Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
f1 Notes Chapter 4
Transféré par
weijeeDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
f1 Notes Chapter 4
Transféré par
weijeeDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Form 1 Science Chapter 4 : The Various Resources on Earth
1. Water, air, soil, minerals, fossil fuels and living things are the important
resources on Earth.
The uses of various resources on Earth
Resource Use
It is needed by living things to carry
_________________ in the body.
It is needed by living things to maintain the body
_________________.
Water It is needed by plants to transport food from the
____________ to other parts of the plant.
It is needed by green plants to make food through
____________________.
It provides a ____________ for all aquatic organisms.
It is needed for process such as _________________,
Air
burning of fuels and photosynthesis.
It contains various organic materials, ____________,
Soil ___________________, water and air.
It also provides a habitat for some organisms.
Minerals are used by humans to make various
objects. Example
Minerals (a) Copper is used to make electric cables and ________.
(b) Aluminium is used to make __________ for drinks
and kitchen utensils.
Fossil fuels such as coal, _______________ and
Fossil fuels natural gas are resources of energy for motorised
vehicles, power stations and factory machines.
Plants and animals are sources of __________,
Living things
building materials, clothes and fuel.
Form 1 Notes Chapter 4 prepared by Ms Sue Page 1
Form 1 Science Chapter 4 : The Various Resources on Earth
4.2 Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
1. An _____________ is a substance which cannot be broken down into two
or more simpler substance by any ______________ or ______________
method.
2. It is the simplest form of _________.
3. An element is made up of atoms of _________ type only. A
___________ of similar atoms is known as a molecule.
Iron is made up of iron atoms Oxygen is made up of oxygen molecules
4. Elements can be classified into ____________ and _________________.
5. All metallic elements, except _____________, are solids at room
temperature.
6. Non-metallic elements exist as liquids, solids and gases at room
temperature.
Examples of metals
Metal State (at room temperature)
Aluminium Solid
Iron Solid
Silver Solid
Copper Solid
Magnesium Solid
Potassium Solid
Tin Solid
Mercury Liquid
Form 1 Notes Chapter 4 prepared by Ms Sue Page 2
Form 1 Science Chapter 4 : The Various Resources on Earth
Example of non-metals
Non-metal State (at room temperature)
Carbon Solid
Sulphur Solid
Iodine Solid
Bromine Liquid
Oxygen Gas
Hydrogen Gas
Chlorine Gas
Nitrogen Gas
Properties of metal and non-metals
Metal Non-metals
Have shiny surfaces Have __________ surfaces
Malleable Brittle
Ductile Not ductile
Have _________ melting points Have _________ melting points
__________ conductors of heat and __________ conductors of heat and
electricity electricity
Compounds
1. A ______________ is a substance made up of two or more elements
chemically combined together.
2. Examples of compounds are ___________, common salt, ____________
_____________ and ammonia.
Form 1 Notes Chapter 4 prepared by Ms Sue Page 3
Form 1 Science Chapter 4 : The Various Resources on Earth
3. The component elements of a compound can be separated by chemical
means such as __________________ or _____________.
4. Compounds are formed by chemical reactions in which heat or light is
______________ or ____________.
5. Compounds have properties that are _______________ from those of the
elements that it contains.
Mixtures
1. A mixture consists of two or more substances that are not
_________________________.
2. A mixture may be formed from two elements, elements and compounds
or two compounds.
______________ _______________ ________________
Examples of mixtures
Mixtures Components
Oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, water
vapour, inert gases, dust, bacteria and
other substances
Stones, sand, silt, humus, minerals, air,
water
Salt, water
Petrol, kerosene, diesel, bitumen
Form 1 Notes Chapter 4 prepared by Ms Sue Page 4
Form 1 Science Chapter 4 : The Various Resources on Earth
3. The following are some general properties of mixtures.
(a) They are formed without any chemical reaction.
(b) They have properties that are the sum of the original properties of their
components.
(c) They can be separated into their components by physical methods of
separation.
Some separation techniques of mixtures
Separation technique Example
Separation of iron fillings from
_________________________
sulphur powder
________________ Separation of sand from water
_______________ Separation of salt from salt solution
Separation of the different grades of
__________________
petrol
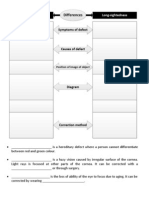
The differences between a compound and a mixture
Compound Mixture
It is prepared from a ______________ It is prepared by any ______________
reaction means
A new substance is formed No new substance is formed
The new substance has properties Each constituent retains its original
which are different from those of the properties
original elements
Elements are combined in a fixed ratio Elements are not combined in a fixed
ratio
The components can only be separated The components can be separate by
by ______________ means ______________ means
___________is absorbed or released ________________ is absorbed or
when it is prepared released when it is prepared
Form 1 Notes Chapter 4 prepared by Ms Sue Page 5
Form 1 Science Chapter 4 : The Various Resources on Earth
4.3 The Importance of Earth’s Resources
1. As Earth’s resources are required to ensure then continuity of life on
Earth, they need to be preserved and conserved.
