Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
SFA RCY - Syllabus
Transféré par
twinklestar1Description originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SFA RCY - Syllabus
Transféré par
twinklestar1Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SINGAPORE RED CROSS
RED CROSS YOUTH
STANDARD FIRST AID
SYLLABUS
SESSION THEORY PRACTICAL
1 a. Introduction to first aid • Primary survey
b. Basic anatomy and physiology of main body systems
c. Emergency action principles • Secondary survey
• Survey the scene
• Do a primary survey • Recovery position
• Call for emergency services
• Do a secondary survey and appropriate emergency first aid • Use of triangular bandage -
d. First Aid Kit introduction to bandaging, folding,
storing, tying, and uses (as slings,
splint, ring pad and pressure pad)
2 a. Respiratory system • Heimlich manoeuvre (abdominal
b. Disorders of breathing - the important ones thrust) for choking casualty
• Choking
• Drowning • Rescue breathing for non
• Asthmatic attack breathing casualty
• Hypoxia from inhalation of fumes, carbon monoxide poisoning,
lung disease
• Hyperventilation
c. Heimlich manoeuvre (abdominal thrust) for choking casualty -
conscious and unconscious; chest thrust for the obese or pregnant
casualty
d. Rescue breathing for non breathing casualty
3 a. Circulatory system • CPR technique for one-man first
b. Disorder of circulation - the important ones aider
• Shock from blood and fluid loss
• Anaphylactic shock • Shock from blood and fluid loss -
• Heart attack first aid treatment
c. CPR
d. Wound - types, first aid • Arrest of bleeding - direct and
indirect pressure (subclavian and
e. Bleeding - types, control of bleeding (direct pressure and indirect
pressure), pressure points (subclavian, brachial and femoral), first brachial pressure points for upper
aid limb and femoral pressure point for
lower limb)
f. Preservation of amputated body part
g. Foreign bodies in
• Bandaging of wounds - various
• finger - fish hook parts of body, cut in the palm
• eyes - splinter
• nose and ear - insect and beads • Use of bandage as pressure pad,
• digestive tract- swallowed fish bone and coin ring pad and slings for wounds and
• respiratory tract - inhaled object or food bleeding
h. Bandage as pressure pad, ring pad and slings for wounds and
bleeding
Last updated 2002 Page 1 of 3
SESSION THEORY PRACTICAL
4 a. The nervous system • First aid to scalp and face wounds
b. Disorders of conscious - the important ones • First aid to chest injury
• Faint • First aid to abdomen injury
• Fit (convulsion, epilepsy, fits)
• Hupoglycaemic coma in diabetic patient (low blood sugar)
• Stroke
• Head injury
• drunkenness - there may be head injury as well
c. Head injury - first aid
d. Face injury
e. Chest injury and abdomen
injury - first aid
5 a. Bones, Joints and Muscles • Use of triangular bandages, ring
pads and slings for fractures]
b. Disorders of musculo-skeletal system
• Fractures • Fractures in specific sites -
• Dislocations immobilisation
• Sprains and strains 1. Jaw
• Cramps 2. Neck (beware of injuring spinal
cord)
c. Open fractures – general principles of first aid 3. Upper limb, collar bone and
shoulder
4. Rib cage
d. Closed fractures and dislocations - general principles
5. Pelvis, lower limb and ankle
6. Spine
e. Complicated fracture - open or closed
f. Sprains - first aid - RICE therapy
g. Cramps - first aid
h. Fractures in specific sites - immobilisation techniques
• Jaw
• Neck (beware of injuring spinal cord)
• Upper limb, collar bone and shoulder
• Rib cage
• Pelvis, lower limb and ankle
• Spine (beware of injuring spinal cord)
6 a. The skin • Lift, carry and move casualty
1. Principles of lifting and carrying
b. Burns (superficial, partial-thickness and full-thickness), scalds and 2. Emergency move - drag
blisters - first aid method, drag and carry method
3. One first aider casualty moves -
c. Heat exhaustion and heat stroke - prevention and first aid human clutch, pick-a-back,
fireman lift and cradle
d. Fever - first aid 4. Two first aider casualty moves -
fore-and-aft carry
e. Cold related injury (wheelbarrow), 2-handed seat
carry, 4-handed seat carry,
chair carry
f. Bites
5. Spine injury lift and carry -
Hammock carry (3-6 persons),
g. Poisoning (swallowed poison, drug overdose, inhaled poisoning,
stretcher carry
plant and chemical contact)
