Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Skin Integrity
Transféré par
Jamaica AbalosDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Skin Integrity
Transféré par
Jamaica AbalosDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
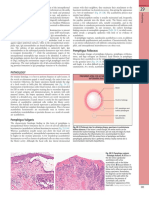
SKIN INTEGRITY
Intact skin refers to the presence of normal skin and skin layers
uninterrupted by wounds. The appearance of the skin and skin integrity are influenced by
internal factors such as genetics, age, and underlying health of the individual as well as
external factors as activity
PRIMARY SKIN LESIONS
1. Macule, Patch - Flat, unelevated change in color. Macules are 1m to 1 cm in size and
circumscribed. Examples: freackles, measles, petechiae, flat moles.
2. Papule - Circumscribed, solid elevation of skin. Papules are less than 1 cm. Examples :
warts ,acne, pimples, elevated moles
3.Plaques - are larger than 1cm. Examples: psoriasis, rubeola.
4. Nodule, Tumor - Elevated, solid, hard mass that extends deeper into the dermis that a
papule. Nodules have a circumscribed border and are 0.5 to 2cm. Examples: squamous
cell carcinoma, fibroma. Tumors are larger than 2cm and may have an irregular border.
Examples: malignant melanoma, hemangioma.
5. Pustule - Vesicles or bulla fiiled with pus. Examples: acne vulgaris, impetigo.
6. Vesicle, Bulla - A circumscribed, round or ova, thin translucent mass filled with serous
fluid or blood. Vesicles are less than 0.5cm. Examples: herpes simplex, early chicken
pox, small burn blister. Bullae are larger than 0.5 cm. Examples: large blister, second-
degree burn, herpes simplex.
7. Cyst - 1 cm or larger elevated, encapsulated, fluid-filled or semi solid mass arising
from the subcutaneous tissue or dermis. Examples: sebaceous and epidermoid cysts,
chalazion of the eyelid.
8. Wheal - reddened, localized collection of edema fluid; irregular in shape. Size varies.
Examples: hives, mosquito bites.
SECONDARY SKIN LESIONS
1. Atrophy - A translucent, dry, paper like, sometimes wriked skin surface
resulting from thinning or wasting of the skin due to loss of collagen and elastin.
Examples: Striae, aged skin
2. Erosion - Wearing away of the superficial epidermis causing a moist, shallow
depression. Examples Scratch marks, ruptured vesicles.
3. Lichenification- rough thickened, hardened area of epidermis resulting from chronic
irritation such as scratching or rubbing. E.g. Chronic dermatitis
4. Scales - shedding flakes of greasy, keratinized skin tissue. Color may be white, gray or
silver. Examples Dry skin, dandruff, psoriasis and eczema
5. Crust - dry blood, serum, or pus left on the skin surface when vesicles or pustules
burst. Can be red-brown, orange or yellow. Examples: Eczema, impetigo, herpes, or
scabs following abrasion
6. Ulcer - deep, irregularly shaped area of skin loss extending into the dermis or
subcutaneous tissue. May bleed. May leave scar. Examples: Decubitus ulcers (pressure
sores), stasis ulcers, chancres.
7. Fissure - linear crack with sharp edges, extending into the dermis. Examples Cracks at
the corners of the mouth or in the hands, athlete's foot.
8. Scar - flat irregular area of connective tissue left after a lesion or wound has healed.
New scars may be red or purple; older scars may be silvery or white. Examples healed
surgical wound or injury, healed once.
9.Keloid - Elevated, irregular ,darkened area or excess scar tissue caused by excessive
collagen formation during healing. Extends beyond the site if the original injury. Higher
incidence in people of African descent. Examples : Keloid from ear piercing or surgery.
