Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Pathomechanics of Structural Foot Deformities Notes
Transféré par
Morgan Lee0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
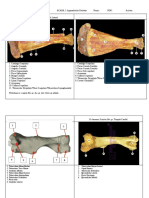
213 vues1 page1. In a normal foot, the plantar condyles of the calcaneus and metatarsal heads lie in the same plane.
2. Subtalar neutral is defined as a zero degree angle between lines bisecting the lower leg and calcaneus, though most have a slight varus angle.
3. The second through fourth metatarsal heads normally lie in the same plane, while the first and fifth are more likely to have deformities and their alignment to the others is clinically important.
Description originale:
Titre original
Pathomechanics of Structural Foot Deformities notes
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
TXT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce document1. In a normal foot, the plantar condyles of the calcaneus and metatarsal heads lie in the same plane.
2. Subtalar neutral is defined as a zero degree angle between lines bisecting the lower leg and calcaneus, though most have a slight varus angle.
3. The second through fourth metatarsal heads normally lie in the same plane, while the first and fifth are more likely to have deformities and their alignment to the others is clinically important.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme TXT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
213 vues1 pagePathomechanics of Structural Foot Deformities Notes
Transféré par
Morgan Lee1. In a normal foot, the plantar condyles of the calcaneus and metatarsal heads lie in the same plane.
2. Subtalar neutral is defined as a zero degree angle between lines bisecting the lower leg and calcaneus, though most have a slight varus angle.
3. The second through fourth metatarsal heads normally lie in the same plane, while the first and fifth are more likely to have deformities and their alignment to the others is clinically important.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme TXT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
Normal Foot:
1. Both plantar condyles of the calcaneus are on the surface
2. All of the metatarsal heads lie in one plane
3. The plane of the met heads is in the same plane as the plantar condyl
es of the calcaneus
Subtalar Neutral
Defined as the measurement of the angle between a line that bisects the
distal 1/3 of the lower leg and a line that bisects the calcaneus
The angle should be zero degrees in the normal foot, but actually is 2-3
degrees of varus (inverted) in most subjects
Metatarsal Heads
The second, third, and fourth met heads are usually in the same plane un
less there has been some trauma or longstanding structural deviation
Deformities are usually found in the first and fifth met heads
Assessing alignment of the first met head to the second and the fifth me
t head to the fourth is clinically important
Forefoot-to-Rearfoot Relationship
Frontal Plane: the calcaneal bisection is commonly used to compare the h
eel with the forefoot. The calcaneal bisection is almost perpendicular to the p
lantar condyles and should be perpendicular to the plane of the metatarsal heads
. If the plane of the metatarsal heads is perpendicular to
the bisection of the calcaneus, the forefoot-to-rear foot relationship i
s normal or "neutral".
is normal or "neutral".
Sagittal Plane: An imaginary plane representing the ground surface is ap
plied to the plantar surface of the calcaneus. The metatarsal heads should rest
upon this plane.
Transverse Plane: The forefoot should have the same longitudinal directi
on as the rear foot. This relationship is observed in the STJ neutral position.
