Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology
Transféré par
Elbert Hermogino ﭢ0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
1K vues6 pagesTuberculosis and Pneumonia Pathophysiology Potentially Modifiable 1. Occupation (e.g health workers) 2. Repeated close contact w / infected 3. Indefinite substance abuse via IV 4. Recurrence of infection Unmodifiable 4. Age 2. Immunosuppression persons -Prolonged corticosteroid therapy 3. Systemic Infection: - Diabetes Mellitus -end-stage Renal Disease -HIV or AIDS infection
Description originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentTuberculosis and Pneumonia Pathophysiology Potentially Modifiable 1. Occupation (e.g health workers) 2. Repeated close contact w / infected 3. Indefinite substance abuse via IV 4. Recurrence of infection Unmodifiable 4. Age 2. Immunosuppression persons -Prolonged corticosteroid therapy 3. Systemic Infection: - Diabetes Mellitus -end-stage Renal Disease -HIV or AIDS infection
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
1K vues6 pagesPathophysiology
Transféré par
Elbert Hermogino ﭢTuberculosis and Pneumonia Pathophysiology Potentially Modifiable 1. Occupation (e.g health workers) 2. Repeated close contact w / infected 3. Indefinite substance abuse via IV 4. Recurrence of infection Unmodifiable 4. Age 2. Immunosuppression persons -Prolonged corticosteroid therapy 3. Systemic Infection: - Diabetes Mellitus -end-stage Renal Disease -HIV or AIDS infection
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 6
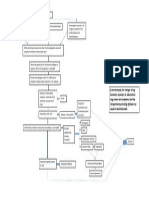
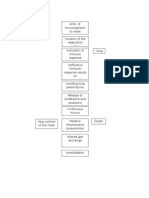
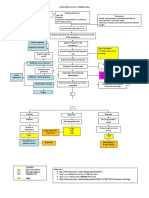
Tuberculosis and Pneumonia Pathophysiology
Potentially Modifiable Unmodifiable
1. Occupation (e.g 1. Age
Health Workers) 2. Immunosuppression
2. Repeated close persons
contact w/ infected -Prolonged corticosteroid
3. Indefinite substance therapy
abuse via IV 3. Systemic Infection:
4. recurrence of infection -Diabetes Mellitus
-End-stage Renal Disease
-HIV or AIDS infection
Exposure or inhalation of
infected
Aerosol through droplet
nuclei
(exposure to infected
clients by coughing,
sneezing, talking)
Tubercle bacilli invasion in
the apices of the
Lungs or near the pleurae
of the lower lobes
Bronchopneumonia
develops in the lung tissue
(Phagocytosed tubercle
bacilli are ingested by
macrophages)
-bacterial cell wall binds with
macrophages
-arrest of a phagosome
which results to bacilli
replication
Necrotic Degeneration
occurs
(production of cavities filled
with cheese-like
mass of tubercle bacilli,
dead WBCs, necrotic lung
tissue)
drainage of necrotic
materials into the
tracheobronchial tree
(eruption of coughing,
formation of lesions)
PRIMARY INFECTION
Lesions may calcify
(Ghon’s Complex)
and form scars and may
heal over a period of time
Tubercle bacilli immunity
develops
(2 to 6 weeks after
infection)
(maintains in the body as
long as living
bacilli remains in the body)
Acquired immunity leads to
further growth
Of bacilli and development
of ACTIVE INFECTION
Pulmonary Symptoms: General Symptoms:
- Dyspnea - Fatigue
- Non-productive or productive - anorexia
cough - Weight loss
- Hemoptysis (blood tinge sputum) - low grade fever with
-Chest pain that may be pleuritic or Signs and Symptoms sweats (often at night)
dull chills and
-Chest tightness
- Crackles may be present on
auscultation
With Medical Intervention Without Medical Intervention
-Early detection/ Acquired immunity leads to
diagnosis of the further growth
dse Of bacilli and development
-Multi-antibacterial of ACTIVE INFECTION
therapy
-Fixed- dose
therapy
-TB DOTS (Direct
Observed Therapy
Reactivation of the tubercle
bacilli
(Due to repeated exposure to
infected Individuals,
Immunosuppression)
No Recurrence
recurrence SECONDARY INFECTION
Good Bad
Prognosis Prognosis
Severe occurrence of
lesions in the lungs
Cavitation in the lungs
occurs
Active infection is spread throughout
the body systems
(infiltration of tubercle bacilli in other
organs)
-TB of the Bones
-Pott’s Disease
-Renal TB
SEVERE OCCURRENCE OF
INFECTION
Client became clinically ill
BAD PROGNOSIS
DEATH
