Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
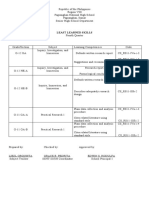
Questions Grade Level Responses Yes (N) % No (N) %: With Internet Connectio N With Access To Internet Signal
Transféré par
liezl vegaTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Questions Grade Level Responses Yes (N) % No (N) %: With Internet Connectio N With Access To Internet Signal
Transféré par
liezl vegaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Senior High
Grade Responses
Questions Level Yes % No %
(n) (n)
Do you have adequate time in which you will be
uninterrupted as you deliver online class? 11&12 x 80
Do you know how to troubleshoot minor hardware
malfunctions? 11&12 x 90
Do you have access to persons who will be able to readily
access you whenever technical problems arise 11&12 x 80
Do you know how to access online help desks whenever
technical glitches arise? 11&12 x 70
Do you have dedicated internet connection for online
learning? 11&12 x 80
Table 3: Teachers’ Proficiency Level/Competence to Use Computer Software Applications
Statements (As a teacher, my Responses
level of proficiency/competence Not % Beginning % Proficient %
in…) knowledgeable (n)
(n)
A. Using different computer
software applications
A.1 MS Word x 80
A.2 MS Excel x 70
A.3 Power Point x 60
A.4 Adobe x 10
A.5 Movie Maker x 60
Table 4: Teachers’ ICT Knowledge and Skills
Responses
Statements (As a teacher, my level Not % Beginning % Proficient %
of proficiency/competence in…) knowledgeabl (n)
e (n)
B. Using online and internet
applications/communication
platforms x 80
B.1 Web Browser
Ex: Internet Explorer, Mozilla,
Firefo, Google, etc). Web browser
is the primary computer tool that
allows you to connect to the
internet. x 95
B.2 Facebook Applications x 97
B. LEARNERS’ READINESS
Table 6: Consolidated Data on Students’ Readiness for Digital Education of Senior High School
Table 3: Teachers’ Proficiency Level/Competence to Use Computer Software Applications
SURVEY OF INCOMING LEARNERS UNDER “NEW NORMAL” SCHOOL SITUATION
SY: 2020 - 2021
CAPABLE FOR ONLINE LEARNING NOT
GRADE LEVEL With With SIGNAL CAPABLE
Internet Access to FOR
ONLINE
Connectio Internet LEARNING
n
CLEAR POOR
Grade 11 100 95 5
Grade 12 150 140 10
Total 250 230 15
Responses
Statements (As a teacher, my level of Knowledgeable % Beginning % Poor %
proficiency/competence in…) (n) (n)
C. Utilizing different Learning Modalities for
Online Learning such as…..
C.1 Blended Learning
(Combine face-to-face with any on Online
distance learning, modular distance learning
and TV, Radio-based instruction. Blended
Learning will enable the schools to limit face- x 60
to-face learning ensure social distancing, and
decreases the volume of people outside the
home at any given time)
C.2 Flipped Classroom
(Is a type of Blended Learning where students
are introduced to content at home and practice
learning through it at school. This is the
reverse of the more common practice of
introducing new content at school. This is the
reverse of the more common practice of x 50
introducing new content at school, than
assigning homework and projects is
completed by the students independently at
home)
C. 3 Google Classroom
A free web service developed by Google for
schools that aims to simplify creating,
distributing and grading assignments. The x 60
primary purpose of Google classroom is to
streamline the process of sharinsg files
between teacher and students)
C. 4 Distant Education
(It features the teacher facilitating Learning and
engaging learners’ active participation using
various technologies accessed through the
internet while they are geographically remote
from each other during instruction.)
Example:
1. Modular Distance Learning
2. Online Distance Learning
3. TV/Radio Based Instruction
Suggested Platforms Resources/Mechanisms:
* The use of Learning Materials/Modules in
Multimedia (slides, video and audio files)
* Digital Packets (Learning Materials)
* The use of e-learning materials
* The use of computer-based learning x 75
resources
Others
* The use of Web-Enhanced Learning
Activities
*Free access to OERs (Open Educational
Resources)
*Access to LR Portals
*Access to Dep Ed Commons
C.5 Mobile Learning
Also known as e-learning is a new way to
access learning content using mobiles. Mobile
Learning supports, with the help of mobile
devices, continuous access to the learning
process. This can be done using devices like
your phones, laptop or tablet. You can learn x 75
wherever and whoever you want. With the
advent of mobile learning, educational systems
are changing.)