Rearfoot Varus
- The most common structural deformity
- Caused by a failure of the calcaneus to complete the ontogenic derotat
ion during childhood
- At heel strike, the STJ is slightly supinated and the lower limb is ad
ducted, resulting in an inverted calcaneus and ground contact occuring on the la
teral aspect of the foot
- The STJ goes through an abnormal amount of pronation in compensating f
or the rear foot varus
Forefoot Varus
- Is a osseous deformity of the forefoot
- The most probable cause of this deformity is insufficient developmenta
l rotation of the head of the talus
Forefoot Valgus
- Two types of forefoot valgus: 1) All of the met heads may be everted,
or 2) the first met head may be plantarflexed while the second-fifth met heads l
ie in the appropriate plane
- A possible cause in excessive ontogenic rotation of the talar head
Forefoot Equinus
- Sagittal plane deformity
- The forefoot structure is plantarflexed when compared to the rearfoot
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Influence of Bones and Muscles on FormD'EverandThe Influence of Bones and Muscles on FormÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Hindfoot Valgus: AP Talocalcaneal Angle (Kite's Angle)Document4 pagesHindfoot Valgus: AP Talocalcaneal Angle (Kite's Angle)JoaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentor-Dr. Momin Mohammad Farhan Moderator-Dr. M. A. Q. AnsariDocument48 pagesPresentor-Dr. Momin Mohammad Farhan Moderator-Dr. M. A. Q. Ansarimohammad farhanPas encore d'évaluation
- the Hoof Balancer: A Unique Tool for Balancing Equine HoovesD'Everandthe Hoof Balancer: A Unique Tool for Balancing Equine HoovesPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 8&9Document35 pagesLec 8&9حسام عادلPas encore d'évaluation
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)D'EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bones of The Upper LimbDocument46 pagesBones of The Upper LimbSoze KeyserPas encore d'évaluation
- Congenital Talipes Equinovarus (Club Foot)Document4 pagesCongenital Talipes Equinovarus (Club Foot)Malueth AnguiPas encore d'évaluation
- Improving Ankle and Knee Joint Stability: Proprioceptive Balancefit Discs DrillsD'EverandImproving Ankle and Knee Joint Stability: Proprioceptive Balancefit Discs DrillsPas encore d'évaluation
- Ankle JointDocument84 pagesAnkle JointPoojitha reddy MunnangiPas encore d'évaluation
- Foot Deformities Infant: AssessmentDocument5 pagesFoot Deformities Infant: AssessmentAnup PednekarPas encore d'évaluation
- Bones of The FootDocument3 pagesBones of The FootHaris ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- CallusDocument1 pageCallusdjoiner45Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Examination of The Foot and AnkleDocument42 pagesPhysical Examination of The Foot and AnkleRhaffy Bearneza RapaconPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Look A Posture Doug KellerDocument9 pagesHow To Look A Posture Doug KelleryogatonPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiology Skeletal Trauma: DR B.B.Gosai July 2013Document48 pagesRadiology Skeletal Trauma: DR B.B.Gosai July 2013riddhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 19 DEFORMITIES OF FOOT UpdatedDocument9 pagesLec 19 DEFORMITIES OF FOOT UpdatedMaheen IrfanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lumbar Spine SectionDocument50 pagesLumbar Spine Sectionsevensaes454Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arches of FootDocument68 pagesArches of FootPoojitha reddy MunnangiPas encore d'évaluation
- (10 F) FOOT - Bones, Ligaments, TendosDocument6 pages(10 F) FOOT - Bones, Ligaments, TendosJeffrey RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio-Mechanics of Ankle-Foot JointDocument70 pagesBio-Mechanics of Ankle-Foot JointIipo ChennaiPas encore d'évaluation
- 3dimensional Modeling of An Ankle Foot Orthosis For Clubfoot DeformityDocument10 pages3dimensional Modeling of An Ankle Foot Orthosis For Clubfoot DeformityVijayaragavan ElumalaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Adosado PDFDocument6 pagesAdosado PDFREBECA ANTONIA JARAPas encore d'évaluation
- Hip Joint 1Document22 pagesHip Joint 1foziiiii100% (2)
- OCPM NotesDocument88 pagesOCPM NotesArthur BlankenshipPas encore d'évaluation
- ARCHDocument63 pagesARCHDebashish Chanda100% (1)
- Ankle and FootDocument31 pagesAnkle and FootmetoPas encore d'évaluation