2. __________________ means maintaining certain areas of the Earth in
their natural condition.
3. Examples of efforts in preservation are the setting up of forest reserves,
national parks and marines parks.
4. __________________ is the protection and management of the resources
of the Earth such as flora and fauna, water, air, mineral salts, fossil fuels
and soil.
5. Preservation and conservation of Earth’s resources prevent
(A)The destruction of resources which provide the basic needs.
(B) The destruction of animals and plants and their habitats.
(C) The destruction of the environment through pollution.
(D)Animals and plants from becoming _____________.
(E) The destruction of the balance of nature.
6. Practising the reuse and the recycle are the common methods used to
preserve and to conserve the Earth’s resources.
7. Reusing and recycling are some of the common methods used to preserve
and to conserve the Earth’s resources.
8. _____________ refers to use discarded or unwanted materials to save
natural resources.
9. _______________ refers to the processing of waste materials to become
new useful things in order to save the Earth’s resources.
10.Examples include the recycling of newspaper, plastic, glass and
aluminium cans.
Form 1 Notes Chapter 4 prepared by Ms Sue Page 6
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Geography Question BankDocument198 pagesGeography Question BankChandan NayakPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry: Study Package Pearl / Oodles Class IxDocument27 pagesChemistry: Study Package Pearl / Oodles Class IxManoj KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Elements, Compounds and Mixtures WS Vrishabh 1Document7 pagesElements, Compounds and Mixtures WS Vrishabh 1Anand Kumar ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Form 3 2020 (Notes, PBD, Exercise) : Chapter: 4 Reactivity of MetalsDocument21 pagesScience Form 3 2020 (Notes, PBD, Exercise) : Chapter: 4 Reactivity of MetalsYusfalina Mohd YusoffPas encore d'évaluation
- Transformer Condition Monitoring Sethuraman MuthukaruppDocument8 pagesTransformer Condition Monitoring Sethuraman MuthukaruppAnantha RkPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 1 Science Chapter 4Document33 pagesForm 1 Science Chapter 4qq23595% (21)
- Elements, Compounds, Mixtures WorksheetDocument6 pagesElements, Compounds, Mixtures WorksheetAlvianica Nanda Utami100% (1)
- Final Exam in DRRR 2020Document4 pagesFinal Exam in DRRR 2020Ryan San LuisPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEM SPM Chapter 4 Periodic Table StudentDocument23 pagesCHEM SPM Chapter 4 Periodic Table Studentangie0812Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fuel CellDocument23 pagesFuel CellYuva RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry - MixturesDocument12 pagesChemistry - MixturesEmmanuel Richard100% (1)
- Heavy Metals in the Environment: Origin, Interaction and RemediationD'EverandHeavy Metals in the Environment: Origin, Interaction and RemediationÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Chemistry of Cell Review: Quick Review Notes Chapter 2D'EverandChemistry of Cell Review: Quick Review Notes Chapter 2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Periodic Table Form 1Document12 pagesChapter 6 Periodic Table Form 1nantheni1779% (14)
- Reviewer 1 Chemical Engineering Day 1Document13 pagesReviewer 1 Chemical Engineering Day 1Romevie Prado100% (2)
- Ernst Mayr What Evolution Is PDFDocument2 pagesErnst Mayr What Evolution Is PDFKayla0% (1)
- Surface and Interface Chemistry of Clay MineralsD'EverandSurface and Interface Chemistry of Clay MineralsPas encore d'évaluation
- Bai Anh Van Hoan ChinhDocument42 pagesBai Anh Van Hoan ChinhPham Van Tin B1909842Pas encore d'évaluation
- Matter ExcerciseDocument3 pagesMatter ExcerciseCyruss MeranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 4 Notesscribble_55Pas encore d'évaluation
- Garde 11 Stem General Chemistry Module PrelimDocument51 pagesGarde 11 Stem General Chemistry Module PrelimYza S.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chem Lecture 1 MSUDocument7 pagesChem Lecture 1 MSURayhan MaddiePas encore d'évaluation
- Lost ElementsDocument2 pagesLost ElementsART JOSHUA MARAPas encore d'évaluation
- F3 SN CHP 4 2023Document38 pagesF3 SN CHP 4 2023NG YI ZHI MoePas encore d'évaluation
- Chemcial Reactions Cloze PassageDocument5 pagesChemcial Reactions Cloze PassageNadia CzeredreckiPas encore d'évaluation
