Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology of Hypertension: RAAS Activation and Organ Damage
Transféré par
Alvin Ramirez0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
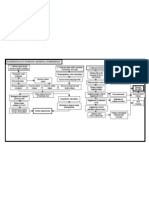
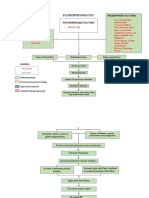
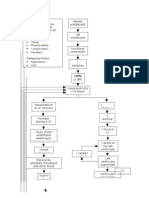
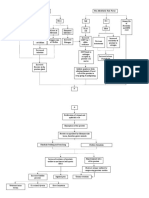
724 vues2 pagesFamily history of hypertension, diabetes, heart failure Stress High salt, high fat intake Age Stiffness of large arteries (such as aorta) as Part of aging process Hypoperfusion of blood to organs (such as kidneys) and tissues RAAS Activation Sensed by the Juxtaglomerular Cells of the kidneys Triggers the release of renin It will go to the liver ANGIOSTENSINOGEN Converted to Angiotensin 1 It
Description originale:
Titre original
final patho-HCVD
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentFamily history of hypertension, diabetes, heart failure Stress High salt, high fat intake Age Stiffness of large arteries (such as aorta) as Part of aging process Hypoperfusion of blood to organs (such as kidneys) and tissues RAAS Activation Sensed by the Juxtaglomerular Cells of the kidneys Triggers the release of renin It will go to the liver ANGIOSTENSINOGEN Converted to Angiotensin 1 It
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
724 vues2 pagesPathophysiology of Hypertension: RAAS Activation and Organ Damage
Transféré par
Alvin RamirezFamily history of hypertension, diabetes, heart failure Stress High salt, high fat intake Age Stiffness of large arteries (such as aorta) as Part of aging process Hypoperfusion of blood to organs (such as kidneys) and tissues RAAS Activation Sensed by the Juxtaglomerular Cells of the kidneys Triggers the release of renin It will go to the liver ANGIOSTENSINOGEN Converted to Angiotensin 1 It
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
V.
Pathophysiology
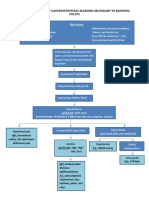
ETIOLOGIC RISK FACTORS
AGENT Family history of hypertension ,
Idiopathic/ unknown diabetes, heart failure
Stress
High salt, high fat intake
Age
Stiffness of large arteries (such as Aorta) as
Part of aging process
Hypoperfusion of blood to organs
(such as kidneys) and tissues
RAAS Activation
Sensed by the Juxtaglomerular
Cells of the kidneys
Triggers the release of renin
It will go to the liver
ANGIOSTENSINOGEN
Converted to Angiotensin 1
It will go to the lungs
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme
Converts Angiotensin 1 to
Angiotensin 2
Stimulates the Adrenal cortex Vasoconstriction
Release of aldosterone
Na retention (increase circulatory decrease Preload increase Afterload
Blood volume)
Increase BP increase RR increase Peripheral Resistance
Increase BP increase chloride Left Ventricle wall stress
Oxygen consumption insufficient Left ventricle Hypertrophy Concentric LVH
Oxygen as shown in Xray
Anaerobic respiration
Pale decreased blood pumped coronary flow reserve Diastolic
By the heart Pressure
Lactic acid, pyruvic acid ATP produced Fibrosis
Production blood supply (vital organs) Diastolic filling
Weakness/ Systolic Heart
Irritation of nerve endings easy fatigability myocardial ischemia failure LVEDP
Chest pain myocardial infarction Pulmonary Atrial Fibrilation Diastolic
congestion Heart
Failure
Shortness of breath/ DOB
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 pagesChronic Renal FailureIvana Yasmin Bulandres100% (2)
- Angina Pectoris PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAngina Pectoris Pathophysiologydana86% (7)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureTrixia Almendral100% (2)
- ACS PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesACS PathophysiologyFerliza OblenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Predisposing Factors Precipitating/Aggravating FactorsDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Predisposing Factors Precipitating/Aggravating Factorsguillermojerry100% (2)
- Pathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisDocument4 pagesPathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisCyrus Ortalla RobinPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysilogy of Primary HypertensionDocument1 pagePathophysilogy of Primary Hypertensionromeo rivera75% (4)
- Pathophysiology of HCVD DM2 CVD Left Basal GangliaDocument1 pagePathophysiology of HCVD DM2 CVD Left Basal GangliaJake Caballo100% (1)
- Qtsoi Concept MapDocument5 pagesQtsoi Concept MapGenella BabantoPas encore d'évaluation
- HELLP Concept Map RevisedDocument1 pageHELLP Concept Map RevisedwandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Patho MIDocument2 pagesPatho MIbanyenye25100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure III With Pleural EffusionDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure III With Pleural EffusionKen100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Pulmonary Embolism (Loria.J)Document2 pagesPathophysiology of Pulmonary Embolism (Loria.J)Justine Mae Loria0% (1)
- PathophysiologyDocument34 pagesPathophysiologyeunams_1195% (20)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailurePerry Oliver AlvarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failuretinayko100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Hypertension, Diabetes, Ubm, BPHDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Hypertension, Diabetes, Ubm, BPHCarly Beth Caparida LangerasPas encore d'évaluation