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Pathophysiology of TuberculosisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of TuberculosisLeikkaPas encore d'évaluation
- B. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyDocument3 pagesB. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyKenneth Torres100% (1)
- Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Etiology, Types, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument6 pagesMycobacterium Tuberculosis Etiology, Types, Diagnosis and TreatmentChloé Jane HilarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Management For PneumoniaDocument2 pagesMedical Management For PneumoniaSue Elaine100% (1)
- Pathophysiology: HIV Infection and AIDSDocument7 pagesPathophysiology: HIV Infection and AIDSmeylin SPas encore d'évaluation
- PneumoniaDocument1 pagePneumoniaAyen FornollesPas encore d'évaluation
- TB Case StudyDocument2 pagesTB Case StudyReisabelle LabianoPas encore d'évaluation
- PathoConceptMap AIDSDocument3 pagesPathoConceptMap AIDSKristen Babauta50% (2)
- Community Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandCommunity Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- (Patho) PTB COPDDocument1 page(Patho) PTB COPDKyle HannahPas encore d'évaluation
- Pneumonia Case Study: Toddler Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument5 pagesPneumonia Case Study: Toddler Diagnosis and TreatmentcrisolandPas encore d'évaluation
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of RabiesDocument5 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of RabiesDavid CalaloPas encore d'évaluation
- AnatomyDocument6 pagesAnatomyKadulum100% (1)
- Influenza PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument3 pagesInfluenza PATHOPHYSIOLOGYElle RosalesPas encore d'évaluation
- HIV/AIDS Definition, Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentDocument2 pagesHIV/AIDS Definition, Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentAC, MDPas encore d'évaluation
- D. Pa Tho Physiology of PneumoniaDocument4 pagesD. Pa Tho Physiology of PneumoniaBill Clinton Lamira BabanPas encore d'évaluation
- ChickenpoxDocument2 pagesChickenpoxyai19100% (2)
- Patho PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPatho Pneumoniaailyne_galicia100% (2)
- Measles (Rubeola) VirusDocument16 pagesMeasles (Rubeola) Virusstudymedic100% (1)
- RRS at RRLDocument19 pagesRRS at RRLNicole MangosanPas encore d'évaluation
- Hiv AidsDocument14 pagesHiv Aidsapi-221532663Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pneumonia Case StudyDocument8 pagesPneumonia Case StudyChristopher John AgueloPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology Schistosomiasis: Table in New WindowDocument7 pagesPathophysiology Schistosomiasis: Table in New WindowKaren Leigh MagsinoPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Prednisolone?Document12 pagesWhat Is Prednisolone?Chandni SeelochanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Leptospirosis and Dengue FeverDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Leptospirosis and Dengue FeverKenneth Lagman100% (1)
- Leptospirosis Case StudyDocument3 pagesLeptospirosis Case StudyMarie Jennifer ParilPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study PNEUMONIADocument40 pagesCase Study PNEUMONIAHomework PingPas encore d'évaluation
- Rabi PurDocument3 pagesRabi PurDiana Laura LeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Studies - Tetralogy of FallotDocument16 pagesCase Studies - Tetralogy of FallotKunwar Sidharth SaurabhPas encore d'évaluation
- Aspiration PneumoniaDocument3 pagesAspiration PneumoniaEllen Hennings100% (1)
- Demographic ProfileDocument8 pagesDemographic ProfileStephanie VillarinPas encore d'évaluation
- Rabies: A Deadly Viral Disease Spread by Animal BitesDocument3 pagesRabies: A Deadly Viral Disease Spread by Animal BitesDavid CalaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study 1 (Pneumonia)Document13 pagesCase Study 1 (Pneumonia)Kate EscotonPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Tuberculosis: Group 5 Latosa, Selene Lee, Guk Lim, Johanna Magalona, Stephen Mendoza, ColeenDocument22 pagesPathophysiology of Tuberculosis: Group 5 Latosa, Selene Lee, Guk Lim, Johanna Magalona, Stephen Mendoza, ColeenAlexander Santiago ParelPas encore d'évaluation
