Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Heart Failure Agents 4 - 6 Questions
Transféré par
beth_rodriguez_70 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
20 vues2 pagesInotropicdrugs that influence the force or energy of muscular contractions, particularly contraction of the heart muscle. Ace Inhibitors inhibit sodium and water resorption by inhibiting aldosterone secretion. Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors increase intracellular cAMP +-produce a positive inotropic response and vasodilation.
Description originale:
Titre original
pharm 23
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentInotropicdrugs that influence the force or energy of muscular contractions, particularly contraction of the heart muscle. Ace Inhibitors inhibit sodium and water resorption by inhibiting aldosterone secretion. Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors increase intracellular cAMP +-produce a positive inotropic response and vasodilation.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
20 vues2 pagesHeart Failure Agents 4 - 6 Questions
Transféré par
beth_rodriguez_7Inotropicdrugs that influence the force or energy of muscular contractions, particularly contraction of the heart muscle. Ace Inhibitors inhibit sodium and water resorption by inhibiting aldosterone secretion. Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors increase intracellular cAMP +-produce a positive inotropic response and vasodilation.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOCX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
23.
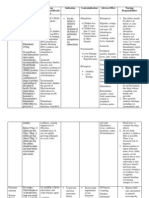
Heart Failure Agents 4 – 6 Questions
a. Pharmacology Overview
i. Inotropic- drugs that influence the force or energy of muscular
contractions, particularly contraction of the heart muscle
ii. Chronotropic- drugs that influence the rate of the heart beat
iii. Dromotropic- drugs that influence the conduction of electrical impulses
within tissues
b. Ace Inhibitors
i. Mechanism of Action
Prevent sodium and water resorption by inhibiting aldosterone secretion
c. Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors
i. Mechanism of Action
Inhibit phosphodiesterase; which increases intracellular cAMP –produce
a positive inotropic response and vasodilation
d. Cardiac Glycosides
i. Indications
Systolic heart failure, to control ventricular response to afib or flutter –
also can be used in adjunct to drugs of other classes, beta blockers,
diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and ARBs.
ii. Adverse Effects
Associated with cardiovascular, CNS, ocular, and GI effects -- Low
therapeutic index, dysrhythmias, headaches, fatigue, malaise, confusion,
convulsions, colored vision, halo vision, flickering lights, anorexia,
nausea, vomiting, diarrhea,
iii. Toxicity and Management of Overdose
Digibind therapy; conditions that predispose toxicity- hypokalemia, use
of cardiac pacemaker, hepatic dysfunction, hypercalcemia, dysrhythmias,
hypothyroid, respiratory, or renal disease, advanced age
iv. Normal Electrolyte Lab Values
Calcium- 8.8-10.3 mg/dl
Chloride- 95-107meq/l
Magnesium- 1.6-2.4meq/l
Phosphate- 2.5-4.5 mg/dl
Potassium- 3.5-5.3 meq/l
Sodium- 135-147meq/l
v. Drug Interactions
Antidysrhythmics, calcium, amohotericin B, chlorthalidone, loop
diuretics, laxatives, adrenal steroids, thiazide diuretics, antacids,
antidiarrheals, cholestyramine, colestipol, sucralfate, anticholinergics,
barbituates, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, quinidine,
verapamil, amiodarone-* most serious
vi. Digitalis Toxicity
Conditions predisposing DT: use of pace maker, hypokalemia,
hypercalcemia, atrioventricular block, dysrhythmias, hyperthyroidism,
respiratory/renal disease, advanced age, ventricular fibrillation.
