATICS UNIT
Tagongtong, Goa, Camarines Sur 4422
Telefax: (054) 453-2048
http://www.brc.pshs.edu.ph
Pursuit of Truth Passion for Excellence Commitment to Service
Math 3-Fourth Quarter, SY 2019-2020
ONLINE COURSE
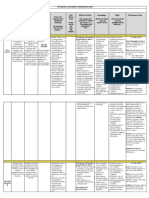
Topics Desired Learning Competencies
A. Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
1. Applications of Exponential and Applies exponential and logarithmic functions in
Logarithmic Functions ( Compound Interest, modelling and solving real life problems.
Exponential Growth,
Exponential/Radioactive Decay,
Continuously Compounded Interest, Richter
Scales)
B. Functions as Mathematical Models
1. Building Functions to Model Relationships Uses knowledge involving functions and
between two Quantities variations to analyze relationships between two
quantities.
Models functions using various strategies,
manipulative devices (e.g. construction tools,
graphing paper) and ICT tools ( e.g. graphing
calculator, spreadsheet, graphing software)
Include problems involving
Uniform motion ( linear function)
Projectile (quadratic function)
Transportation fare or freight charges, change
relationship over a period of time, e.g. foreign
exchange rate, body mass ( piecewise-defined
function)
2. Using Functions to Model Relationships of
Real Life Data Half-life ( logarithmic function)
Exponential growth (exponential function)
Uses knowledge of the graphs and properties of
functions to determine the appropriate function
that best describes a real life data.
Models the relationship found in real life data
using different forms: tabular method, graphical
method, equation form, mapping notations.
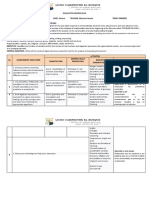
C. Sequences and Series
1. Sequences
1.1. Definition of a Sequence Define a sequence.
Differentiates between finite and infinite
sequences.
Uses mathematical terms to describe sequences.
Finds the sequence function/rule for a given
sequence.
1.2. Arithmetic Sequence Finds a particular term or the nth term in a given
sequence.
Defines an arithmetic sequence and related terms
1.3. Geometric Sequence such as common difference, arithmetic mean
Finds the nth term of an arithmetic sequence
1.4. Other Types of Sequences Defines a geometric sequence and related terms
such as common ratio, geometric mean
Finds the nth term of a geometric sequence
Explores harmonic sequence and Fibonacci
sequence
Exclude:
2. Series Sequences other than harmonic and Fibonacci.
2.1. Arithmetic Series Harmonic mean
2.2. Geometric Series Defines an arithmetic series and notations used to
represent an arithmetic series
Finds the partial sums of an arithmetic series.
Defines a geometric series and notations used to
represent a geometric series.
2.3.Applications Differentiates between finite and infinite
geometric series
Finds the sum of the terms in a finite geometric
sequence.
Differentiates between convergent and divergent
infinite geometric series
Finds the sum of an infinite geometric sequence.
Solves problems involving arithmetic and
geometric series ( e.g. simple interest, “bouncing”
ball, geometric patterns, family tree, binary tree)
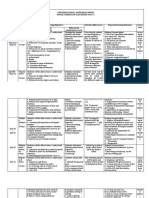
D. Pascal’s Triangle
1. Patterns in the Pascal’s Triangle Identifies the entries in the Pascal’s Triangle.
Identifies different patterns in the Pascal’s
Triangle.
2. Binomial Expansion
Revisits products involving binomials.
Expands powers of binomials using Pascal’s
Triangle.
Finds a particular term in a binomial expansion.
Exclude:
Binomial expansion with degree higher than 6.