10. Excoriation - Linear erosion. Examples: scratches, some chemical burns
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Module 3 HomeworkDocument6 pagesModule 3 HomeworkCj LincePas encore d'évaluation
- Feline DermatologyDocument55 pagesFeline DermatologySilviuPas encore d'évaluation
- SOP For Dermatologist For DOH PuplicationDocument13 pagesSOP For Dermatologist For DOH Puplicationhitham shehataPas encore d'évaluation
- Blistering DisordersDocument7 pagesBlistering DisordersSaman SarKoPas encore d'évaluation
- Dermatology Approach: Fayza RayesDocument108 pagesDermatology Approach: Fayza RayesMinghan Shi100% (2)
- Skin Disorders and Diseases: Chapter OutlineDocument22 pagesSkin Disorders and Diseases: Chapter Outlinejessafesalazar100% (1)
- Mycosis Fungoides: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesMycosis Fungoides: A Case ReportnanonanditoPas encore d'évaluation
- Vulva Biopsias HistopatologiaDocument10 pagesVulva Biopsias HistopatologiamariajoseoyanederPas encore d'évaluation
- Pemphigus Foliaceus: Fig. 29.13BDocument1 pagePemphigus Foliaceus: Fig. 29.13BCristian QuitoPas encore d'évaluation
- DR Hany Abo Alwafa - Pathology GlossaryDocument31 pagesDR Hany Abo Alwafa - Pathology GlossaryHalimatunSyadiah ARPas encore d'évaluation
- Dermatology HandbookDocument70 pagesDermatology Handbookrobchris1975100% (12)
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument2 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisRiena Austine Leonor NarcillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anthracinum. - THE GUIDING SYMPTOMS OF OUR MATERIA MEDICA by CONSTANTINE HERINGDocument17 pagesAnthracinum. - THE GUIDING SYMPTOMS OF OUR MATERIA MEDICA by CONSTANTINE HERINGHarrison DavidsonPas encore d'évaluation
- WJCC 6 322Document18 pagesWJCC 6 322Intan PermatasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Penyakit Kulit Dan KelaminDocument97 pagesPenyakit Kulit Dan KelaminSelvi Putri Oktari100% (1)
- Cutaneous Manifestation of HivDocument36 pagesCutaneous Manifestation of Hivyunita hapsariPas encore d'évaluation
- DERMATOLOGY Notes From Uworld, DR-KYDocument22 pagesDERMATOLOGY Notes From Uworld, DR-KYLayan Mohammad100% (1)
- Good Practice in Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology - Anna Maria Fulghesu - 2018Document256 pagesGood Practice in Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology - Anna Maria Fulghesu - 2018Tan ManPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment of The IntegumentaryDocument3 pagesAssessment of The IntegumentaryMona ArabiaPas encore d'évaluation
- 101-Normal Skin MCQsDocument25 pages101-Normal Skin MCQsHybat ElsheikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Elementary Skin LesionsDocument5 pagesElementary Skin LesionsYdeli DetanPas encore d'évaluation
- LEPROSY Part 2 - DR HannahDocument36 pagesLEPROSY Part 2 - DR HannahStase IKM FK UPHPas encore d'évaluation
- Case #1: Case Study Assignment Assignment #3Document10 pagesCase #1: Case Study Assignment Assignment #3api-536664543Pas encore d'évaluation
- Stom ProfileDocument71 pagesStom ProfileStefan CretuPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.long ExamDocument29 pages1.long ExamSweetyPas encore d'évaluation
- DermaDocument20 pagesDermaALSA MAHEK0% (1)
- Dermatology MCQDocument9 pagesDermatology MCQNiwashiny CnyPas encore d'évaluation
- Approach To Reticulate Hyperpigmentation: Clinical Dermatology - Review ArticleDocument8 pagesApproach To Reticulate Hyperpigmentation: Clinical Dermatology - Review ArticledelfiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Impetigo: Referat Makassar - 2016Document19 pagesImpetigo: Referat Makassar - 2016keluargacendanaPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Patho Skin PathologyDocument27 pages10 Patho Skin PathologyMartin Tan100% (1)