Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Lund Ki Pyasi
Transféré par
ldTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Lund Ki Pyasi
Transféré par
ldDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1.
In terms of the scientific method, how does astronomy differ from a lab science
like chemistry or biology? How can astronomers be confident of their
understanding of objects that are remote from the Earth?
ANS:
Astronomy is different from other sciences because the evidence comes
from remote electromagnetic radiations. It’s not a lab science and we can’t
control the experiments of universe.
Scientific method involves systematic observation, measurement, and
experiment, and the formulation, testing, and modification of hypotheses.
The basic difference is that in chemistry and biology experiments can be
performed in laboratory under specified set of conditions and a controlled
environment while in astronomy experiments can neither be performed in
labs (like we can’t study about black holes by generating them in labs ) nor
the environment can be controlled. They are happening all the times in the
far reaches of the ever expanding universe.
In chemistry, physics, and biology, evidence often comes from experiments
in a laboratory and they can be repeated and reproduced for arriving to a
solid definite conclusion in short period of time. In astronomy, objects are
very remote,(they are millions, billions and even trillions of light years away
from us) thus most of the evidence comes in the form of remote
electromagnetic radiation and patience is required to collect large set of
data over a long period of time even to observe slightest variation in
observations. Sometimes it is difficult to reach to a concrete conclusion
from the available set of data.
Now answering how can astronomers be confident of their understanding
of objects that are remote from the Earth.
The main source on which any conclusions can be made is the information
extracted from the EM Radiations received from remote celestial objects
collected through large telescopes.
If any astronomical law, hypothesis and theories constructed explain the
observations and fit the observed set of data, and supported by a large
body of observations and measurements and can make new predictions
which future measurements and observations can confirm then
astronomers can be pretty much sure that their understanding of the
observed phenomena is correct.
Many new methods and techniques (ex-gravitational lensing) have been
developed in recent times which further helps to get results from different
methods and thus helps to reach to a solid conclusion.
For instance, we can look at a star using a camera that captures radio
waves, microwaves, infrared waves, ultraviolet rays, x-rays, or gamma
rays. We can measure the star's composition using spectral analysis. We
can measure a star's relative velocity using redshift observations. In this
way, certainty about a star's nature can be established by observing it
using many different methods, and checking to make sure all these
observations agree.
2. Ancient cultures built some impressive structures that incorporated astronomical functions
and information (Stonehenge, Chichen Itza, the Great Pyramid). A friend or acquaintance of
yours tries to argue that some of these structures and artifacts are evidence of "ancient
astronauts" or visits by intelligent aliens. How would you rebut or argue against this ideas?
ANS :
Those structures symbolises our ancient culture and throws light on
thinking and understanding of astronomy by our ancestors. These
structures were mainly build as a time keeping device. These iconic
structures were based on motion of sun and moon in the sky. Baically
these were solar and lunar calendars.
The length of shadow casted by these structures would help people to
guess the time of the year which was essential for activities like
agriculture and other religious activities and festivals.
For ex- archeoastronomers have investigated the alignments of stones
at Stonehenge and found that it represents an exquisite calendar, not
just a solar calendar but also an eclipse predictor able to predict
patterns in the sky occurring on near century timescales.Other
alignments in Stonehenge give indications that they're tracking Venus,
the phases of the moon, and perhaps Mars position in the sky as well.
Yet another magnificent example is Chaco Canyon. In a canyon and on
a high tour of rock, light is admitted through a slit in the rock and cast a
dagger like shadow on the far face. On that far face etched is a spiral in
charcoal, and the dagger on the longest day passes through the center
of the spiral. At the equinoxes, spring and fall, the dagger passes
tangents through the edges of the spiral. So this is yet another form of a
solar calendar.
The best argument lies in the statement that intelligent life from some
other world would not visit our planet just to make these obscure
structures and not establish any communication with us.