- Kardex, Drug Study and CheckDocument12 pagesKardex, Drug Study and CheckJemina Rafanan RacadioPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument19 pagesCase Study Pulmonary TuberculosisJester GalayPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Schematic Diagram of PneumoniaDocument1 pageSimple Schematic Diagram of PneumoniaJason A. AdoyoganPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Pneumoniaoxidalaj97% (31)
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaAzria John DemetriPas encore d'évaluation
- Community Acquired Pneumonia: Ang Gobonseng, Ed Gerard R. MedclerkDocument66 pagesCommunity Acquired Pneumonia: Ang Gobonseng, Ed Gerard R. MedclerkRyn Anfone100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of AIDS: Transmission and Immune System DestructionDocument1 pagePathophysiology of AIDS: Transmission and Immune System DestructionJason A. Adoyogan0% (1)
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)D'EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology: School OF Health AND Allied Sciences Bachelor of Science in Nursing - Level IiiDocument4 pagesPathophysiology: School OF Health AND Allied Sciences Bachelor of Science in Nursing - Level IiiLadybelle GototosPas encore d'évaluation
- History: Symptoms Associated With Specific Viral InfectionsDocument12 pagesHistory: Symptoms Associated With Specific Viral InfectionsFatima Love Ariate-ArcasetasPas encore d'évaluation
- HIV Simple Case StudyDocument13 pagesHIV Simple Case StudyJanna Pimentel100% (1)
- Pathophysiology TBDocument2 pagesPathophysiology TBJhen DeguzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- LeptospirosisDocument3 pagesLeptospirosisJessie Cauilan Cain100% (1)
- Pathophysiology SARSDocument4 pagesPathophysiology SARSStephanie Joy Escala71% (7)
- SinusitisDocument6 pagesSinusitisRae Marie AquinoPas encore d'évaluation
- BFCDocument8 pagesBFCIrene GunongPas encore d'évaluation
- The Pathophysiology of LabyrinthitisDocument2 pagesThe Pathophysiology of LabyrinthitisSurya Michael ChancePas encore d'évaluation
- Patho Pleural EffusionDocument2 pagesPatho Pleural EffusionJess Prodigo50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of TuberculosisDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of TuberculosisFirenze Fil96% (56)
- Pathophysiology of Koch's Disease (Tuberculosis) : Primary InfectionDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Koch's Disease (Tuberculosis) : Primary InfectionbijelPas encore d'évaluation
- Path o Physio TB EffusionDocument2 pagesPath o Physio TB EffusionSergi Lee OratePas encore d'évaluation
- I. Definition: Pulmonary TuberculosisDocument6 pagesI. Definition: Pulmonary Tuberculosisjulie-pearl-6329Pas encore d'évaluation
- TuberculosisDocument5 pagesTuberculosiscecil100% (6)
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis: PGI Leichel Ann N. AlbertoDocument82 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis: PGI Leichel Ann N. AlbertoLeichel AlbertoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of TBDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of TBEddie Lou GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Koch's Disease (Tuberculosis) : Primary InfectionDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Koch's Disease (Tuberculosis) : Primary InfectionStephanie GapuzPas encore d'évaluation
- NCM 107 TheoristDocument15 pagesNCM 107 TheoristElbert Hermogino ﭢPas encore d'évaluation
- Behavioral Management in Chronically Ill and Older AdultsDocument18 pagesBehavioral Management in Chronically Ill and Older AdultsElbert Hermogino ﭢPas encore d'évaluation
- Calcium Channel Blocker Norvasc (Amlodipine) Treatment GuideDocument2 pagesCalcium Channel Blocker Norvasc (Amlodipine) Treatment GuideElbert Hermogino ﭢPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of The Heart and BloodDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The Heart and BloodElbert Hermogino ﭢPas encore d'évaluation
- CCRN-PCCN Review RenalDocument11 pagesCCRN-PCCN Review RenalGiovanni MictilPas encore d'évaluation
