Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Revision For Functions and Trigonometry
Transféré par
Imama Aamir0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
17 vues4 pagesTitre original
Revision for functions and trigonometry
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
17 vues4 pagesRevision For Functions and Trigonometry
Transféré par
Imama AamirDroits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 4
Functions and Trigonometry
Trigonometric Identities
1 + tan2θ = sec2θ
cos2θ + sin2θ = 1 cot2θ + 1 = cosec2θ
When asked to show by counter-example that a statement is false, sub a
value in and show that LHS is not equal to RHS.
Formulae for sin (A + B), cos (A + B), tan (A + B)
Sin (A + B) = sin A cos B + cos A sin B
Sin (A - B) = sin A cos B - cos A sin B
Cos (A + B) = cos A cos B - sin A sin B
Cos (A - B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B
Transformations of Graphs
The transformations so far follow these rules:
f(x) + a is f(x) shifted upward a units
f(x) – a is f(x) shifted downward a units
f(x + a) is f(x) shifted left a units
f(x – a) is f(x) shifted right a units
–f(x) is f(x) flipped upside down ("reflected about the x-axis")
f(–x) is the mirror of f(x) ("reflected about the y-axis")
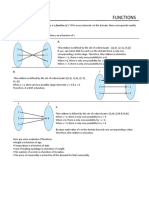
Functions
Using the domain to find the
range:
(-1,4]
(-1,4] means
means all
all the
the numbers
numbers between
between -1
-1 and
and 4,
4, To find the y-values on the
including 4 but not -1.
including 4 but not -1. graph, substitute the limits of
the domain into the equation.
This will give you your range.
In general, the domain of a composed
function is either the same as the
domain of the first function, or else lies inside
it.
The range of a composed function is either
the same as the range of the second function,
or else lies inside it.
The range of f-1(x) = domain of f(x)
The domain of f-1(x) = range of f(x)
Graphs of Functions
More
graphs of functions
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- General Mathematics Reviewer!Document4 pagesGeneral Mathematics Reviewer!Jane Anonas100% (8)
- Functions PDFDocument7 pagesFunctions PDFPaolo NaguitPas encore d'évaluation
- Shirt Poem AnalysisDocument2 pagesShirt Poem AnalysisImama AamirPas encore d'évaluation
- IMSO 2008 Short AnswersDocument9 pagesIMSO 2008 Short AnswersWoon Chet ChoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus With Analytic GeometryDocument33 pagesCalculus With Analytic GeometryMUHAMMAD BILAL AMJADPas encore d'évaluation
- FunctionsDocument12 pagesFunctionsMuhammad Aamir FeroziPas encore d'évaluation
- Inverse Functions: Teks Focus VocabularyDocument7 pagesInverse Functions: Teks Focus VocabularyAadarsh BalireddyPas encore d'évaluation
- DocScanner 17 Apr 2024 8 49 AmDocument2 pagesDocScanner 17 Apr 2024 8 49 Amjeenikalnahai07Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exactly One ElementDocument20 pagesExactly One ElementhazimahPas encore d'évaluation
- Relations and FunctionsDocument8 pagesRelations and FunctionssraikreePas encore d'évaluation
- Gen. Math Module 4Document4 pagesGen. Math Module 4Robert ClavoPas encore d'évaluation
- General MathematicsDocument13 pagesGeneral MathematicsStephen Carl EsguerraPas encore d'évaluation
- General Mathematics: Functions and Their GraphsDocument5 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Functions and Their GraphsPrincess VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Relations and FunctionsDocument2 pagesRelations and FunctionsCheMPas encore d'évaluation
- Genmath. 1st Quarter ReviewerDocument16 pagesGenmath. 1st Quarter ReviewerAlexa NicolePas encore d'évaluation
- ECC3001 F - (Continue) : UnctionsDocument39 pagesECC3001 F - (Continue) : Unctionsnur hashimahPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - Functions and ContinuityDocument59 pages1 - Functions and ContinuityJmPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1 Review On FunctionsDocument24 pages1.1 Review On Functionskiki lovemePas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 Inverse FunctionsDocument3 pagesModule 2 Inverse FunctionsRodante P Hernandez Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Horizontal Translations of Functions HWDocument2 pagesHorizontal Translations of Functions HWapi-368121935Pas encore d'évaluation
- FunctionsDocument28 pagesFunctionsParamveer SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Precalculus: Quarter I - ILM 2 FunctionsDocument15 pagesPrecalculus: Quarter I - ILM 2 FunctionsFreya AparisPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen. Math Module 3Document3 pagesGen. Math Module 3Robert ClavoPas encore d'évaluation