C.6 Traditional Face-to-Face
(Students and the teacher are both physically
present in the classroom, and there are
opportunities for active engagement,
immediate feedback, and socio-emotional
development of learners.)
Examples:
1. Modified shifting of Classes
2. Shifting of Classes with Dyadic
Teaching
3. Focused Teaching (Elem/JHS) x 85
4. Core/Specialized –Focused Teaching
(SHS)
Or use of the ff. existing Dep Ed
Programs/Projects (e.g. MISOSA, IMPACT,
OHSP, Project EASE, Face to Face and
Modular Learning, Community-based
Instruction (ALS))
C.7 Home Schooling
(It is an alternative delivery mode (ADM) that
aims to provide learners with equal access to
quality basic education through a home-based x 85
environment to be facilitated by qualified
parents, guardians or tutors who have
undergone relevant training)
D. AVAILABILITY OF RESOURCES
Table 10. AVAILABILITY OF LEARNING MATERIALS
SUBJECTS
Grade (Write the subject you are handling, then below the number of books available)
Level English for
Academic and Practical Research Practical Inquiries,Investigation
Professional 1 Research 2 And Immersion
Purposes
Grade 11
0
Grade 12 100 0 0
Total 100 0 0 0
The table above indicates the availability of learner’s materials per grade level by subject area
Table 11. ASSESSMENT ON ADEQUACY OF SCHOOL ICT FACILITIES
None Inadequate Adequate
1. The School has provision of software installed in a
computer for e-learning x
2. The School has access to internet service providers for
a stable connection x
3.The school has available equipment such as modem
and routers to ensure wide access to internet. x
4.The school has presence of e-book, online library and
other media technology for learners and teachers x
The table above indicates the preparedness of the school for online learning through adequacy of
its ICT facilities to support this mode of learning
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Emptech DLL2Document44 pagesEmptech DLL2Judel LumberaPas encore d'évaluation
- Emptech DLLDocument45 pagesEmptech DLLJudel Lumbera100% (2)
- ks5 CsDocument6 pagesks5 Csapi-265219702Pas encore d'évaluation
- CBA Course Outline (Fall 2015) Prepared by MH NahidDocument5 pagesCBA Course Outline (Fall 2015) Prepared by MH NahidArif BokhtiarPas encore d'évaluation
- DLL Empowerment Week 3Document4 pagesDLL Empowerment Week 3Emilyn Mae Nebril PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Misy 1013Document9 pagesMisy 1013dawnPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis and InterpretationDocument35 pagesAnalysis and InterpretationLilia Priscilla Tuibuen AureusPas encore d'évaluation
- Ashley BudgetDocument4 pagesAshley Budgetapi-241594635Pas encore d'évaluation
- CCN1016 Introduction To Internet Technology PDFDocument3 pagesCCN1016 Introduction To Internet Technology PDFdnlkabaPas encore d'évaluation
- LCP Sample (Domrac)Document4 pagesLCP Sample (Domrac)Chris John TenorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 10 - Kayla TurnerDocument2 pagesModule 10 - Kayla Turnerapi-438285591Pas encore d'évaluation
- TTL01 Syllabus - Technology For Teaching in Elementary GradesDocument7 pagesTTL01 Syllabus - Technology For Teaching in Elementary GradesAntonio VallejosPas encore d'évaluation
- Northlink: Course SyllabusDocument4 pagesNorthlink: Course SyllabusFlor CabillarPas encore d'évaluation
- EJ990635Document8 pagesEJ990635Semmi SemPas encore d'évaluation
- Empowermnet q1 Week 3Document3 pagesEmpowermnet q1 Week 3Michelle Cañedo VerdeflorPas encore d'évaluation
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log School G Rade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterDocument8 pagesGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log School G Rade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterKaren Anne Briones RufinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Emp Tech 1stQ Week3Document6 pagesEmp Tech 1stQ Week3Angelo VillafrancaPas encore d'évaluation
- Review PaperDocument8 pagesReview Paperabc xyzPas encore d'évaluation
- Okane John Lesson Plan 3 5 1 17 12 PMDocument4 pagesOkane John Lesson Plan 3 5 1 17 12 PMapi-356000194Pas encore d'évaluation
- Project TALA (Technology - Based Activity and Learning Assistant) An Intervention To Maximize Performance of ICT LearnersDocument6 pagesProject TALA (Technology - Based Activity and Learning Assistant) An Intervention To Maximize Performance of ICT LearnersIOER International Multidisciplinary Research Journal ( IIMRJ)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Northlink: Course SyllabusDocument3 pagesNorthlink: Course SyllabusFlor CabillarPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 PDFDocument9 pages12 PDFDlanor NablagPas encore d'évaluation
