Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Ias 23 - Borrowing Cost
Transféré par
Mohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri AttariCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Ias 23 - Borrowing Cost
Transféré par
Mohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri AttariDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
FFQA 1
IAS 23
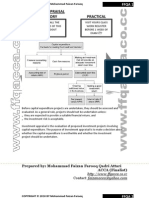
Objective of IAS 23
The objective of IAS 23 is to prescribe the accounting treatment
for borrowing costs. Borrowing costs include interest on bank
overdrafts and borrowings, amortisation of discounts or
premiums on borrowings, finance charges on finance leases and
exchange differences on foreign currency borrowings where they
are regarded as an adjustment to interest costs.
Key Definitions
Borrowing cost may include:
• interest expense calculated by the effective interest method
under IAS 39,
• finance charges in respect of finance leases recognised in
accordance with IAS 17 Leases, and
• exchange differences arising from foreign currency
borrowings to the extent that they are regarded as an
adjustment to interest costs
This standard does not deal with the actual or imputed cost of
equity, including any preferred capital not classified as a liability
pursuant to IAS 32.
A qualifying asset is an asset that takes a substantial period of
time to get ready for its intended use or sale. [IAS 23.5] That
could be property, plant, and equipment and investment property
during the construction period, intangible assets during the
development period, or "made-to-order" inventories.
Two types of assets that would otherwise be qualifying assets
are excluded from the scope of IAS 23:
• qualifying assets measured at fair value, such as biological
assets accounted for under IAS 41 Agriculture
• inventories that are manufactured, or otherwise produced,
in large quantities on a repetitive basis and that take a
substantial period to get ready for sale (for example,
maturing whisky)
FFQA 2
Accounting Treatment
Recognition
Borrowing costs that are directly attributable to the acquisition,
construction or production of a qualifying asset form part of the
cost of that asset and, therefore, should be capitalised. Other
borrowing costs are recognised as an expense.
The foregoing reflects revisions to IAS 23 adopted by the IASB in
March 2007 that prohibit immediate expensing of borrowing
costs. Those revisions are effective for borrowing costs relating
to qualifying assets for which the commencement date for
capitalisation is on or after 1 January 2009. Earlier application is
permitted.
Until that revision was effective, an entity could apply the
previous version of IAS 23, which permitted, as an accounting
policy option, the 'immediate expensing model'. Under that
model, all borrowing costs should be expensed in the period in
which they are incurred.
Measurement
Where funds are borrowed specifically, costs eligible for
capitalisation are the actual costs incurred less any income
earned on the temporary investment of such borrowings Where
funds are part of a general pool, the eligible amount is
determined by applying a capitalisation rate to the expenditure
on that asset. The capitalisation rate will be the weighted
average of the borrowing costs applicable to the general pool.
Capitalisation should commence when expenditures are being
incurred, borrowing costs are being incurred and activities that
are necessary to prepare the asset for its intended use or sale
are in progress (may include some activities prior to
commencement of physical production). [IAS 23.17-18]
Capitalisation should be suspended during periods in which
active development is interrupted. [IAS 23.20] Capitalisation
should cease when substantially all of the activities necessary to
prepare the asset for its intended use or sale are complete. If
FFQA 3
only minor modifications are outstanding, this indicates that
substantially all of the activities are complete.