- Brahmastra FunctionDocument19 pagesBrahmastra FunctionAshmit RanjanPas encore d'évaluation
- General Mathematics NotesDocument18 pagesGeneral Mathematics NotesMs. CcPas encore d'évaluation
- CPT MathDocument4 pagesCPT Mathsome-thin-kingPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus: Name Xianglan CaoDocument41 pagesCalculus: Name Xianglan CaoUsmanSwiftPas encore d'évaluation
- Section 3.2Document4 pagesSection 3.2Diane DianePas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd Year Math Full Book PBDocument215 pages2nd Year Math Full Book PBFAizan AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- 2018 G12 Math E PDFDocument215 pages2018 G12 Math E PDFhamza50% (2)
- 0 BooksDocument23 pages0 BooksAjay KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1-Function22Document58 pagesLecture 1-Function22Tafa WelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Abdul Azeez N.P. Aligarh Muslim UniversityDocument49 pagesDr. Abdul Azeez N.P. Aligarh Muslim UniversityMD Shadan KausarPas encore d'évaluation
- MHF 4U - Advanced Functions (DZ) Unit 1 - Characteristics and Properties of FunctionsDocument9 pagesMHF 4U - Advanced Functions (DZ) Unit 1 - Characteristics and Properties of FunctionsWU YANPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Pre NotesDocument3 pages2 Pre NoteskgizachewyPas encore d'évaluation
- Functions and Limits: Animation 1.1: Function Machine Source and Credit: Elearn - PunjabDocument23 pagesFunctions and Limits: Animation 1.1: Function Machine Source and Credit: Elearn - PunjabAhmadAwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Concepts On FunctionsDocument32 pagesBasic Concepts On FunctionsChelsea RoquePas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Bhilai Study MaterialDocument97 pagesMaths Bhilai Study MaterialVarun SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- General MathDocument5 pagesGeneral MathKaireen OzPas encore d'évaluation
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedDocument13 pagesThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedsekharsudhansuPas encore d'évaluation
- Genmath 1Document9 pagesGenmath 1Sunshine Isabel CalayagPas encore d'évaluation
- One To OneDocument114 pagesOne To OneHazel SajuelaPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT 1 MODULE 1 FinalDocument20 pagesUNIT 1 MODULE 1 FinalHunter 004Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rational FunctionDocument14 pagesRational Functionawyne nozulPas encore d'évaluation
- Functions: Definition 1.2.1Document17 pagesFunctions: Definition 1.2.1Javian CampbellPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER ONE OrignalDocument33 pagesCHAPTER ONE Orignalmark okoriePas encore d'évaluation
- II Puc - Maths - 01 - Relations and FunctionsDocument6 pagesII Puc - Maths - 01 - Relations and FunctionspcmbacademicsPas encore d'évaluation
- FunctionsDocument54 pagesFunctionsLORENZO PALUMBOPas encore d'évaluation
- Convexity-Print Version PDFDocument13 pagesConvexity-Print Version PDFRitesh Pratap SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Background Information:: Name of Learner: - SectionDocument8 pagesBackground Information:: Name of Learner: - SectionNormalah D LalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4.2Document7 pagesUnit 4.2Wajahat KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- A2 Chapter 2 SummaryDocument1 pageA2 Chapter 2 Summaryamaz1ingPas encore d'évaluation
- Functions Kenneth Rosen BookDocument20 pagesFunctions Kenneth Rosen BookZubair AlamPas encore d'évaluation
- Relations and FunctionsDocument2 pagesRelations and FunctionsayeshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Representation of Functions: Aaron Paul A. CasabarDocument78 pagesRepresentation of Functions: Aaron Paul A. CasabarM MPas encore d'évaluation
- 13 Fourier Series (Zill)Document13 pages13 Fourier Series (Zill)Rara salsabila simanjuntakPas encore d'évaluation
- English For Mathematics-ThuyDocument34 pagesEnglish For Mathematics-ThuyChiến TrầnPas encore d'évaluation
- Functions: A X A X +a X+a A, A,, ADocument21 pagesFunctions: A X A X +a X+a A, A,, AMelchor Jaramilla OronosPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Function NotationDocument17 pages1 Function NotationKhloe WoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear FunctionDocument15 pagesLinear Functionkishnikamarielozano13Pas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction to Lebesgue Integration and Fourier SeriesD'EverandAn Introduction to Lebesgue Integration and Fourier SeriesPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry A Levels Worksheet EquilibriaDocument57 pagesChemistry A Levels Worksheet EquilibriaImama AamirPas encore d'évaluation