Last updated 2002 Page 2 of 3
SESSION THEORY &. PRACTICAL
6 h. Lift, carry and move casualty • Revision - first aid for wounds and
(cont’d) • Principles of lifting and carrying bleeding
• emergency move - drag method, drag and carry method
• one first aider casualty move - human clutch, pick-a-back, • Revision - first aid for sprains,
fireman lift and cradle method dislocations and fractures
• Two first aider casualty move - fore-and-aft carry
(wheelbarrow), 2-handed seat carry, 3-handed seat
carry, 4-handed seat carry, chair carry
• Neck and spine injury - lift and carry methods - Hammock
carry (3 persons), stretcher carry (beware of damaging the
spinal cord)
7 Theory Revision
• any question or doubt to clarify
• MCQs - past question papers
Practical test revision
• Unconscious casualty
required to do a casualty survey and give appropiate emergency first aid
Heimlich manoeuvre or CPR followed by secondary survey and recovery position
• Conscious casualty
required to treat a bleeding wound and immobilise 1 fracture
Bleeding wound - direct and indirect bleeding control; pressure point to choose from:
a. subclavian
b. brachial or femoral
c. dressing the wound
i. primary dressing
ii. secondary dressing
iii. support
Fracture or dislocation - Possibilities to choose from:
a. shoulder dislocation
b. ankle sprain
c. upper limb or collar bone fracture
d. pelvis or lower limb fracture
e. suspected neck or spine fracture
8 EXAMINATION
• Theory test - 30 MCQs
• Practical test - Two scenario - 10 min each
• Unconscious casualty
required to do a casualty survey and give appropriate emergency first aid - recovery position, Heimlich
manoeuvre or CPR
• Conscious casualty
required to treat a bleeding wound and immobilise 1 fracture.
Bleeding wound - direct and indirect bleeding control, pressure points to choose from:
1. subclavian
2. brachial,
3. femoral
Dressing the wound:
1. primary dressing
2. bandaging
3. support
Fracture or dislocation - possibilities to choose from:
1. shoulder dislocation
2. ankle sprain
3. upper limb or collar bone fracture
4. pelvis or lower limb fracture
5. suspected neck or spine fracture
Suggestion: Practical test be conducted after the written test so that candidates have something to do while
waiting for the second part of the test.
Last updated 2002 Page 3 of 3
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
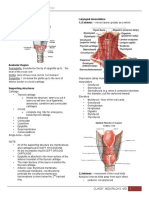
- LarynxDocument5 pagesLarynxGeraldine Marie SalvoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hamstring Injury - Diagnosis and Injury Management DiagnosisDocument5 pagesHamstring Injury - Diagnosis and Injury Management Diagnosisgemichan26Pas encore d'évaluation
- Thoracic Outlet SyndromeDocument5 pagesThoracic Outlet SyndromeMd Ahsanuzzaman PinkuPas encore d'évaluation
- Maurice Blanchot Thomas The Obscure 1Document124 pagesMaurice Blanchot Thomas The Obscure 1backwardsduchamp100% (2)
- Overgranulation: A. Muhammad Reva A.MDocument21 pagesOvergranulation: A. Muhammad Reva A.Mgalih widodoPas encore d'évaluation
- Case 1Document6 pagesCase 1Nico AguilaPas encore d'évaluation
- B20M3L5 - Neck InjuriesDocument4 pagesB20M3L5 - Neck InjuriesBarda GulanPas encore d'évaluation
- Airway Emergencies: ObjectivesDocument8 pagesAirway Emergencies: ObjectivespratiwiPas encore d'évaluation
- Group Courage - Multiple Injured Patient (Case Discussion)Document19 pagesGroup Courage - Multiple Injured Patient (Case Discussion)Jimmy V. Venturina, Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Primary SurveyDocument3 pagesPrimary SurveyNabighah ZukriPas encore d'évaluation
- A B C D E: Advanced Trauma Life Support - AtlsDocument2 pagesA B C D E: Advanced Trauma Life Support - AtlsAnnsha VeimernPas encore d'évaluation
- Apley Reading - Management of Major InjuriesDocument16 pagesApley Reading - Management of Major InjuriesPatrick LukitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cerebellum-Rr - 1 (Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry)Document215 pagesCerebellum-Rr - 1 (Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry)REACT ATTRACTSPas encore d'évaluation
- 10,11,12-Head & Neck I, II and III (Only F1)Document14 pages10,11,12-Head & Neck I, II and III (Only F1)Safi MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency Room AssessmentDocument3 pagesEmergency Room AssessmentJULIANNE BEA ACADEMIA BABIERAPas encore d'évaluation
