Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
CABLE Calcula
Transféré par
Jayashree Sheware0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
51 vues2 pagesChart applies to bunched cables made up of 100 or fewer identical Single Wires or Twisted Pairs. The overall diameter of the cabled components may be calculated by multiplying the outside diameter of a single wire by the K factor.
Description originale:
Titre original
CABLE calcula
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentChart applies to bunched cables made up of 100 or fewer identical Single Wires or Twisted Pairs. The overall diameter of the cabled components may be calculated by multiplying the outside diameter of a single wire by the K factor.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
51 vues2 pagesCABLE Calcula
Transféré par
Jayashree ShewareChart applies to bunched cables made up of 100 or fewer identical Single Wires or Twisted Pairs. The overall diameter of the cabled components may be calculated by multiplying the outside diameter of a single wire by the K factor.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
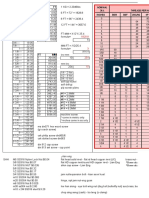
This chart applies to bunched cables made up of 100 or fewer identical single wires or twisted pairs.
The overall diameter of the cabled components may be calculated by multiplying the outside diameter
of a single wire by the K factor.
K K K K K K
FACTOR FACTOR FACTOR FACTOR FACTOR FACTOR
No. of Single Twisted No. of Single Twisted No. of Single Twisted
Comp. Wires Pairs Comp. Wires Pairs Comp. Wires Pairs
1 1.00 2.0 35 6.80 10.9 69 9.55 15.0
2 2.00 3.5 36 6.90 11.0 70 9.62 15.5
3 2.17 3.8 37 6.99 11.0 71 9.69 15.6
4 2.42 4.2 38 7.09 11.1 72 9.76 15.6
5 2.57 4.8 39 7.18 11.2 73 9.83 15.6
6 2.82 5.0 40 7.27 11.6 74 9.89 15.7
7 3.00 5.0 41 7.36 11.7 75 9.96 15.8
8 3.25 5.6 42 7.45 11.8 76 10.03 15.9
9 3.45 6.0 43 7.54 12.0 77 10.09 15.9
10 3.64 6.5 44 7.63 12.5 78 10.16 15.9
11 3.81 6.6 45 7.71 12.6 79 10.22 16.0
12 3.98 6.8 46 7.80 12.6 80 10.29 16.2
13 4.15 6.9 47 7.88 12.7 81 10.35 16.3
14 4.30 7.2 48 7.97 12.8 82 10.41 16.3
15 4.45 7.4 49 8.05 12.9 83 10.48 16.3
16 4.60 7.8 50 8.13 12.9 84 10.54 16.4
17 4.75 7.9 51 8.21 13.0 85 10.60 16.8
18 4.88 8.0 52 8.29 13.2 86 10.67 16.9
19 5.01 8.0 53 8.37 13.3 87 10.73 16.9
20 5.14 8.2 54 8.45 13.3 88 10.79 16.9
21 5.27 8.6 55 8.53 13.4 89 10.85 16.9
22 5.39 8.8 56 8.61 13.8 90 10.91 17.0
23 5.51 9.0 57 8.68 13.9 91 10.97 17.0
24 5.63 9.5 58 8.76 13.9 92 11.03 17.1
25 5.75 9.6 59 8.83 13.9 93 11.09 17.1
26 5.86 9.6 60 8.91 14.0 94 11.15 17.1
27 5.98 9.8 61 8.98 14.0 95 11.21 17.2
28 6.09 9.9 62 9.06 14.1 96 11.27 17.6
29 6.19 10.0 63 9.13 14.1 97 11.33 17.7
30 6.30 10.2 64 9.20 14.2 98 11.38 17.7
31 6.40 10.3 65 9.27 14.6 99 11.44 17.7
32 6.51 10.4 66 9.34 14.7 100 11.50 ---
33 6.60 10.8 67 9.41 14.7
34 6.71 10.9 68 9.48 14.8
For you clarification of Transfomer Sizing calculation could be followed as
1. Calculate Total Connected Load(KW)(
2. Calc the Total I/P in KW ( Considereing 85% efficiency)
3. Calc Total I/P in KVA (Considering 0.92 Power Factor)
4. Required KVA by mutiplying the Total I/P in KVA by 1.2 times.
Calculation Example
1. Say Total Connected load in KW=1100
2. Therefore Total I/P in kw = 1100/0.86 = 1279
3. Total I/P in KVA = 1390
4. Total KVA required = 1390*1.2=1668
Therefore by considering the future connection you can select 2000 KVA transformer for the above
said example.
