Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment 2.1: Simple Pendulum
Transféré par
zoulezDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Experiment 2.1: Simple Pendulum
Transféré par
zoulezDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
EXPERIMENT 2.
1: SIMPLE PENDULUM
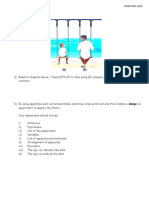
Figure 1 and Figure 2 show two positions of a boy on a swing. The angle of oscillation in both
diagrams is at the same angle from the iron pole. He noticed that the shorter swing moves faster
than the longer swing.
(Rajah 1 dan Rajah 2 menunjukkan dua kedudukan seorang budak di atas buaian. Sudut anyunan dalam
kedua-dua rajah adalah sama sudut daripada palang besi tersebut. Dia mendapati buaian yang pendek
bergerak lebih laju berbanding buaian panjang.)
Figure 1 Figure 2
Based on the information and observation,
Berdasarkan maklumat dan pemertian tersebut:
(a) Make one suitable inference.
Nyatakan satu inferens yang sesuai. [1 mark]
(b) State one appropriate hypothesis that could be investigated.
Nyatakan satu hipotesisi yang sesuai. [1 mark]
(c) With the use of apparatus such as thread, brass bob, plywood and other apparatus, describe
one experimental framework to investigate the hypothesis stated in (b).
Dengan menggunakan radas seperti benang, pendulum bob, kepingan plywood dan radas lain,
terangkan satu rangka kerja eksperimen untuk menyiasat hipotesis yang dinyatakan dalam (b).
In your description, state clearly the following:
Dalam penerangan anda, jelaskan perkara berikut:
(i) Aim of the experiment.
Tujuan eksperimen.
(ii) Variables in the experiment.
Pembolehubah dalam eksperimen.
(iii) List of apparatus and materials.
Senarai radas dan bahan.
(iv) Arrangement of the apparatus.
Susunan radas.
(v) The procedure of the experiment which include the method of controlling the
manipulated variable and the method of measuring the responding variable.
Prosedur eksperimen yang mengandungi cara mengawal pembolehubah yang
dimanipulasikan dan cara mengukur pembolehubah yang bergerak balas.
(vi) The way you would tabulate the data.
Cara untuk menjadualkan data.
(vii) The way you would analyse the data.
Cara untuk menganalisis data [10 marks]
EXPERIMENT 2.2: VELOCITY VS HEIGHT OF THE SLIDE
Figures show two slides P and Q of different height in a playground.
The two boys
of the same
mass are
sliding down from the top of slides P and Q . The boy at slide P found that he reaches the ground at a
higher speed than a boy at slide Q .
Based on the information and observation above :
(a) Satate one suitable inference. [ 1 mark ]
(b) State one suitable hypotesis. [ 1 mark ]
(c) With the use of apparatus as such as runway, trolleys and other apparatus, describe an
experiment framework to investigate the hypothesis stated in (b)
In your description, state slearly the following :
(i) Aim of the experiment.
(ii) Variables in the experiment.
(iii) List of apparatus and materials.
(iv) Arrangement of the apparatus.
(v) The procedure of the experiment which include the method
of controlling the manipulated variable and the method of
measuring the responding variable.
(vi) The way you would tabulate the data.
(vii) The way you would analyse the data.
[ 10 marks ]
EXPERIMENT 2.4: MASS AND INERTIA
Figure
A boxer tried to push a sandbag which was hanging stationary as shown in Figure (a).
He noticed that initially it was difficult to get the sandbag to start moving. He then tried
to stop the motion of the swinging sandbag as shown in Figure (b). He noticed that it
was more difficult to stop the sandbag than to move it.
Based on the observations;
a. State one suitable inference that can be made.
[1 mark]
b. State one appropriate hypothesis for an investigation.
[1 mark]
c. With the use of apparatus such as G-clamp, jigsaw blade and other
apparatus, describe an experimental framework to test your hypothesis.
