Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Ph.D-Syll Botany
Transféré par
irc_avtar0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
198 vues4 pagesMicrobiology, Phycology and Mycology. Ultra structure of bacterial cell. Reproduction and genetics of bacteria., transformation, conjugation, transduction. Plant viruses with emphasis on TMV and bacteriophages.
Description originale:
Titre original
Ph.D-Syll_Botany
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentMicrobiology, Phycology and Mycology. Ultra structure of bacterial cell. Reproduction and genetics of bacteria., transformation, conjugation, transduction. Plant viruses with emphasis on TMV and bacteriophages.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
198 vues4 pagesPh.D-Syll Botany
Transféré par
irc_avtarMicrobiology, Phycology and Mycology. Ultra structure of bacterial cell. Reproduction and genetics of bacteria., transformation, conjugation, transduction. Plant viruses with emphasis on TMV and bacteriophages.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
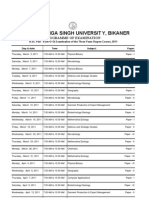
SYLLABUS FOR Ph.D.
ELIGIBILITY ENTRANCE TEST
BOTANY
VINOBA BHAVE UNIVERSITY, HAZARIBAG – 825301
JHARKHAND
F.M. – 100
Time –
SECTION ‘A’: 30 objective questions each carrying 2 marks, are to be set
covering the whole syllabus [ 30 x 2 = 60 ]
SECTION ‘B’ : 12 short questions, each carrying 5 marks, are to be set out of
which 8 questions are to be answered. [ 8 x 5 = 40 ]
Microbiology, Phycology & Mycology
1. Ultra structure of bacterial cell
2. Reproduction and genetics of bacteria., transformation, conjugation, transduction
3. Structure and nature of plant viruses with emphasis on TMV and bacteriophages.
4. Thallus organisation in algae.
5. Algal blooms and Algal biofertilizers
6. Heterothallism, Hetrokaryosis, Parasexuality,
7. Fungi in industry, medicine and as food, Mycotoxins
8. Mushroom cultivation
9. Mycorrhizae; General account, their role and applications in agriculture and forestry
Cell biology, Molecular biology & Cytology
10. Chromosome structure and packaging of DNA, Euchromatin and hetrochromatin,
banding patterns, Specialized types of chromosomes: - B-chromosomes, sex
chromosomes, polytene and lamp brush chromosomes.
11. Structural alterations in chromosomes : Origin, meiosis and breeding behavior of
duplication, deficieny, inversion. And translocation heterozygotes.
12. Numerical alterations in chromosomes : Origin, occurrence, production and meiosis
of haploids, euploids and aneuploids; origin and production of autopolyploids;
types, genome constitution and analysis of allopolyploids, induction and
characterization of trisomics and monosomics, effect of aneuploidy on phenotype in
plants.
13. Mutations : Spontaneous and induced mutations, physical and chemical mutagens;
molecular basis of gene mutations ; mutations induced by transposons ; site directed
mutagenesis.
14. DNA structure : A, B and Z forms of DNA; replication, damage and repair
mechanism.
Plant physiology & Biochemistry
15. Enzymes : Nomenclature and classification; nature and properties Coenzymes and
Prosthetic groups : Enzyme kinetics, Mechanism and mode of enzyme action;
Active site, Activator and inhibitory, Isoenzymes; Allosteric enzymes; Ribozyme;
Factors affecting enzyme activity; Enzyme immobilization.
16. Photosynthesis : Photosynthetic apparatus and pigments, Electron transport and
photophosphorylation ; C3, C4, and CAM pathway, Photorespiration, Glycolyte
metabolism.
17. Respiration: Glycolysis; Tricarboxylic acid cycle; Pentose phosphate pathway;
Electron transport system and oxidative phosphoryration.
18. Phytohormones : Chemical nature, biosynthesis, mode of action and role of Auxins,
Gibberellins, Cytokinins, ABA and Ethylene.
Ecology and Environmental Biology
19. Modern concept, structural components trophic structure, Food chain, food web and
ecological pyramids.
20. Dynamics : Succession –Hydrosere and Xerosere
21. Water pollution : sources, effect and control with emphasis on Eutrophication.
22. Forest : Forest types found in India, Importance of forest, strategies for
conservation and management of forest with special reference to deforestation ,
chipko movement, Social forestry, Biosphere reserve and Gene Bank; National
Forest Policy.
23. Soil : Soil erosion and soil conservation
24. ( a) Biosphere (b) Endemism
(c) Bioindicators (d) Wasteland Reclamation
(e) Environmental impact assessment (f) Damodar basin
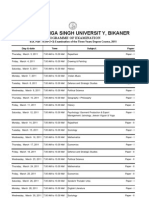
Plant Biotechnology
25. Plant cell and tissue culture : General introduction, history, scope, concept of
cellular differentiation, totipotency; principles and techniques of cell and tissue
culture.