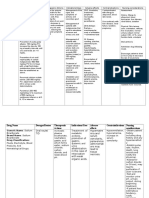
e. Nursing Process
i. Implementation: First Line Drugs
Give cautiously, intensive care setting, close monitoring, monitor for
severe effects, concern of syncope, peripheral neuritis, monitor VS
ii. Patient Teaching Tips
Radial pulse before administration, daily weight, report adverse effects
or abnormal VS immediately, keep journal, wear medical alert bracelet,
take at same time every morning, don’t stop abruptly, consume foods
high in potassium if diuretic ordered as well, avoid using antacids or
eating milk products or bran 2 hours before or 2 hours after taking med
f. Digoxin (lanoxin)
i. Indication for Use
Heart failure, a fib, flutter
ii. Digitalis Toxicity
From long duration of action and long half life
iii. Therapeutic Levels
0.5-2 ng/ml
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesD'EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesCardiovascular SystemRegineCuasSulibPas encore d'évaluation
- CVS PART 1 DiureticsDocument31 pagesCVS PART 1 Diureticshishamasmaa5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes Ready Reference for Nurse Practitioners: Clear, Concise Guidelines for Effective Patient CareD'EverandDiabetes Ready Reference for Nurse Practitioners: Clear, Concise Guidelines for Effective Patient CarePas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Product Characteristics 1 Name of The Medicinal ProductDocument9 pagesSummary of Product Characteristics 1 Name of The Medicinal Productddandan_2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology Test 3 ReviewDocument6 pagesPharmacology Test 3 ReviewNatalia BortellPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardio-Vascular DrugsDocument6 pagesCardio-Vascular DrugsElizabella Henrietta TanaquilPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyudntnid2knwme100% (4)
- Labs Drug Study 1Document17 pagesLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study On DigoxinDocument8 pagesDrug Study On DigoxinDonald BidenPas encore d'évaluation
- MM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM MDocument9 pagesMM MM MM MM MMM MMMMM M MM M MMMM MMMMM MMM MM MMM MM!M M!"M#MM MM M $M M %MMM MM "M "MM M MMM M배기숭Pas encore d'évaluation
- Treatment For Adverse Effects of PsychotropicsDocument73 pagesTreatment For Adverse Effects of PsychotropicsferdzeptrpPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Classification Drug Name Adverse EffectsDocument3 pagesDrug Classification Drug Name Adverse EffectsninapotPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug 25Document17 pagesDrug 25carol_gigliotti24100% (1)
- Drug Study Case PresentationDocument5 pagesDrug Study Case PresentationRobert MedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology Chapter 45Document4 pagesPharmacology Chapter 45angela garrotePas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyEzshkha OnguePas encore d'évaluation
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuPas encore d'évaluation
- Pedia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPedia Drug StudyPeetah PanPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study 1230913067634079 1Document4 pagesDrug Study 1230913067634079 1Jowel Cruz De LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Med Surg Medication Study GuideDocument8 pagesMed Surg Medication Study Guidetina100% (1)
- Brand Name Generic Name Classification: PerindoprilDocument3 pagesBrand Name Generic Name Classification: PerindoprilPoinsithia OrlandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Allopurinol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument9 pagesAllopurinol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComifyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ify Drug StudiesDocument15 pagesIfy Drug StudiesifyPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study (Medication Nurse)Document42 pagesDrug Study (Medication Nurse)Ellen Grace CalayPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyTeanu Jose Gabrillo TamayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit VI Drugs Used On Urinary SystemDocument46 pagesUnit VI Drugs Used On Urinary SystemHarshika KDGPas encore d'évaluation
- CONCERTA Extended-Release Tablets PILDocument37 pagesCONCERTA Extended-Release Tablets PILRezaul RazibPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.CVS DrugsDocument98 pages1.CVS DrugsHarshika KDGPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyKenneth ManalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyAnn Therese C. GutierrezPas encore d'évaluation
- High Risk DrugsDocument12 pagesHigh Risk Drugsarshiya.manasekiPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs Increased Risk of DiabetesDocument5 pagesDrugs Increased Risk of Diabetesk9cfxtdfqmPas encore d'évaluation
- Spironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationDocument5 pagesSpironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationShermalyn SalahuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Diazepam, Lanoxin, Hemostan, NaprexDocument6 pagesDiazepam, Lanoxin, Hemostan, NaprexRene John Francisco100% (1)
- Pharmacology Review For NursesDocument11 pagesPharmacology Review For Nursesisabel_avancena100% (4)
- Drug Study 2Document8 pagesDrug Study 2rey_tengPas encore d'évaluation
- PropanolDocument8 pagesPropanolStacey CamillePas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study ICUDocument15 pagesDrug Study ICUJulie Nambatac100% (1)
- Drug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument15 pagesDrug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesitsmechachaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology HESI ReviewDocument13 pagesPharmacology HESI Reviewhkw0006164% (11)
- Hand Out Lect P HarmDocument4 pagesHand Out Lect P HarmReynaKatPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypertension (HTN or HT), Also Known As High Blood Pressure (HBP), Is ADocument4 pagesHypertension (HTN or HT), Also Known As High Blood Pressure (HBP), Is AReynaKatPas encore d'évaluation
- CONNDocument1 pageCONNPhilip Gene II MalacasPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology Nursing ReviewDocument19 pagesPharmacology Nursing Reviewp_dawg50% (2)
- Indapamid SR Pliva 15 MG Tablete S Produljenim Oslobadjanjem SPCDocument10 pagesIndapamid SR Pliva 15 MG Tablete S Produljenim Oslobadjanjem SPCDuje ErcegovicPas encore d'évaluation
- MedSurg Medication Study Guide Test 1Document12 pagesMedSurg Medication Study Guide Test 1Sarah PlunkettPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnesium Sulfate Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMagnesium Sulfate Drug StudyMaan Molinyawe81% (16)
- Chlorpromazine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesChlorpromazine Drug StudyEmJay Balansag100% (5)
- Generic Name Brand NameDocument7 pagesGeneric Name Brand NameKathrina CravePas encore d'évaluation
- DrugsDocument20 pagesDrugsLee Won100% (1)