In your description, state clearly the following:
(i) Aim of the experiment
(ii) Variables in the experiment
(iii) List of apparatus and materials
(iv) Arrangement of the apparatus
(v) The procedure of the experiment which include the method of controlling
the manipulated variable and the method of measuring the responding
variable
(vi) Describe how you would tabulate the data
(vii) Describe how you would analyse the data
[10 marks]
EXPERIMENT 2.5: MASS VS ACCELERATION (F = ma)
Diagram 3.1 shows a car pulling a heavily packed trailer. The trailer is attached to the car
with a locking mechanism. The car’s engine is exerting a constant force that causes the car
and the trailer to accelerate together. Diagram 3.2 shows what happens when the locking
mechanism fails and the trailer is dislodged. The car lurches forward with an increased
acceleration on its own.
(Rajah 3.1 menunjukkan sebuah kereta sedang menarik sebuah trailer yang penuh muatan.
Suatu mekanisma kunci menghubungkan kereta dengan trailer. Enjin kereta mengenakan satu
daya yang tetap menyebabkan kereta dan trailer mengalami pecutan yang sama.]
Diagram 3.1
Rajah 3.1
Diagram 3.2
Rajah 3.2
Based on the effect onto the car’s acceleration;
Berdasarkan kesan ke atas pecutan kereta:
(a) make an inference.
buat satu inferens.
(b) state an appropriate hypothesis that could be investigated
nyatakan satu hipotesis yang sesuai yang boleh disiasat.
(c) design an experiment to test the hypothesis, using ticker timer, trolley and other
suitable apparatus.
Reka satu eksperimen untuk menguji hipotesis, menggunakan jangka masa detik, troli
dan lain-lain radas yang sesuai
In your description, state clearly the following;
Dalam penerangan anda, jelaskan perkara berikut:
(i) aim of the experiment,
tujuan eksperimen,
(ii) variables in the experiment,
pembolehubah yang terlibat dalam eksperimen,
(iii) list of apparatus and materials,
senarai radas dan bahan,
(iv) arrangement of the apparatus,
susunan radas,
(v) the procedure of the experiment, including the method of controlling the
manipulated variable and the method of measuring the responding variable,
prosedur eksperimen termasuk kaedah mengawal pembolehubah dimanipulasi
dan kaedah mengukur pembolehubah bergerak balas,
(vi) the way you would tabulate the data, and
cara bagaimana anda akan menjadualkan data, dan
(vii) the way you would analyse the data.
cara bagaimana anda akan menganalisis data.
EXPERIMENT 2.7: HOOKE’S LAW
Diagram 4.1 shows a cradle with a new born baby. Diagram 4.2 shows another cradle with a 1
year old baby. Both cradle use identical cradle’s spring. We notice that, the cradle’s spring in
Diagram 4.2 is longer than Diagram 4.1.
Cradle’s spring
Spring buaian Cradle’s spring
Spring buaian
New born baby
Bayi baru lahir
1 year old baby
Bayi berusia 1 tahun
Diagram 4.1 Diagram 4.2
Rajah 4.1 Rajah 4.2
Based on the above information and observations:
(a) State one suitable inference, [1 mark]
(b) State one suitable hypothesis [1 mark]
(c) With the use of apparatus such as a spring, a pin and others, describe one experiment to
investigate the hypothesis stated in (b).
In your description, state clearly the following:
(i) Aim of the experiment.
(ii) Variables in the experiment.
(iii) List of apparatus and materials.
(iv) Arrangement of the apparatus.
(v) The procedure of the experiment which include one method of controlling
the manipulated variable and one method of measuring the responding
variable.
(vi) The way you would tabulate the data.
(vii) The way you would analyse the data.
[10 marks]
EXPERIMENT 2.8: CHANGE IN LENGTH VS VELOCITY
Diagram 3.1 and 3.2 each shows two position of a solid ball which is pressed towards the wall.
The initial position in each diagram is different. The ball moves away from the spring when the
compressive force is removed.
Observe the initial and the final position of the ball in each diagram.
Based on the above information and observations:
(a) State one suitable inference, [1 mark]
(b) State one suitable hypothesis [1 mark]
(c) With the use of apparatus such as a ticker timer, friction compensated track, trolley and
others, describe one experiment to investigate the hypothesis stated in (b).
In your description, state clearly the following:
(i) Aim of the experiment.
(ii) Variables in the experiment.
(iii) List of apparatus and materials.
(iv) Arrangement of the apparatus.
(v) The procedure of the experiment which include one method of controlling
the manipulated variable and one method of measuring the responding
variable.
(vi) The way you would tabulate the data.
(vii) The way you would analyse the data.
