Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
CHN Family Health
Transféré par
Rose Athena SibalaDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CHN Family Health
Transféré par
Rose Athena SibalaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
FAMILY HEALTH NURSING
INITIAL DATA BASE FOR FAMILY NURSING PRACTICE
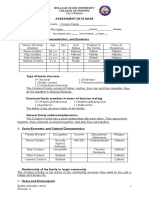
A. FAMILY STRUCTURE & CHARACTERISTICS
1. Members of the household & relationship to the head of the family
2. Demographic data: age, sex, civil status, position in the family
3. Place of residence of each member whether living with family or elsewhere
4. Type of family structure: patriarchal, matriarchal, nuclear, extended
5. Dominant family members in terms of decision making in matters of health
care
6. General family relationship – presence of any obvious/readily observable
conflict between members; characteristic communication patterns among
members
B. SOCIO-ECONOMIC & CULTURAL FACTORS
1. Income & Expenses
a. Occupation, place of work & income of each working member
b. Adequacy to meet basic necessities (food, clothing, shelter)
c. Who makes decisions about the money & how is it spent?
2. Educational attainment of each member
3. Ethnic background & religious affiliation
4. Significant others: roles they play in the family’s life
5. Relationship of the family to larger community – what is the participation of
the family in community activities?
C. ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS
1. Housing
a. Adequacy of living space
b. Sleeping arrangement
c. Adequacy of the furniture
d. Presence of insects & rodents
e. Presence of accident hazards
f. Food storage & cooking facilities
g. Water supply – source, ownership, potability
h. Toilet facility – type, ownership, sanitary condition
i. Garbage/refuse disposal – type, sanitary condition
j. Drainage system – type, sanitary condition
2. Kind of neighborhood
3. Social & health facilities available
4. Communication & transportation facilities available
D. HEALTH ASSESSMENT OF EACH MEMBER
1. Medical & nursing history indicating past significant illnesses, beliefs &
practices conducive to illness
2. Nutritional assessment (especially for vulnerable or at risk member)
a. Anthropometric data – weight, height, mi-upper arm circumference
b. Dietary history indicating quality & quantity of food intake per day
c. Eating/feeding habits/practices
3. Current health status indicating presence of illness (diagnosed or undiagnosed
by medical practitioner)
E. VALUE PLACED ON PREVENTION OF DISEASE
1. Immunization status of children
2. Use of other preventive services
TYPOLOGY OF NURSING PROBLEMS IN FAMILY NURSING
PRACTICE
A. FIRST LEVEL ASSESSMENT
Look out for presence of health threats, health deficits & foreseeable crisis or
stress points in the family
1. HEALTH THREATS – conditions that are conducive to disease, accident or
failure to realize one’s health potential
Examples:
a.Health history of specific conditions/disease (e.g. family history of DM)
b. Threat of cross infection from communicable disease case
c.Family size beyond what family resources can adequately provide
d. Accident hazards (broken stairs, pointed/sharp objects, poisons & medicines
improperly kept)
e.Nutritional (inadequate food intake both in quantity & quality; excessive
intake of certain nutrients; faulty eating habits, unsanitary food handling &
preparation)
f. Stress-provoking factors (strained marital relationship, strained parent-sibling
relationship, interpersonal conflicts between family members)
g. Poor environmental sanitation
• Inadequate living space
• Inadequate personal belongings/utensils
• Lack of food storage facilities
• Polluted water supply
• Presence of breeding places of insects & rodents
• Improper garbage/refuse disposal
• Unsanitary waste disposal
• Improper drainage system
• Poor lighting & ventilation
• Noise pollution
• Air pollution
h. Personal habits/practices
• Frequent drinking of alcohol
• Excessive smoking
• Walking barefooted
• Eating raw meat/fish
