Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Structural Foam Process
Transféré par
muhmmadafzal730 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
93 vues5 pagesStructural foam molded parts have a low density cellular core surrounded by a dense skin. This gives the part strength from the skin while keeping weight low with the core. The process involves injecting gas and plastic into a mold through multiple nozzles to form the layered structure. Benefits include high strength to weight, stiffness, lower costs from using less material, and the ability to combine multiple parts into one.
Description originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentStructural foam molded parts have a low density cellular core surrounded by a dense skin. This gives the part strength from the skin while keeping weight low with the core. The process involves injecting gas and plastic into a mold through multiple nozzles to form the layered structure. Benefits include high strength to weight, stiffness, lower costs from using less material, and the ability to combine multiple parts into one.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
93 vues5 pagesStructural Foam Process
Transféré par
muhmmadafzal73Structural foam molded parts have a low density cellular core surrounded by a dense skin. This gives the part strength from the skin while keeping weight low with the core. The process involves injecting gas and plastic into a mold through multiple nozzles to form the layered structure. Benefits include high strength to weight, stiffness, lower costs from using less material, and the ability to combine multiple parts into one.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 5
Structural Foam Molding (Low Pressure Injection)
Structural Foam Parts
Structural foam molded parts have low density cellular cores surrounded by near-solid integral skins.
The transition from skin to core is gradual. The solid skin gives the molded part its form and toughness,
while the core contributes to the high strength-to-weight characteristics normally associated with this type
structure.
Cross Section of Structural Foam Part
Structural foam molded parts are usually large, heavy and have thick walls. Wall thickness is typically in the
range in excess of 4 mm (.150 in) up to 12.7 mm (.500 in). Parts weighting over 68 kg (150 lbs) are being
structurally foam molded.
Advantages of Structural Foam Molded Parts
•High strength-to-weight ratio.
•3 to 4 times more rigid than a solid part of the same weight due primarily to the thicker wall cross
sections.
•Greater part stiffness and resulting load carrying capacity than conventional IM part.
•Lower part weight due to reduced density.
•Lower raw material cost due to reduced density or use of less expensive resins. Commodity
resins may be utilized in load bearing applications.
•Lower manufacturing costs due to less costly production methods.
•Ability to combine many parts and functions into a simplified single part design.
•Minimize sink marks even on parts with unequal section thicknesses.
•Low stress concentrations due to cellular structure.
•Bowing and warping are greatly reduced.
•Characteristics include chemical resistance, sound-deadening, electrical and thermal insulating
qualities.
•Parts can be painted or nailed.
Low Pressure Structural Foam Molding Process
Structural foam molding is similar to conventional
injection molding with the exception that it is a two-
stage extrusion/injection molding process, normally
uses inert gas as a foaming agent, and injects a short
shot into the mold(s) The machine has some unique
features including a multiple nozzle system, an
external hot manifold, and building block manifold
extensions. The nozzles can be mounted at any
location along a six-inch grid drilled into the stationary
platen. They can be located in ideal locations to inject
at multiple points into a single mold or multiple molds.
The flow lengths can be minimized by strategic
placement of the nozzles. The main manifold mounted
externally on the fixed platen with building block
manifold extensions act as hot runner systems and
can be repositioned accordingly.
Configurable Multi-Nozzle Manifold
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Injection Molding Design GuidelinesDocument13 pagesInjection Molding Design GuidelinesSreedhar PugalendhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of Mold DesignDocument15 pagesBasics of Mold DesignPedro Agirre IturbePas encore d'évaluation
- Injection Molding DesignDocument17 pagesInjection Molding DesignprasathbalaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Fundamentals of Segmented Woodturning: Projects, Techniques & Innovations for Today’s WoodturnerD'EverandThe Fundamentals of Segmented Woodturning: Projects, Techniques & Innovations for Today’s WoodturnerÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- 02 Multilayercompositefilms 110322072335 Phpapp02Document48 pages02 Multilayercompositefilms 110322072335 Phpapp02naveenjeswaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Fiberglassing - Moldless CompositesDocument5 pagesFiberglassing - Moldless CompositesMata Bana NajouPas encore d'évaluation
- Ineos Polypropylene Processing GuideDocument18 pagesIneos Polypropylene Processing GuideLe Toan100% (1)
