Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Derivation of Root Means Square (RMS Voltage)
Transféré par
Wilson (Electrical Engineer)Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Derivation of Root Means Square (RMS Voltage)
Transféré par
Wilson (Electrical Engineer)Droits d'auteur :
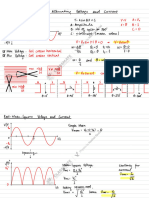
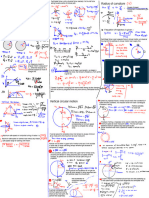
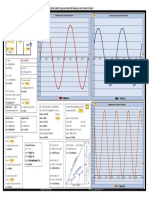
Note:This graph shown completes 1 cycle
6.2832
3.1416
Vp (Peak Value)
x(t)
(+) VM f(x)=sin wt
VRMS w= 2 π f
f = 50Hz or 50 cycles/sec
1.0000
VAVE
Vp
T= 1/f
Area
0.7071
0.6366
270° t
Vp-p
2.0000
0° 45° d0 π2 2π
180°
ᴓ
90° 360°
0.7854
VRMS=VP (sin wt) Vp = Peak Value
VRMS=VP (sin ᴓ) Vp-p = Peak to Peak
(-) d 0 = instantaneous rate of change 1.5708
3.1416 3.1416
T
6.2832
stands for Root Mean Square, and is a way of expressing an AC quantity of voltage or current in terms functionally equivalent to DC.
value is the effective value of a varying voltage or current. It is the equivalent steady DC (constant) value which gives the same effect.
AC voltmeters and ammeters show the RMS value of the voltage or current.
The average voltage (or current) of a periodic waveform whether it is a sine wave, square wave or triangular waveform is defined as: “the quotient of the area under the waveform with respect to time (t)”
Mean or average value of alternating current is that value of steady current which sends the same amount of charge through a circuit in a certain time interval as is sent by an alternating current through the same circuit in the same time interval.
Root-Mean-Square Voltage (Vrms) Average Voltage (Vavg)
VRMS 2= VP sin ᴓ 2
VRMS = VP sin ᴓ V AVE = VP sin ᴓ
2 2 2 V AVE = VP sin ᴓ dᴓ
VRMS = VP sin ᴓ dᴓ limit-- 0 to π Period T π
2 2 π 2 V AVE =VP sin ᴓ dᴓ
VRMS =VP sin ᴓ dᴓ Under the sinusoidal half wave of the curve 0 to π 0
π
0
π π
2 2 π V AVE = VP cos ᴓ dᴓ
VRMS = VP 1-cos 2ᴓ dᴓ 0
π 0
2 2
2
π V AVE = VπP cos ᴓ
VRMS = VP ᴓ -sin 2ᴓ 0
π V AVE = VP cos cos 0
0
2
2 2 π
VRMS = VP ᴓ -sin 2x π - 0-sin 2x0
2π 2 2 V AVE = VP
π 1+1
2 2 2
VRMS = VP π- 0 - 0+0 = VP - 0 - 0+0
2π 2 2 2π VAVE : 2VP
π = 0.6366VP = Area of under the curve
2 2 2 π
VRMS = VP π == VP
π 2 2
2 2 2
VRMS = VP = VP
2 2
VRMS : VP = 0.7071 VP
2
Prepare by: Engr. Wilson Fernandez
Form Factor: VRMS = 0.6366
0.7071
= 1.11
VAVE engr_wilson@yahoo.com
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Sheet 2Document4 pagesSheet 2fatima.alansari55Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gu17 1Document1 pageGu17 1k3nouPas encore d'évaluation
- SYN Alternating CurrentsDocument9 pagesSYN Alternating CurrentsamnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Set 7Document2 pagesProblem Set 7Ykhay ElfantePas encore d'évaluation
- Ejercicios Entrega Tema 5Document4 pagesEjercicios Entrega Tema 5Andrea Garcia EstellesPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronics Self StudyDocument1 pageElectronics Self Studysama.fahmyPas encore d'évaluation
- جداول انتقال حرارة - كاملةDocument9 pagesجداول انتقال حرارة - كاملةhoorPas encore d'évaluation
- AnalogDocument9 pagesAnalogPHANUWAT PHROMBUTPas encore d'évaluation
- Tecnologia 2 Bat 2Document1 pageTecnologia 2 Bat 2Sofia Benet IranzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Low Frequency Characteristic Analysis of Voltage Mode Boost ConverterDocument4 pagesLow Frequency Characteristic Analysis of Voltage Mode Boost Converterkakkunuru kashyapPas encore d'évaluation
- GAIN +-6 DB Potensio Linier.: Decoupling Capacitor Untuk Op-Amp Tidak DigambarDocument1 pageGAIN +-6 DB Potensio Linier.: Decoupling Capacitor Untuk Op-Amp Tidak Digambar90d0n9 J4m8uPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6Document7 pagesChapter 6William LeitePas encore d'évaluation
- Img 20130707 0001Document1 pageImg 20130707 0001Esminaj321Pas encore d'évaluation
