Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Applied Mechanics Lab.: Worm Geared Screw Jack
Transféré par
Abhijeet KumarDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Applied Mechanics Lab.: Worm Geared Screw Jack
Transféré par
Abhijeet KumarDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
APPLIED MECHANICS LAB.
INSTRUCTION SHEET
WORM GEARED SCREW JACK.
************************************************************************
1. AIM:
To determine Mechanical Advantage (M.A), Velocity Ratio (V.R), efficiency (h ) and to check Law
of machine of a worm geared screw jack.
2. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED.
2.1 Worm geared screw jack.
2.2 Weights.
2.3 Vernier caliper
2.4 Rope.
2.5 Effort pan & hanger.
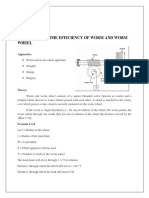
3. DESCRIPTION ABOUT MACHINE.
Pitch of screw jack (p) =
Diameter of screw head (D) =
No of teeth on the gear wheel.(T) =
4. THEORY.
Worm geared screw jack is a combination of worm gearing and a simple screw jack. The
worm gear consists of a worm axle and a gear wheel. The gearwheel is rigidly attached with the lifting
screw. The worm axle is provided with a effort wheel, if the effort is applied on the pan, the worm axle
will rotate and it will rotate the gearwheel. Ultimately the lifting screw will rotate. As the nut is fixed and
the screw is rotating, the Screw will move up or down. The worm has single started thread,i.e, when the
worm axle rotates one revolution the gear wheel moves by one teeth.
4.1 MECHANICAL ADVANTAGE
The Mechanical Advantage is the ratio of Load (W) lifted to Effort (P) Applied.
Thus, M.AÞ W/P
4.2 VELOCITY RATIO
The Velocity Ratio (V.R) is the ratio of the distance moved by effort (y) to the distance moved
by Load (x).
Thus, V.RÞ y/x
Þ y/x =
where, T = No of teeth on the gear wheel.
D = Diameter of effort wheel
p = Pitch of screw.
4.3 EFFICIENTY(h ):-
(h )= output / input
4.4 LAW OF MACHINE
It provides the relationship between effort and the corresponding load lifted by the application of
effort.
P = MW + C -------------------- (1)
where P = Effort applied
M = Const. called coefficient of friction which equal to slope of the line.
W = Load lifted.
C = Const. called machine friction.
5.PROCEDURE:
5.1 Measure pitch of screw, dia of pulley and no. of teeth on the gear wheel then find outV.R.
5.2 Measure machine friction ‘C’ at no load condition.
5.3 Take ten readings taking different loads and efforts.
5.4 Calculate efficiency in each time and calculate mean efficiency.
5.5 Draw the graph between load Vs effort.
5.6 Determine the coefficient of friction ‘M’ from the graph.
5.7 By putting the values of ‘M’and ‘C’ in equation (1) we determine from which the law of
machine, we can find out the amount of effort required to lift any load.
4 OBJERVATION:
‘M’
‘C’ Coefficient W P Mechanical h Mean
Sl no Machine Of V.R in in (kg) Advantage efficiency (h )
friction Machine (kg) W/P
friction
7. CALCULATION:
8. CONCLUSION:
Because of the worm and worm wheel the velocity ratio is T times bigger that of a simple screw jack.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Experiment 9 PDFDocument3 pagesExperiment 9 PDFdarshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 7 PDFDocument3 pagesExperiment 7 PDFdarshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Em ManualDocument31 pagesEm ManualsarumaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Mec 291: Dynamics and Materials LAB Mechanism and Machine ElementsDocument22 pagesMec 291: Dynamics and Materials LAB Mechanism and Machine ElementsHaFiy HaZimPas encore d'évaluation
- To Calculate The Efficiency ofDocument10 pagesTo Calculate The Efficiency ofMayank BarserPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple MachinesDocument12 pagesSimple MachinesR MathewPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual For Compound Screw Jack-1Document4 pagesManual For Compound Screw Jack-1Yesupadam ValavalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 5 RevisedDocument3 pagesLab 5 RevisedONLINE WORKSHOPIAPas encore d'évaluation
