Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1-Introduction of Science
Transféré par
nixleonDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Chapter 1-Introduction of Science
Transféré par
nixleonDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
KC TUITION: 012 – 3877 265
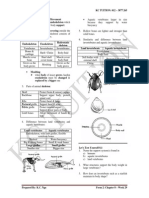
Chapter One: Introduction to Science Flat bottomed flask Round bottomed flask
1. Science = systematic study of natural world
through observations & experiments and
how it affects the environment & us.
Let’s Test Yourself 1.1
1. Scientists carry out __________ to Filter funnel Retort stand
understand the things happening around us
that we call __________ __________.
However these studies must be __________
because there must be a series of steps to be
followed before the scientists can find any
answers.
Tripod stand Evaporating dish
2. List three careers in science and state what
the job is about.
3. State the area of science that studies the
following natural phenomena. (Biology,
Chemistry or Physics)
a) Plants need sunlight to grow Pipette Burette
b) Oil floats on water
c) Air cannot be compressed
d) Heat flows from a hotter region to a
colder region
e) There are three stages in the life cycle
of a butterfly
2. Apparatus: Wire gauze Crucible
Test tube Boiling tube
Test tube holder Spatula
3. Filter funnel:
Measuring cylinder Bunsen burner
• Used to separate insoluble solid
substances from a liquid
Beaker Conical flask
Prepared By: K.C. Ngu Form 1: Chapter 1 – Week 1
KC TUITION: 012 – 3877 265
4. How to use Bunsen burner: Let’s Test Yourself 1.2
1. Tick the correct boxes.
Non –
Luminous
luminous
flame
flame
(a) Has a higher
temperature
(b) Produces a lot
of soot
2. Which of the following are safety
precautions in the laboratory? Tick in the
i) Close the air – hole by turning collar
spaces provided.
ii) Bring a lit match to the top of the
a) Use a test tube holder when handling
barrel corrosive substances ( )
iii) Turn on the gas slowly
b) Return used chemicals to the original
iv) Adjust the collar until obtain a steady
bottles ( )
blue flame c) Turn off the Bunsen burner after use
( )
5. Types of flame:
d) Use a spatula to handle solid substances
( )
Types Luminous Non – luminous e) Point the mouth of the test tube towards
Air – hole Closed Opened the person beside you when heating any
Colour Yellow Blue chemicals ( )
Temperature Hot Hotter
Soot A lot Absent 3. What do these symbols represent?
Heating No suitable Suitable
6. Hazard symbols:
Flammable Toxic/Poisonous
(Alcohol, petrol, (Mercury, lead,
ethanol, kerosene) chloroform, benzene)
Irritant/Harmful Explosive
(Ammonia, chloroform, (Hydrogen, Sodium,
dilute acids/alkalis) Potassium, air mixture)
Radioactive Corrosive
(Concentrated
(Uranium, plutonium, acids/alkalis, bromine,
radium) hydrogen peroxide)
Prepared By: K.C. Ngu Form 1: Chapter 1 – Week 1
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- KelDocument26 pagesKelnixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- Format Peperiksaan SPM Add MathDocument1 pageFormat Peperiksaan SPM Add MathJaybeeAngelPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision of Form 4 Add MathsDocument9 pagesRevision of Form 4 Add MathsnixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - Unit and Measurement ToolsDocument18 pagesChapter 1 - Unit and Measurement ToolsnixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - Introduction of ScienceDocument27 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction of SciencenixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- Trial Mara 2015 Paper 2 MTDocument22 pagesTrial Mara 2015 Paper 2 MTnixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- Trial Mara 2015 Paper 1Document25 pagesTrial Mara 2015 Paper 1nixleon0% (1)
- 2014 PercubaanDocument6 pages2014 PercubaannixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 1Document3 pagesQuiz 1nixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- PT3 Kelantan SainsDocument27 pagesPT3 Kelantan Sains纪泽勇60% (5)
- Graph and TableDocument1 pageGraph and TablenixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- c1 Exersice 2 Ms Gauge CalliperDocument2 pagesc1 Exersice 2 Ms Gauge CallipernixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- Hitungkan Luas Keratan Rentas, A, Dawai Tersebut.: Nyatakan Hubungan Antara R Dengan LDocument3 pagesHitungkan Luas Keratan Rentas, A, Dawai Tersebut.: Nyatakan Hubungan Antara R Dengan LnixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1Document26 pagesModule 1zackyzekPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Test 1 - Objectives (5,6,7)Document8 pagesFinal Test 1 - Objectives (5,6,7)nixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- KC Tuition: 012 - 3877 265: U R S T VDocument1 pageKC Tuition: 012 - 3877 265: U R S T VnixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 2.1Document3 pagesTutorial 2.1nixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 2.1Document3 pagesTutorial 2.1nixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 5.1Document2 pagesTutorial 5.1nixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 2.2Document2 pagesTutorial 