• Poor personal hygiene
• Self-medication
• Use of dangerous drugs/narcotics
• Sexual promiscuity
• Engaging in dangerous sports
i. Inherent personal characteristics (ex. short temper)
j. Inappropriate role assumption
k. Health history which may precipitate/induce the occurrence of a health
deficit (ex. previous history of difficult labor)
l. Lack of immunization/inadequate immunization status especially of children
2. HEALTH DEFICITS – instances of failure in health maintenance
Examples:
a. Illness states; regardless whether it is diagnosed or undiagnosed by medical
practitioner
b. Failure to thrive/develop according to normal rate
c. Disability arising from illness, whether transient/temporary (ex. aphasia or
temporary paralysis after a CVA) or permanent (e. leg amputation secondary
to DM; blindness from measles; lameness from polio)
3. STRESS POINTS/FORESEEABLE CRISIS – anticipated periods of unusual
demand on the individual or family in terms of adjustment/family resources
Examples:
a.Marriage
b. Pregnancy, labor, puerperium
c.Parenthood
d. Additional member (newborn, lodger)
e.Abortion
f. Entrance at school
g. Loss of job
h. Death of a member
i. Resettlement in a new community
j. Illegitimacy
B. SECOND LEVEL ASSESSMENT
1. INABILITY TO RECOGNIZE THE PRESENCE OF A PROBLEM DUE
TO:
a. Ignorance of facts
b. Fear of consequences of diagnosis of problem (ex. social stigma, loss of
respect of peer & significant others, economic cost, physical/psychological
consequences)
c. Attitude or philosophy in life
2. INABILITY TO MAKE DECISIONS WITH RESPECT TO TAKING
APPROPRIATE HEALTH ACTION DUE TO:
a. Failure to comprehend the nature, magnitude/scope of the problem
b. Low salience of the problem
c. Feeling of confusion &/or resignation brought about by failure to break down
problems into manageable units of attack
d. Lack of knowledge/insight as to alternative courses of action open to them
e. Inability to decide which action to take from among a list of alternatives
f. Conflicting opinions among family members/significant others regarding
action to take
g. Ignorance of community resources for care
h. Fear of consequences of action (ex. social, economic, physical/psychological)
i. Negative attitude towards the health problem (one that interferes with rational
decision making)
j. Inaccessibility of appropriate resources of care (physical – location; cost)
k. Lack of trust/confidence in the health personnel/agency
l. Misconceptions or erroneous information about proposed course(s) of action
3. INABILITY TO PROVIDE ADEQUATE NURSING CARE TO THE
SICK, DISABLED OR VULNERABLE/AT RISK MEMBER OF THE
FAMILY DUE TO:
a. Ignorance of facts about the disease/health condition (nature of severity,
complications, prognosis & management); child development & child care
b. Ignorance of the nature & extent of nursing care needed
c. Lack of the necessary facilities (equipment & supplies) for care
d. Lack of knowledge & skill in carrying out the necessary
treatment/procedure/care
e. Inadequate family resources for care (responsible member, financial, physical
resources – ex. isolation room)
f. Negative attitude towards the sick, disables, dependent, vulnerable/at risk
member
g. Attitude/philosophy in life
h. Members’ preoccupation with own concerns/interests
4. INABILITY TO PROVIDE A HOME ENVIRONMENT WHICH IS
CONDUCIVE TO HEALTH MAINTENANCE & PERSONAL
DEVELOPMENT DUE TO:
a. Inadequate family resources (financial, physical – lack of space to construct
facility)
b. Failure to see benefits (especially long term ones) of investment in home
environment improvement
c. Ignorance of importance of hygiene & sanitation
d. Ignorance of preventive measures
e. Lack of skill in carrying out measures to improve home environment
f. Ineffective communication patterns
g. Attitude/philosophy in life
5. FAILURE TO UTILIZE COMMUNITY RESOURCES FOR HEALTH
CARE DUE TO:
a. Ignorance or lack of awareness of community resources for health care
b. Failure to perceive the benefits of health care/services