- Transformerless Grid-Connected PV Array: Ir M MDocument1 pageTransformerless Grid-Connected PV Array: Ir M MHarshal PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- Bloc de Notas Sin TítuloDocument3 pagesBloc de Notas Sin TítuloSofía Escobar LondoñoPas encore d'évaluation
- TP 07Document1 pageTP 07iago villaPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 10Document3 pagesTopic 10洪允升Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe Culvert DesignDocument6 pagesPipe Culvert Designgagan kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cee 235a HW 5Document9 pagesCee 235a HW 5Nguyen DuyPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework 5: Force System Resultants: Due: Thursday, April 13, 2023Document3 pagesHomework 5: Force System Resultants: Due: Thursday, April 13, 2023shadeoppressorPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch8 SecondOrder2Document10 pagesCh8 SecondOrder2Nutthaphat ToopanichPas encore d'évaluation
- A350 Ac2spdDocument14 pagesA350 Ac2spdMohamad Al khamisPas encore d'évaluation
- Miscelánea de Dinamica - TrabajoDocument3 pagesMiscelánea de Dinamica - TrabajoSandra Quispe BeltránPas encore d'évaluation
- Mohammed Ahmned Tahhab-392027113-HW9-MEDrawingDocument1 pageMohammed Ahmned Tahhab-392027113-HW9-MEDrawingengineer.mohammedtahhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Heimadæmi 2 Burðarþol Eva Dís Og DíanaDocument5 pagesHeimadæmi 2 Burðarþol Eva Dís Og DíanadianamgenedyPas encore d'évaluation
- NOTAS PARA PARCIAL3 FísicaDocument4 pagesNOTAS PARA PARCIAL3 FísicaJuan David Caicedo BarrantesPas encore d'évaluation
- 20Document12 pages20Rajat Verma X D 39Pas encore d'évaluation
- 419C202C 作業考古Document58 pages419C202C 作業考古ken76chenPas encore d'évaluation
- Instrumentation LaboratoryDocument203 pagesInstrumentation LaboratoryswapnilPas encore d'évaluation
- Actividad 2-1Document9 pagesActividad 2-1Nicole ZapataPas encore d'évaluation
- Yoga Maulana Putra (17063072)Document10 pagesYoga Maulana Putra (17063072)Yoga MaulanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Delatore - STM25 - Physics - Da1Document5 pagesDelatore - STM25 - Physics - Da1Mikela DelatorePas encore d'évaluation
- Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceDocument3 pagesElectrostatic Potential and Capacitancenethraprasanna07Pas encore d'évaluation
- Intermediate Algebra Within Reach (Larson, Ron)Document693 pagesIntermediate Algebra Within Reach (Larson, Ron)mohammed MaktoumPas encore d'évaluation
- FINALSDocument2 pagesFINALSjrcruzpogi0242424Pas encore d'évaluation
- Homework Phy PDFDocument1 pageHomework Phy PDFThorung BOONKAEWPas encore d'évaluation
- 9c KreisbewegungDocument3 pages9c KreisbewegungplanpracyworkPas encore d'évaluation
- Formula CheatsheetDocument1 pageFormula CheatsheetGABRIEL LOUIS GUANOPas encore d'évaluation
- Circular Motion RevisionDocument2 pagesCircular Motion RevisionSuchit GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Tank PlumbingDocument1 pageWater Tank Plumbingmusiomi2005Pas encore d'évaluation
- Example Problem Solutions - Chapter 8Document18 pagesExample Problem Solutions - Chapter 8Nguyen Tien DungPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 A) B) C) D)Document2 pages1 A) B) C) D)Helder CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Wuolah Free CMCSDocument3 pagesWuolah Free CMCSLuisPas encore d'évaluation
- Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFormula SheetArcylea FerrerPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Files James Ford Seale 03Document198 pagesCase Files James Ford Seale 03limitlesscable.llcPas encore d'évaluation
- Ild 22Document1 pageIld 22Felipe GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Off GRD Solar InverterDocument2 pagesOff GRD Solar InverterSreedharPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise F1Document5 pagesExercise F1cristinaanton0302Pas encore d'évaluation
- ClasemmmDocument1 pageClasemmmAlexa JimenezPas encore d'évaluation
- Motion in Plane - Mind MapDocument1 pageMotion in Plane - Mind Mapsarthakyedlawar04Pas encore d'évaluation