26. Protoplast culture and Somatic hybridization; Cybrids.
27. Anther and pollen cultue ; haploidy.
28. Tools of genetic engineering with special reference to Restriction endonucleases;
Vectors: Plasmids, cosmids and phages.
29. Construction of genomic and c DNA libraries and their uses.
30. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) ; DNA fingerprinting.
31. Gene transfer in plants : Vectors mediated transformation ; Agrobacterium – The
natural genetic engineer; Methods of direct gene transfer.
32. Molecular markers ( RFLP, VNTR)
Bryophta, Pteridophyta, and Gymnosperm
33. Evolution of gametophytes and sporophytes in bryophytes.
34. Fossil bryophytes.
35. Stelar organization and its evolution in pteridophytes.
36. Telome concept ; its merits and demerits
37. Heterospory and seed habit in pteridophytes.
38. Distribution of living and fossil gymnosperms in India.
39. Ginkgoales
40. Gentales ( with emphasis on angiospermic features)
41. Apogamy, apospory & parthenogenesis
Systematic Botany, Anatomy and Embryology
42. Taxomomic evidence : Morphology, anatomy, Palynology, embryology, cytology,
Phytochemistry, genome analysis and nucleic acid hybridization.
43. System of angiosperm classification : Phenetic verses phylogenetic system.
Cladistics in taxonomy; relative merits and demerits of major system of
classification: relevance of taxonomy to conservation
44. Apical meristem : shoot apex and root apex organistion.
45. Periderm : formation and functions, Lenticles: Abscission and wound healing
46. Vascular cambium (Structure and functions)
47. Endosperm : development, types, functions, cytology, morphogenetic studies.
48. Polyembryony – Causes, experimental induction, classification, practical value.
49. Apomixis, Diplospory, Apospory; parthenogenetic development of embryos.
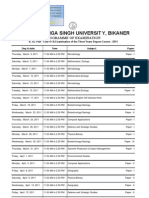
Resource Biology
50. (A) Origin, evolution, botany, cultivation and uses of the following with special
reference to Jharkhand :
(i) Food, forage and fodder crops. (ii) Fibre crops
(iii) Medicinal plants (iv) Aromatic plants
(v) Vegetable oil yielding crops
51. Role and impact of following
(i) Remote sensing. (ii) Floriculture
(iii) Dry-land farming (iv) Agro forestry
(iv) Organic farming
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Vidu SchdulOfEXmsDocument2 pagesVidu SchdulOfEXmsirc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- VIdu-DE ProposdSchdulPGDocument1 pageVIdu-DE ProposdSchdulPGirc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- DU ThreeYrDegriCoursPrt3Document2 pagesDU ThreeYrDegriCoursPrt3irc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- UOB BAPart1Document2 pagesUOB BAPart1irc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- JU PhyReunionDocument1 pageJU PhyReunionirc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- UOB-B ScPart2Document1 pageUOB-B ScPart2irc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- UOL VivaVocenPraDocument2 pagesUOL VivaVocenPrairc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- JU AcaCalScncDocument2 pagesJU AcaCalScncirc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- JU AcaCalArtsDocument2 pagesJU AcaCalArtsirc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- BU PGFinlVivaXmProgDocument9 pagesBU PGFinlVivaXmProgirc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- UOB BAPart2Document2 pagesUOB BAPart2irc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- UOB BAPart3Document2 pagesUOB BAPart3irc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- UOB-B ScPart1Document2 pagesUOB-B ScPart1irc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- UOB-B ScPart3Document1 pageUOB-B ScPart3irc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- Part 3Document1 pagePart 3irc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- UOB-B ScHmScPart1Document1 pageUOB-B ScHmScPart1irc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- UOB BFAPart1Document1 pageUOB BFAPart1irc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- UOB-B ScHmScPart3Document1 pageUOB-B ScHmScPart3irc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- BHU AyurvedaVachaspatiDocument6 pagesBHU AyurvedaVachaspatiirc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- CRET March2011Document17 pagesCRET March2011kunal084Pas encore d'évaluation
- DBRA UnivMainXmDocument1 pageDBRA UnivMainXmirc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- BHU-M Ed (PT)Document4 pagesBHU-M Ed (PT)irc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- Nhus de PgprofdipspeduDocument1 pageNhus de Pgprofdipspeduirc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- Mgkvu-Llb Bca Bbasem1& 3xmttDocument1 pageMgkvu-Llb Bca Bbasem1& 3xmttirc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- NG BachelorsDegriXmCntrsDocument4 pagesNG BachelorsDegriXmCntrsirc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- BTechProgramme2011 040111Document3 pagesBTechProgramme2011 040111Roikka HazarikaPas encore d'évaluation