2.2nixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 2.3Document1 pageTutorial 2.3nixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- KC Tuition: 012 - 3877 265Document1 pageKC Tuition: 012 - 3877 265nixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- 10.notes - Simple Machine PDFDocument2 pages10.notes - Simple Machine PDFnixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.notes - Appliaction Air Pressure PDFDocument2 pages6.notes - Appliaction Air Pressure PDFnixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- 7.notes Work PDFDocument1 page7.notes Work PDFnixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.notes - Support System PDFDocument1 page8.notes - Support System PDFnixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.notes Filtralisation PDFDocument1 page5.notes Filtralisation PDFnixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- 7.notes Frictional PDFDocument1 page7.notes Frictional PDFnixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.notes - Support System PDFDocument1 page8.notes - Support System PDFnixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.notes AcidDocument2 pages5.notes AcidnixleonPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Whitner, Contingency Planning For The Household Hazardous Waste FacilityDocument17 pagesWhitner, Contingency Planning For The Household Hazardous Waste FacilityMike AdvinculaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/43Document24 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/43Dhruva VengalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Answer Assignment 02 Salt Analysis & Practical Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesAnswer Assignment 02 Salt Analysis & Practical Organic Chemistryhemachaturvedi560Pas encore d'évaluation
- NEW Laboratory ReportDocument10 pagesNEW Laboratory ReportShōyōHinataPas encore d'évaluation
- Mms Health Recovery Guidebook 1 October 2016Document346 pagesMms Health Recovery Guidebook 1 October 2016omar hazard94% (50)
- Investigatory Project: Submitted byDocument11 pagesInvestigatory Project: Submitted byDav BroPas encore d'évaluation
- 0620 s15 QP 62Document12 pages0620 s15 QP 62Mohammed Murtada0% (1)
- Experiment 4 1Document7 pagesExperiment 4 1joannamarie583Pas encore d'évaluation
- Artikel Asli: Volume 1, Nomor 1 Januari - April 2016Document8 pagesArtikel Asli: Volume 1, Nomor 1 Januari - April 2016Eliza PutriPas encore d'évaluation
- Bright Star's MDMA Synthesis For The First Time Chemist - (WWWDocument7 pagesBright Star's MDMA Synthesis For The First Time Chemist - (WWWSCRUPEUSSPas encore d'évaluation
- 11.4 Dyeing of Cotton With Azoic DyesDocument13 pages11.4 Dyeing of Cotton With Azoic DyesPraveen NagarajanPas encore d'évaluation
- N L Chauhan PPT - 1Document124 pagesN L Chauhan PPT - 1JAI BHATUPas encore d'évaluation
- Grinard Reagent LabDocument4 pagesGrinard Reagent LabZach McCartyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pneumatic HosesDocument17 pagesPneumatic HosesJamin SmtpngPas encore d'évaluation
- Tese Nswparte 2Document153 pagesTese Nswparte 2AndrelslPas encore d'évaluation
- Acid and Base 5 PDFDocument22 pagesAcid and Base 5 PDFZenonissya GalwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bab 7 Diagram Alir ProsesDocument2 pagesBab 7 Diagram Alir ProsesWisnu Center'zPas encore d'évaluation
- Accessories Catalog PDFDocument186 pagesAccessories Catalog PDFanush_swaminathan100% (1)
- Ionac MembraneDocument2 pagesIonac Membranemarsur100% (1)
- The Effect of Mos - and Graphene Nanoparticles On The Properties & Performance of Polymer /salt Treated Bentonite Drilling FluidDocument13 pagesThe Effect of Mos - and Graphene Nanoparticles On The Properties & Performance of Polymer /salt Treated Bentonite Drilling FluidGéssica PalaoroPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 1 Calc 1 and 2 PDFDocument7 pagesActivity 1 Calc 1 and 2 PDFonyxPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Guidelines For The Inspection and Repair of Hot Dip Galvanized CoatingsDocument8 pagesPractical Guidelines For The Inspection and Repair of Hot Dip Galvanized CoatingsIan FletcherPas encore d'évaluation
- P.N.Anglo Sanskrit: SR Secondary School, Nayatola, Patna-4Document17 pagesP.N.Anglo Sanskrit: SR Secondary School, Nayatola, Patna-4AKSHAY KUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- Since The Beginning of The 20 Century, Between Tradition and InnovationDocument6 pagesSince The Beginning of The 20 Century, Between Tradition and InnovationrimshadtpPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology of Medications For Skin Disease 2019Document40 pagesPharmacology of Medications For Skin Disease 2019Dapot SianiparPas encore d'évaluation
- Inorganic ChemistryDocument10 pagesInorganic Chemistrydebraj sethi100% (1)
- Kluber LubricantsDocument17 pagesKluber LubricantsBenjamin Jr Limbaga100% (1)
- Product 6Document5 pagesProduct 6TsabitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Guide EdexcelDocument43 pagesPractical Guide EdexcelUsman BokhariPas encore d'évaluation
- November 2022 (9701 - 13) QPDocument16 pagesNovember 2022 (9701 - 13) QPHung Mang ThiPas encore d'évaluation