- I Yre"ʳR ( - R Aa - Y: Capacitor F-Ñ JwliDocument9 pagesI Yre"ʳR ( - R Aa - Y: Capacitor F-Ñ JwliCheckPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment - 5Document3 pagesAssignment - 5shreya sriPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem 201 Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesChem 201 Lecture NotesProtect btsrvPas encore d'évaluation
- MekanikaDocument5 pagesMekanikaSalsabila Putri AndriantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Dimensi: Segitiga Ta BQ CP Éav3 Ia TaDocument10 pagesDimensi: Segitiga Ta BQ CP Éav3 Ia TaDavina AlmaPas encore d'évaluation
- ElectrostaticsDocument1 pageElectrostaticsSamPas encore d'évaluation
- IGCSE Velocity & AccelerationDocument1 pageIGCSE Velocity & AccelerationhosannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheet 5Document5 pagesSheet 5fatima.alansari55Pas encore d'évaluation
- Valvula Expansion Electronica AlcoDocument17 pagesValvula Expansion Electronica Alcorggarcia89Pas encore d'évaluation
- Star Delta Motor Starter Wiring DiagramDocument1 pageStar Delta Motor Starter Wiring DiagramWilson (Electrical Engineer)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Parallel RLC Circuits Calculation For Electrical SystemDocument1 pageParallel RLC Circuits Calculation For Electrical SystemWilson (Electrical Engineer)100% (1)
- Resistivity, Conductivity & ResistanceDocument3 pagesResistivity, Conductivity & ResistanceWilson (Electrical Engineer)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Measurement of Total Earth Fault Loop ImpedanceDocument2 pagesMeasurement of Total Earth Fault Loop ImpedanceWilson (Electrical Engineer)50% (2)
- Lux Level Calculation: WILSON ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING BOOKS (Simplified Edition 2020)Document1 pageLux Level Calculation: WILSON ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING BOOKS (Simplified Edition 2020)Wilson (Electrical Engineer)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Enter The Data Below: Sample PDF Only From Excel CalculationDocument1 pageEnter The Data Below: Sample PDF Only From Excel CalculationWilson (Electrical Engineer)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Installation of Earth Leakage RelayDocument2 pagesInstallation of Earth Leakage RelayWilson (Electrical Engineer)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Earthing System: WILSON ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING BOOKS (Simplified Edition 2020)Document3 pagesEarthing System: WILSON ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING BOOKS (Simplified Edition 2020)Wilson (Electrical Engineer)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Design of DC GeneratorDocument1 pageDesign of DC GeneratorWilson (Electrical Engineer)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Series RLC Circuits Calculation For Electrical SystemDocument1 pageSeries RLC Circuits Calculation For Electrical SystemWilson (Electrical Engineer)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Setting of Electrical Circuit Breaker: WILSON ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING BOOKS (Simplified Edition 2020)Document4 pagesSetting of Electrical Circuit Breaker: WILSON ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING BOOKS (Simplified Edition 2020)Wilson (Electrical Engineer)100% (1)
- Pure Capacitor (C) in Circuits AC SystemDocument1 pagePure Capacitor (C) in Circuits AC SystemWilson (Electrical Engineer)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Method Statement Installation of GeneratorDocument5 pagesMethod Statement Installation of GeneratorWilson (Electrical Engineer)100% (3)
- Yarn Eveness TesterDocument32 pagesYarn Eveness TestervasineyPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Paper Breadth in PhysicsDocument28 pagesQuestion Paper Breadth in PhysicsRafay BilalPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Symbols GuideDocument13 pagesElectrical Symbols GuideGEEPas encore d'évaluation