Where construction is completed in stages, which can be used
while construction of the other parts continues, capitalisation of
attributable borrowing costs should cease when substantially all
of the activities necessary to prepare that part for its intended
use or sale are complete.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Summary of Ias 23 Borrowing CostsDocument2 pagesSummary of Ias 23 Borrowing CostsenzoPas encore d'évaluation
- IAS 23 - Borrowing CostDocument1 pageIAS 23 - Borrowing CostMarc Eric RedondoPas encore d'évaluation
- Borrowing CostDocument3 pagesBorrowing Costsimply PrettyPas encore d'évaluation
- Borrowing Costs NotesDocument2 pagesBorrowing Costs NotesMariella Olympia PanuncialesPas encore d'évaluation
- Ias 23Document2 pagesIas 23SarmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Objective of IAS 23Document2 pagesObjective of IAS 23asad19Pas encore d'évaluation
- Or Sale.: MODULE 3: Borrowing CostsDocument1 pageOr Sale.: MODULE 3: Borrowing CostsPauline Joy GenalagonPas encore d'évaluation
- Ias 23 Borrowing CostsDocument4 pagesIas 23 Borrowing CostsMevika MerchantPas encore d'évaluation
- IAS 23Document3 pagesIAS 23AtifPas encore d'évaluation
- IAS 23 Borrowing CostsDocument11 pagesIAS 23 Borrowing Costsksmuthupandian2098Pas encore d'évaluation
- Borrowing Costs IAS 23Document15 pagesBorrowing Costs IAS 23NataliePas encore d'évaluation
- BORROWING COSTS With AnswerDocument3 pagesBORROWING COSTS With AnswerMaePas encore d'évaluation
- Article Review IAS 23Document3 pagesArticle Review IAS 23belay27hailePas encore d'évaluation
- FR - Accounting For Transactions in Financial Statements: Borrowing Costs - IAS23Document2 pagesFR - Accounting For Transactions in Financial Statements: Borrowing Costs - IAS23User Upload and downloadPas encore d'évaluation
- These Questions Help You Recognize Your Existing Background Knowledge On The Topic. Answer Honestly. Yes NoDocument2 pagesThese Questions Help You Recognize Your Existing Background Knowledge On The Topic. Answer Honestly. Yes NocykenPas encore d'évaluation
- Borrowing Costs: International Accounting Standard 23Document19 pagesBorrowing Costs: International Accounting Standard 23Bakhtawer Awan0% (1)
- IAS 23 Borrowing CostsDocument25 pagesIAS 23 Borrowing Costsঅরূপ মিস্ত্রী বলেছেনPas encore d'évaluation
- IAS 23 Borrowing Costs Standard SummaryDocument10 pagesIAS 23 Borrowing Costs Standard SummaryTJ PalancaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ias 23 PDFDocument4 pagesIas 23 PDFArvind PremPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting For Borrowing CostDocument25 pagesAccounting For Borrowing CostOKORIE UKAMAKAPas encore d'évaluation
- Borrowing CostDocument47 pagesBorrowing CostHaseeb Ullah KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- IAS 23 BORROWING COST ACCOUNTINGDocument3 pagesIAS 23 BORROWING COST ACCOUNTINGmae acuestaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ias 23Document18 pagesIas 23Shah KamalPas encore d'évaluation
- Ancillary Costs Incurred in Connection With The Arrangement of BorrowingDocument2 pagesAncillary Costs Incurred in Connection With The Arrangement of BorrowingRazel TercinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Borrowing CostDocument2 pagesBorrowing CostNICOLE HIPOLITOPas encore d'évaluation
- 19 Borrowing CostsDocument2 pages19 Borrowing CostsLara Jane Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Borrowing CostDocument2 pagesBorrowing CostNICOLE HIPOLITOPas encore d'évaluation
- Borrowing Cost PDFDocument2 pagesBorrowing Cost PDFVillaruz Shereen MaePas encore d'évaluation
- IndAS23 2020 10112020Document11 pagesIndAS23 2020 10112020VIVEK M VPas encore d'évaluation
- Borrowed Funds ExplainedDocument2 pagesBorrowed Funds ExplainedOm JogiPas encore d'évaluation
- Borrowing Costs PDFDocument9 pagesBorrowing Costs PDFanjcabsPas encore d'évaluation
- IndAS 23Document2 pagesIndAS 23ca.sanket1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reviewer Borrowing Cost Sec. 1-10Document4 pagesReviewer Borrowing Cost Sec. 1-10imsana minatozakiPas encore d'évaluation
- IAS 23 - Borrowing CostDocument4 pagesIAS 23 - Borrowing CostMuhammad QamarPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting Standard 16Document7 pagesAccounting Standard 16Gaurav JadhavPas encore d'évaluation
- Compromise Settlements and Technical Write-OffsDocument5 pagesCompromise Settlements and Technical Write-OffsSaurabh MalooPas encore d'évaluation
- Borrowing CostsDocument19 pagesBorrowing CostsIrfan100% (20)
- CH 2 Real EstateDocument8 pagesCH 2 Real EstateRia ChoithaniPas encore d'évaluation
- CFAS Notes For FINALS PDFDocument26 pagesCFAS Notes For FINALS PDFMarife PangesbanPas encore d'évaluation