https://www.coursera.org/learn/astro/peer/CXYv7/writing-assignment-no-1-science-past-and-
present/review/SCn6vrUWEeqJmA5kT-X02w
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Astronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the UniverseD'EverandAstronomy 101: From the Sun and Moon to Wormholes and Warp Drive, Key Theories, Discoveries, and Facts about the UniverseÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (15)
- Astronomy: Beginner’s Guide to Astronomy: Resources, Stargazing Guides, Apps and Software!: Beginner's Guide to Astronomy, #2D'EverandAstronomy: Beginner’s Guide to Astronomy: Resources, Stargazing Guides, Apps and Software!: Beginner's Guide to Astronomy, #2Évaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (1)
- The Secrets of the Universe: Exploring the Great UnknownD'EverandThe Secrets of the Universe: Exploring the Great UnknownPas encore d'évaluation
- подготовки за одговор на астрономија прашањеDocument2 pagesподготовки за одговор на астрономија прашањеChryseisAlicePas encore d'évaluation
- Astronomy - Writing Assignment 1Document2 pagesAstronomy - Writing Assignment 1annaPas encore d'évaluation
- Senior Presentation AstroDocument35 pagesSenior Presentation Astroapi-316833026Pas encore d'évaluation
- Astronomy: Cosmology, Photometry, and Spectroscopy Explained (3 in 1)D'EverandAstronomy: Cosmology, Photometry, and Spectroscopy Explained (3 in 1)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cosmic Odyssey: A Journey Through the Wonders of AstronomyD'EverandCosmic Odyssey: A Journey Through the Wonders of AstronomyPas encore d'évaluation
- Exploring the Unknown: An Intergalactic Expedition of Space and AstronomyD'EverandExploring the Unknown: An Intergalactic Expedition of Space and AstronomyPas encore d'évaluation
- From the Beginning of Space and Time: Modern Science and the Mystic UniverseD'EverandFrom the Beginning of Space and Time: Modern Science and the Mystic UniversePas encore d'évaluation
- Astrophysics For ScientistsDocument3 pagesAstrophysics For Scientistskumara10910Pas encore d'évaluation
- Astronomy - Act. 1Document1 pageAstronomy - Act. 1Meangel QuillaoPas encore d'évaluation
- AstronomyDocument1 pageAstronomyHITPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper Inggris Tugas 2Document8 pagesPaper Inggris Tugas 2Rifa adawiyyahPas encore d'évaluation
- The Stardust Universe by Advaith VaithianathanDocument28 pagesThe Stardust Universe by Advaith VaithianathanAdvaith VaithianathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Astrophysics for People in a Hurry by Neil deGrasse TysonD'EverandSummary of Astrophysics for People in a Hurry by Neil deGrasse TysonPas encore d'évaluation
- Astrology to Astronomy - The Study of the Night Sky from Ptolemy to Copernicus - With Biographies and IllustrationsD'EverandAstrology to Astronomy - The Study of the Night Sky from Ptolemy to Copernicus - With Biographies and IllustrationsPas encore d'évaluation
- The Observer's Guide to Planetary Motion: Explaining the Cycles of the Night SkyD'EverandThe Observer's Guide to Planetary Motion: Explaining the Cycles of the Night SkyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Great Scientists in Bite-sized ChunksD'EverandThe Great Scientists in Bite-sized ChunksÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (1)
- Astronomy for Beginners: Ideal guide for beginners on astronomy, the Universe, planets and cosmologyD'EverandAstronomy for Beginners: Ideal guide for beginners on astronomy, the Universe, planets and cosmologyÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Methods For Measuring The Age of The Universe - General Science & Ability NotesDocument4 pagesMethods For Measuring The Age of The Universe - General Science & Ability NotesdanishrazaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unknown Universe: A New Exploration of Time, Space, and Modern CosmologyD'EverandThe Unknown Universe: A New Exploration of Time, Space, and Modern CosmologyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- The Universe: Observational ToolsDocument5 pagesThe Universe: Observational ToolsallanPas encore d'évaluation
- How Do Scientists Discover New Planets? Astronomy Book 2nd Grade | Children's Astronomy & Space BooksD'EverandHow Do Scientists Discover New Planets? Astronomy Book 2nd Grade | Children's Astronomy & Space BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Questions About The Solar System I Can Ask To A Professional AstronomerDocument23 pagesBasic Questions About The Solar System I Can Ask To A Professional AstronomerLeandro Rocha RímuloPas encore d'évaluation
- Observational Astronomy: To The References Provided in The Bibliography at The End of These NotesDocument17 pagesObservational Astronomy: To The References Provided in The Bibliography at The End of These Notesbobjane_tmartPas encore d'évaluation
- Semester 5 Open Course - I: (Problems Not Required)Document12 pagesSemester 5 Open Course - I: (Problems Not Required)kcameppadi123Pas encore d'évaluation
- ASTRONOMY AnswersheetsDocument54 pagesASTRONOMY Answersheetspio manoPas encore d'évaluation
- History of Man's Achievements in Space ScienceDocument22 pagesHistory of Man's Achievements in Space ScienceOlabintan AdewalePas encore d'évaluation