- BooksDocument388 pagesBooksMayank GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Body Conformation of HorseDocument32 pages01 Body Conformation of HorseDrSagar Mahesh Sonwane100% (3)
- 4 - Ankle and FootDocument65 pages4 - Ankle and Footxj74fr4ddxPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Skeleton of FootDocument14 pages5 Skeleton of FootDilpreetPas encore d'évaluation
- Imp Questions For Anatomy (MBBS 1st Year)Document6 pagesImp Questions For Anatomy (MBBS 1st Year)MeowPas encore d'évaluation
- Pearls and Tricks in Adolescent Flat FootDocument14 pagesPearls and Tricks in Adolescent Flat FootVijay KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lower LimbDocument53 pagesLower LimbRupesh M DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ankle&fEET Written Procedure-MagsombolDocument2 pagesAnkle&fEET Written Procedure-Magsombolhazell_aseronPas encore d'évaluation
- First Page PDFDocument1 pageFirst Page PDFAkhil ABPas encore d'évaluation
- MUSCULOSKELETALDocument27 pagesMUSCULOSKELETALCassandra Mae PerochoPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy Lac.1Document43 pagesAnatomy Lac.1minayayoongi2004Pas encore d'évaluation
- Foot Orthotics - FDLDocument19 pagesFoot Orthotics - FDLDiamoniq AyuningtiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biomechanics BHIP JOINTDocument68 pagesBiomechanics BHIP JOINTLinmayee SamalPas encore d'évaluation
- Lower Limb Anatomy Class NotesDocument87 pagesLower Limb Anatomy Class NotesSalina Amir88% (16)
- BFO-Biomechanics of The FootDocument5 pagesBFO-Biomechanics of The FootnovitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologySarah CabalquintoPas encore d'évaluation
- CTEVDocument57 pagesCTEVAmal AlahmariPas encore d'évaluation
- Bone CongenitalDocument33 pagesBone CongenitalRadio ResidentPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hip ComplexDocument8 pagesThe Hip ComplexVIRESH VPas encore d'évaluation
- Deformities: Learning ObjectiveDocument4 pagesDeformities: Learning ObjectiveEimad AtifPas encore d'évaluation
- L12Document45 pagesL12Ahmed El goharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding The Foot's Functional Anatomy in Physiological and Pathological Conditions: The Calcaneopedal Unit ConceptDocument13 pagesUnderstanding The Foot's Functional Anatomy in Physiological and Pathological Conditions: The Calcaneopedal Unit ConceptAren BizdikianPas encore d'évaluation
- The Vertebral Column - Joints - Vertebrae - Vertebral StructureDocument5 pagesThe Vertebral Column - Joints - Vertebrae - Vertebral StructureVucci VistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomi Ankle 1Document114 pagesAnatomi Ankle 1Zera DirgantaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Cavus Foot, From Neonates To AdolescentsDocument16 pagesCavus Foot, From Neonates To AdolescentshardbonePas encore d'évaluation
- Rat Dissection Protocol - Intro BiologyDocument10 pagesRat Dissection Protocol - Intro BiologyValar Mathei PadmanadhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Labor and DeliveryDocument14 pagesLabor and Deliverydexter100% (15)
- Revmar2013 Wr2 Ys1e Tulangfraktur VFDocument41 pagesRevmar2013 Wr2 Ys1e Tulangfraktur VFselubung linePas encore d'évaluation
- Snell Lower LimbDocument44 pagesSnell Lower LimbBen100% (3)
- Thoracic (Dorsal) SpineDocument77 pagesThoracic (Dorsal) Spineeashoor100% (2)
- The Superficial Fibular Nerve - Course - Motor - TeachMeAnatomyDocument2 pagesThe Superficial Fibular Nerve - Course - Motor - TeachMeAnatomyLaiba AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Surgical TechniqueDocument6 pagesSurgical TechniqueDavid PalomequePas encore d'évaluation
- Iliopsoas The Hidden Muscle - Anatomy, Diagnosis, and Treatment (2020)Document9 pagesIliopsoas The Hidden Muscle - Anatomy, Diagnosis, and Treatment (2020)yuliPas encore d'évaluation
- Hind Limb Myology of The Ringtail (Bassariscus Astutus) and The Myology of Hind Foot ReversalDocument23 pagesHind Limb Myology of The Ringtail (Bassariscus Astutus) and The Myology of Hind Foot ReversalAdolfo SalazarPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomi OrigoDocument32 pagesAnatomi OrigoUga Cahyani SilalahiPas encore d'évaluation
- Most Common Surfing Injuries and Accidents - SurflineDocument2 pagesMost Common Surfing Injuries and Accidents - Surflineapi-549909228Pas encore d'évaluation
