Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Abnormality/Abnormal Disorder: Agoraphobia-Fear of Open Places, Social Phobia Stage
Transféré par
EugeneDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Abnormality/Abnormal Disorder: Agoraphobia-Fear of Open Places, Social Phobia Stage
Transféré par
EugeneDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
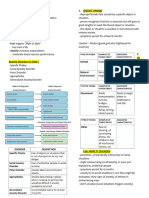
Abnormality/Abnormal Disorder- any Depersonalization- feeling of being outside of
disorder that has a free-floating cause and usually self/watching self from a distance = distortion of
defined through: surroundings anxiety, depression.
i. Statistical Definition- after taking a certain test, the Causes:
score is taken and is plotted against a bell curve. Freud et al.- habituation of repressing sth.
When it hits the middle area, you are normal. Cognitive and behavioural- it is a willful forgetting
ii. Social Norm Deviance- society is used as a basis for
normal/ not normal behaviour. 4. Mood Disorders- disorders where emotions are
iii. Subjective Discomfort- the emotional distress disrupted/disturbed.
experienced in a certain activity. Types (according to gravity):
iv. Maladaptivity- the behaviour prevents one from 1. Mild: has a cause
executing his/her daily routine. • Dysthymia ‘bad spirit’- a long lasting depression,
usu. >2 years.
Types: • Cyclothymia ‘circumambulating spirit’- from sad
1. Anxiety Disorders- disorders involving intense to happy, v.v.
irrational fear/uneasiness in four types: 2. Severe: has no obvious physical cause
i. Phobias- persistent fear of a specific stimulus (eg. • Major Depression- a sudden depression w/o an
Agoraphobia- fear of open places, social phobia=stage external cause and/or being sad for a long time
fright) >6mos.
ii. Panic disorders- sudden onset of much panic • Bipolar Disorder- severe mood swings from one
that leads to palpitations, ‘feeling of outside of self’ extreme to another.
iii. Obsessive Compulsive Disorder- constant fear Causes:
of sth. leads to repeating behaviour. Freud et al.- repressed anger
iv. Generalized Anxiety Disorder- anxiety Behavioralists- related to learned helplessness
experienced without a real cause. Socio-cognitive- negative thinking
Causes: Biological- dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine
Freud et al.- signal to repress sth.
Behaviorists- learned anxiety
1
Cognitive- irrational thinking
Biological- inherited, nervous problems
Sociocultural- context-dependent
2. Somatoform Disorders- bodily problems without
a real physical cause
Psychosomatic Disorders- psychological stress that
causes physical problems
i. Hypochondrosis- getting over-concerned about
with being ill symptoms
ii. Somatization Disorder- the patient complains
about a symptom too much without a real physical
cause.
iii. Conversion Disorder- the patient experiences a
symptom without a real physical cause.
Why do these happen?
Freud et al.- traumatic events associated with that
symptom
Behaviorists- it is a way of getting PR and NR
Cognitive- false belief, magnification
3. Dissociative Disorders- disorders that involve a
“breaking away” from consciousness
Dissociative amnesia- usually involves memory loss
and usually caused by trauma, abuse or events (more
common among relatives and women)
Dissociative fugue- adapting a new identity in every
new location, lodging a gap from self and may lead to
confusion
MPD (Multiple Personality Disorder)- different
personalities, one person.