- 3475331Document41 pages3475331Nguyen Trong TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ribs & Structure DesignDocument17 pagesRibs & Structure DesignHemanth KathaPas encore d'évaluation
- DG - 1411114236 - 3plastic Part Design GuidelinesDocument38 pagesDG - 1411114236 - 3plastic Part Design GuidelinesK S RANJITH ランジットPas encore d'évaluation
- Rules of Thumb For Plastic Part Design: WallsDocument4 pagesRules of Thumb For Plastic Part Design: WallsrasinvPas encore d'évaluation
- Injection Molding Explained: The Essential Process for Plastic ManufacturingDocument23 pagesInjection Molding Explained: The Essential Process for Plastic ManufacturingAditya DhikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm-A707 CS As LTS PDFDocument5 pagesAstm-A707 CS As LTS PDFGoutam Kumar DebPas encore d'évaluation
- Maintenance Manual: Models 7200/7300/7310 Reach-Fork TrucksDocument441 pagesMaintenance Manual: Models 7200/7300/7310 Reach-Fork TrucksMigue Angel Rodríguez Castro100% (2)
- Plastics Product DesignDocument295 pagesPlastics Product DesignMousam ChoudhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- Injection Molding Design GuidelinesDocument28 pagesInjection Molding Design GuidelinesVinay Kumar KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Ship ConstructionDocument18 pagesFundamentals of Ship ConstructionWAREKARPas encore d'évaluation
- Prefabricated UNIT IIDocument52 pagesPrefabricated UNIT IIkavya sundaramPas encore d'évaluation
- Maintenance & Trouble Shooting of Voith CouplingDocument20 pagesMaintenance & Trouble Shooting of Voith Couplingsen_subhasis_58100% (1)
- Basics of Injection Molding DesignDocument20 pagesBasics of Injection Molding DesignAdeniyiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sandwich PanelsDocument25 pagesSandwich PanelsGajaraj GajapathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nonwoven Material StandardsDocument5 pagesNonwoven Material StandardsRajesh Dwivedi0% (1)
- Injection Molding - Design Guidelines - Solid Concepts IncDocument12 pagesInjection Molding - Design Guidelines - Solid Concepts InckaranPas encore d'évaluation
- HVDC Grid Feasibility StudyDocument189 pagesHVDC Grid Feasibility StudyDeoudrafPas encore d'évaluation
- Form WorkDocument35 pagesForm Workcdnaveen100% (4)
- Pultrusion Process - Composite ManufacturingDocument25 pagesPultrusion Process - Composite ManufacturingChetan100% (8)
- CompositesDocument24 pagesCompositesjrevanthmaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Composite Manufacturing ProcessesDocument20 pagesComposite Manufacturing ProcessesNiranjanBandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Doka SystemDocument47 pagesDoka SystembappanaduPas encore d'évaluation
- JFDD Assignment No - 04Document7 pagesJFDD Assignment No - 04LowEnd GamerPas encore d'évaluation
- Functions of A Matrix: 1.holds The Fibres Together. 2.protects The Fibres From EnvironmentDocument45 pagesFunctions of A Matrix: 1.holds The Fibres Together. 2.protects The Fibres From EnvironmentNaveen NaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Large Format Additive ManufacturingDocument29 pagesLarge Format Additive ManufacturingWei QuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Form Systems: Back To TopDocument17 pagesForm Systems: Back To Toparslan_iqbal89Pas encore d'évaluation
- INVESTMENT CASTING (Shiv)Document12 pagesINVESTMENT CASTING (Shiv)2K20CH39 Kshitij ShubhamPas encore d'évaluation
- EIM FinalDocument11 pagesEIM FinalMaRk KenchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM)Document28 pagesLaminated Object Manufacturing (LOM)mkatwePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1Document76 pagesUnit 1RajkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- m243 ch08Document26 pagesm243 ch08Kuscar GasperPas encore d'évaluation
- SHAPE-FORMING PROCESSESDocument91 pagesSHAPE-FORMING PROCESSESakshay kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- AdvantagesDocument1 pageAdvantagesSarath Krishnan SPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Guidelines for Plastic Parts Under 40 CharactersDocument30 pagesDesign Guidelines for Plastic Parts Under 40 Charactersmaran.suguPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermoforming and plastic molding processesDocument19 pagesThermoforming and plastic molding processesmuhammad tariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotationalmoulding 180215050228Document25 pagesRotationalmoulding 180215050228RizwanSaifiPas encore d'évaluation
- Baff Iguana Project ReportDocument22 pagesBaff Iguana Project ReportCharukaPas encore d'évaluation
- 20IN027 - Arslan AhmedDocument12 pages20IN027 - Arslan AhmedArsalan SidikiPas encore d'évaluation
- Composites Strength PropertiesDocument12 pagesComposites Strength Propertiesبلسم محمود شاكرPas encore d'évaluation
- Guia para Diseño de Moldes de SopladoDocument5 pagesGuia para Diseño de Moldes de SopladosuperalitosPas encore d'évaluation
- Formwork:: Requirements of A Good Formwork SystemDocument8 pagesFormwork:: Requirements of A Good Formwork SystemJonah ScottPas encore d'évaluation
- Manufacturing Processes AssignmentDocument23 pagesManufacturing Processes AssignmentAdarshAgrawalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tooling For Composite-BasicDocument3 pagesTooling For Composite-BasicmaheshPas encore d'évaluation