- Prelims Disaster Skills 1st NotesDocument6 pagesPrelims Disaster Skills 1st NotesbercoaprilgracePas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy RR CerebellumDocument106 pagesAnatomy RR Cerebellumभईया भोसडिकाPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple TraumaDocument5 pagesMultiple TraumaChristabel EdithPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency and Disaster NursingDocument6 pagesEmergency and Disaster Nursinganon_720827871Pas encore d'évaluation
- RVT ATLS Review & General Principles in TraumaDocument91 pagesRVT ATLS Review & General Principles in TraumaJamaluddin Ahmad A.MPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency Nursing CompleteDocument9 pagesEmergency Nursing CompleteggukPas encore d'évaluation
- First Aid Lesson HandoutsDocument3 pagesFirst Aid Lesson HandoutsGuia Camandang100% (1)
- Why Basic Survival Skills Are Important To Know (By: Aqsa Khan)Document3 pagesWhy Basic Survival Skills Are Important To Know (By: Aqsa Khan)Joycee BurtanogPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Life Support: Elements of The Survey The SceneDocument5 pagesBasic Life Support: Elements of The Survey The SceneMarrianne MortaPas encore d'évaluation
- NSTP 002 - Midterm ReviewerDocument8 pagesNSTP 002 - Midterm ReviewerDENIEL MIKE DUKAPas encore d'évaluation
- Веб-страница 2Document1 pageВеб-страница 2Zalina IvanovaPas encore d'évaluation
- Trans SaVi Oto Lec 10 Head and Neck Anatomy and Benign Masses 1st SemDocument7 pagesTrans SaVi Oto Lec 10 Head and Neck Anatomy and Benign Masses 1st SemJoherPas encore d'évaluation
- Neck Trauma DR Hauwa Shitu 1Document40 pagesNeck Trauma DR Hauwa Shitu 1Hauwa shitu.B100% (1)
- Anaesthesia For BurnsDocument51 pagesAnaesthesia For BurnsAnulatkPas encore d'évaluation
- ShoulderDocument17 pagesShoulderNehaPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency Medicine 2001 PDFDocument44 pagesEmergency Medicine 2001 PDFJoel Antonio García AlvarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Breathing SkillsDocument3 pagesBreathing SkillsydtrgnPas encore d'évaluation
- NeckDocument67 pagesNeckdr_asaleh100% (1)
- Basic Life SupportDocument10 pagesBasic Life SupportAudi Kyle SaydovenPas encore d'évaluation
- HerniasDocument6 pagesHerniasYalin AbouhassiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency MedicineDocument42 pagesEmergency Medicinedrliza75% (8)
- Trochanteric FracturesDocument32 pagesTrochanteric FracturesMbah GapinbissiPas encore d'évaluation
- CWTSDocument7 pagesCWTSprincess.pinedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessing The NeckDocument18 pagesAssessing The NecksrslytrdPas encore d'évaluation
- Emergency ManagementDocument69 pagesEmergency Managementgiya nursingPas encore d'évaluation
- MUB Kuliah Narasumber (Bedah Orthopedi) PDFDocument117 pagesMUB Kuliah Narasumber (Bedah Orthopedi) PDFNaura QotrunnadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aml - Ibrahiem - 5-Primary and Secondary Survey in Multiple Trauma PatientDocument62 pagesAml - Ibrahiem - 5-Primary and Secondary Survey in Multiple Trauma PatientAlaa BahjatPas encore d'évaluation
- Bite Splints 14 PDFDocument14 pagesBite Splints 14 PDFmegahedhazeemPas encore d'évaluation
- 6disaster Nursing SAS Session 6Document6 pages6disaster Nursing SAS Session 6Beverly Mae Castillo JaymePas encore d'évaluation
- Perioperative PeriodDocument14 pagesPerioperative Periodvinzy acainPas encore d'évaluation
- Iontophoresis TENNIS ELBOW (Lateral Humeral Epicondylitis)Document2 pagesIontophoresis TENNIS ELBOW (Lateral Humeral Epicondylitis)Ikre19Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Examination TemplateDocument9 pagesPhysical Examination Templatedhuha_minozPas encore d'évaluation
- National NORCET Prelims Test-1Document43 pagesNational NORCET Prelims Test-1SHIVANIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Venoms, Poisons and ToxinsDocument54 pagesVenoms, Poisons and ToxinsFatality FatalityPas encore d'évaluation
- Parkinso N'S Disease: Grou p1Document15 pagesParkinso N'S Disease: Grou p1Mada mada DanePas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Abdominal TraumaDocument9 pages7 Abdominal TraumaMyrtle Yvonne RagubPas encore d'évaluation