Proof of the Binomial Theorem
Use of combination to find the nth term in a
binomial expansion
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Mathematics Grade 8: Op Sienna System Consensus Map Subject Area: Grade LevelDocument5 pagesMathematics Grade 8: Op Sienna System Consensus Map Subject Area: Grade LevelDionel RizoPas encore d'évaluation
- Discrete Math Course for B.Ed. StudentsDocument6 pagesDiscrete Math Course for B.Ed. StudentsExtra MailPas encore d'évaluation
- 4th form syllabus 16-17Document5 pages4th form syllabus 16-17RealGenius (Carl)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ncert Learning Outcomes 9 t0 12 MathematicsDocument23 pagesNcert Learning Outcomes 9 t0 12 MathematicsAyush SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- KS4+Curriculum+Overview+ (F) + +2022.23Document4 pagesKS4+Curriculum+Overview+ (F) + +2022.23Isra MehmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Map Math 10Document10 pagesCurriculum Map Math 10Richimon LicerioPas encore d'évaluation
- MathDocument3 pagesMathJehu Rosario SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Algebra - Module 1Document22 pagesLinear Algebra - Module 1api-619738021Pas encore d'évaluation
- G8DLL Q3W2Document5 pagesG8DLL Q3W2NEithan DeldocPas encore d'évaluation
- Math-10-Week-1-Richard DominguezDocument8 pagesMath-10-Week-1-Richard DominguezCharizz DominguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1: Patterns and Sequences (Module 1) Week 1Document11 pagesChapter 1: Patterns and Sequences (Module 1) Week 1hanazan87Pas encore d'évaluation
- G 11 AddmaDocument5 pagesG 11 AddmaJoshuaPas encore d'évaluation
- BSCE Course Outline - PreCalculusDocument4 pagesBSCE Course Outline - PreCalculusClaire GubatPas encore d'évaluation
- G 12 AddmaDocument2 pagesG 12 AddmaJoshuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cmo 61 S. 2006 Course Specification For The BS ArchitectureDocument83 pagesCmo 61 S. 2006 Course Specification For The BS ArchitectureAlwyn Ramos100% (4)
- Genmath Most Essential Learning Competencies MelcsDocument3 pagesGenmath Most Essential Learning Competencies MelcsJerson FulgencioPas encore d'évaluation
- Crosscutting Concepts Graphic OrganizersDocument9 pagesCrosscutting Concepts Graphic Organizersapi-550508557Pas encore d'évaluation
- T.C. 10°-N°8Document12 pagesT.C. 10°-N°8vogosoc129Pas encore d'évaluation
- Course Syllabus in General Mathematics: Semester No. of Hours/Semester: 80hours/semesterDocument6 pagesCourse Syllabus in General Mathematics: Semester No. of Hours/Semester: 80hours/semesterPrincess Racquel DizonPas encore d'évaluation
- You Will Find The Student Text, Newsletter Standards For The Module, Homework Help Links and More!Document4 pagesYou Will Find The Student Text, Newsletter Standards For The Module, Homework Help Links and More!Sangeetha SumamPas encore d'évaluation
- Content Standards: Course Outline in Grade 8 MathematicsDocument3 pagesContent Standards: Course Outline in Grade 8 MathematicsJessica Bascon AlidonPas encore d'évaluation
- Dlp-8 (Week 4 Day 3)Document4 pagesDlp-8 (Week 4 Day 3)JESSA CANOPINPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 7 Sequences and Series Unit PlanDocument6 pagesUnit 7 Sequences and Series Unit PlanRonard OriolPas encore d'évaluation
- Mastering Math ConceptsDocument9 pagesMastering Math ConceptsJoecel De Guzman TorrefrancaPas encore d'évaluation
- Quarter 3 - Week 1Document5 pagesQuarter 3 - Week 1Valein PrincenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Specifications - PSG For BS Architecture (Approved 20 PDFDocument83 pagesCourse Specifications - PSG For BS Architecture (Approved 20 PDFAna Arcangel100% (1)
- Formato de Planificacion Semestral - PrecalculusDocument6 pagesFormato de Planificacion Semestral - PrecalculusErvin Isaac RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- YRLY SCHEME F4 2018 Tukar ChapterDocument8 pagesYRLY SCHEME F4 2018 Tukar ChaptercasbenxPas encore d'évaluation
- MELCs MATHEMATICSDocument19 pagesMELCs MATHEMATICSNiel Marc TomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Annex A (EE)Document19 pagesAnnex A (EE)Shibing DibingPas encore d'évaluation
- Applying sequences and polynomials to design round banquet tablesDocument49 pagesApplying sequences and polynomials to design round banquet tablesSarah Faye Mercado BedañaPas encore d'évaluation
- Year 11 Maths Methods Term 2 2023 V2Document3 pagesYear 11 Maths Methods Term 2 2023 V2Hannah LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus DLL Week 6Document7 pagesCalculus DLL Week 6Gianmarie Sumagaysay HiladoPas encore d'évaluation
- Further Mathematics or Mathematics ElectiveDocument18 pagesFurther Mathematics or Mathematics ElectiveBukola AdewalePas encore d'évaluation