1 In four types: Magnification (making sth. small look
big), All-or-Nothing thinking (false dilemma),
Over[Hasty]generalization, Minimization (not looking at
the positive side at all)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- OBESITY - Cayce Health DatabaseDocument4 pagesOBESITY - Cayce Health Databasewcwjr55Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders.Document9 pagesChapter 14 Psychological Disorders.BorisVanIndigoPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychological Disorders: AP Psychology Mr. HollandDocument20 pagesPsychological Disorders: AP Psychology Mr. Hollandyummywords1254Pas encore d'évaluation
- CRIM 3 Human Behavior and VictimologyDocument18 pagesCRIM 3 Human Behavior and VictimologyRommel Ilang-ilang100% (11)
- Mass Responses and Commentator's CuesDocument6 pagesMass Responses and Commentator's CuesEugene100% (2)
- 2006 Info For MpjeDocument28 pages2006 Info For Mpjemina75% (4)
- Some Categories of Mental IllnessesDocument5 pagesSome Categories of Mental IllnessesLiezel-jheng Apostol LozadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Somatic Symptoms and Related Disorders, Dissociative Disorders and Psychotic DisorderDocument6 pagesSomatic Symptoms and Related Disorders, Dissociative Disorders and Psychotic DisorderMarco RagaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Symbol Digit Modalities TestDocument2 pagesThe Symbol Digit Modalities TestAnonymous S7P7gMtiL50% (2)
- CHAPTER 4 - NotesDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 4 - NotesAquamsha FahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacological Screeing of DrugsDocument59 pagesPharmacological Screeing of Drugsrajender100% (1)
- Psychological DisordersDocument52 pagesPsychological Disordersember_memoriesPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Behavior and Crisis Management Review: BY: Rachma M. Juda TOP 9, CLE DEC.2018Document67 pagesHuman Behavior and Crisis Management Review: BY: Rachma M. Juda TOP 9, CLE DEC.2018Kiddo VelascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Behavior and VictiminologyDocument20 pagesHuman Behavior and VictiminologyKhristel Alcayde100% (1)
- Schizophrenia Lecture NotesDocument9 pagesSchizophrenia Lecture NotesDale Buckman100% (1)
- Signs and Symptoms of Mental Disorders: Naama AlyaseenDocument60 pagesSigns and Symptoms of Mental Disorders: Naama Alyaseengerrgiytryahoo100% (1)
- MH NotesDocument28 pagesMH NotesNyein Nu Winn100% (2)
- Jurnal Mata Sodium Hyaluronate PDFDocument7 pagesJurnal Mata Sodium Hyaluronate PDFAstrid RumbiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Paper On BanditryDocument8 pagesFinal Paper On BanditryEugenePas encore d'évaluation
- Stop the Fear: Learn to Stop Anxiety Panic Attacks and Take Control of Your LifeD'EverandStop the Fear: Learn to Stop Anxiety Panic Attacks and Take Control of Your LifePas encore d'évaluation
- Q & A Human BehaviorDocument189 pagesQ & A Human BehaviorAngel King RelativesPas encore d'évaluation
- ScoliosisDocument38 pagesScoliosiskimPas encore d'évaluation
- Chinese Mass ResponsesDocument2 pagesChinese Mass ResponsesEugene100% (3)
- Algoritma Penatalaksanaan Cedera Kepala PDFDocument1 pageAlgoritma Penatalaksanaan Cedera Kepala PDFMiftahul Khairat Musmar ElbamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Crim 201Document50 pagesCrim 201Tabaosares JeffrePas encore d'évaluation
- Anxiety DisordersDocument35 pagesAnxiety DisordersmulugetaPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Behavior Midterm Class AbnormalitiesDocument4 pagesHuman Behavior Midterm Class Abnormalitieswensly intongPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychological Aspects of PolygraphyDocument7 pagesPsychological Aspects of PolygraphyALJHON SABINOPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3Document10 pagesChapter 3WATI KAKIPas encore d'évaluation
- Psy201 Final NotesDocument12 pagesPsy201 Final NotesNagham KDPas encore d'évaluation
- Crim 3 Lesson 3Document3 pagesCrim 3 Lesson 3JEAH REDOBLEPas encore d'évaluation
- Mental DisordersDocument5 pagesMental DisordersBanaay, Ronell JosephPas encore d'évaluation
- Anxietydisorders 220401155226Document38 pagesAnxietydisorders 220401155226Neharika KumariPas encore d'évaluation
- PsychologicalDocument15 pagesPsychologicalmanasvPas encore d'évaluation
- PsychoneurosisDocument23 pagesPsychoneurosisanitha1118Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4Document42 pagesChapter 4Athira RaghuPas encore d'évaluation