- Standered Journal EM 2016-17Document37 pagesStandered Journal EM 2016-17Samyak Saraf100% (1)
- EXP Performance MV Lab Winch ApparatusDocument5 pagesEXP Performance MV Lab Winch ApparatusMuhammad ZameerPas encore d'évaluation
- Bme Exp 8Document3 pagesBme Exp 8Sanjay KajalPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No. 9: Aim: To Find The Mechanical Advantage, Velocity Ratio and Efficiency of Simple andDocument2 pagesExperiment No. 9: Aim: To Find The Mechanical Advantage, Velocity Ratio and Efficiency of Simple andShiva Krishna Bhagavatula50% (2)
- 2nd Chapter Notes Mechanical Engineering DiplomaDocument7 pages2nd Chapter Notes Mechanical Engineering DiplomaUsmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Worm and Worm WheelDocument8 pagesWorm and Worm WheelMBilal MughalPas encore d'évaluation
- Efficiency of Screw JackDocument6 pagesEfficiency of Screw JackNuyara VithanagePas encore d'évaluation
- 111111111Document3 pages111111111Gargi DesaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Msa Lab ManualDocument16 pagesMsa Lab ManualAcchyutjhPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab ManualsDocument13 pagesLab ManualssaqibPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 4Document4 pagesLab 4Mechanics of Material labPas encore d'évaluation
- Epicyclic Gear TrainDocument5 pagesEpicyclic Gear TrainRachan PanchePas encore d'évaluation
- 3314 Ijmech 11Document8 pages3314 Ijmech 11Burak KoyuncuogluPas encore d'évaluation
- Propeller Performance CharacteristicsDocument9 pagesPropeller Performance CharacteristicsNaga Manohar UmmadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics MachineDocument28 pagesMechanics MachineamitautomaticPas encore d'évaluation
- Session No 02Document5 pagesSession No 02Mohsin EhsanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Session 4: ApparatusDocument4 pagesLab Session 4: ApparatusamnaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Slider-Crank Experiment To Determine The Action of Static ForcesDocument10 pagesA Slider-Crank Experiment To Determine The Action of Static ForcesRazali Yusoff100% (1)
- MuhammadSharjeelChawla (Labreport3)Document4 pagesMuhammadSharjeelChawla (Labreport3)Engineer ChawlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 07Document8 pagesLab 07tanoli9596Pas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 6 PDFDocument3 pagesExperiment 6 PDFdarshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report No 7Document10 pagesLab Report No 7Mansoob Bukhari67% (3)
- 機工9 10 B09502081Document6 pages機工9 10 B09502081Alton S H ChenPas encore d'évaluation
- Islam College of Engineering & Management Sciences Sialkot, (Icems) - Mechanics of Machine (Lab) - (4 Semester, Spring2022)Document5 pagesIslam College of Engineering & Management Sciences Sialkot, (Icems) - Mechanics of Machine (Lab) - (4 Semester, Spring2022)Ayesha MunnirPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Fly Wheel (Lecture-05)Document36 pagesDesign of Fly Wheel (Lecture-05)Waqas IbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Flywheel +Document46 pagesFlywheel +mhd efriyansyah0% (2)
- Torsion Test Experiment 2Document5 pagesTorsion Test Experiment 2Ryan Hasnan HPas encore d'évaluation
- Torsion Test Experiment 2Document5 pagesTorsion Test Experiment 2Ryan Hasnan HPas encore d'évaluation
- Double Purchase Crab: Objective: TheoryDocument3 pagesDouble Purchase Crab: Objective: TheorydarshanPas encore d'évaluation
- Power ScrewsDocument13 pagesPower ScrewsKelvin YipPas encore d'évaluation