- CSJM AcaCalendarDocument1 pageCSJM AcaCalendarirc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- Jain Vishva Bharati University, Ladnun (Rajasthan) : ACADEMIC CALENDAR: 2010-2011Document4 pagesJain Vishva Bharati University, Ladnun (Rajasthan) : ACADEMIC CALENDAR: 2010-2011irc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- NHUs-DE - FC SEDE AN26-2-11Document1 pageNHUs-DE - FC SEDE AN26-2-11irc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- North - Eastern Hill University Permanent Campus:: Shillong - 7930022 NotificationDocument5 pagesNorth - Eastern Hill University Permanent Campus:: Shillong - 7930022 Notificationirc_avtarPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- 11 - Chapter 5 PDFDocument35 pages11 - Chapter 5 PDFlouisPas encore d'évaluation
- 373 07 2Document143 pages373 07 2fpttmmPas encore d'évaluation
- Optical Fiber Design Modification for Medical ImagingDocument6 pagesOptical Fiber Design Modification for Medical ImagingNAJMILPas encore d'évaluation
- Standard:: SS2H1 The Student Will Read About and Describe The Lives of Historical Figures in Georgia HistoryDocument4 pagesStandard:: SS2H1 The Student Will Read About and Describe The Lives of Historical Figures in Georgia Historyjeffmiller1977Pas encore d'évaluation
- "Difference Between Private and Public Nuisance": Law of TortsDocument4 pages"Difference Between Private and Public Nuisance": Law of Tortsaridaman raghuvanshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Qdoc - Tips Select Readings 2nd Pre IntermediateDocument178 pagesQdoc - Tips Select Readings 2nd Pre IntermediateFarzana BatoolPas encore d'évaluation
- Citizen Journalism Practice in Nigeria: Trends, Concerns, and BelievabilityDocument30 pagesCitizen Journalism Practice in Nigeria: Trends, Concerns, and BelievabilityJonathan Bishop100% (3)
- Escaping The Digital Dark AgeDocument5 pagesEscaping The Digital Dark AgeKarlos lacallePas encore d'évaluation
- Work From Home Policy LeadsquaredDocument5 pagesWork From Home Policy LeadsquaredAnthonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Loads Dead Loads Imposed Loads Floor Roof Determining Load Per M and m2 WindDocument58 pagesLoads Dead Loads Imposed Loads Floor Roof Determining Load Per M and m2 Windwaheedopple3998Pas encore d'évaluation
- Constructed Wetland Design Guidelines for DevelopersDocument32 pagesConstructed Wetland Design Guidelines for DevelopersBere QuintosPas encore d'évaluation
- 1634858239Document360 pages1634858239iki292100% (1)
- Guia de Manejo Sdra 2019Document27 pagesGuia de Manejo Sdra 2019Jorge VidalPas encore d'évaluation
- Controversial Aquatic HarvestingDocument4 pagesControversial Aquatic HarvestingValentina RuidiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Lpi - 101-500Document6 pagesLpi - 101-500Jon0% (1)
- The Benefits of Radio Broadcasting As Perceived by The People in Rural AreasDocument10 pagesThe Benefits of Radio Broadcasting As Perceived by The People in Rural AreasMaePas encore d'évaluation
- Thinking Maps in Writing Project in English For Taiwanese Elementary School StudentsDocument22 pagesThinking Maps in Writing Project in English For Taiwanese Elementary School StudentsThilagam MohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Oracle® Database: Administrator's Reference 11g Release 1 (11.1) For Linux and UNIX-Based Operating Sys-TemsDocument174 pagesOracle® Database: Administrator's Reference 11g Release 1 (11.1) For Linux and UNIX-Based Operating Sys-TemsPrakash MohantyPas encore d'évaluation
- SQL Server DBA Daily ChecklistDocument4 pagesSQL Server DBA Daily ChecklistLolaca DelocaPas encore d'évaluation
- Moon Phases 2023Document2 pagesMoon Phases 2023Maira RodaPas encore d'évaluation
- Signal Sampling, Quantization, Binary Encoding: Oleh Albert SagalaDocument46 pagesSignal Sampling, Quantization, Binary Encoding: Oleh Albert SagalaRamos D HutabalianPas encore d'évaluation
- Abdul Azim Resume NewDocument9 pagesAbdul Azim Resume NewSayed WafiPas encore d'évaluation
- Damplas damp proof membranes CE Marked to EN 13967Document5 pagesDamplas damp proof membranes CE Marked to EN 13967Vikram MohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Variable frequency drives for electric submersible pumpsDocument34 pagesVariable frequency drives for electric submersible pumpshermit44535Pas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Citizenship RubricDocument1 pageDigital Citizenship Rubricapi-300964436Pas encore d'évaluation
- Newsletter April.Document4 pagesNewsletter April.J_Hevicon4246Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bangla Web AddressDocument5 pagesBangla Web Addressapi-3864412100% (5)
- 2nd Perdev TestDocument7 pages2nd Perdev TestBETHUEL P. ALQUIROZ100% (1)
- Notes On Unit - 4 - Employees Roles in Service MarketingDocument3 pagesNotes On Unit - 4 - Employees Roles in Service MarketingSridhar Gowda67% (3)
- Computational Chunking in Chess PDFDocument211 pagesComputational Chunking in Chess PDFTran VuPas encore d'évaluation