***SUPPOSE WE USE COPPER CONDUCTOR AND WE ALLOW A MAXIMUM OF
5V MAX. VOLTAGE DROP:
5= 2*12*15*230/CSA
CSA= 82800/5
CSA= 16560 CM
FROM COMMERCIAL REFERRENCES:
15560 CM IS CLOSEST TO 16510 CM WHICH IS #8 COPPER OR 8 SQMM
WIRE.
NOTE:
1. IN THIS CASE A MAXIMUM OF 5 VOLTS WAS CONSIDERED IN THE
CALCULATION.
2. THIS CALCULATION IS NOT VALID FOR LARGE MOTORS. BECAUSE
MOTORS DRAWS A MAXIMUM OF 7OO% TIMES ITS FULL LOAD TORQUE
DEPENDING ON THE MOTOR CONTROL STARTING METHODS USED BY THE
DESIGNING ENGINEER.
65 Sq mm is the cross section of copper.
= 0.65 sq. cm
volume of 1 meter cable = cross section x length.
=0.65 x 100 = 65 cubic cm.
Density of copper is 8.9 gms / cc
Weight of 1 mtr length cable = 65x 8.9 gms
= 578.5 gms
= 0.5785 kgs
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Pipe's Wall Thickness: ASTM A312, A358, A778, A53, A106, API 5L ASME/ANSI B36.19 B36.10Document1 pagePipe's Wall Thickness: ASTM A312, A358, A778, A53, A106, API 5L ASME/ANSI B36.19 B36.10Theodosios StergiouPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Install&Owner CPLDocument20 pagesManual Install&Owner CPLRuss DuQuainePas encore d'évaluation
- Pc160lc 7e0 S N 20001 Up TierDocument475 pagesPc160lc 7e0 S N 20001 Up TierLucasPas encore d'évaluation
- 14.0 PP 317 318 Asymptotic Critical ValuesDocument2 pages14.0 PP 317 318 Asymptotic Critical Valueselhombredenegro3000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tabel NPS Dan SCH Pipa Carbon - Stainless SteelDocument3 pagesTabel NPS Dan SCH Pipa Carbon - Stainless SteelAdhi Erlangga0% (1)
- Nominal Size Outside Diameter Wall Thickness Plain-End Weight Inch MM Inch MM LB/FT KG/MDocument8 pagesNominal Size Outside Diameter Wall Thickness Plain-End Weight Inch MM Inch MM LB/FT KG/Mgauhip007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe's Wall Thickness: ASTM A312, A358, A778, A53, A106, API 5L ASME/ANSI B36.19 B36.10Document1 pagePipe's Wall Thickness: ASTM A312, A358, A778, A53, A106, API 5L ASME/ANSI B36.19 B36.10Theodosios StergiouPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe's Wall Thickness: ASTM A312, A358, A778, A53, A106, API 5L ASME/ANSI B36.19 B36.10Document1 pagePipe's Wall Thickness: ASTM A312, A358, A778, A53, A106, API 5L ASME/ANSI B36.19 B36.10Mohamed BencharifPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe's Wall Thickness: ASTM A312, A358, A778, A53, A106, API 5L ASME/ANSI B36.19 B36.10Document1 pagePipe's Wall Thickness: ASTM A312, A358, A778, A53, A106, API 5L ASME/ANSI B36.19 B36.10Kagira Drawing SoltuionPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe Wall ThicknessDocument1 pagePipe Wall ThicknessFurkan Burak MuhammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculo de Longitud Maxima en Tuberia LateralDocument11 pagesCalculo de Longitud Maxima en Tuberia LateralVega MiguelPas encore d'évaluation
- Distribusi F: WWW - Smartstat.infoDocument4 pagesDistribusi F: WWW - Smartstat.infonew accountPas encore d'évaluation
- A-100 Sprinkler Spray Patterns PDFDocument22 pagesA-100 Sprinkler Spray Patterns PDFGabriel LopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe's Wall Thickness: ASTM A312, A358, A778, A53, A106, API 5L ASME/ANSI B36.19 B36.10Document1 pagePipe's Wall Thickness: ASTM A312, A358, A778, A53, A106, API 5L ASME/ANSI B36.19 B36.10Scribd mePas encore d'évaluation