- Preview of Period 7: Simple Machines and Mechanical AdvantageDocument12 pagesPreview of Period 7: Simple Machines and Mechanical AdvantageAnonymous mKdAfWifPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics Simple MachinesDocument17 pagesMechanics Simple MachineseetuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadcopter Propeller Design and Performance Analysis: Endrowednes Kuantama, Dan Craciun, Ioan Tarca and Radu TarcaDocument9 pagesQuadcopter Propeller Design and Performance Analysis: Endrowednes Kuantama, Dan Craciun, Ioan Tarca and Radu Tarcanguyễn namPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Aided Modeling Cost Estimation of A Hand TruckDocument4 pagesComputer Aided Modeling Cost Estimation of A Hand TruckIJARP PublicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- 668-Article Text-1216-1-10-20171231Document7 pages668-Article Text-1216-1-10-20171231galataataaddesaaPas encore d'évaluation
- V3i4 1177Document4 pagesV3i4 1177RockPas encore d'évaluation
- Mass Moment of Inertia of FlywheelDocument8 pagesMass Moment of Inertia of Flywheelabdulaziz67% (3)
- Symposium On The Lift and Escalator TechnologiesDocument5 pagesSymposium On The Lift and Escalator TechnologiesfreddyjoertyPas encore d'évaluation
- Me 309 Experimental AnalysisDocument6 pagesMe 309 Experimental AnalysisNeha HebbarPas encore d'évaluation
- The Pelton Wheel: 1 ObjectivesDocument8 pagesThe Pelton Wheel: 1 ObjectivesAbelBayartPas encore d'évaluation
- Coreless Motor 720Document15 pagesCoreless Motor 720anikmandal106Pas encore d'évaluation
- Design and Testing of Actuator For Butterfly Valve: Aniket R. Thorat and Suresh M. SawantDocument6 pagesDesign and Testing of Actuator For Butterfly Valve: Aniket R. Thorat and Suresh M. SawantGourav SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- To Find The Mechanical Advantage, Velocity Ratio and Efficiency of A Simple Screw JackDocument12 pagesTo Find The Mechanical Advantage, Velocity Ratio and Efficiency of A Simple Screw Jackitsmeersaurabh69% (13)
- FORMATO MATPR EES 8-PagDocument8 pagesFORMATO MATPR EES 8-Pagarlette caizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Phase 2.1Document13 pagesPhase 2.1Neil Allison Najorda CabilbilPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics ReportDocument18 pagesDynamics Reportvalentinembajiogu2020Pas encore d'évaluation
- Screw Jack: B.I.T., Mesra Engg - Mechanics LabDocument5 pagesScrew Jack: B.I.T., Mesra Engg - Mechanics LabSanatan MurmuPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Simple MachineDocument13 pagesPhysics Simple Machinesamcj4realPas encore d'évaluation
- Differential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksD'EverandDifferential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Ref. LinksDocument2 pagesRef. LinksAbhijeet KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Recommendation LetterDocument1 pageRecommendation LetterAbhijeet KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Abhijeet Kumar Sahu Resume MechanicalDocument2 pagesAbhijeet Kumar Sahu Resume MechanicalAbhijeet KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Abhijeet Kumar Sahu Resume MechanicalDocument2 pagesAbhijeet Kumar Sahu Resume MechanicalAbhijeet KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- SerialsDocument1 pageSerialsAbhijeet KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Business TermsDocument1 pageBusiness TermsAbhijeet KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- SerialsDocument1 pageSerialsAbhijeet KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Contact UsDocument1 pageContact UsAbhijeet KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- TaglinesDocument1 pageTaglinesAbhijeet KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- TaglinesDocument1 pageTaglinesAbhijeet KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- A Cup of Coffee... and You Are Ready For Anything. Drink It in Minutes. Feel It For HoursDocument1 pageA Cup of Coffee... and You Are Ready For Anything. Drink It in Minutes. Feel It For HoursAbhijeet KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- MNG113 Brand Management 1Document5 pagesMNG113 Brand Management 1Nikunj BhanushaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Values, Attitudes and Behaviors: FLW EO OfficeDocument18 pagesValues, Attitudes and Behaviors: FLW EO OfficeAbhijeet KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Bajaj Pulsar 180 UG IV (Maintainance Guidelines)Document2 pagesBajaj Pulsar 180 UG IV (Maintainance Guidelines)manhojkumar G0% (1)
