Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Montano
Transféré par
karl montanoTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Drug Study Montano
Transféré par
karl montanoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
A Drug Study on leucovorin
____________________
A Drug Study Presented to
The faculty of Nursing Department
Josephine Magno, RN, MN
____________________
In Partial fulfilment of the
Requirements in NCM-212
By:
Karl Angelo Montano, Stn
BSN 3B
September 10, 2020
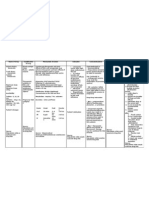
Generic Name: leucovorin
Brand Name: Wellcovorin
CLASSIFICATION: Vitamin/folic acid antagonist antidote
Mode of Action: Needed for normal growth
Therapeutic outcome: patterns; prevents toxicity during antineoplastic therapy by
protecting normal cells reversal of severe toxic effects of folic acid antagonists
INDICATION: Megaloblastic or macrocytic anemia caused by folic acid deficiency,
overdose of folic acid antagonist, methotrexate toxicity, toxicity caused by
pyrimethamine/trimethoprim/trime-trexate, pneumocystosis, toxoplasmosis
CONTRAINDICATION: Hypersensitivity to this product or folic acid, benzyl alcohol,
anemias other than megaloblastic not associated with vit B12 deficiency
ADVERSE EFFECTS:
HEMA: Thrombocytosis (intraarterial)
INTEG: Rash, pruritus, erythema, urticaria
RESP: Wheezing
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES:
Assessment
• Obtain CCr before leucovorin rescue and daily to detect nephrotoxicity,
methotrexate level
• Monitor I&O, urine pH q6hr; maintain at .7 to prevent neurotoxicity; watch for
nausea and vomiting; if vomiting occurs IM or IV route may be necessary
• Assess products currently taken: alcohol, hydantoins, trimethoprim may cause
increased folic acid use by body
• Assess for allergic reactions: rash, dyspnea, wheezing
• Assess neurologic status (rescue), weakness, fatigue
• Monitor calcium levels
• Assess for megaloblastic anemia, plasma lactic acid, reticulocyte count, Hct, Hgb
Patient/family education
• For leucovorin rescue: Drink 3 L fluid day of rescue
• Advise patient to take product exactly as prescribed; to notify prescriber of side
effects immediately
• Advise patient to report signs of hypersensitivity reaction immediately
• Advise patient with folic acid deficiency to eat folic acid–rich foods: bran, yeast,
dried beans, nuts, fruits, fresh green leafy vegetables, asparagus
• Advise patient to avoid breastfeeding
Evaluation Positive therapeutic outcome
• Increased weight
• Improved orientation, well-being
• Absence of fatigue
• Reversal of toxicity: methotrexate, folic acid antagonist overdose
References
Vallerand, A.H. (2009). Davis’s Drug Guide for Nurses. F.A. Davis Company. Philadelphia.
(11th ed.)
Karch, A.M.(2011). Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Guide. Lippincott Williams Rwilkins. Rochester,
New York.
Hodgson, B.B.(2011).Saunders Nursing Drug Handbook. Elsevier Saunders. St. Louis,
Missouri.