- OD Wall Thickness (MM) SS CS DN NPS SCH 5S SCH 10S SCH 40S SCH 80S SCH 10 SCH 20 SCH 30 SCH 40 STD SCH 60 Nominal Pipe SizeDocument2 pagesOD Wall Thickness (MM) SS CS DN NPS SCH 5S SCH 10S SCH 40S SCH 80S SCH 10 SCH 20 SCH 30 SCH 40 STD SCH 60 Nominal Pipe SizeAmirul AsyrafPas encore d'évaluation
- kN/m3 % kN/m3 m kN/m3 m kN/m3 kN/m3: γ1 E γ2 Df γ1sat NAF γ2sat γ h2oDocument24 pageskN/m3 % kN/m3 m kN/m3 m kN/m3 kN/m3: γ1 E γ2 Df γ1sat NAF γ2sat γ h2ojuliospcardonaPas encore d'évaluation
- Steel Pipe Dimensions ChartDocument1 pageSteel Pipe Dimensions ChartERIC GERARDPas encore d'évaluation
- Theoretical CoverageDocument1 pageTheoretical Coverageazdhim ghazaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Handling UnitsDocument14 pagesAir Handling UnitsMichael FutolPas encore d'évaluation
- Table 7 - 7Document1 pageTable 7 - 7Diego VergaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Carry Mark Principle of Economics (ECO 3100) Bil Matrik ASS 1 (G) ASS 2 (I) T1 T2 TotalDocument3 pagesCarry Mark Principle of Economics (ECO 3100) Bil Matrik ASS 1 (G) ASS 2 (I) T1 T2 TotalChee Hou OppaPas encore d'évaluation
- ELMDocument260 pagesELMDiánelis OcampoPas encore d'évaluation
- TP8Document9 pagesTP8Youssef FahmyPas encore d'évaluation
- Balingit Earl Jerome G BSME 1A Activity 4 Excel Functions and ChartDocument4 pagesBalingit Earl Jerome G BSME 1A Activity 4 Excel Functions and ChartEarl Jerome BalingitPas encore d'évaluation
- DN Nominal Pipe Size Chart Metric MMDocument1 pageDN Nominal Pipe Size Chart Metric MMNguyên Bùi50% (2)
- Commutation Factor Table 7 CPC 01012016Document1 pageCommutation Factor Table 7 CPC 01012016SandeepPas encore d'évaluation
- DN Nominal Pipe Size Chart Metric MMDocument1 pageDN Nominal Pipe Size Chart Metric MMteguh.setionoPas encore d'évaluation
- Excel Worksheet 1Document20 pagesExcel Worksheet 1faisal58650Pas encore d'évaluation
- Radish PlantDocument38 pagesRadish Plantmercy sacrizPas encore d'évaluation
- DuctileIronPipeDesign2013Document1 pageDuctileIronPipeDesign2013Ozan AtıcıPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe (Carbon Steel) (OK)Document1 pagePipe (Carbon Steel) (OK)Phan Tri ThongPas encore d'évaluation
- D1275 - Hallberg-Rassy 64 (Half Load) VPP OutputDocument1 pageD1275 - Hallberg-Rassy 64 (Half Load) VPP OutputmentolPas encore d'évaluation
- Inspection Timings of M&M Clutch HousingDocument2 pagesInspection Timings of M&M Clutch HousingaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hartley PDFDocument1 pageHartley PDFPaola Rivera DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Varillas Sistema Ingles PDFDocument1 pageVarillas Sistema Ingles PDFDiederich GarcíaPas encore d'évaluation
- Friction Pipe Loss Chart: GPM GPM Pipe Size IN. Pipe Size INDocument2 pagesFriction Pipe Loss Chart: GPM GPM Pipe Size IN. Pipe Size INOscar PettersPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe's Wall Thickness: ASTM A312, A358, A778, A53, A106, API 5L ASME/ANSI B36.19 B36.10Document6 pagesPipe's Wall Thickness: ASTM A312, A358, A778, A53, A106, API 5L ASME/ANSI B36.19 B36.10Nuta AnghelachePas encore d'évaluation