- Lugols Solution Schillers Test IFU V9 EN4Document1 pageLugols Solution Schillers Test IFU V9 EN4Mary's CatzPas encore d'évaluation
- Turner Syndrome, Klinefelter Syndrome, Down SyndromeDocument78 pagesTurner Syndrome, Klinefelter Syndrome, Down SyndromeTasya100% (3)
- Chemical Resistance Chart GlovesDocument8 pagesChemical Resistance Chart Glovesjitendertalwar1603Pas encore d'évaluation
- Current Opinion Hematol RR AML 2019Document8 pagesCurrent Opinion Hematol RR AML 2019Ernesto PiconPas encore d'évaluation
- Urine AnalysisDocument41 pagesUrine AnalysisAjay SomeshwarPas encore d'évaluation
- [Journal of Neurosurgery Spine] To operate, or not to operate Narrative review of the role of survival predictors in patient selection for operative management of patients with metastatic spine diseaseDocument15 pages[Journal of Neurosurgery Spine] To operate, or not to operate Narrative review of the role of survival predictors in patient selection for operative management of patients with metastatic spine diseasecogajoPas encore d'évaluation
- Evolving lesion• Family history• Multiple lesionsDocument95 pagesEvolving lesion• Family history• Multiple lesionsmedicoprakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Celiac DiseaseDocument42 pagesCeliac DiseaseTri P BukerPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnosing and Managing Barrett's EsophagusDocument32 pagesDiagnosing and Managing Barrett's EsophagusAldy BimaPas encore d'évaluation
- GI Disorders NursingDocument93 pagesGI Disorders NursingAmy100% (4)
- Cleaning and Sanitizing Methods PDFDocument21 pagesCleaning and Sanitizing Methods PDFLinnuha UlinPas encore d'évaluation
- Uveal Coloboma: The Related SyndromesDocument3 pagesUveal Coloboma: The Related Syndromeslavinia diaPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of A HospitalDocument24 pagesDepartment of A HospitalAnonymous YcdK9FWtH100% (2)
- Middle-Range Theory of Chronic Sorrow: A Framework for Understanding Recurring GriefDocument6 pagesMiddle-Range Theory of Chronic Sorrow: A Framework for Understanding Recurring GriefRizkia100% (2)
- Callon - Hybrid ForumsDocument58 pagesCallon - Hybrid ForumsLuis HermosillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre TestDocument6 pagesPre TestPRINTDESK by DanPas encore d'évaluation
- Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument40 pagesGestational Trophoblastic DiseaseAayupta Mohanty100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan With A FractureDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan With A FractureHasanah EkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Odontogenic Tumours - (2) L5Document28 pagesOdontogenic Tumours - (2) L5nooraaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rulerships and Qualities Anatomy and Physiology Correlated To The ZodiacDocument4 pagesRulerships and Qualities Anatomy and Physiology Correlated To The Zodiactushar100% (1)
- Breast MRIDocument170 pagesBreast MRICosas CuponaticPas encore d'évaluation
- Horace Joules: Early Life and EducationDocument8 pagesHorace Joules: Early Life and Educationadh30aPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Coding Test Q&ADocument24 pagesMedical Coding Test Q&ALeah Lee100% (1)
- Ovarian CancerDocument3 pagesOvarian CancerKaija PouporePas encore d'évaluation
- Spss Sig 0.05Document14 pagesSpss Sig 0.05xetijoPas encore d'évaluation
- Akupuntur InfertilityDocument7 pagesAkupuntur Infertilitybustanul aswatPas encore d'évaluation
- Uterine FibroidsDocument21 pagesUterine FibroidsPrasun BiswasPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus of KU MBBS PDFDocument147 pagesSyllabus of KU MBBS PDFAnshu Thapa69% (13)
- SIADH, DI, Cerebral Salt WastingDocument20 pagesSIADH, DI, Cerebral Salt Wastingmaged_najehPas encore d'évaluation

































































![[Journal of Neurosurgery Spine] To operate, or not to operate Narrative review of the role of survival predictors in patient selection for operative management of patients with metastatic spine disease](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/553636897/149x198/e412b60a83/1710528645?v=1)






