- Borrowing Cost (Ind AS-23) - Taxguru - inDocument5 pagesBorrowing Cost (Ind AS-23) - Taxguru - inalok kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 23 Borrowing CostsDocument10 pages23 Borrowing CostsChelsea Anne VidalloPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 11 - Borrowing CostsDocument6 pagesModule 11 - Borrowing CostsJehPoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting StandardDocument8 pagesAccounting StandardOnkar Ashok KeljiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ias 23Document2 pagesIas 23mnhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting PolicyDocument28 pagesAccounting PolicyAkshay AnandPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 3 - Borrowing CostsDocument3 pagesModule 3 - Borrowing CostsLui100% (1)
- Assignment 7 Accounting Theory Darma Yulia 21043031Document8 pagesAssignment 7 Accounting Theory Darma Yulia 21043031Darma YuliaPas encore d'évaluation
- IAS 11 Construction ContractsDocument15 pagesIAS 11 Construction ContractsIsrahayda LuPas encore d'évaluation
- Borrowing Costs: IAS Standard 23Document10 pagesBorrowing Costs: IAS Standard 23JorreyGarciaOplasPas encore d'évaluation
- Borrowing Costs, Investment Properties PensionsDocument38 pagesBorrowing Costs, Investment Properties PensionsArchana DevdasPas encore d'évaluation
- Revised IAS 23 Capitalizes All Borrowing CostsDocument8 pagesRevised IAS 23 Capitalizes All Borrowing Costssalehin1969Pas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Ias 39Document17 pagesSummary of Ias 39Rajshree LaturiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting Standard (As) 16Document20 pagesAccounting Standard (As) 16vvs176975Pas encore d'évaluation
- IFRS 9 Financial Instruments SummaryDocument17 pagesIFRS 9 Financial Instruments SummaryrasfazzzataPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting Standard (AS) 16 Borrowing Costs: ExplanationDocument5 pagesAccounting Standard (AS) 16 Borrowing Costs: ExplanationArshad Hussain MazumderPas encore d'évaluation
- Case 7.3 and 8Document24 pagesCase 7.3 and 8Bertha Muhammad SyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Mega Project Assurance: Volume One - The Terminological DictionaryD'EverandMega Project Assurance: Volume One - The Terminological DictionaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost BehaviourDocument34 pagesCost BehaviourMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri AttariPas encore d'évaluation
- Motivation: Prepared By: Mohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri Attari ACCA (Finalist) ContactDocument9 pagesMotivation: Prepared By: Mohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri Attari ACCA (Finalist) ContactMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri AttariPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost ClassificationDocument19 pagesCost ClassificationMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri Attari100% (1)
- Limiting Factors & Linear ProgrammingDocument8 pagesLimiting Factors & Linear ProgrammingMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri AttariPas encore d'évaluation
- Control, Audit and Security - ACCA F1Document13 pagesControl, Audit and Security - ACCA F1Mohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri AttariPas encore d'évaluation
- Bank ReconciliationDocument7 pagesBank ReconciliationMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri AttariPas encore d'évaluation
- Kaplan Exam Tips - FfqaDocument7 pagesKaplan Exam Tips - FfqaMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri AttariPas encore d'évaluation
- Throughput AccountingDocument5 pagesThroughput AccountingMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri AttariPas encore d'évaluation
- Profiles of The Faculty Members FNRDocument1 pageProfiles of The Faculty Members FNRFaizan Farooq Qadri AttariPas encore d'évaluation
- IAS 16 by FFQADocument9 pagesIAS 16 by FFQAMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri Attari0% (1)
- Law of PartnershipDocument8 pagesLaw of PartnershipMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri AttariPas encore d'évaluation
- F2 Main MockDocument38 pagesF2 Main MockMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri AttariPas encore d'évaluation
- Law of AgencyDocument12 pagesLaw of AgencyMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri Attari100% (2)
- Ias 37Document7 pagesIas 37Mohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri AttariPas encore d'évaluation
- Ias 10 - Events After Reporting PeriodDocument3 pagesIas 10 - Events After Reporting PeriodMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri AttariPas encore d'évaluation
- Investment Appraisal Theory Practical: Prepared By: Mohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri Attari ACCA (Finalist) ContactDocument19 pagesInvestment Appraisal Theory Practical: Prepared By: Mohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri Attari ACCA (Finalist) ContactMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri Attari100% (3)
- Ias 17 - LeasingDocument4 pagesIas 17 - LeasingMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri AttariPas encore d'évaluation
- Variance AnalysisDocument11 pagesVariance AnalysisMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri AttariPas encore d'évaluation