- The Stargazer's Guide: How to Read Our Night SkyD'EverandThe Stargazer's Guide: How to Read Our Night SkyÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (7)
- Beyond the Horizon: Exploring the Mysteries of SpaceD'EverandBeyond the Horizon: Exploring the Mysteries of SpacePas encore d'évaluation
- AstronomyDocument2 pagesAstronomyshruti.welspunPas encore d'évaluation
- AstronomyDocument16 pagesAstronomyapi-3741779Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Universe: The book of the BBC TV series presented by Professor Brian CoxD'EverandThe Universe: The book of the BBC TV series presented by Professor Brian CoxÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- The Outbreak of The French RevolutionDocument8 pagesThe Outbreak of The French RevolutionldPas encore d'évaluation
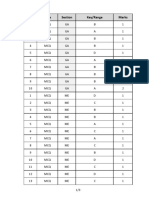
- Q.No. Type Section Key/Range MarksDocument3 pagesQ.No. Type Section Key/Range MarksldPas encore d'évaluation
- Big Indian Nude Ass 3Document3 pagesBig Indian Nude Ass 3ldPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Mathematics and Computing IIT (ISM) Dhanbad Lecture PlanDocument1 pageDepartment of Mathematics and Computing IIT (ISM) Dhanbad Lecture PlanldPas encore d'évaluation
- Savita Ki ChutDocument4 pagesSavita Ki ChutldPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple Choice Test:1Document3 pagesMultiple Choice Test:1ldPas encore d'évaluation
- Theories On The Origin of The UniverseDocument4 pagesTheories On The Origin of The UniverseG17. Ozaeta, Justine L.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tides-2015 LectureDocument17 pagesTides-2015 Lectureapi-169639475Pas encore d'évaluation
- Visualizing Physical Geography: The Earth As A Rotating PlanetDocument31 pagesVisualizing Physical Geography: The Earth As A Rotating PlanetAsadAliBaigPas encore d'évaluation
- Soal Latihan Modul (Tbi)Document17 pagesSoal Latihan Modul (Tbi)Auditia Deka Febriana.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Answers To Chapter Review Questions and Problems For The Amateur Astronomer's Introduction To The Celestial SphereDocument39 pagesAnswers To Chapter Review Questions and Problems For The Amateur Astronomer's Introduction To The Celestial Sphereuujaval pavarPas encore d'évaluation
- Kwanghyun Sung (Samuel Sung) : EducationDocument1 pageKwanghyun Sung (Samuel Sung) : EducationhummingsungPas encore d'évaluation
- Ps Module 5 2nd Sem 2nd Quarter Grade 11 Abm Rizal Humss Bonifacioagoncillo Mr. Arnold PaombongDocument9 pagesPs Module 5 2nd Sem 2nd Quarter Grade 11 Abm Rizal Humss Bonifacioagoncillo Mr. Arnold PaombongArnold PaombongPas encore d'évaluation
- Riyadh WeatherDocument9 pagesRiyadh WeatherSiva SubramaniyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ufo Sightings in CyprusDocument4 pagesUfo Sightings in CypruskatburnerPas encore d'évaluation
- 1IntroductionTheSun PDFDocument19 pages1IntroductionTheSun PDFAastha JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- META19 Poster TemplateDocument1 pageMETA19 Poster Templatearijit mannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dinosaur Lesson by SlidesgoDocument41 pagesDinosaur Lesson by SlidesgoDonalyn PaderesPas encore d'évaluation
- Extra Assignment Astronomy - Telescope SimulationsDocument3 pagesExtra Assignment Astronomy - Telescope SimulationsgabriellarataPas encore d'évaluation
- Kepler's Law of Planetary MotionDocument2 pagesKepler's Law of Planetary MotionFritziePas encore d'évaluation
- The Qur'an On Cosmology - Part TwoDocument49 pagesThe Qur'an On Cosmology - Part Twosamiur rahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ingles Evau Modelo21Document7 pagesIngles Evau Modelo21besamundo100% (1)
- Short Report - Personal Portrait: Add A New Person Edit Data ForDocument5 pagesShort Report - Personal Portrait: Add A New Person Edit Data ForTina NikolacPas encore d'évaluation
- Astronomy Lesson 1Document5 pagesAstronomy Lesson 1Kristin WilsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan Ini ConstellationDocument19 pagesLesson Plan Ini ConstellationPaula April ToledoPas encore d'évaluation
- Rim Es-Sagar - Tok ExhibitionDocument4 pagesRim Es-Sagar - Tok Exhibitionapi-543376640Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Outer Planets and The AnglesDocument83 pagesThe Outer Planets and The AnglesNina Elezovic Simunovic100% (1)
- Celestial Mechanics With MatlabDocument151 pagesCelestial Mechanics With MatlabEyjay Samson100% (2)
- Timing Marriage Using VD and Transits of JU SaDocument3 pagesTiming Marriage Using VD and Transits of JU SaRavi Sankar TekuruPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Houses LayoutDocument1 page12 Houses Layoutatmannirvana.penangPas encore d'évaluation
- EssayDocument9 pagesEssayAkash PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of The Horoscope of COVIDDocument7 pagesAnalysis of The Horoscope of COVIDKrungthep MahanakornPas encore d'évaluation
- Astrophysics Practice Test 2Document6 pagesAstrophysics Practice Test 2sharm111069Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tesis Raquel Martinez ArnaizDocument222 pagesTesis Raquel Martinez Arnaizhhjder_bag8995Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assan LI: Academic RecordDocument4 pagesAssan LI: Academic Recordilyas muhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Demo ScriptDocument4 pagesDemo ScriptRuby Feudo- MercadoPas encore d'évaluation