- Ix. Pharmacologic Management Brand Name Classification Indication Mechanism of Action Dosage and Frequency Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationDocument21 pagesIx. Pharmacologic Management Brand Name Classification Indication Mechanism of Action Dosage and Frequency Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationDizerine Mirafuentes RolidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEDocument12 pagesDiuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEJR BetonioPas encore d'évaluation
- Philippine Nursing Organizations Org Name DescriptionDocument8 pagesPhilippine Nursing Organizations Org Name DescriptionShehada Marcos BondadPas encore d'évaluation
- A Simplified List of All Protocols - HubermanLabDocument2 pagesA Simplified List of All Protocols - HubermanLabMorten NessPas encore d'évaluation
- CSR ReportDocument38 pagesCSR ReportlitonashadPas encore d'évaluation
- Robots in Shipbuilding Industry (1160) PDFDocument9 pagesRobots in Shipbuilding Industry (1160) PDFWahyu WahyurachmatdhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- The Bethesda System For Reporting Cervical Cytolog PDFDocument359 pagesThe Bethesda System For Reporting Cervical Cytolog PDFsurekhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Health and Safety in The Kitchen: Lesson 8Document18 pagesHealth and Safety in The Kitchen: Lesson 8Mary Grace Lamarroza RosagaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Regulatory Affairs Coordinator - StrykerDocument3 pagesRegulatory Affairs Coordinator - StrykerSrinivas ByreddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Excoriation Disorder: Body-Focused Repetitive Behavior (BFRB) Kirti PawarDocument10 pagesExcoriation Disorder: Body-Focused Repetitive Behavior (BFRB) Kirti PawarkirtiPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument11 pagesNCPJohnhinePas encore d'évaluation
- Forgiveness Leads To Anger ManagementDocument15 pagesForgiveness Leads To Anger Managementjai_tutejaPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic: Magnesium Sulphate (Mgso4: Group 5Document11 pagesTopic: Magnesium Sulphate (Mgso4: Group 5Wan Ahmad FaizFaizalPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Human BodyDocument57 pagesIntroduction To Human Bodyjunitria13Pas encore d'évaluation
- Human Population ControlDocument10 pagesHuman Population ControlDiego Villa CaballeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Juvenile Justice Act 2015 8460163.ppsxDocument20 pagesJuvenile Justice Act 2015 8460163.ppsxKiran KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Tug Master - Performance AssessmentDocument6 pagesTug Master - Performance AssessmentSafix YazidPas encore d'évaluation
- Sustaina-Loo Sanitation Solution EWB ChallengeDocument83 pagesSustaina-Loo Sanitation Solution EWB ChallengeRichard WolfePas encore d'évaluation
- Proposed Research BudgetDocument3 pagesProposed Research BudgetAndreMostertPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Cbjip Book of Barangay Kauswagan 1Document38 pagesSample Cbjip Book of Barangay Kauswagan 1Johana Pinagayao AngkadPas encore d'évaluation
- South Dakota Hunting HandbookDocument64 pagesSouth Dakota Hunting HandbookTheo BlevinsPas encore d'évaluation
- Effectiveness of An Anterior Mini-Screw in Achieving Incisor IntrusionDocument10 pagesEffectiveness of An Anterior Mini-Screw in Achieving Incisor IntrusionAbdel Hadi KanjPas encore d'évaluation
- Social and Behavior Change: CommunicationDocument36 pagesSocial and Behavior Change: CommunicationKenan SakallıPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Potings List 2021-22Document1 pageClinical Potings List 2021-22Dani ursPas encore d'évaluation
- 3-2. Assessing Production DocumentsDocument48 pages3-2. Assessing Production DocumentsSandeep sharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Worst Mistake in The History of The Human Race - Summary by Patricia DeesDocument1 pageThe Worst Mistake in The History of The Human Race - Summary by Patricia DeesPatricia Dees100% (1)
- NCERT Class 9 Political Science Chapter 6 YouTube Lecture HandoutsDocument5 pagesNCERT Class 9 Political Science Chapter 6 YouTube Lecture Handoutsarjun anjana anjanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Husky Air Compressor Operator ManualDocument60 pagesHusky Air Compressor Operator ManualJ DavisPas encore d'évaluation
- Past ContinuousDocument2 pagesPast ContinuousJoaquin GabilondoPas encore d'évaluation
- TOPICCal ApplicationsDocument3 pagesTOPICCal ApplicationsSpeech & Language Therapy in Practice100% (3)
- MSC 1st Year RequirementsDocument6 pagesMSC 1st Year RequirementsSilja Manoj100% (1)
- Module I - Introduction To Occupational Health and SafetyDocument13 pagesModule I - Introduction To Occupational Health and Safetyangeh morilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedD'EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (81)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossD'EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (6)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionD'EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (404)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDD'EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityD'EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (29)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeD'EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeÉvaluation : 2 sur 5 étoiles2/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsD'EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsPas encore d'évaluation
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)D'EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Évaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (1)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (42)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityD'EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsD'EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsD'EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaD'EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.D'EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (110)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessD'EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (328)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearD'EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (23)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningD'EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsD'EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (170)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Empath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainD'EverandEmpath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (95)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisD'EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (8)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsD'EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (6)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlD'EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (59)