- Ias 10 - Events After Reporting PeriodDocument1 pageIas 10 - Events After Reporting PeriodMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri AttariPas encore d'évaluation
- Ias 36 - ImpairmentDocument6 pagesIas 36 - ImpairmentMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri AttariPas encore d'évaluation
- Control, Audit and Security - ACCA F1Document13 pagesControl, Audit and Security - ACCA F1Mohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri AttariPas encore d'évaluation
- Inroduction of Financial Management and Ratio AnalysisDocument17 pagesInroduction of Financial Management and Ratio AnalysisMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri AttariPas encore d'évaluation
- Marginal Costing - WWW - Ffqacca.co - CCDocument5 pagesMarginal Costing - WWW - Ffqacca.co - CCMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri Attari100% (1)
- Job Costing - WWW - Ffqacca.co - CCDocument4 pagesJob Costing - WWW - Ffqacca.co - CCMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri AttariPas encore d'évaluation
- Service CostingDocument2 pagesService CostingMohammad Faizan Farooq Qadri Attari100% (1)
- Closing Circular 30.09.2013Document53 pagesClosing Circular 30.09.2013umesh39Pas encore d'évaluation
- SCF WorksheetDocument19 pagesSCF WorksheetAngelo Gian CoPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Annual Report - UnileverDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Annual Report - UnileverUmair KhizarPas encore d'évaluation
- ES 301 Assignment #1 engineering economy problems and solutionsDocument2 pagesES 301 Assignment #1 engineering economy problems and solutionsErika Rez LapatisPas encore d'évaluation
- APC311 CompletedDocument7 pagesAPC311 CompletedShahrukh Abdul GhaffarPas encore d'évaluation
- SHORT WRITE ABOUT STOCK SHARE AND RISK Electiva CPCDocument7 pagesSHORT WRITE ABOUT STOCK SHARE AND RISK Electiva CPCyarima paterninaPas encore d'évaluation
- Foriegn Exchange of Social Islami Bank LimitedDocument20 pagesForiegn Exchange of Social Islami Bank LimitedRipa AkterPas encore d'évaluation
- Union Bank 1Document12 pagesUnion Bank 1bindu mathaiPas encore d'évaluation
- M.ed Challan FormDocument1 pageM.ed Challan Formshakeel manshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fixed Income Fundamentals: Interest Rate CalculationsDocument167 pagesFixed Income Fundamentals: Interest Rate CalculationsRavi KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Fa BobadillaDocument11 pagesFa BobadillaKamille ValdezPas encore d'évaluation
- Background of The Study:: Financial Analysis of Himalayan Bank LimitedDocument31 pagesBackground of The Study:: Financial Analysis of Himalayan Bank Limitedram binod yadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Partnership Accounting - Paula GozunDocument8 pagesPartnership Accounting - Paula GozunPaupauPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering EconomicsDocument2 pagesEngineering EconomicsGoverdhan ShresthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Report On Mutual Fund Schemes of SBIDocument43 pagesProject Report On Mutual Fund Schemes of SBIRonak Jain100% (2)
- Marketing of Banking Services (Urban Areas)Document82 pagesMarketing of Banking Services (Urban Areas)ganga123456Pas encore d'évaluation
- STQ1A: FORECASTING EXCHANGE RATESDocument5 pagesSTQ1A: FORECASTING EXCHANGE RATESMoud KhalfaniPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Run EscapeDocument3 pages1 Run EscapeRJ Melgar BayotPas encore d'évaluation
- Mt103 Qonto Bank 100 e EuroDocument2 pagesMt103 Qonto Bank 100 e Eurohaleighcrissy49387Pas encore d'évaluation
- NSE Yield Curve and Implied Yields ReportDocument2 pagesNSE Yield Curve and Implied Yields ReportCarl RossPas encore d'évaluation
- Effects of Exchange Rate Fluctuations On The Balance of Payment in The Nigerian EconomyDocument8 pagesEffects of Exchange Rate Fluctuations On The Balance of Payment in The Nigerian EconomyRev. Kolawole, John APas encore d'évaluation
- Tax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash MemoDocument1 pageTax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash MemoCentralised NumberPas encore d'évaluation
- New Financial Instruments Chapter 11Document16 pagesNew Financial Instruments Chapter 11Dipali DavdaPas encore d'évaluation
- Global RecessionDocument15 pagesGlobal RecessionsureshsusiPas encore d'évaluation
- RRLDocument2 pagesRRLJOHN AXIL ALEJOPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial ConclusionDocument2 pagesFinancial ConclusionjsinPas encore d'évaluation
- ICICI Financial StatementsDocument9 pagesICICI Financial StatementsNandini JhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Zimbabwean Banks Which Offer USD MasterCards or Visa Cards StartupBiz ZimbabweDocument1 pageZimbabwean Banks Which Offer USD MasterCards or Visa Cards StartupBiz ZimbabweemmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Revised SWORN STATEMENT FormDocument2 pagesRevised SWORN STATEMENT Formanaliza elliPas encore d'évaluation
- Managing Working CapitalDocument16 pagesManaging Working Capitalsalehin1969Pas encore d'évaluation