- CeVD, MI, HCVD & Atrial Fibrillation PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesCeVD, MI, HCVD & Atrial Fibrillation PathophysiologyJjessmar Bolivar FamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)Document1 pagePathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)rexale ria100% (1)
- Pathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocument1 pagePathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisRan Ma100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular AccidentByron Paz Te100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CVDDocument1 pagePathophysiology CVDPamela Shiermaine FilomenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease (HCVDDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease (HCVDNicolne Lorraine100% (1)
- Angina Pectoris PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAngina Pectoris PathophysiologyALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTOPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysio CRF RevisedDocument2 pagesPathophysio CRF Revisedroseanne18Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bladder Cancer Types, Symptoms, Tests & TreatmentDocument1 pageBladder Cancer Types, Symptoms, Tests & TreatmentCarmina AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureLeng Royo BrionesPas encore d'évaluation
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocument3 pagesAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryJane Arian Berzabal0% (1)
- Liver Cirrhosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorDocument22 pagesLiver Cirrhosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorJorie RocoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology Sickle Cell Anemia PDFDocument1 pagePathophysiology Sickle Cell Anemia PDFTine GuibaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAyPas encore d'évaluation
- BPH Pathophysio 4CDocument2 pagesBPH Pathophysio 4CPatricia Camille Ponce JonghunPas encore d'évaluation
- Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument3 pagesPrecipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseGrace Jane DionaldoPas encore d'évaluation
- Liver Cirrhosis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageLiver Cirrhosis PathophysiologyCaren ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of GI Bleeding from Bleeding PolypsDocument1 pagePathophysiology of GI Bleeding from Bleeding PolypsGinoTevesPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Hospital CaseDocument3 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 Hospital CaseAngel FiloteoPas encore d'évaluation
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyDocument3 pages"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano50% (2)
- Schistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Document10 pagesSchistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Tiger Knee100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Patent Ductus Arteroisus (PDA)Document2 pagesPathophysiology of Patent Ductus Arteroisus (PDA)Rodel YacasPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology HPN CvaDocument1 pagePathophysiology HPN Cvatresdos09Pas encore d'évaluation
- HCVDDocument5 pagesHCVDkhrizaleehPas encore d'évaluation
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia BPH Pathophysiology Schematic Diagram PDFDocument2 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia BPH Pathophysiology Schematic Diagram PDFgailPas encore d'évaluation
- PathophyDocument2 pagesPathophymharz_astilloPas encore d'évaluation
- End Stage Renal Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramDocument2 pagesEnd Stage Renal Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramSharmaine Camille de LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology Hemor CVADocument4 pagesPathophysiology Hemor CVAMatthew Emmanuel M. Martinez100% (2)
- Non-Modifiable, Partially Modifiable, and Modifiable Risk Factors for Atherothrombotic DiseaseDocument15 pagesNon-Modifiable, Partially Modifiable, and Modifiable Risk Factors for Atherothrombotic DiseaseWiljohn de la CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology - HyperthyroidismDocument2 pagesPathophysiology - HyperthyroidismCaren Reyes100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Gastroenteritis, Dehydration, and NecatoriasisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Gastroenteritis, Dehydration, and NecatoriasisRalph Delos Santos100% (2)
- Dobutamine It Stimulates Heart Muscle and Improves Blood Flow by Helping The Heart Pump BetterDocument3 pagesDobutamine It Stimulates Heart Muscle and Improves Blood Flow by Helping The Heart Pump BetterJinky Nacar DomingoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of AMLDocument1 pagePathophysiology of AMLjake251996100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Hyperthyroidism and Thyroid StormDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Hyperthyroidism and Thyroid StormPen MontantePas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Heart Failure Due to Myocardial DysfunctionDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Heart Failure Due to Myocardial DysfunctionabbeeyyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology CVD InfarctDocument1 pagePathophysiology CVD InfarctElisa KerrPas encore d'évaluation