- Minerals and RocksDocument64 pagesMinerals and RockspedrayacaseyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Compounds and MixturesDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Compounds and MixturesteacherkitPas encore d'évaluation
- Las Science 7 Q1 W2-3Document6 pagesLas Science 7 Q1 W2-3Eileen NagaPas encore d'évaluation
- S7MT-id-e-2: Common Elements and Their Uses Element Common Uses &/or DescriptionsDocument4 pagesS7MT-id-e-2: Common Elements and Their Uses Element Common Uses &/or DescriptionsCarissa Mae CañetePas encore d'évaluation
- Ammonia (NH: A B C D EDocument6 pagesAmmonia (NH: A B C D EJhinrie BarceloPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen Chem Exam 1Document2 pagesGen Chem Exam 1Roj M. AramayPas encore d'évaluation
- Note Chapter 4Document9 pagesNote Chapter 4Mandy VoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Limitations and All Other NotesDocument25 pagesLimitations and All Other NotesHuda HalanePas encore d'évaluation
- MatterDocument57 pagesMatterJaresa DecierdoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry-2 Module-2 TOLENTINO OLDocument10 pagesChemistry-2 Module-2 TOLENTINO OLJhun Lerry TayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Help Online Worksheet 1-4d Classification of MatterDocument2 pagesScience Help Online Worksheet 1-4d Classification of MatterfabzyshoesPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes Unit 2 Matter, Properties & ChangeDocument12 pagesNotes Unit 2 Matter, Properties & Changeria wuPas encore d'évaluation
- Coal and Petroleum - Notes - 220908 - 185218Document14 pagesCoal and Petroleum - Notes - 220908 - 185218VENKATESH PRABHUPas encore d'évaluation
- 6chemistry - RWS-1 & 2Document2 pages6chemistry - RWS-1 & 2VM OPas encore d'évaluation
- GRADE 9 PRE-TEST IN GENERAL CHEMISTRY With AnswersDocument5 pagesGRADE 9 PRE-TEST IN GENERAL CHEMISTRY With AnswersBreeza Marie VeralloPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet 14.1 Metals and Alloys Metals 1.: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Document10 pagesWorksheet 14.1 Metals and Alloys Metals 1.: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Apple kokPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 8 Science WorksheetDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 8 Science WorksheetISHAAN GOYALPas encore d'évaluation
- Materials - Metals and Non Metals - Important Qs - Important QuestionsDocument3 pagesMaterials - Metals and Non Metals - Important Qs - Important QuestionsMayankPas encore d'évaluation
- General Chemistry: Physical and Chemical Principles 1. Board Problem, January 1974Document20 pagesGeneral Chemistry: Physical and Chemical Principles 1. Board Problem, January 1974tinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Board Problem in ChemistryDocument20 pagesBoard Problem in ChemistryAudreyWalangareDimalibotPas encore d'évaluation
- PME9 ChemistryDocument33 pagesPME9 ChemistryDenmark ManlusocPas encore d'évaluation
- The Chemical Earth NotesDocument9 pagesThe Chemical Earth NotesRianna BunnPas encore d'évaluation
- Module Chapter 4Document21 pagesModule Chapter 4Hannan NashruddinPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.is Matter Around Us Pure-NotesDocument20 pages2.is Matter Around Us Pure-NotesBlaster-brawl starsPas encore d'évaluation
- SMILE Science 9 Q2W4 5 EditedDocument8 pagesSMILE Science 9 Q2W4 5 EditedRaven Third-partyAccPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Form 1 Chapter 4Document26 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 4Beevy GB73% (11)
- Cycles WorksheetDocument4 pagesCycles WorksheetJenniferPas encore d'évaluation
- Diversity of Materials in The EnvironmentDocument19 pagesDiversity of Materials in The EnvironmentMarjorie TrinidadPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 2 The AtmosphereDocument4 pagesCH 2 The AtmosphereHa YeungPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 9 - Q2 - Week 5-M13-M16Document32 pagesScience 9 - Q2 - Week 5-M13-M16Rhyan Zero-four BaluyutPas encore d'évaluation
- ModuleDocument9 pagesModuleEspie Rose DumalagPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Worksheet Grade X 2023Document10 pagesPractice Worksheet Grade X 2023Muhammad ShafayPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuels & Fairness Study Guide v1Document32 pagesFuels & Fairness Study Guide v1ChunkyLuverRudyPas encore d'évaluation
- AK-Grade 7-Chem-VADocument5 pagesAK-Grade 7-Chem-VAMuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 3 and 4Document17 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Section 3 and 4Soraya DeenPas encore d'évaluation