- The Open Schoolhouse: Building a Technology Program to Transform Learning and Empower StudentsD'EverandThe Open Schoolhouse: Building a Technology Program to Transform Learning and Empower StudentsPas encore d'évaluation
- CPT101Document4 pagesCPT101Engr SayedPas encore d'évaluation
- PIVOT 4A Lesson Exemplar: Learning Area Empowerment Technologies Learning Delivery Modality All ModalityDocument3 pagesPIVOT 4A Lesson Exemplar: Learning Area Empowerment Technologies Learning Delivery Modality All ModalityJe RebanalPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3. Positive Use of Information and Communications TechnologyDocument7 pagesLesson 3. Positive Use of Information and Communications TechnologyJona Mae Degala DordasPas encore d'évaluation
- Developing in The ClassroomDocument2 pagesDeveloping in The ClassroomMin KyawPas encore d'évaluation
- Research-Poster (San Jose, Cauntay, Catapang)Document1 pageResearch-Poster (San Jose, Cauntay, Catapang)Steven Lee San JosePas encore d'évaluation
- E-LEARNING 2020 BBCDocument9 pagesE-LEARNING 2020 BBCReagan SsebbaalePas encore d'évaluation
- LE - Weeks 7-9 Programming 12 (.Net Technology Programming)Document10 pagesLE - Weeks 7-9 Programming 12 (.Net Technology Programming)AileenD.EnriquezPas encore d'évaluation
- DLL Empowerment Week 3 - CompressDocument3 pagesDLL Empowerment Week 3 - CompressArgel SalamancaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tan Ling TingDocument5 pagesTan Ling TingjohnlyantudlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Week1 ICT Competency Worksheet-FinalDocument4 pagesWeek1 ICT Competency Worksheet-FinalJaemee RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 EltDocument13 pages2 Eltlala.rahimli29Pas encore d'évaluation
- Apresentação 1Document16 pagesApresentação 1Domingos Tolentino Saide DtsPas encore d'évaluation
- Technology FacadeDocument7 pagesTechnology FacadetazboyvtPas encore d'évaluation
- Leap-Help (: Earning Nhancement Ctivity Rogram Hrough Ands-On Xposure With The Help of Earning ArtnersDocument21 pagesLeap-Help (: Earning Nhancement Ctivity Rogram Hrough Ands-On Xposure With The Help of Earning ArtnersRex YuzonPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacity Building For Educational Action Research and Innovation © 2023 GsdigoDocument11 pagesCapacity Building For Educational Action Research and Innovation © 2023 GsdigoFatima Ann Alfonso BartolomePas encore d'évaluation
- 1stQ Week1-EmpowermentDocument4 pages1stQ Week1-EmpowermentArvin OcampoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 3. Positive Use of Information and Communications TechnologyDocument7 pagesLesson 3. Positive Use of Information and Communications TechnologyJona Mae Degala DordasPas encore d'évaluation
- EDT 524 DR Adamu ContinuationDocument5 pagesEDT 524 DR Adamu ContinuationLeo EmmanuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Sorsogon State College: Page 1 of 5Document5 pagesSorsogon State College: Page 1 of 5Mark DipadPas encore d'évaluation
- DCCN SyllabusDocument4 pagesDCCN SyllabusRaj SinghaniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Framework For Evaluation of Programming Language Examinations (2014) Recent Advancements in The Field of eDocument2 pagesFramework For Evaluation of Programming Language Examinations (2014) Recent Advancements in The Field of enezclarkPas encore d'évaluation
- Participate and Assist: Learning EpisodeDocument4 pagesParticipate and Assist: Learning EpisodeshennaPas encore d'évaluation
- CSS 11 Le Week4bDocument2 pagesCSS 11 Le Week4bJe_RebanalPas encore d'évaluation
- 2016 TELI-Handbook Q1Document12 pages2016 TELI-Handbook Q1RajeevPas encore d'évaluation
- WEEK 1 Technology-Evaluation-FormDocument2 pagesWEEK 1 Technology-Evaluation-FormNgan DaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Technology Literacy: Readiness of Teacher, Student, and Environment in Border AreaDocument13 pagesTechnology Literacy: Readiness of Teacher, Student, and Environment in Border AreaOxtapianus TawarikPas encore d'évaluation
- Empowerment-Technologies WEEK 1Document3 pagesEmpowerment-Technologies WEEK 1Arlene Diño AmuraoPas encore d'évaluation
- Education - PresmatDocument28 pagesEducation - PresmatKin EmonPas encore d'évaluation
- SOTE - Educational Technology 2 (Mercado, Jaiden Christopher)Document32 pagesSOTE - Educational Technology 2 (Mercado, Jaiden Christopher)jaiden narcellesPas encore d'évaluation
- Comp 9 - 3q ModuleDocument27 pagesComp 9 - 3q ModuleMark Vincent SevillePas encore d'évaluation