Roth, Linda Skidmore.(2011). Mosby’s Nursing Drug Reference. Mosby’s Inc. St. Louis,
Missouri.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Activity 4 - LeucovorinDocument1 pageActivity 4 - LeucovorinMelissa Fatima Laurente DosdosPas encore d'évaluation
- Folic Acid Presentation PDFDocument13 pagesFolic Acid Presentation PDFAngela IlustrisimoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug Studycruz_johnraymond100% (1)
- Omeprazole and Polynerv (B1,6,12)Document3 pagesOmeprazole and Polynerv (B1,6,12)Rene John Francisco100% (1)
- Pott's Drug Study. AdelDocument6 pagesPott's Drug Study. AdelAdelle SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Vit. ADocument3 pagesVit. AJule Santoya100% (1)
- 5th Draft DrugsDocument7 pages5th Draft DrugsShayne Jessemae AlmarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Update On Vitamin B12 DeficiencyDocument6 pagesUpdate On Vitamin B12 Deficiencyrizqi_cepiPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studyjanelee2824Pas encore d'évaluation
- DRUG STUDY DETAILS FOR CEFLEXIN, MULTIVITAMINS, AND FOLIC ACIDDocument7 pagesDRUG STUDY DETAILS FOR CEFLEXIN, MULTIVITAMINS, AND FOLIC ACIDKrishna BalsarzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Generic NameDocument10 pagesGeneric NameConadel AlicdanPas encore d'évaluation
- Keto LogDocument7 pagesKeto LogKim Justin InfantadoPas encore d'évaluation
- 05 NCP - Drug StudyDocument23 pages05 NCP - Drug StudyRene John FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study on MethergineDocument6 pagesDrug Study on MethergineGian kyle AradillosPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Food InteractionsDocument8 pagesDrug Food InteractionsDecky Aditya ZPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunosuppressants in Pregnancy Part 1Document43 pagesImmunosuppressants in Pregnancy Part 1Mehul ChoudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- MOriamin ForteDocument1 pageMOriamin Forteianecunar100% (3)
- Mizollen Tablets: 1. Name of The Medicinal ProductDocument6 pagesMizollen Tablets: 1. Name of The Medicinal Productddandan_2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Labor and Delivery DrugsDocument8 pagesLabor and Delivery DrugsDing EmilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Metformin: Dosing & UsesDocument8 pagesMetformin: Dosing & UsesMaria Alejandra Siachoque JaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug OrderDocument8 pagesDrug OrderRiezza BalicaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Vitamin ADocument5 pagesVitamin AAWPas encore d'évaluation
- Calcium Gluconate Drug Classification, Dosage and Side EffectsDocument4 pagesCalcium Gluconate Drug Classification, Dosage and Side EffectsStacy MC PelitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nrn101 and Nrn102 Drug Card: 500mg BID 10-16yrs 850mg QD 2000mg Max 2550mg Max Daily DoseDocument1 pageNrn101 and Nrn102 Drug Card: 500mg BID 10-16yrs 850mg QD 2000mg Max 2550mg Max Daily DoseJanet SheldonPas encore d'évaluation
- Teratology, Teratogens, and Fetotoxic AgentsDocument92 pagesTeratology, Teratogens, and Fetotoxic AgentsKaren EstavilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Anthemether Lumefrantine and RifampincineDocument12 pagesDrug Study Anthemether Lumefrantine and RifampincineAnonymous K99UIf1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Phenobarbital Tablets BP 60mg - Electronic Medicines Compendium (eMC) - Print FriendlyDocument6 pagesPhenobarbital Tablets BP 60mg - Electronic Medicines Compendium (eMC) - Print FriendlyBrian HarrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Folic Acid Benefits, Uses, InteractionsDocument15 pagesFolic Acid Benefits, Uses, InteractionsLene Derlene Gerona100% (2)
- Drug-Study_PsycheDocument4 pagesDrug-Study_PsycheKim TangoPas encore d'évaluation
- Paracetamol and Levofloxacin Drug StudyDocument9 pagesParacetamol and Levofloxacin Drug StudyKevin Sam AguirrePas encore d'évaluation
- College of Nursing drug study guideDocument5 pagesCollege of Nursing drug study guideDivine Mercy De JulianPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyChristine MatasPas encore d'évaluation
- Teratology and Medications That Affect The FetusDocument67 pagesTeratology and Medications That Affect The Fetusneripearl100% (1)
- Folic AcidDocument1 pageFolic AcidCassie100% (2)
- LevotiroxinaDocument4 pagesLevotiroxinaIsidora GreenePas encore d'évaluation
- Warfarin Guide: Uses, Dosing, Interactions & MonitoringDocument4 pagesWarfarin Guide: Uses, Dosing, Interactions & MonitoringekramPas encore d'évaluation
- Melatonina (2008) Poisoning and ToxicologyDocument3 pagesMelatonina (2008) Poisoning and ToxicologyAlumno del Doctorado FarmacologiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Metabolic Precautions and ER Reccomendations (Parikh, MD, 2007)Document5 pagesMetabolic Precautions and ER Reccomendations (Parikh, MD, 2007)F4AR100% (1)