- 'Class-6 Planning GuideDocument53 pages'Class-6 Planning GuideImama AamirPas encore d'évaluation
- The City School: Alternate Day ModelDocument3 pagesThe City School: Alternate Day ModelImama AamirPas encore d'évaluation
- MeasurementsDocument15 pagesMeasurementsImama AamirPas encore d'évaluation
- Judicial Precedent 1Document4 pagesJudicial Precedent 1Imama AamirPas encore d'évaluation
- The City School: University Road CampusDocument1 pageThe City School: University Road CampusImama AamirPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision Questions: Howards End Is A Critical Examination of Margaret Schlegel'sDocument4 pagesRevision Questions: Howards End Is A Critical Examination of Margaret Schlegel'sImama AamirPas encore d'évaluation
- Song by Lady Mary WrothDocument2 pagesSong by Lady Mary WrothImama AamirPas encore d'évaluation
- Why Was Russia Defeated in The RussoDocument3 pagesWhy Was Russia Defeated in The RussoImama AamirPas encore d'évaluation
- Judicial Precedent 3Document1 pageJudicial Precedent 3Imama AamirPas encore d'évaluation
- IGCSE Class 10 Test - MathematicsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Class 10 Test - Mathematicspapia.bera1994Pas encore d'évaluation
- Teori BilanganDocument1 pageTeori BilanganRahmi Nurul MaulidyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 9 - Quadrilateral and Heron's Formula MCQ'sDocument9 pagesClass 9 - Quadrilateral and Heron's Formula MCQ'sPradyot ChakrabortyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ddpi Office Udupi-Beo Office KundapuraDocument8 pagesDdpi Office Udupi-Beo Office KundapuraSundari RameshPas encore d'évaluation
- Chain Rule To Extreme Value and Saddle PointsDocument83 pagesChain Rule To Extreme Value and Saddle PointsVishwas SainiPas encore d'évaluation
- Q3 Week5 Proportionality TheoremDocument20 pagesQ3 Week5 Proportionality TheoremMark Julian CadapanPas encore d'évaluation
- Table of Mathematical SymbolsDocument13 pagesTable of Mathematical Symbolsflaviofs1888Pas encore d'évaluation
- CE BOARD AlgebraDocument2 pagesCE BOARD AlgebraZherrinore Rasay0% (2)
- Mathematical SystemDocument6 pagesMathematical SystemSabino Alfonso RalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module in Mathematics 10Document55 pagesModule in Mathematics 10Kaye SibilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Math ExercisesDocument2 pagesMath ExercisesRes GosanPas encore d'évaluation
- Origami Calendario 2011Document19 pagesOrigami Calendario 2011Alan MGPas encore d'évaluation
- Math Part 2.0Document2 pagesMath Part 2.0Pam SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- LP For Co2 2023 Mathematics 1 & 2Document10 pagesLP For Co2 2023 Mathematics 1 & 2JUSTINE ANN EUPENAPas encore d'évaluation
- SAT Test 1 Math Answers and ExplanationsDocument20 pagesSAT Test 1 Math Answers and ExplanationsHolloGramPas encore d'évaluation
- Top 50 Quant Questions For XAT PDFDocument41 pagesTop 50 Quant Questions For XAT PDFKishan kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch2 Notes of Logical ConditionDocument40 pagesCh2 Notes of Logical Conditionsara shafaqPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.05 Geometry Foundations ActivityDocument2 pages1.05 Geometry Foundations ActivityYousef Hamdan100% (1)
- 2010 Shortlist JBMO - Problems: 1.1 AlgebraDocument2 pages2010 Shortlist JBMO - Problems: 1.1 Algebrastanislaus sitompulPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Paper Bonus HigherDocument21 pagesPractice Paper Bonus HigherShriep kebabaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4MA0 4HR Que 20160609Document24 pages4MA0 4HR Que 20160609Jia HaoPas encore d'évaluation
- VIII Notes 2 Algebraic ExpressionsDocument10 pagesVIII Notes 2 Algebraic ExpressionsKavita DhootPas encore d'évaluation
- Class X Math Study Material 2022-23Document174 pagesClass X Math Study Material 2022-23SumitPas encore d'évaluation
- CPT Maths NotesDocument9 pagesCPT Maths Notesanchal0% (1)
- Grade 4 Fractions To Decimals ADocument2 pagesGrade 4 Fractions To Decimals AMonica ViverosPas encore d'évaluation
- Math g4 m4 Topic A OverviewDocument2 pagesMath g4 m4 Topic A OverviewzeynepPas encore d'évaluation
- Category 2 - R1 - Int'l Math Challenge VIIDocument7 pagesCategory 2 - R1 - Int'l Math Challenge VIIEmrah ozkanPas encore d'évaluation
- Differential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces 3. Regular SurfacesDocument16 pagesDifferential Geometry of Curves and Surfaces 3. Regular SurfacesyrodroPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 Section ADocument7 pagesChapter 7 Section AmuzzPas encore d'évaluation