c. Lack of trust/confidence in the agency/personnel
d. Previous unpleasant experience with health worker
e. Fear of consequences of action (preventive, diagnostic, therapeutic,
rehabilitative) – physical/psychological, financial, social (ex. loss of self-
esteem of peer/significant others)
f. Unavailability of required care/service
g. Inaccessibility of required care/service (cost, physical location)
h. Lack of or inadequate family resources (manpower – ex. baby sitter; financial
– ex. cost of medicine prescribed)
i. Feeling of alienation to/lack of support from the community (ex. mental
illness)
j. Attitude or philosophy in life
SCALE FOR RANKING FAMILY HEALTH PROBLEMS ACCORDING
TO PRIORITIES
CRITERIA WEIGHT
1. Nature of the problem presented 1
Health Threat 2
Health Deficit 3
Foreseeable Crisis 1
2. Modifiability of the problem 2
Easily Modifiable 2
Partially Modifiable 1
Not Modifiable 0
3. Preventive potential 1
High 3
Moderate 2
Low 1
4. Saliency 1
A serious problem; immediate attention needed 2
A problem but not needing immediate attention 1
Not a felt need/problem 0
SCORING:
1. Decide on a score for each of the criteria
2. Divide the score by the highest possible score & multiply by the weight
3. Sum up the scores for all the criteria. The highest score is 5 equivalent to the total
weight.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Typology of Nursing Problems in Family Nursing PracticeDocument8 pagesA Typology of Nursing Problems in Family Nursing PracticeClifford Ogad0% (1)
- CCM Nur1217Document310 pagesCCM Nur1217Booz Waief CaluzaPas encore d'évaluation
- FNCP Final FinalDocument51 pagesFNCP Final FinalMichael Piduca100% (1)
- Rinciples and Practice of The HospiceDocument1 pageRinciples and Practice of The HospiceCake ManPas encore d'évaluation
- Community Duty Problem SheetDocument7 pagesCommunity Duty Problem SheetReed Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Level of Assessment FNCPDocument10 pagesLevel of Assessment FNCPLore Anne Mhae SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Ambeguia Elijah - BulSU-OP-CON-23F10-Assessment-Data-Base - Part1Document11 pagesAmbeguia Elijah - BulSU-OP-CON-23F10-Assessment-Data-Base - Part1Ambeguia ElijahPas encore d'évaluation
- OB Gyne Ward PretestDocument3 pagesOB Gyne Ward PretestCHRISTIAN RAY ALPAS PASILIAOPas encore d'évaluation
- Santos Family - Prob IDDocument3 pagesSantos Family - Prob IDchubachenes100% (2)
- Care of The Mother, Child and Adolescent (Well Client) Related Learning ExperienceDocument7 pagesCare of The Mother, Child and Adolescent (Well Client) Related Learning ExperienceIvy VillalobosPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 6 - FILIPINO CULTURE, VALUES AND PRACTICES IN RELATION TO MATERNAL AND CHILD CAREDocument4 pagesModule 6 - FILIPINO CULTURE, VALUES AND PRACTICES IN RELATION TO MATERNAL AND CHILD CAREKatie Holmes0% (1)
- Unit 1: Introduction To Community Health Nursing Chapter 1: Fundamental Concepts of Community Health NursingDocument140 pagesUnit 1: Introduction To Community Health Nursing Chapter 1: Fundamental Concepts of Community Health NursingChevelle Valenciano-GaanPas encore d'évaluation
- Objectives - Surgical WardDocument3 pagesObjectives - Surgical WardAzhly AntenorPas encore d'évaluation
- FNCPDocument3 pagesFNCPChloie Marie RosalejosPas encore d'évaluation
- Family Nursing Care PlanDocument14 pagesFamily Nursing Care PlanTenth Ann ModanzaPas encore d'évaluation
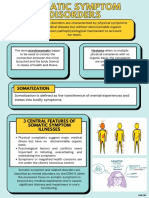
- NCM 117-Somatic DisordersDocument5 pagesNCM 117-Somatic DisordersJa DimasPas encore d'évaluation
- 2vjvn14i8 - Virtues, Vices and Habits - BioethicsDocument5 pages2vjvn14i8 - Virtues, Vices and Habits - BioethicsEvelyn MedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diets Modified in Composition RSUDocument3 pagesDiets Modified in Composition RSUResimer Natividad100% (1)
- Activity 9 and 10. Calso Kriselle AnnDocument12 pagesActivity 9 and 10. Calso Kriselle AnnKriselle Ann CalsoPas encore d'évaluation