- Stoke Pathophysiology 1228539935337551 8Document7 pagesStoke Pathophysiology 1228539935337551 8Mark Anthony Taña GabiosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology CHF MineDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CHF MineCalimlim KimPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureMel Izhra N. MargatePas encore d'évaluation
- Biology 1 EditedDocument336 pagesBiology 1 EditedEmperor GoosePas encore d'évaluation
- Pre Gestational 1Document12 pagesPre Gestational 1Fatima TañedoPas encore d'évaluation
- Control of Blood PressureDocument14 pagesControl of Blood PressureallerasicPas encore d'évaluation
- Prometric Sample For DentistryDocument43 pagesPrometric Sample For DentistryAlvin RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- Updated Guidelines on Management of Animal Bite PatientsDocument15 pagesUpdated Guidelines on Management of Animal Bite PatientsKaren ArchesPas encore d'évaluation
- Copd PathoDocument2 pagesCopd PathoAlvin RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- Nbs 3Document17 pagesNbs 3Alvin RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- ApplicantDocument1 pageApplicantAlvin RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- Toto Na DawDocument30 pagesToto Na DawAlvin RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Zurenix Classification: Doctor's Order: 750 Date Started: Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name: Zurenix Classification: Doctor's Order: 750 Date Started: Nursing ConsiderationsAlvin RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument7 pagesFluids and ElectrolytesAngelica QuimnoPas encore d'évaluation
- HypertensionDocument1 pageHypertensionAlvin RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S0735109716332739 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S0735109716332739 MainBhagya Narayan PanditPas encore d'évaluation
- Hopkins Status ReportDocument56 pagesHopkins Status ReportJeffrey GillespiePas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Lead EKG Interpretation PDFDocument251 pages12 Lead EKG Interpretation PDFRobert So JrPas encore d'évaluation
- Laporan PRB RsucmDocument12 pagesLaporan PRB RsucmKurnia WatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan (MI)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan (MI)Krisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Kardiovaskular Patologi AnatomiDocument37 pagesKardiovaskular Patologi AnatomiAngga AhadiyatPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG Interpretation For ACLSDocument27 pagesECG Interpretation For ACLSZH. omg sarPas encore d'évaluation
- Nephrotic and Nephritic - SyndromeDocument35 pagesNephrotic and Nephritic - SyndromeadinayPas encore d'évaluation
- Supp B RRC 2015 LowResDocument360 pagesSupp B RRC 2015 LowResstoicea catalinPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular Review PDFDocument6 pagesCardiovascular Review PDFMacy Grace Yuzon GuingabPas encore d'évaluation
- 2019 Esc PPCMDocument17 pages2019 Esc PPCMJayden WavePas encore d'évaluation
- BASIC ECG GUIDE FOR NURSESDocument112 pagesBASIC ECG GUIDE FOR NURSESSam jr TababaPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG-Naming The PRST Waves - (6!19!2012)Document7 pagesECG-Naming The PRST Waves - (6!19!2012)cornondaPas encore d'évaluation
- DKD and Sglt2iDocument61 pagesDKD and Sglt2iماكريلا المصريPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic ECG InterpretationDocument62 pagesBasic ECG Interpretationmohannadalkwiese3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Compact ECG Arrhythmia SimulatorDocument2 pagesCompact ECG Arrhythmia SimulatorismailshajjiPas encore d'évaluation
- Acls Drug OverviewDocument2 pagesAcls Drug OverviewBruce Abramowitz100% (1)
- Unstable Angina Differential DiagnosesDocument5 pagesUnstable Angina Differential DiagnosesSanda-ana BogdanPas encore d'évaluation
- Buku Panduan ACLS Perki Cetakan 2021 - Hal 11Document1 pageBuku Panduan ACLS Perki Cetakan 2021 - Hal 11yandriasPas encore d'évaluation
- Degree), Intermittent Degree), or Complete Conduction Failure (3 Degree) - inDocument1 pageDegree), Intermittent Degree), or Complete Conduction Failure (3 Degree) - inLwin Maung Maung ThikePas encore d'évaluation
- Patho Worksheet Right Heart FailureDocument1 pagePatho Worksheet Right Heart FailureMindy Leigh LayfieldPas encore d'évaluation
- Adult Congenital Heart Disease - Cardiovascular Medicine - MKSAP 17Document13 pagesAdult Congenital Heart Disease - Cardiovascular Medicine - MKSAP 17alaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Patient Implantable Medical DevicesDocument1 pagePatient Implantable Medical DevicesTracy100% (1)
- Stress TestingDocument20 pagesStress Testingaishwarya desaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Template EchoreportDocument1 pageTemplate EchoreportArijitArikNath100% (1)
- Nejmoa 1805374Document10 pagesNejmoa 1805374Lia Diana RaileanuPas encore d'évaluation
- 急救藥物泡法Document3 pages急救藥物泡法Edward KaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Master Content ListDocument418 pagesMaster Content ListCristian CalinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument54 pagesChronic Renal Failuresanjivdas100% (3)
- Defense-3 0Document24 pagesDefense-3 0Harold GoPas encore d'évaluation