- Nursing ResponsibilityDocument9 pagesNursing Responsibilityايام اول الشحيPas encore d'évaluation
- Amoxicillin for sinus, pneumonia, and skin infectionsDocument6 pagesAmoxicillin for sinus, pneumonia, and skin infectionsLeofe CorregidorPas encore d'évaluation
- Metabolic Alkalosis CausesDocument15 pagesMetabolic Alkalosis CausesRajiv Kabad100% (1)
- TDM of PhenytoinDocument5 pagesTDM of PhenytoinMounika16 PedamalluPas encore d'évaluation
- Beta Karoten: (BAY Ta KARE Oh Teen)Document9 pagesBeta Karoten: (BAY Ta KARE Oh Teen)Nisa'ul KhoiriyahPas encore d'évaluation
- 2NDDocument176 pages2NDArjay NasirinPas encore d'évaluation
- LIVOLIN FORTE ACTIONS AND USESDocument5 pagesLIVOLIN FORTE ACTIONS AND USESDick Morgan FerrerPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Safety Monitoring GuidelinesDocument6 pagesDrug Safety Monitoring GuidelinesShivam Malik100% (1)
- I.Nutrition and Electrolytes A. Vitamins Classification: Fat Soluble Vitamin Generic Name: Vitamin E BRAND NAME: Aquasol EDocument176 pagesI.Nutrition and Electrolytes A. Vitamins Classification: Fat Soluble Vitamin Generic Name: Vitamin E BRAND NAME: Aquasol EFatima Doran PandaogPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 2016 GI Agents - LomotilDocument6 pages01 2016 GI Agents - LomotilmodayearPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugstudy For ElderlyDocument14 pagesDrugstudy For ElderlyJenniferP.BarrosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Folic AcidDocument3 pagesFolic Acidapi-37979410% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyLea FestejoPas encore d'évaluation
- Acetazolamide drug profileDocument33 pagesAcetazolamide drug profileAshley Topp100% (1)
- Prevpac Drug StudyDocument7 pagesPrevpac Drug StudyAngela ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Risperidone and Ascorbic AcidDocument3 pagesDrug Study Risperidone and Ascorbic AcidElcid PimentelPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyRoderick BajamundiPas encore d'évaluation
- Medications For Primary ComplexDocument8 pagesMedications For Primary ComplexMary CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Oxybutynin Hydrochloride Tablets 5 MG - Summary of Product Characteristics (SMPC) - Print Friendly - (Emc)Document7 pagesOxybutynin Hydrochloride Tablets 5 MG - Summary of Product Characteristics (SMPC) - Print Friendly - (Emc)surafelPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemotherapy DrugsDocument43 pagesChemotherapy Drugsbrigette_lagat100% (2)
- Vital SignsDocument28 pagesVital Signskarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Slides I Colorectal CancerDocument11 pagesSlides I Colorectal Cancerkarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Slides F Breast CADocument9 pagesSlides F Breast CAkarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Vital Signs Written ReportDocument7 pagesVital Signs Written Reportkarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Slides C (Radiation)Document10 pagesSlides C (Radiation)karl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Slides A (Cells&Types)Document10 pagesSlides A (Cells&Types)karl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Slides J Bone TumorDocument9 pagesSlides J Bone Tumorkarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Slides G Brain TumorDocument16 pagesSlides G Brain Tumorkarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Slides F Breast CADocument9 pagesSlides F Breast CAkarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- NURSING THEORY and RRLDocument3 pagesNURSING THEORY and RRLkarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- TemperatureDocument3 pagesTemperaturekarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Slides E Pain in CancerDocument4 pagesSlides E Pain in Cancerkarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Slides D (Chemo)Document10 pagesSlides D (Chemo)karl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Slides D (Chemo)Document10 pagesSlides D (Chemo)karl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Charting MontanoDocument1 pageSample Charting Montanokarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading MontanoDocument4 pagesReading Montanokarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- SymptomatologyDocument2 pagesSymptomatologykarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- ReferencesDocument1 pageReferenceskarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- HODGKINDocument2 pagesHODGKINkarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study MontanoDocument4 pagesDrug Study Montanokarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- ProcDocument3 pagesProckarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Montano NSG DiagnosisDocument1 pageMontano NSG Diagnosiskarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Ovarian