- Manufacturing process guide for polymers, ceramics and compositesDocument40 pagesManufacturing process guide for polymers, ceramics and compositesmuhammad tariqPas encore d'évaluation
- GE Structural Foam Design Processing GuideDocument78 pagesGE Structural Foam Design Processing GuideRJCIIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Textile Composites III-composite MFGDocument10 pagesTextile Composites III-composite MFGYared FikrePas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Preparation for Metallographic ExaminationDocument83 pagesSample Preparation for Metallographic ExaminationErdi Sofyandra AdikriPas encore d'évaluation
- Lectures CompositeDocument5 pagesLectures CompositeMuhammad AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Bubble Deck Slab REPORTDocument29 pagesBubble Deck Slab REPORTMangesh ShindePas encore d'évaluation
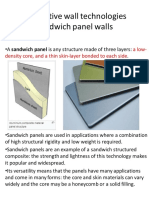
- Alternative Wall Technologies-Sandwitch PanelsDocument14 pagesAlternative Wall Technologies-Sandwitch PanelsDiya MakanurPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Tips For Injection Molding Polypropylene ResinsDocument52 pages10 Tips For Injection Molding Polypropylene ResinsaynudeenPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Assisted Injection MoldingDocument10 pagesGas Assisted Injection MoldingMarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Investment CastingDocument6 pagesInvestment CastingSparsh DeepPas encore d'évaluation
- Investment Casting Guide: Process, Advantages & Applications /TITLEDocument88 pagesInvestment Casting Guide: Process, Advantages & Applications /TITLEraymon sharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Prefabricated Structural Components DesignDocument86 pagesPrefabricated Structural Components DesignAravinda NatikeriPas encore d'évaluation
- Core Materials For Sandwich StructuresDocument4 pagesCore Materials For Sandwich StructuresVivek BhandarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit IDocument40 pagesUnit IHari KannanPas encore d'évaluation
- Testing and Maintenance of Steam TrapsDocument8 pagesTesting and Maintenance of Steam TrapsAjaypalsinh GohilPas encore d'évaluation
- High Efficiency in Cementitious WaterproofingDocument12 pagesHigh Efficiency in Cementitious WaterproofingMumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Conversion Factors GuideDocument2 pagesConversion Factors GuideAndri MPPas encore d'évaluation
- MSOFTX3000 BICC Data Configuration 20090227 B 1 0Document52 pagesMSOFTX3000 BICC Data Configuration 20090227 B 1 0Amjad VtPas encore d'évaluation
- CCH Power CalculateDocument4 pagesCCH Power Calculateangga measPas encore d'évaluation
- Silo Fluidizer: Keep Dry Bulk Materials MovingDocument2 pagesSilo Fluidizer: Keep Dry Bulk Materials MovingHùng Thanh NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- ECOSYS M6526cdn Fax SetupDocument204 pagesECOSYS M6526cdn Fax SetupAnonymous gn8qxxPas encore d'évaluation
- PuleyDocument9 pagesPuleynicolasPas encore d'évaluation
- My Oracle Support - Knowledge Browser - 1441364Document9 pagesMy Oracle Support - Knowledge Browser - 1441364Aman Khan Badal KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Thomson VTH 7090 VCR ManualDocument33 pagesThomson VTH 7090 VCR ManualTrickyDicky2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Documentation For: Bank - MasterDocument6 pagesDocumentation For: Bank - MastervijucoolPas encore d'évaluation
- Netsys NVF-200EKIT User Guide 1.0.6Document19 pagesNetsys NVF-200EKIT User Guide 1.0.6pkramellaPas encore d'évaluation
- JGEE UG Syllabus 2013-14Document65 pagesJGEE UG Syllabus 2013-14Animesh MannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Manufacturing of Urea Through Synthetic Ammonia Project ReportDocument5 pagesManufacturing of Urea Through Synthetic Ammonia Project ReportvishnuPas encore d'évaluation
- Applications: H D P TDocument2 pagesApplications: H D P TEnrique MurgiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Categoria ApiDocument61 pagesCategoria ApiHector MARTINEZ DEL ANGELPas encore d'évaluation
- Simatic Hmi Wincc V7.0 Sp3 Setting Up A Message SystemDocument123 pagesSimatic Hmi Wincc V7.0 Sp3 Setting Up A Message Systemalrighting619Pas encore d'évaluation
- Irc - 24-2010 PDFDocument128 pagesIrc - 24-2010 PDFkiranPas encore d'évaluation
- ANSI-IsA 77.13.01-1999 Fossil Fuel Power Plant Steam Turbine Bypass SystemDocument42 pagesANSI-IsA 77.13.01-1999 Fossil Fuel Power Plant Steam Turbine Bypass SystemArzu AkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Eco Web Server III Instruction Manual - OperatingDocument0 pageEco Web Server III Instruction Manual - OperatingAndrew MaverickPas encore d'évaluation
- Lightning Protection SystemDocument5 pagesLightning Protection SystemRifki FathurrahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- PLKKKDocument36 pagesPLKKKelecompinnPas encore d'évaluation
- Preparatory Year Program Computer Science (PYP 002)Document34 pagesPreparatory Year Program Computer Science (PYP 002)Hassan AlfarisPas encore d'évaluation
- JAYCO CARAVANS - 2016 Silverline and Starcraft PDFDocument12 pagesJAYCO CARAVANS - 2016 Silverline and Starcraft PDFBrisbane CamperlandPas encore d'évaluation