- Ap Unit 4Document21 pagesAp Unit 4Vaishnavi RaveendranPas encore d'évaluation
- Mental Illness Schizophrenia - Greek For "Split" (From Reality) and "Mind"Document7 pagesMental Illness Schizophrenia - Greek For "Split" (From Reality) and "Mind"Alaina AndersonPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Psychology: Psychological DisorderDocument41 pagesUnderstanding Psychology: Psychological DisorderDannah Mae CaballeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Abnormal PsychologyDocument11 pagesAbnormal Psychologyannistafford04Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Different Factors That Cause Frustrations Are As FollowsDocument5 pagesThe Different Factors That Cause Frustrations Are As FollowsChristian Joseph ClavelPas encore d'évaluation
- Human BehaviorDocument37 pagesHuman Behaviortrorse7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4Document23 pagesChapter 4Eimun PurtiPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychology Chapter SevenDocument25 pagesPsychology Chapter Sevenmelaku zegeyePas encore d'évaluation
- Crim 3 Part 2Document9 pagesCrim 3 Part 2Jana May Faustino MedranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Crim3 Semis 1Document14 pagesCrim3 Semis 1kharinaluna3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Psychological Disorders 2016Document40 pagesPsychological Disorders 2016Jonah the mixerPas encore d'évaluation
- 6anxiety DisordersDocument40 pages6anxiety Disorderswwamed18Pas encore d'évaluation
- Crim 3Document40 pagesCrim 3Almonicar Amadeo Ed EdepPas encore d'évaluation
- Outline Ch. 14Document12 pagesOutline Ch. 14bechiePas encore d'évaluation
- Psychology 1 TestDocument8 pagesPsychology 1 TestCarlos HurtadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12 Abnormal PsychologyDocument4 pagesChapter 12 Abnormal PsychologyAfiya KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment For PsychDocument3 pagesAssignment For PsychJadeRuinsPas encore d'évaluation
- ATI Mental Health CH 11: Anxiety DisordersDocument4 pagesATI Mental Health CH 11: Anxiety DisordersRuthie BellaPas encore d'évaluation
- EMOTIONAL DISORDER (Depression Mania)Document20 pagesEMOTIONAL DISORDER (Depression Mania)Anna Sofia ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Classifying Abnormal BehaviorDocument4 pagesClassifying Abnormal BehaviorLyanna MormontPas encore d'évaluation
- Theories of PersonalityDocument16 pagesTheories of PersonalityaubPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Notes Symptoms Psych IlnessesDocument5 pagesAssessment Notes Symptoms Psych IlnessesderrickPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychological DisordersDocument8 pagesPsychological DisordersDenise NicolePas encore d'évaluation
- Yoga Paper 2Document52 pagesYoga Paper 2jayamohanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Mental and Sexual DisordersDocument5 pagesThe Mental and Sexual DisordersGrace BrionesPas encore d'évaluation
- Psy 10Document5 pagesPsy 10Shishir SubbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anxiety DisorderDocument3 pagesAnxiety DisorderfebiePas encore d'évaluation
- Mental and Emotional DisordersDocument4 pagesMental and Emotional DisordersStifanny Jean FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychology Chapter 4 - Psychological DisorderDocument71 pagesPsychology Chapter 4 - Psychological DisorderkhushiPas encore d'évaluation
- Psychological DisordersREVDocument18 pagesPsychological DisordersREVlucas OmondiPas encore d'évaluation
- SESSION 13 Abnormal PsychologyDocument47 pagesSESSION 13 Abnormal PsychologyKainaat YaseenPas encore d'évaluation
- Phobias You Might Not Know You Have:Let's Explore The SymptomsD'EverandPhobias You Might Not Know You Have:Let's Explore The SymptomsPas encore d'évaluation
- Schizophrenia Unmasked: Personal Stories and Proven Techniques to Reclaim Your LifeD'EverandSchizophrenia Unmasked: Personal Stories and Proven Techniques to Reclaim Your LifePas encore d'évaluation
- How to Stop Negative Thinking and Unlocking Positivity: Overcoming Negative Thoughts for a Brighter FutureD'EverandHow to Stop Negative Thinking and Unlocking Positivity: Overcoming Negative Thoughts for a Brighter FuturePas encore d'évaluation
- Galatians Report OutlineDocument3 pagesGalatians Report OutlineEugenePas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Editorial SmorgasbordDocument2 pages1st Editorial SmorgasbordEugenePas encore d'évaluation