- SDL3Document2 pagesSDL3Margaux BaynosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tpo Ward BMDocument3 pagesTpo Ward BMAhl A PurujiPas encore d'évaluation
- Prevalence of Bioethical IssuesDocument4 pagesPrevalence of Bioethical IssuesPatricia Jean FaeldoneaPas encore d'évaluation
- Famacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 3Document3 pagesFamacion - CHN - General Requirements Week 3Kyra Bianca R. FamacionPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction Case StudyDocument10 pagesIntroduction Case StudyJoshua VillarbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Funda ReviewerDocument8 pagesFunda ReviewerChamelli RobinPas encore d'évaluation
- NCM 114: Care of The Older Adult Instructor: Gino Paulo A. Buizon, R.NDocument9 pagesNCM 114: Care of The Older Adult Instructor: Gino Paulo A. Buizon, R.NJay VillasotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 8 - Activity (Case Scenario)Document7 pagesWeek 8 - Activity (Case Scenario)Jollan Marie BuenvenidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Course Task 2 - Laboratory Module Week 1Document4 pagesCourse Task 2 - Laboratory Module Week 1BOBO GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Ethical Principles Stewards 1. StewardshipDocument7 pagesBasic Ethical Principles Stewards 1. StewardshipElla EllaPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 3. Formulating and Evaluating Family Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesActivity 3. Formulating and Evaluating Family Nursing Care Planjoannamae molagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Finished FNCPDocument12 pagesFinished FNCPAbcd TolibasPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Informatics Lecture:: Notes On Information Technology System Applicable in Nursing PracticeDocument6 pagesNursing Informatics Lecture:: Notes On Information Technology System Applicable in Nursing PracticeCatherine PradoPas encore d'évaluation
- FNCPDocument17 pagesFNCPRaquel M. MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Community AccomplishmentDocument2 pagesCommunity AccomplishmentRudy Mark ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- EPI - AND - IMCI - Docx Filename - UTF-8''EPI AND IMCIDocument14 pagesEPI - AND - IMCI - Docx Filename - UTF-8''EPI AND IMCIYvonne Carmel Aguilar SunigaPas encore d'évaluation
- FNCP PrioritizationDocument10 pagesFNCP PrioritizationSteven ConejosPas encore d'évaluation
- Diet Modified in CompositionDocument34 pagesDiet Modified in Compositionprecyusman50% (2)
- Contents of FDAR ChartingDocument1 pageContents of FDAR Chartingkaycelyn jimenezPas encore d'évaluation
- School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences: St. Paul University Philippines Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500Document5 pagesSchool of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences: St. Paul University Philippines Tuguegarao City, Cagayan 3500CLARENCE REMUDAROPas encore d'évaluation
- Discharge Plan of Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument4 pagesDischarge Plan of Abnormal Uterine BleedingDenise Louise PoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 5 RebolosDocument5 pagesLab 5 RebolosAisha MariePas encore d'évaluation
- ZegenDocument2 pagesZegenianecunar100% (3)
- Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has A Neurologic DisorderDocument8 pagesNursing Care of A Family When A Child Has A Neurologic DisorderBern NerquitPas encore d'évaluation
- Republic Act 6675 - Generics Act of 1988Document5 pagesRepublic Act 6675 - Generics Act of 1988Katrina Javier BolivarPas encore d'évaluation
- Typology of Nursing Problems in Family Nursing PracticeDocument2 pagesTypology of Nursing Problems in Family Nursing PracticeAnthony A. CelerianPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 3 CHN 1Document4 pagesModule 3 CHN 1Danz Kie100% (1)
- Family Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesFamily Nursing Care Plankaycelyn jimenezPas encore d'évaluation