- Coal and Petroleum Notes Science Chapter 5Document2 pagesCoal and Petroleum Notes Science Chapter 5Ritom SaikiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Content in Science ChemistryDocument6 pagesContent in Science ChemistryChloe EisenheartPas encore d'évaluation
- Nicholas Edwards - Ink Handout-Per TableDocument2 pagesNicholas Edwards - Ink Handout-Per TableNicole EdwardsPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Solving in Chemical Engineering With MatlabDocument7 pagesProblem Solving in Chemical Engineering With MatlabweijeePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 The World Through Our SensesDocument18 pagesChapter 1 The World Through Our SensesNurul Ain RazaliPas encore d'évaluation
- 168 Defects of VisionDocument1 page168 Defects of VisionweijeePas encore d'évaluation
- N44 Ts Fuis 9 C 6Document2 pagesN44 Ts Fuis 9 C 6weijeePas encore d'évaluation
- Fermentation PDF NotesDocument24 pagesFermentation PDF NotesJay-zee Shandu100% (5)
- Physics - 61 - Week - 5 - Exercises and Solved Problems PDFDocument2 pagesPhysics - 61 - Week - 5 - Exercises and Solved Problems PDFSebastian SmythePas encore d'évaluation
- Chang Chemistry - Assessment Chapter 7Document10 pagesChang Chemistry - Assessment Chapter 7haha_le12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Trade Theory N2: National CertificateDocument48 pagesElectrical Trade Theory N2: National CertificateAdriaan MyburghPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic - 5 - and - 15 - Mixed - Questions ChemistryDocument12 pagesTopic - 5 - and - 15 - Mixed - Questions ChemistryRanem Ahmed Nasser Al ShibaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Numbers, Protons, Neutrons and Electrons: Name DateDocument1 pageAtomic Numbers, Protons, Neutrons and Electrons: Name Datenoob noobPas encore d'évaluation
- AITS Schedule 2023Document2 pagesAITS Schedule 2023Pushpanjay KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Me 312cpdfDocument241 pagesMe 312cpdfEricson PalsarioPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.2 Porosity PDFDocument49 pages2.2 Porosity PDFmemo100% (1)
- The Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument3 pagesThe Kinetic Theory of GaseszaedmohdPas encore d'évaluation
- GIS 1st Unit - PDF.WWW - Chennaiuniversity.net - NotesDocument32 pagesGIS 1st Unit - PDF.WWW - Chennaiuniversity.net - NotesvanamgouthamPas encore d'évaluation
- Extended Essay Final DraftDocument39 pagesExtended Essay Final DraftAnupriy 'Pri' KantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Otc8776 The Wax Deposition Envelope of Gas Condensates: Kosta Leontaritis, Asphwax, IncDocument8 pagesOtc8776 The Wax Deposition Envelope of Gas Condensates: Kosta Leontaritis, Asphwax, IncKelly Jhoanna JimenezPas encore d'évaluation
- Origin of The Earth Geomorphology Geography Optional UPSCDocument12 pagesOrigin of The Earth Geomorphology Geography Optional UPSCabhimmanyu2013Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bladeless HydraulicDocument6 pagesBladeless HydraulicQuike Flores SuárezPas encore d'évaluation
- Reboita Impact Teleconections SouthAmerica 2021Document38 pagesReboita Impact Teleconections SouthAmerica 2021Lucas BauerPas encore d'évaluation
- Climate Change Information TableDocument2 pagesClimate Change Information TableDallas Ha Hong SonPas encore d'évaluation
- KRSD CompressorDocument7 pagesKRSD CompressorMohit PanchalPas encore d'évaluation
- Development of Biogas Compression System For Using in HouseholdDocument6 pagesDevelopment of Biogas Compression System For Using in Householdanand sahuPas encore d'évaluation
- LIFE SCIENCES P2 QP GR10 NOV2018 - EnglishDocument16 pagesLIFE SCIENCES P2 QP GR10 NOV2018 - Englishonthabiseng mathPas encore d'évaluation
- Jntuk 2 1 T&HPM Nov 2017 Q.PDocument8 pagesJntuk 2 1 T&HPM Nov 2017 Q.Panon_920598081Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrology Dissertation IdeasDocument8 pagesHydrology Dissertation IdeasBuyWritingPaperElgin100% (1)
- ID167 Valentine Chandra Component 2Document7 pagesID167 Valentine Chandra Component 2Audrey Patricia GunawanPas encore d'évaluation
- s6 Physics p1 BugandaDocument7 pagess6 Physics p1 BugandaWafula EricPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 7 Q4Document309 pagesScience 7 Q4Milyn Robles100% (1)
- 6470b0e5f337ed00180c05a4 - ## - Atomic Structure - DPP-01 (Of Lec-03) - Arjuna NEET 2024Document3 pages6470b0e5f337ed00180c05a4 - ## - Atomic Structure - DPP-01 (Of Lec-03) - Arjuna NEET 2024Lalit SinghPas encore d'évaluation