- Survival Techniques PrelimDocument26 pagesSurvival Techniques PrelimIsaackurt AdaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Newer Physiology in Surgical and General PracticeD'EverandThe Newer Physiology in Surgical and General PracticePas encore d'évaluation
- The Inner Ear: Including Otoneurology, Otosurgery, and Problems in Modern WarfareD'EverandThe Inner Ear: Including Otoneurology, Otosurgery, and Problems in Modern WarfarePas encore d'évaluation
- Methods of Animal Experimentation: Volume ID'EverandMethods of Animal Experimentation: Volume IÉvaluation : 1 sur 5 étoiles1/5 (1)
- Carigie's Neuroanatomy of the RatD'EverandCarigie's Neuroanatomy of the RatWolfgang ZemanPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Surgery and Care of the Research Animal: Surgical Approaches to the Organ SystemsD'EverandResearch Surgery and Care of the Research Animal: Surgical Approaches to the Organ SystemsPas encore d'évaluation
- SalpingitisDocument25 pagesSalpingitisAnonymous NDAtNJyKPas encore d'évaluation
- Octenisept Praep-Info VIII 11.13 G PDFDocument2 pagesOctenisept Praep-Info VIII 11.13 G PDFCharis PapadopoulosPas encore d'évaluation
- Post Thoracotomy Physiotherapy ManagementDocument25 pagesPost Thoracotomy Physiotherapy ManagementSiva Shanmugam100% (5)
- Traducere in Engleza Site Spring Dental Mihaela VelcuDocument11 pagesTraducere in Engleza Site Spring Dental Mihaela VelcuFlorin Cornel VelcuPas encore d'évaluation
- The Dystopian NovelDocument17 pagesThe Dystopian NovelafiPas encore d'évaluation
- L1 - BB LecDocument11 pagesL1 - BB LecJUDEA WILCH ORJEPas encore d'évaluation
- CN 9-12Document6 pagesCN 9-12The Real UploaderPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Pressure in Non-Critically Ill Preterm and Full-Term NeonatesDocument9 pagesBlood Pressure in Non-Critically Ill Preterm and Full-Term NeonatesEduardo Rios DuboisPas encore d'évaluation
- Anders Sandberg - Asatru The Nordic Subtradition of The Verbena Cd9 Id1061308219 Size156Document16 pagesAnders Sandberg - Asatru The Nordic Subtradition of The Verbena Cd9 Id1061308219 Size156Baud WolfPas encore d'évaluation
- Modic Type 1 Vs Tuberculous SpondylitisDocument5 pagesModic Type 1 Vs Tuberculous SpondylitisAgnes JauwPas encore d'évaluation
- Pet Insurance: Because Pets Are Family TooDocument10 pagesPet Insurance: Because Pets Are Family ToomeeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Aminacid MetabolismDocument84 pagesAminacid MetabolismAaronJose100% (1)
- Credit Functions - Developmental and Promotional Functions - Supervisory FunctionsDocument32 pagesCredit Functions - Developmental and Promotional Functions - Supervisory FunctionscrajkumarsinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal IPSG 5Document7 pagesJournal IPSG 5marissa ulkhairPas encore d'évaluation
- Histology of Heart and Vessels - ANAT3888 - 2023Document41 pagesHistology of Heart and Vessels - ANAT3888 - 2023RachaelPas encore d'évaluation
- TerminologiesDocument65 pagesTerminologiesErika Mae PascuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tuberculosis SlidesDocument18 pagesTuberculosis SlidesmedeviPas encore d'évaluation
- Thesis Statement For Animal ResearchDocument5 pagesThesis Statement For Animal Researchtit0feveh1h3100% (1)
- Villanueva General Ordinance of 2009Document148 pagesVillanueva General Ordinance of 2009Rogelio E. SabalbaroPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Most Common College DiseasesDocument13 pages8 Most Common College DiseasesgizlePas encore d'évaluation
- DescargarDocument7 pagesDescargarJonathan NaulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mycobacterium Leprae: DR Retno Budiarti Microbiology DepartmentDocument25 pagesMycobacterium Leprae: DR Retno Budiarti Microbiology DepartmentPrincess QumanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pink Mohawk Rulebook v2Document68 pagesPink Mohawk Rulebook v2Cat of Many FacesPas encore d'évaluation
- Walt Disney: SpeechDocument2 pagesWalt Disney: SpeechBuşuMihaiCătălinPas encore d'évaluation
- Unacadmey Basic Organic Chemistry PDFDocument92 pagesUnacadmey Basic Organic Chemistry PDFAbhishek VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Public SpeakingDocument490 pagesPublic SpeakingDewa Putu Tagel100% (8)
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2021Document25 pagesMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2021Gaia PhyllisPas encore d'évaluation