- HMT Lab Instruction ManualDocument6 pagesHMT Lab Instruction ManualAkash SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit I - Radn & Antennas - 2022Document92 pagesUnit I - Radn & Antennas - 2022Chandrashekher CPas encore d'évaluation
- LightDocument26 pagesLightAn BautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Parabolic Dish Antenna 3.5Ghz Operation: Data SheetDocument2 pagesParabolic Dish Antenna 3.5Ghz Operation: Data SheetDanielPas encore d'évaluation
- Second Floor Reflected Ceiling Plan: Legends/SymbolsDocument1 pageSecond Floor Reflected Ceiling Plan: Legends/SymbolsWilfredo Gabata SinoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Caterpillar c6.6 Electrical Schematic Diagnostic CodesDocument6 pagesCaterpillar c6.6 Electrical Schematic Diagnostic CodesjadliftboatsetorecordsPas encore d'évaluation
- A Project Report ONDocument15 pagesA Project Report ONshiv infotechPas encore d'évaluation
- Study of Effects of Lightning Strikes To An Aircraft: February 2012Document23 pagesStudy of Effects of Lightning Strikes To An Aircraft: February 2012reza mirzakhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Sensors: Dinesh Gopinath Department of Electrical Engineering College of Engineering Trivandrum Dinesh@cet - Ac.inDocument41 pagesCurrent Sensors: Dinesh Gopinath Department of Electrical Engineering College of Engineering Trivandrum Dinesh@cet - Ac.inakhilnandanPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding The Rotating Magnetic Field by Eric P. DollardDocument6 pagesUnderstanding The Rotating Magnetic Field by Eric P. Dollardanakin68100% (7)
- 3406C Electronic Diesel Truck Engine Electrical System: Electrical Schematic Symbols and DefinitionsDocument2 pages3406C Electronic Diesel Truck Engine Electrical System: Electrical Schematic Symbols and DefinitionsAnonymous nhF45C100% (4)
- (Amaleaks - Blogspot.com) Phyc2122 First Quarter ExamDocument17 pages(Amaleaks - Blogspot.com) Phyc2122 First Quarter ExamNiño Delfin T. Coliao IIPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Transformer Protection-R1Document53 pagesPower Transformer Protection-R1Dragana NikolicPas encore d'évaluation
- Tominaka 2006 Eur. J. Phys. 27 1399Document11 pagesTominaka 2006 Eur. J. Phys. 27 1399ra101208Pas encore d'évaluation
- SIROLUX F Installation InstructionsDocument30 pagesSIROLUX F Installation InstructionsГригорийPas encore d'évaluation
- Bigbang Theory ScriptDocument3 pagesBigbang Theory ScriptMA. ALTHEA SANTILLANAPas encore d'évaluation
- Secret High Power Free Energy CircuitDocument23 pagesSecret High Power Free Energy Circuitvladcoinstal100% (1)
- Mini Series (New) - Catalogue - New GreenDocument2 pagesMini Series (New) - Catalogue - New GreenKunjan SutharPas encore d'évaluation
- Renr7884renr7884-02 SisDocument2 pagesRenr7884renr7884-02 Sisboureima coulibalyPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 3 Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)Document7 pagesExperiment 3 Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)Muhammad Azri HaziqPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical System 320, 323, and 323 GC Excavator: View of Area "A"Document6 pagesElectrical System 320, 323, and 323 GC Excavator: View of Area "A"Jefferson SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- A VHF-UHF Television Turret Tuner-ujCDocument15 pagesA VHF-UHF Television Turret Tuner-ujCjulio perezPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDocument12 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric CurrentayushPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors Affecting Potential and Kenetic EnergyDocument14 pagesFactors Affecting Potential and Kenetic EnergyTrixy Eunice B. Camiling G8 - QUARTZPas encore d'évaluation
- Alternator: SpecificationsDocument4 pagesAlternator: SpecificationsjogremaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Newage MX321 Automatic Voltage RegulatorDocument6 pagesNewage MX321 Automatic Voltage RegulatorManuel Otero100% (10)