- Family Health Assessment FormDocument7 pagesFamily Health Assessment FormBiway RegalaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCM 117J (Maladaptive Pattern of Behavior) : Overview of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing Module 1/7Document41 pagesNCM 117J (Maladaptive Pattern of Behavior) : Overview of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing Module 1/7Abdelmar Susulan100% (1)
- Ethical ConsiderationsDocument6 pagesEthical ConsiderationsBern NerquitPas encore d'évaluation
- FNCP MalnutritionDocument2 pagesFNCP Malnutritionann camposPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1 NCM 210 RLE - Types of Family-Nurse ContactDocument6 pages2.1 NCM 210 RLE - Types of Family-Nurse ContactLYRIZZA LEA BHEA DESIATAPas encore d'évaluation
- Historical Backgroud of DOHDocument4 pagesHistorical Backgroud of DOHAna LuisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study 2: A Matter of Freedom: AnswerDocument1 pageCase Study 2: A Matter of Freedom: AnswerApple Mae ToñacaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Significant Dates Historical Event/ Person or Agency Involved Implication To The Practice of Public Health NursingDocument5 pagesSignificant Dates Historical Event/ Person or Agency Involved Implication To The Practice of Public Health NursingJenylbajado28Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Database in Family Nursing PracticeDocument4 pagesAssessment Database in Family Nursing PracticeTamayo, Shaina AngelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Family Nursing ProcessDocument25 pagesFamily Nursing ProcessJAMES ROD MARINDUQUE100% (1)
- CHN 1 Assessment Tools 2021Document6 pagesCHN 1 Assessment Tools 2021Yori Nicole Martine CuyosPas encore d'évaluation
- Typhology of Nursing ProblemDocument4 pagesTyphology of Nursing ProblemSteffi AubreyPas encore d'évaluation
- Path o Physiology TablesDocument4 pagesPath o Physiology TablesRose Athena SibalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Epistaxis & TonsillectomyDocument1 pageEpistaxis & TonsillectomyRose Athena SibalaPas encore d'évaluation
- MigraineDocument9 pagesMigraineRose Athena SibalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rose Athena Baja-Sibala, RNDocument22 pagesRose Athena Baja-Sibala, RNRose Athena SibalaPas encore d'évaluation
- TR189 Kathuria PDFDocument168 pagesTR189 Kathuria PDFuqiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cateora2ce IM Ch012Document9 pagesCateora2ce IM Ch012Priya ShiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Zetor Crystal 150 170 Tractor Operator Manual PDFDocument234 pagesZetor Crystal 150 170 Tractor Operator Manual PDFAntonPas encore d'évaluation
- Civil Engineering Topics V4Document409 pagesCivil Engineering Topics V4Ioannis MitsisPas encore d'évaluation
- Under Pass Wing Wall (4.1m)Document12 pagesUnder Pass Wing Wall (4.1m)Naveed NazPas encore d'évaluation
- Ge Druck PTX 7535Document2 pagesGe Druck PTX 7535ICSSPas encore d'évaluation
- Macleod - 1974 - Lucian's Knowledge of TheophrastusDocument2 pagesMacleod - 1974 - Lucian's Knowledge of TheophrastusSIMONE BLAIRPas encore d'évaluation
- Infrastructure Definition:: Economic Infrastructure Includes BroadlyDocument3 pagesInfrastructure Definition:: Economic Infrastructure Includes Broadlyabraha gebruPas encore d'évaluation
- Additive Manufacturing Objective QuestionsDocument7 pagesAdditive Manufacturing Objective Questionsmohammad shaqib100% (4)
- KZPOWER Perkins Stamford Genset Range CatalogueDocument2 pagesKZPOWER Perkins Stamford Genset Range CatalogueWiratama TambunanPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2Adam HakimiPas encore d'évaluation
- NURS1108 Lecture 10 - Nervous System ENHANCEDDocument40 pagesNURS1108 Lecture 10 - Nervous System ENHANCEDJacia’s SpaceshipPas encore d'évaluation
- z482 E3b en (3a2)Document2 pagesz482 E3b en (3a2)Gerencia General ServicesPas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile Communication Networks: Exercices 4Document2 pagesMobile Communication Networks: Exercices 4Shirley RodriguesPas encore d'évaluation