- Helping The Fallen Arches May 2010Document5 pagesHelping The Fallen Arches May 2010ERUTHKPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ Biomechanics of Hip JointDocument16 pagesMCQ Biomechanics of Hip Jointdrng48100% (9)
- Glute Guide EbookDocument50 pagesGlute Guide EbookJustin C. King100% (3)
- Cauda EquinaDocument9 pagesCauda EquinaMuhammad Iqbal Farhan RodhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Prakash Knee Book PDFDocument506 pagesPrakash Knee Book PDFJafild Fild river100% (4)
- Zumba Fitness Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesZumba Fitness Lesson PlanDivinity Of The Sun67% (3)
- AFO Orthometry Form OptDocument1 pageAFO Orthometry Form OptaryogaPas encore d'évaluation
- Buff Dudes Mobility Band Workout PlanDocument80 pagesBuff Dudes Mobility Band Workout PlanLeandro Aisa75% (8)
- Clubfoot PresentationDocument74 pagesClubfoot Presentationnovia khairulbaria100% (2)
- Atribut Definisi Indikator Bobot Score NilaiDocument3 pagesAtribut Definisi Indikator Bobot Score NilaiharienPas encore d'évaluation
- LKP Osteologi 2 Appendicular SkeletonDocument8 pagesLKP Osteologi 2 Appendicular Skeletoneunike gloriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Limb AxisDocument18 pagesLimb AxisBadea Mihai LaurentiuPas encore d'évaluation
- The Lower Limb MusclesDocument95 pagesThe Lower Limb MusclesNur Ain RaihanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hip Biomechanics SRSDocument119 pagesHip Biomechanics SRSSreeraj S RPas encore d'évaluation
- UME Radiology Musculoskeletal Imaging (Review)Document52 pagesUME Radiology Musculoskeletal Imaging (Review)Nguyễn Hoàng SơnPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Exercitii Durere de SpateDocument3 pages7 Exercitii Durere de SpateLUMINITA-CLAUDIA GIUCAPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification and Nomenclature: Progressive Collapsing Foot DeformityDocument6 pagesClassification and Nomenclature: Progressive Collapsing Foot DeformityHoracio CavigliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscle Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Chart Muscles of Upper Extremity Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action InnervationDocument11 pagesMuscle Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Chart Muscles of Upper Extremity Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action InnervationNurul Afiqah Fattin AmatPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Common Compensation Patterns and Movement Dysfunctions - PreHab ExercisesDocument17 pagesList of Common Compensation Patterns and Movement Dysfunctions - PreHab ExercisesEmiliano BezekPas encore d'évaluation
- Side Kick Height TrainingDocument12 pagesSide Kick Height TrainingTiago MinelliPas encore d'évaluation
- Usg 16054Document9 pagesUsg 16054Nikita NanwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- OsteoMed ExtremiLOCK Foot Surgical Guide PDFDocument30 pagesOsteoMed ExtremiLOCK Foot Surgical Guide PDFViston Cahya SandhikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Knee Joint RadiographyDocument50 pagesKnee Joint RadiographyRitu pantaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pes CavusDocument4 pagesPes CavusPurohit_RPas encore d'évaluation
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)D'EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsD'EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.D'EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeD'EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (2)
- Math Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeD'EverandMath Workshop, Grade K: A Framework for Guided Math and Independent PracticeÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersD'EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (6)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormD'EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (5)
- Images of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryD'EverandImages of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingD'EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (21)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldD'EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (80)
- ParaPro Assessment Preparation 2023-2024: Study Guide with 300 Practice Questions and Answers for the ETS Praxis Test (Paraprofessional Exam Prep)D'EverandParaPro Assessment Preparation 2023-2024: Study Guide with 300 Practice Questions and Answers for the ETS Praxis Test (Paraprofessional Exam Prep)Pas encore d'évaluation