- MenuDocument1 pageMenuEugenePas encore d'évaluation
- Economics 102 F Pre-Final Grade: Student IDDocument1 pageEconomics 102 F Pre-Final Grade: Student IDEugenePas encore d'évaluation
- On MemoryDocument1 pageOn MemoryEugenePas encore d'évaluation
- NT ReviewerDocument1 pageNT ReviewerEugenePas encore d'évaluation
- APPENDIX: Raw Data For Tables GDP Per Capita and GNP Per Capita From 1980-2010 (Constant Prices)Document7 pagesAPPENDIX: Raw Data For Tables GDP Per Capita and GNP Per Capita From 1980-2010 (Constant Prices)EugenePas encore d'évaluation
- Alchemy, A Part of The Occult Tradition, Is Both ADocument2 pagesAlchemy, A Part of The Occult Tradition, Is Both AEugenePas encore d'évaluation
- On LearningDocument2 pagesOn LearningEugenePas encore d'évaluation
- ReviewerDocument2 pagesReviewerEugenePas encore d'évaluation
- Crustacea Species DescriptionDocument2 pagesCrustacea Species DescriptionEugenePas encore d'évaluation
- SkizofreniaDocument1 pageSkizofreniaMarsiano QendroPas encore d'évaluation
- Rhopalurus Junceus: and The Treatment of CancerDocument17 pagesRhopalurus Junceus: and The Treatment of CancerAmalia Tri UtamiPas encore d'évaluation
- 8-Veria Technique of Cochlear Implantation Our ExperienceDocument4 pages8-Veria Technique of Cochlear Implantation Our ExperienceAnonymous ST1Ot2GAHxPas encore d'évaluation
- Gso 2294 2012Document8 pagesGso 2294 2012anish_habibaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1-Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs (This)Document96 pages1-Thyroid and Antithyroid Drugs (This)hamidPas encore d'évaluation
- PathophysiologyDocument13 pagesPathophysiologyJan Phi LipPas encore d'évaluation
- Resume UpdatedDocument2 pagesResume Updatedapi-253794925Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cghs RatesDocument34 pagesCghs RatescjrrreddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ota 1210 - Professional Inserice Presentaion - Ergonomics in The Work PlaceDocument13 pagesOta 1210 - Professional Inserice Presentaion - Ergonomics in The Work Placeapi-284910245Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ryujin™ Plus - RX PTCA Balloon Catheter: Product CharacteristicsDocument1 pageRyujin™ Plus - RX PTCA Balloon Catheter: Product CharacteristicssunanPas encore d'évaluation
- Infective EndocarditisDocument66 pagesInfective Endocarditissanjivdas100% (4)
- TUGAS 1 (Cause-Effect)Document3 pagesTUGAS 1 (Cause-Effect)raden bayuPas encore d'évaluation
- Daftar Pustaka MeytaDocument3 pagesDaftar Pustaka MeytaAbraham TheodorePas encore d'évaluation
- International Journal of Scientific Research and ReviewsDocument11 pagesInternational Journal of Scientific Research and ReviewsHanif ZakariPas encore d'évaluation
- Arbor Acres Nutrional GuideDocument20 pagesArbor Acres Nutrional GuidePetre Marius100% (1)
- 8 PDFDocument4 pages8 PDFGilang IndraPas encore d'évaluation
- Surgical DressingDocument2 pagesSurgical Dressinggao1989Pas encore d'évaluation
- Shoma Morita - WikipediaDocument8 pagesShoma Morita - WikipediacamicrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Howard County [Md] Public Schools Athletic Director Annual Report to Bd of Ed, Re High School Sports Program p. 15 Concussion Stats by Sport p. 14 Limit on In-season Football Contact Practices to 2 Per WeekDocument15 pagesHoward County [Md] Public Schools Athletic Director Annual Report to Bd of Ed, Re High School Sports Program p. 15 Concussion Stats by Sport p. 14 Limit on In-season Football Contact Practices to 2 Per WeekConcussion_MCPS_MdPas encore d'évaluation
- Theories, Models, and Frameworks Related To Sleep-Wake Disturbances in The Context of CancerDocument38 pagesTheories, Models, and Frameworks Related To Sleep-Wake Disturbances in The Context of CancerLeahCris ByunPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Asthma ExacerbationDocument3 pagesAcute Asthma ExacerbationRoa Al-SajjanPas encore d'évaluation
- Guideline Perkeni 2019 PDFDocument36 pagesGuideline Perkeni 2019 PDFCut Aulia MaulizaPas encore d'évaluation


































































































![Howard County [Md] Public Schools
Athletic Director Annual Report to Bd of Ed,
Re High School Sports Program
p. 15 Concussion Stats by Sport
p. 14 Limit on In-season Football Contact Practices to 2 Per Week](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/124077961/149x198/5a472ee067/1360115263?v=1)