- IUnits ChartDocument1 pageIUnits ChartThomas EntersPas encore d'évaluation
- Pinned Base PlateDocument7 pagesPinned Base PlatevtalexPas encore d'évaluation
- Unclassified: So A o ADocument3 pagesUnclassified: So A o AErick Santiago CubillosPas encore d'évaluation
- Unclassified: So A o ADocument3 pagesUnclassified: So A o AErick Santiago CubillosPas encore d'évaluation
- Demag CC600Document4 pagesDemag CC600Reza SalimiPas encore d'évaluation
- Wall Thickness (MM) Nominal Pipe Size Stainless Steel Carbon Steel DN NPS Outside Diameter (MM)Document1 pageWall Thickness (MM) Nominal Pipe Size Stainless Steel Carbon Steel DN NPS Outside Diameter (MM)Murali Fabtool100% (1)
- Pipe ScheduleDocument2 pagesPipe ScheduleVipin PeterPas encore d'évaluation
- Pump. Slurry Selection Typical Warman-1Document51 pagesPump. Slurry Selection Typical Warman-1Christopher LloydPas encore d'évaluation
- WindChart-Golf W-Quarterback PWR 1 QuasarDocument1 pageWindChart-Golf W-Quarterback PWR 1 QuasarmaskedpianistPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe Dimensions Chart Rev Jan 2012Document1 pagePipe Dimensions Chart Rev Jan 2012eljammalPas encore d'évaluation
- Tugas Grafik Time SeriesDocument4 pagesTugas Grafik Time SeriesArdi RamdaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Yamaha 99-05 R6Document1 pageYamaha 99-05 R6ZachLovingPas encore d'évaluation
- Water - Hammer - Calculation - of Gravitational - AdductionDocument36 pagesWater - Hammer - Calculation - of Gravitational - AdductionAnonymous cuOIjrLIPas encore d'évaluation
- Interest TablesDocument10 pagesInterest Tablesander leungPas encore d'évaluation
- Wall Thickness11Document1 pageWall Thickness11Mohammad ghanaatpishePas encore d'évaluation
- PVC WT Per Meter 2Document2 pagesPVC WT Per Meter 2webhareggebru06Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe Schedule Table - PT. PUSTEKDocument1 pagePipe Schedule Table - PT. PUSTEKOpen Knowledge and Education Book ProgramsPas encore d'évaluation
- Hdpe Pe80 Din 8074 / Iso 4427Document11 pagesHdpe Pe80 Din 8074 / Iso 4427juan_saavedra_10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Intraday Taxes NewDocument6 pagesIntraday Taxes NewRahul Kumar SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- Balance HídricoDocument8 pagesBalance HídricodiegoPas encore d'évaluation
- For FinalDocument6 pagesFor FinalFlora PatrickPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.modelo LutzDocument379 pages2.modelo LutzR Christian Rodriguez BautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Putting SpeedsDocument452 pagesPutting SpeedsNaqi AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Formate Brine TableDocument12 pagesFormate Brine Tables v poyil100% (1)
- Viscoy Company ProfileDocument10 pagesViscoy Company ProfilejsprtanPas encore d'évaluation
- Baa lkv2008 en v3 01 201403Document60 pagesBaa lkv2008 en v3 01 201403NguyễnNgọcMinhPas encore d'évaluation
- Plumbing Material (PNEUMATIC PIPES PN 10 & FITTINGS PN 25) SR No Material Description Dimension Make Remark Qty Unit Rate/Unit TotalDocument1 pagePlumbing Material (PNEUMATIC PIPES PN 10 & FITTINGS PN 25) SR No Material Description Dimension Make Remark Qty Unit Rate/Unit Totalprajakt_piePas encore d'évaluation