- Course Number Course Title Credit/s Semester/Term/School Year Schedule College or DepartmentDocument8 pagesCourse Number Course Title Credit/s Semester/Term/School Year Schedule College or DepartmentHarvey RatunilPas encore d'évaluation
- MELCS Pre CalculusDocument2 pagesMELCS Pre CalculusLiedi Brigette100% (4)
- Mathematics 10 Course Guide SY 2021-2022: Topic Coverage Learning CompetenciesDocument3 pagesMathematics 10 Course Guide SY 2021-2022: Topic Coverage Learning CompetenciesMarc Angelo C. CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- MELCS-General MathematicsDocument3 pagesMELCS-General MathematicsLiedi BrigettePas encore d'évaluation
- DAILY-LESSON-LOG-QUARTER-3-WEEK-3-Math 8-MillanDocument5 pagesDAILY-LESSON-LOG-QUARTER-3-WEEK-3-Math 8-MillanNoah Anne Sunga MillanPas encore d'évaluation
- Yeomans CM Educ350 4 17 2022Document3 pagesYeomans CM Educ350 4 17 2022api-609846266Pas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Math 1 OutlineDocument9 pagesEngineering Math 1 OutlineIbrahim AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometric constructions unit focuses on artistryDocument6 pagesGeometric constructions unit focuses on artistryDeema El Masri100% (1)
- Assessment Section 3.1Document6 pagesAssessment Section 3.1ROSE MARIE REVILLAPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 8 SyllabusDocument14 pagesMath 8 SyllabusJamoi Ray VedastoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Calculus Curriculum GuideDocument9 pagesPre-Calculus Curriculum GuideShajara Del RosarioPas encore d'évaluation
- CM - Mathematics 10Document5 pagesCM - Mathematics 10Emalyn CataytayPas encore d'évaluation
- Matriz 1er Periodo Grado Octavo. 2023 MathDocument2 pagesMatriz 1er Periodo Grado Octavo. 2023 MathMauricio Javier Acosta SolerPas encore d'évaluation
- Division of City Schools-Angeles CityDocument4 pagesDivision of City Schools-Angeles CityReylaine Mitz BaldonPas encore d'évaluation
- 0606 Teaching PlanDocument9 pages0606 Teaching PlanKyle ZhangPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Algebra SyllabusDocument4 pagesLinear Algebra SyllabusroniloPas encore d'évaluation
- MathDocument3 pagesMathJehu Rosario SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Scheme of Work For Form 4 Physics Yearly Teaching Plan 2013: Learning Area: 1. Introduction To PhysicsDocument19 pagesScheme of Work For Form 4 Physics Yearly Teaching Plan 2013: Learning Area: 1. Introduction To PhysicsbighaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics_XIDocument7 pagesMathematics_XIDhanalakshmi ThiyagarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Annex III-Course Specifications For ChEDocument94 pagesAnnex III-Course Specifications For ChETheresa TuliaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bow-Math 10Document5 pagesBow-Math 10marissa turlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus in Mathematics (Grade 9)Document5 pagesSyllabus in Mathematics (Grade 9)Nestor Abante Valiao Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Most Essential Learning Module in Mathematics 2020Document14 pagesMost Essential Learning Module in Mathematics 2020Mary Jane De YroPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical Methods: Linear Algebra / Normed Spaces / Distributions / IntegrationD'EverandMathematical Methods: Linear Algebra / Normed Spaces / Distributions / IntegrationPas encore d'évaluation
- Measure and Integration Theory on Infinite-Dimensional Spaces: Abstract harmonic analysisD'EverandMeasure and Integration Theory on Infinite-Dimensional Spaces: Abstract harmonic analysisPas encore d'évaluation
- A Geometric Algebra Invitation to Space-Time Physics, Robotics and Molecular GeometryD'EverandA Geometric Algebra Invitation to Space-Time Physics, Robotics and Molecular GeometryPas encore d'évaluation
- Violet Evergarden MedleyDocument9 pagesViolet Evergarden Medleyedi santosoPas encore d'évaluation
- BIO 1 - LT 2 For 3rd Quarter 2020Document2 pagesBIO 1 - LT 2 For 3rd Quarter 2020Neon ZPas encore d'évaluation
- Binomial DistributionDocument34 pagesBinomial DistributionNeon ZPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistics Assignment - Probability QuestionsDocument1 pageStatistics Assignment - Probability QuestionsNeon ZPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment - Probability Distribution PDFDocument1 pageAssignment - Probability Distribution PDFNeon ZPas encore d'évaluation
- PSHS-Bicol Region year-end clearance proceduresDocument2 pagesPSHS-Bicol Region year-end clearance proceduresNeon ZPas encore d'évaluation
- Essay RubricDocument3 pagesEssay RubricRobertPas encore d'évaluation