CancerDocument1 page10 Ovarian Cancerkarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Liver CancerDocument1 page7 Liver Cancerkarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 Cervical CancerDocument1 page9 Cervical Cancerkarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lydia HallDocument1 pageLydia Hallkarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 LeukemiaDocument1 page11 Leukemiakarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Uterine CancerDocument1 page6 Uterine Cancerkarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Lung CancerDocument1 page8 Lung Cancerkarl montanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bruno, Gene - Using Betaine Hydrochloride & Digestive Enzymes For Indigestion - Huntington College (2014)Document3 pagesBruno, Gene - Using Betaine Hydrochloride & Digestive Enzymes For Indigestion - Huntington College (2014)pedpixPas encore d'évaluation
- Weekly Activity Report: Number of AttendeesDocument7 pagesWeekly Activity Report: Number of AttendeestabilinPas encore d'évaluation
- Food Allergy and HomeopathyDocument10 pagesFood Allergy and HomeopathyKuldeep KoulPas encore d'évaluation
- Audrey PeraultDocument1 pageAudrey Peraultapi-526621065Pas encore d'évaluation
- Twenty Pages in The Life of Scheussler Cell Salts FinalDocument23 pagesTwenty Pages in The Life of Scheussler Cell Salts FinalSadia AfrozePas encore d'évaluation
- Pete SnyderDocument48 pagesPete SnyderHariahranPas encore d'évaluation
- Jason A. Ohayon MD FRCPC: Nickel Free DietDocument3 pagesJason A. Ohayon MD FRCPC: Nickel Free DietLudmilaMerlinPas encore d'évaluation
- Inservice HandoutDocument2 pagesInservice Handoutapi-341835458Pas encore d'évaluation
- Management of Food Allergy and Development of An Anaphylaxis Treatment PlanDocument13 pagesManagement of Food Allergy and Development of An Anaphylaxis Treatment PlanApt. Mulyadi PrasetyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Allergy Voices Volume 2 CompressedDocument47 pagesAllergy Voices Volume 2 CompressedHermiPas encore d'évaluation
- Dominos-Global-Store-Food-Safety-Standard-2021-V3.0 2Document57 pagesDominos-Global-Store-Food-Safety-Standard-2021-V3.0 2f4tgbxgnt4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Choose The Word Whose Stress Pattern Is Different From The RestDocument3 pagesChoose The Word Whose Stress Pattern Is Different From The RestKim Ngân NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- MG Naturkosmetik PRODUKTE SENSISANA Broschüre EDocument13 pagesMG Naturkosmetik PRODUKTE SENSISANA Broschüre EArcadiTiticaPas encore d'évaluation
- Study of Common Insect in West Bengal: Vidyasager UniversiytDocument22 pagesStudy of Common Insect in West Bengal: Vidyasager UniversiytÁdíțyà RôyPas encore d'évaluation
- MycotoxicosesDocument5 pagesMycotoxicosesmihret genenePas encore d'évaluation
- Virgin coconut oil helps reverse autism symptomsDocument4 pagesVirgin coconut oil helps reverse autism symptomsdanielwongts0% (1)
- Beekeeping in South KoreaDocument10 pagesBeekeeping in South KoreadrhminooPas encore d'évaluation
- Latihan Soal USDocument7 pagesLatihan Soal USBianka ChristinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gastrointestinal Microflora PPT 19.1.11.Document51 pagesGastrointestinal Microflora PPT 19.1.11.सुमेर सिंह मीणाPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Obimin PlusDocument2 pagesDrug Study Obimin PlusPauline AñesPas encore d'évaluation
- Food Safety Policy: PurposeDocument9 pagesFood Safety Policy: PurposekarthikPas encore d'évaluation
- The Essentials: Heal Candida & Leaky Gut with Foods, Supplements & TechniquesDocument36 pagesThe Essentials: Heal Candida & Leaky Gut with Foods, Supplements & TechniquesadamdwaldropPas encore d'évaluation
- Crazy FearsDocument2 pagesCrazy Fearsdeeksha2502Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Advanced Art of Baking PastryDocument653 pagesThe Advanced Art of Baking PastryThaisa Torres Botelho100% (7)
- 3gallergy™ Menu: Answers For LifeDocument7 pages3gallergy™ Menu: Answers For LifeОлександрPas encore d'évaluation
- The Human Diet Dairy Delusion (Eric Edmeades)Document32 pagesThe Human Diet Dairy Delusion (Eric Edmeades)kurt_90Pas encore d'évaluation
- Đề 24.Mh2022.Key Chi TiếtDocument20 pagesĐề 24.Mh2022.Key Chi TiếtThao Thanh PhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Acad Dermatol Venereol - 2020 - Wollenberg - ETFAD EADV Eczema Task Force 2020 Position Paper On Diagnosis and Treatment ofDocument28 pagesAcad Dermatol Venereol - 2020 - Wollenberg - ETFAD EADV Eczema Task Force 2020 Position Paper On Diagnosis and Treatment ofmaituuyen1997Pas encore d'évaluation
- How Matter ChangesDocument33 pagesHow Matter ChangesHazel L IbarraPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument19 pagesBiology Investigatory ProjectDebkanti Gupta BhayaPas encore d'évaluation