- Recetario TransistoresDocument23 pagesRecetario TransistoresTitán SotoPas encore d'évaluation
- What's The Use of Neuroticism?: G. Claridge, C. DavisDocument18 pagesWhat's The Use of Neuroticism?: G. Claridge, C. DavisNimic NimicPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Sheet: W-Series WSI 6/LD 10-36V DC/ACDocument12 pagesData Sheet: W-Series WSI 6/LD 10-36V DC/ACLUIS FELIPE LIZCANO MARINPas encore d'évaluation
- Nammiaca 000032Document5 323 pagesNammiaca 000032gangadhark196Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wic ReflectionDocument3 pagesWic Reflectionapi-307029735Pas encore d'évaluation
- Study of Mosquito Larvicidal Effects of (Bitter Gourd) Extracts As NanopowderDocument3 pagesStudy of Mosquito Larvicidal Effects of (Bitter Gourd) Extracts As NanopowderAnonymous AkoPas encore d'évaluation
- Progress Report Week#9 UlubeluDocument6 pagesProgress Report Week#9 UlubelutiantaufikPas encore d'évaluation
- Novel Image Enhancement Technique Using CLAHE and Wavelet TransformsDocument5 pagesNovel Image Enhancement Technique Using CLAHE and Wavelet TransformsInnovative Research PublicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.4 Assembly ManualDocument139 pages2.4 Assembly Manualgustavo dlsPas encore d'évaluation
- Smart Locker - A Sustainable Urban Last-Mile Delivery Solution: Benefits and Challenges in Implementing in VietnamDocument14 pagesSmart Locker - A Sustainable Urban Last-Mile Delivery Solution: Benefits and Challenges in Implementing in VietnamQuynh LePas encore d'évaluation
- WRP Examination Extension 1 2012Document12 pagesWRP Examination Extension 1 2012Belinda JadePas encore d'évaluation
- Leaflet CycleManager Ep CycleManager ErDocument7 pagesLeaflet CycleManager Ep CycleManager ErValeska ArdilesPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Acetylation Method On Characterization of Cellulose Acetate Based Sago "Hampas"Document18 pagesEffect of Acetylation Method On Characterization of Cellulose Acetate Based Sago "Hampas"myrraPas encore d'évaluation
- FPAL Product Code GuideDocument53 pagesFPAL Product Code GuideSRARPas encore d'évaluation
- Your Heart: Build Arms Like ThisDocument157 pagesYour Heart: Build Arms Like ThisNightPas encore d'évaluation
- EB-300 310 Service ManualDocument32 pagesEB-300 310 Service ManualVictor ArizagaPas encore d'évaluation
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsD'EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (42)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityD'EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (24)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearD'EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (23)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeD'EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeÉvaluation : 2 sur 5 étoiles2/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedD'EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (80)
- An Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyD'EverandAn Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossD'EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsD'EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsD'EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (169)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerD'EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (392)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsD'EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityD'EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.D'EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (110)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaD'EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDD'EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisD'EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessD'EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (328)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeD'EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (253)