- SMF&W 851-01-07 Manual Arc Welding 220319Document9 pagesSMF&W 851-01-07 Manual Arc Welding 220319Shahid RazaPas encore d'évaluation
- OMM-00044 HS100 Maintenance Guide - ADDocument62 pagesOMM-00044 HS100 Maintenance Guide - ADBruce CampanelliPas encore d'évaluation
- Industrial Training Institute, Lakhani Graded Exercise: W S A F E T Y C O N S C IDocument6 pagesIndustrial Training Institute, Lakhani Graded Exercise: W S A F E T Y C O N S C IganpatPas encore d'évaluation
- Keysight Technologies - RF and Microwave Test AccessoriesDocument219 pagesKeysight Technologies - RF and Microwave Test AccessoriestgregoricPas encore d'évaluation
- Zeb-Companion 110 UmDocument5 pagesZeb-Companion 110 UmJad JdPas encore d'évaluation
- Section Ix Khb5G Super Ii: Parts ListDocument12 pagesSection Ix Khb5G Super Ii: Parts ListALEX DIEGOPas encore d'évaluation
- Irc Blipper Non Ride by Wire Quickshifter InstructionsDocument5 pagesIrc Blipper Non Ride by Wire Quickshifter InstructionstweencupPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 Unit 5Document42 pagesModule 2 Unit 5DnaneshwarPas encore d'évaluation
- JLG-3369 LE Parts 3120769 5-31-13 ANSI EnglishDocument128 pagesJLG-3369 LE Parts 3120769 5-31-13 ANSI EnglishFranzPas encore d'évaluation
- Jsa FormDocument7 pagesJsa FormDheeraj Chowdary DhanekulaPas encore d'évaluation
- ACS 1000 Medium Voltage Drives: 315 - 5000 KW 400 - 6200 HPDocument64 pagesACS 1000 Medium Voltage Drives: 315 - 5000 KW 400 - 6200 HPmoahmed100% (1)
- Method Statement For Testing & Commissioning of AHUDocument4 pagesMethod Statement For Testing & Commissioning of AHUsamsul maarif100% (1)
- Weapons The Walking Zombie 2 Wiki FandomDocument1 pageWeapons The Walking Zombie 2 Wiki FandomAden Maggioli-RohrPas encore d'évaluation
- Using Petrol-Driven Chainsaws: FISA Safety Guide 301Document2 pagesUsing Petrol-Driven Chainsaws: FISA Safety Guide 301Garden GrillPas encore d'évaluation
- X RAY AlignmentDocument28 pagesX RAY AlignmentAndreas DurerPas encore d'évaluation
- Spare Parts Catalog: 16 S 1620 TD Material Number: 1341.001.009Document75 pagesSpare Parts Catalog: 16 S 1620 TD Material Number: 1341.001.009Vladislav OdintsovPas encore d'évaluation
- Ajex Manual1 PDFDocument4 pagesAjex Manual1 PDFVikram JitPas encore d'évaluation
- Unwinding StationDocument34 pagesUnwinding StationDeniMestiWidiantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cooling of A Synchronous GeneratorDocument3 pagesCooling of A Synchronous GeneratorBonaventure NzeyimanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet Transformador de PotenciaDocument2 pagesDatasheet Transformador de Potenciajoseandrion2008Pas encore d'évaluation
- Telemecanique XMLA010A2S11 DatasheetDocument5 pagesTelemecanique XMLA010A2S11 DatasheetIsaac AwudiPas encore d'évaluation
- MeasurementDocument3 pagesMeasurementstormyhsPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Gun Series: Maximum Strength at Your FingertipsDocument2 pagesManual Gun Series: Maximum Strength at Your FingertipsZamroni KarimPas encore d'évaluation
- J4675 Component List Rev FDocument2 pagesJ4675 Component List Rev FDaniel ReyPas encore d'évaluation
- JDocument132 pagesJJRPas encore d'évaluation