- Memorization Movemen Costume/Attire Diction, Projection, and Vocal Variety Emotion Focal Point and FocusDocument3 pagesMemorization Movemen Costume/Attire Diction, Projection, and Vocal Variety Emotion Focal Point and FocusNeon ZPas encore d'évaluation
- Lucrecia KasilagDocument140 pagesLucrecia KasilagNJ LinPas encore d'évaluation
- Lucrecia KasilagDocument140 pagesLucrecia KasilagNJ LinPas encore d'évaluation
- Music and Health 3Document11 pagesMusic and Health 3Neon ZPas encore d'évaluation
- Flight of The Bumblebee PDFDocument3 pagesFlight of The Bumblebee PDFNeon ZPas encore d'évaluation
- OLD1 - Earth Lab Volcanoes FillableDocument2 pagesOLD1 - Earth Lab Volcanoes FillableNeon ZPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistics Assignment - Probability QuestionsDocument1 pageStatistics Assignment - Probability QuestionsNeon ZPas encore d'évaluation
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumentNeon ZPas encore d'évaluation
- Vivaldi Mandolin Concerto in C Major RV425Document5 pagesVivaldi Mandolin Concerto in C Major RV425Cristina E. CiortanPas encore d'évaluation
- Binomial DistributionDocument34 pagesBinomial DistributionNeon ZPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Handling - WS7Document5 pagesData Handling - WS7Anshu MakinPas encore d'évaluation
- Fractions, Decimals, and Percentages Math Quiz with AnswersDocument11 pagesFractions, Decimals, and Percentages Math Quiz with AnswersRuth AbrogarPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet MicorDocument42 pagesSheet MicorFiras TaherPas encore d'évaluation
- WEEK 3 - Q2 - Math 7Document14 pagesWEEK 3 - Q2 - Math 7JENNILYN MAKALINTALPas encore d'évaluation
- Gr.10 First PTDocument4 pagesGr.10 First PTericmilamattim50% (2)
- 121ax007 CN Exp 08Document6 pages121ax007 CN Exp 08rrrPas encore d'évaluation
- EE 5324 - VLSI Design IIDocument63 pagesEE 5324 - VLSI Design IINarasimhan KaushikPas encore d'évaluation
- Fibonacci 0Document8 pagesFibonacci 0sergejbmtPas encore d'évaluation
- CpE 71: Boolean functionsDocument3 pagesCpE 71: Boolean functionsSiva ChPas encore d'évaluation
- 100 Algebra For CalculusDocument11 pages100 Algebra For Calculusmvlada137368Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of FractionsDocument5 pagesFundamentals of FractionssingenaadamPas encore d'évaluation
- Noise in and As MusicDocument259 pagesNoise in and As MusicDougy McDougerson100% (1)
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument16 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesKim DomingoPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd Mock Test........Document24 pages3rd Mock Test........fahad AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Slides XDocument241 pagesSlides XParveen DagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Speaking Mathematically: Prepared By: Jan Marie P. LubuguinDocument31 pagesSpeaking Mathematically: Prepared By: Jan Marie P. LubuguinElle Villanueva VlogPas encore d'évaluation
- Sequences of Real NumbersDocument55 pagesSequences of Real NumbersVijay ChhipaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assembly Language For x86 Processors: Chapter 1: Basic ConceptsDocument41 pagesAssembly Language For x86 Processors: Chapter 1: Basic ConceptsGhulam HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- AE305 Numerical MethodsDocument7 pagesAE305 Numerical MethodsgarkinPas encore d'évaluation
- Accuplacer Sample Questions For Students PDFDocument26 pagesAccuplacer Sample Questions For Students PDFSusmita SapkotaPas encore d'évaluation
- Observarion + (+1) TH Median of Continuous Frequency9Document9 pagesObservarion + (+1) TH Median of Continuous Frequency9Arpit SadotraPas encore d'évaluation
- Logarithm (Trigonometry)Document9 pagesLogarithm (Trigonometry)Axel Joy AlonPas encore d'évaluation
- Permutation and Combination Problems from JEE Main ExamDocument12 pagesPermutation and Combination Problems from JEE Main ExamVineet VijaykumarPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAP 1-5-Business Mathematics-Updated July 7Document56 pagesCHAP 1-5-Business Mathematics-Updated July 7Cressa Catacutan100% (2)
- Maths WorksheetDocument220 pagesMaths WorksheetViraj J DakshPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical InductionDocument13 pagesMathematical InductionysannynielhanadatucaliPas encore d'évaluation
- n5 PercentagesDocument59 pagesn5 PercentagesamerzPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet 1-2Document3 pagesSheet 1-2mira CyrusPas encore d'évaluation
- In Partial Fulfilment of The Requirements For Bsem 21Document7 pagesIn Partial Fulfilment of The Requirements For Bsem 21Mylene RiegoPas encore d'évaluation
- Abm Bus Math Q1 M1Document6 pagesAbm Bus Math Q1 M1Renny Romero LuzadaPas encore d'évaluation