- E-Learning in English Language Teaching and LearningDocument24 pagesE-Learning in English Language Teaching and LearningAlmhaPas encore d'évaluation
- EPISODE 7 Ramos, MaryRoseDocument4 pagesEPISODE 7 Ramos, MaryRoseMary Rose RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 Beyond The Basic Prductivity Tools Lesson Idea TemplateDocument2 pages04 Beyond The Basic Prductivity Tools Lesson Idea Templateapi-475787811Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sanchez Information Assurance and SecurityDocument9 pagesSanchez Information Assurance and SecurityMarneil Allen SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Education: Survey On The Readiness of Online Teaching in The Division of Dapitan City For Sy 2020 - 2021Document10 pagesDepartment of Education: Survey On The Readiness of Online Teaching in The Division of Dapitan City For Sy 2020 - 2021Eden Shen SumilayPas encore d'évaluation
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VIII Division of SamarDocument11 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VIII Division of Samarliezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Competency Directory (LCD) FOR SCHOOL YEAR 2018-2019Document38 pagesLearning Competency Directory (LCD) FOR SCHOOL YEAR 2018-2019liezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VIII Division of SamarDocument11 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VIII Division of Samarliezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VIII Division of SamarDocument11 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VIII Division of Samarliezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VIII Division of SamarDocument11 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VIII Division of Samarliezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VIII Division of SamarDocument11 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VIII Division of Samarliezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VIII Division of SamarDocument11 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VIII Division of Samarliezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 2 Wordscapes Direction:: Iplibarotby-Epmils - Fedisratit - Icsysetamt - ResluctDocument3 pagesActivity 2 Wordscapes Direction:: Iplibarotby-Epmils - Fedisratit - Icsysetamt - Resluctliezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- RPMS Tool For Teacher I-III (Proficient Teachers) : Position and Competency ProfileDocument23 pagesRPMS Tool For Teacher I-III (Proficient Teachers) : Position and Competency ProfileMaKenJi EscalantePas encore d'évaluation
- Direction: Write The Word of The Correct AnswerDocument2 pagesDirection: Write The Word of The Correct Answerliezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Education: Weekly Lesson Log SheetDocument1 pageDepartment of Education: Weekly Lesson Log Sheetliezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 2 - The Importance of Quantitative Research Across Fields-2 PDFDocument33 pagesLesson 2 - The Importance of Quantitative Research Across Fields-2 PDFMarky Zhaijan Ramos82% (65)
- Department of Education: Schools Division of Samar District of Panghan Bangon Elementary School Bangon, Pagsanghan, SamarDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Schools Division of Samar District of Panghan Bangon Elementary School Bangon, Pagsanghan, Samarliezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 3 Concept Discovery Group 1 Situation 1Document7 pagesActivity 3 Concept Discovery Group 1 Situation 1liezl vega100% (1)
- Office/School/Clc Workweek PlanDocument3 pagesOffice/School/Clc Workweek PlanAlbinMae Caroline Intong-Torres Bracero-CuyosPas encore d'évaluation
- LLS 4thquarterDocument1 pageLLS 4thquarterliezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Questions Grade Level Responses Yes (N) % No (N) %: With Internet Connectio N With Access To Internet SignalDocument3 pagesQuestions Grade Level Responses Yes (N) % No (N) %: With Internet Connectio N With Access To Internet Signalliezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- School Form 1 School Register For Senior High School (SF1-SHS)Document6 pagesSchool Form 1 School Register For Senior High School (SF1-SHS)liezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reporters in Practical Research 2Document1 pageReporters in Practical Research 2liezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- CardinalDocument1 pageCardinalliezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- In Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For Secondary Education Curriculum General Academic Program Research TitleDocument33 pagesIn Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For Secondary Education Curriculum General Academic Program Research Titleliezl vega0% (2)