- Volvo BL60B (Sistemas Elétricos)Document228 pagesVolvo BL60B (Sistemas Elétricos)Willian HenriquePas encore d'évaluation
- TKE-GEC-24 - Códigos de Falhas e Alertas-PortuguêsDocument6 pagesTKE-GEC-24 - Códigos de Falhas e Alertas-PortuguêsValdo100% (1)
- Tecumseh Engine Parts Manual TVS100 44050GDocument7 pagesTecumseh Engine Parts Manual TVS100 44050Greply-to-addPas encore d'évaluation
- Finding Top Center Position For No. 1 PistonDocument3 pagesFinding Top Center Position For No. 1 PistonmanuelPas encore d'évaluation
- TGB 50 BK1 B Parts List WWW - ManualedereparatieDocument52 pagesTGB 50 BK1 B Parts List WWW - ManualedereparatieNutter1340100% (1)
- CF 500cc Service Manual PDFDocument254 pagesCF 500cc Service Manual PDFJonathan RojasPas encore d'évaluation
- 36 - Eaton CL 450 Transmission Service Manual PDFDocument36 pages36 - Eaton CL 450 Transmission Service Manual PDFSomadbsiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cable SizeDocument7 pagesCable SizePrabir Bhowmik50% (4)
- Bosch GBH 2 SE 0611226542 240 Volt Spare PartsDocument9 pagesBosch GBH 2 SE 0611226542 240 Volt Spare PartsIlie CheraPas encore d'évaluation
- Earthing CatalogueDocument148 pagesEarthing CatalogueMusthafa ShaikPas encore d'évaluation
- Tyre Press: Ep Equipment Co.,LtdDocument2 pagesTyre Press: Ep Equipment Co.,LtdJamyansuren TseveendorjPas encore d'évaluation
- Samcr23112021 ASDocument2 pagesSamcr23112021 ASAbhishek MongaPas encore d'évaluation
- Harley Davidson 99450-96 Parts Manual 95-96 All 1340cc PDFDocument400 pagesHarley Davidson 99450-96 Parts Manual 95-96 All 1340cc PDFJustin Davis50% (4)
- Desarmado y Armado Bomba 312cDocument22 pagesDesarmado y Armado Bomba 312cJhon VillamizarPas encore d'évaluation
- Maclean ESNA - Fastner - Nyloc Nut PDFDocument94 pagesMaclean ESNA - Fastner - Nyloc Nut PDFVinay PawarPas encore d'évaluation
- 30168700Document38 pages30168700gr8rlPas encore d'évaluation
- Jigs and Tools Specification: Model of Special Production ToolsDocument7 pagesJigs and Tools Specification: Model of Special Production ToolsRafaelPas encore d'évaluation
- X 057 Colour Abbreviations According To VDE and IECDocument1 pageX 057 Colour Abbreviations According To VDE and IECAlexanderPas encore d'évaluation
- Single Slider Crank ChainDocument9 pagesSingle Slider Crank ChainSunny RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Torque Chart For ASTM A193 Grade B7 StudsDocument3 pagesTorque Chart For ASTM A193 Grade B7 Studssarip83100% (4)
- CLSU ABE Review 2022 APE Chap 04 Internal Combustion EngineDocument55 pagesCLSU ABE Review 2022 APE Chap 04 Internal Combustion EngineBilly AgustinPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Tailgate For Range Rover Evoque 2013Document5 pagesElectric Tailgate For Range Rover Evoque 2013LIRO ROMAPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Valves Training Material 2Document103 pagesControl Valves Training Material 2Marcelo Fabián PurrettaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jsa Engines Part 1Document3 pagesJsa Engines Part 1Avenash BabooramPas encore d'évaluation
- Capacidades y Dimensiones de MontacargasDocument16 pagesCapacidades y Dimensiones de MontacargasFredy ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.nuts and Bolts PDFDocument9 pages5.nuts and Bolts PDFAnonymous sbOPJbcPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 - V-P055AZOR-00-30-4-V78048 ManualDocument91 pages2 - V-P055AZOR-00-30-4-V78048 ManualDion Alfred EucogcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Evinrude Carburetor Group Parts For 1966 18hp 18602 Outboard MotorDocument8 pagesEvinrude Carburetor Group Parts For 1966 18hp 18602 Outboard MotorWouter GrootPas encore d'évaluation
- SHEPPARD Kenworth Medium Duty HD94 ALTERNATE Steering-Gear Bleed Procedure 2Document3 pagesSHEPPARD Kenworth Medium Duty HD94 ALTERNATE Steering-Gear Bleed Procedure 2Mas Inyeccion ElectronicaPas encore d'évaluation