- CONFIRMATIONDocument1 pageCONFIRMATIONliezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- TABBINGDocument3 pagesTABBINGliezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Attendance g12 Ga A (Eapp)Document58 pagesAttendance g12 Ga A (Eapp)liezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- TABBINGDocument3 pagesTABBINGliezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Attendance g12 Ga A (Eapp)Document58 pagesAttendance g12 Ga A (Eapp)liezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Attendance g12 Ga A (Eapp)Document58 pagesAttendance g12 Ga A (Eapp)liezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Attendance g12 Ga A (Eapp)Document58 pagesAttendance g12 Ga A (Eapp)liezl vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- NSTP Course Intro and ModulesDocument87 pagesNSTP Course Intro and ModulesSHIENNA MAE ALVISPas encore d'évaluation
- Skripsi Devi BismillahDocument41 pagesSkripsi Devi BismillahDevi RIPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument3 pagesReview of Related LiteratureCLINT DELGADOPas encore d'évaluation
- UG Prospectus 2022-23Document53 pagesUG Prospectus 2022-23MuveenPas encore d'évaluation
- The Evolving Role of TeachersDocument165 pagesThe Evolving Role of TeachersKhritish SwargiaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Notebook-OstulanoDocument34 pagesStudy Notebook-OstulanoJonathan BulawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 Education and LearningDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Education and Learningthuthuyen doPas encore d'évaluation
- Taylor Assignment 2 - Learning Unit For A Mooc EnvironmentDocument26 pagesTaylor Assignment 2 - Learning Unit For A Mooc Environmentapi-247487873Pas encore d'évaluation
- ContentDocument78 pagesContentharshitajhalani_2554Pas encore d'évaluation
- IELTS Education VocabularyDocument3 pagesIELTS Education VocabularySardor NarzullaevPas encore d'évaluation
- Distance Learning MBA: Warwick or LondonDocument36 pagesDistance Learning MBA: Warwick or LondonTimothy CrusePas encore d'évaluation
- Booz Allen Hamilton PIE E-LearningDocument17 pagesBooz Allen Hamilton PIE E-LearningNibblsPas encore d'évaluation
- Technology-Based Learning ReserchDocument38 pagesTechnology-Based Learning Reserchciedelle aranda100% (1)
- Report On IGNOU DPE Prog by NCTE ExpertsDocument22 pagesReport On IGNOU DPE Prog by NCTE Expertsknsvel20005966Pas encore d'évaluation
- Courtney L. Teague Assignment 4Document13 pagesCourtney L. Teague Assignment 4iteach08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exploring Educational Platforms and Community Behavior To Support - 2016Document7 pagesExploring Educational Platforms and Community Behavior To Support - 2016archtofaPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Hnu Edge PrimerDocument23 pages01 Hnu Edge PrimerJasper Shin D DizonPas encore d'évaluation
- Soal SKB SetDocument16 pagesSoal SKB SetFebri CurupPas encore d'évaluation
- GROUP 7 Literature ReviewDocument10 pagesGROUP 7 Literature ReviewFrancis Miguel PetrosPas encore d'évaluation
- FS1 2 Guidelines Rubric Grading System 1Document11 pagesFS1 2 Guidelines Rubric Grading System 1Jomar SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- 479 Magsaysay Avenue Cogon Sorsogon CityDocument27 pages479 Magsaysay Avenue Cogon Sorsogon Cityalbert matandagPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan (Torotoro, Jessel BTLED 3-A H.E)Document3 pagesLesson Plan (Torotoro, Jessel BTLED 3-A H.E)Jessel TorotoroPas encore d'évaluation
- Aui 2601Document14 pagesAui 2601cykfkkxgs7Pas encore d'évaluation
- DR Nazir A SangiDocument6 pagesDR Nazir A SangisrkhalidpkPas encore d'évaluation
- IDL D Prog Handbook - 201617 Version II 120916Document78 pagesIDL D Prog Handbook - 201617 Version II 120916Mala RattanPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Business CorrespondenceDocument27 pagesPrinciples of Business CorrespondencePoison IvyPas encore d'évaluation
- LDM2 Module 3A With AnswersDocument8 pagesLDM2 Module 3A With AnswersRia Lingatong BasolPas encore d'évaluation
- Is Social Media Good For Our Society? If Not, Then What Do We Do To Fix It?Document23 pagesIs Social Media Good For Our Society? If Not, Then What Do We Do To Fix It?Shaikh Saifullah KhalidPas encore d'évaluation
- B.A. PHILOSOPHY Part I (Sem I&II)Document20 pagesB.A. PHILOSOPHY Part I (Sem I&II)RanDeep SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Agri ExtensionDocument18 pagesAgri ExtensionWynnie RondonPas encore d'évaluation