[10 marks]
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Science and Design of the Hybrid Rocket EngineD'EverandThe Science and Design of the Hybrid Rocket EngineÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Experiment 2.1: Simple PendulumDocument8 pagesExperiment 2.1: Simple PendulumzoulezPas encore d'évaluation
- Kerja Cuti 5stDocument17 pagesKerja Cuti 5stzoulezPas encore d'évaluation
- PhysicsDocument7 pagesPhysicsiffafifinuhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics SPM F5 and F4: Quiz 1Document2 pagesPhysics SPM F5 and F4: Quiz 1imposter131Pas encore d'évaluation
- Light Paper 3Document9 pagesLight Paper 3Yana AzieyanaPas encore d'évaluation
- F4 Physics Paper 3 Section B Experiments PDFDocument7 pagesF4 Physics Paper 3 Section B Experiments PDFahbingPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment by ChapterDocument18 pagesExperiment by ChapterRed KitePas encore d'évaluation
- Ramalan SPM 2010 FIZIK - Analisa Trial Kertas 3 Bahagian B34 2010Document27 pagesRamalan SPM 2010 FIZIK - Analisa Trial Kertas 3 Bahagian B34 2010A. Suhaimi100% (1)
- Fizik k3 Ting 4Document2 pagesFizik k3 Ting 4dyraidoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Soalan Sains No 10 Latihan Dan JawapanDocument10 pagesSoalan Sains No 10 Latihan Dan JawapanroroyaakopPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Questions and Answers For Paper 3 Section B1Document10 pagesSample Questions and Answers For Paper 3 Section B1Adsham100% (3)
- Homework Week 6Document7 pagesHomework Week 6Rayonesh Rayana100% (1)
- Section A p3Document8 pagesSection A p3Zunaidi JaafarPas encore d'évaluation
- SPM Physics Paper 3Document10 pagesSPM Physics Paper 3Ivan TehPas encore d'évaluation
- P3 2003 QuestionDocument8 pagesP3 2003 QuestionaNNa_RaiHaNPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 3 Section B 2018 BI1Document44 pagesPaper 3 Section B 2018 BI1afham hafiziPas encore d'évaluation
- F4 Mid-Year '09 P3Document9 pagesF4 Mid-Year '09 P3Marz ZamzuriPas encore d'évaluation
- 2018 PDFDocument12 pages2018 PDFDiaa SaberPas encore d'évaluation
- Coimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Eaving Ertificate XaminationDocument12 pagesCoimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Eaving Ertificate XaminationMartim LemePas encore d'évaluation
- Coimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Eaving Ertificate XaminationDocument12 pagesCoimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Eaving Ertificate Xaminationfrank mutalePas encore d'évaluation
- Coimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Eaving Ertificate XaminationDocument12 pagesCoimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Eaving Ertificate Xaminationfrank mutalePas encore d'évaluation
- PBS Band 5 Form 2 Chapter 9Document4 pagesPBS Band 5 Form 2 Chapter 9lccjane8504Pas encore d'évaluation
- SPM Physics Paper 3 GuideDocument5 pagesSPM Physics Paper 3 GuideMohamad HanifPas encore d'évaluation
- Inkuiri Berstruktur - Fizik F4Document2 pagesInkuiri Berstruktur - Fizik F4WAN NOOR AZILAH BT WAN UMAR MoePas encore d'évaluation
- Paper IIIDocument4 pagesPaper IIIyokecheng20003826Pas encore d'évaluation
- P3 2003 QuestionDocument8 pagesP3 2003 QuestionWong ChinPas encore d'évaluation
- Section A Study Guide Plus QuestionsDocument31 pagesSection A Study Guide Plus QuestionsCameronPas encore d'évaluation
- Coimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Eaving Ertificate XaminationDocument12 pagesCoimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Eaving Ertificate XaminationBrãñdøn DzîñgáíPas encore d'évaluation
- Coimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Eaving Ertificate XaminationDocument12 pagesCoimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Eaving Ertificate Xaminationfrank mutalePas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet: Hooke's Law: Q1.A Student Suspended A Spring From A Laboratory Stand and Then Hung A Weight From TheDocument11 pagesWorksheet: Hooke's Law: Q1.A Student Suspended A Spring From A Laboratory Stand and Then Hung A Weight From Thefatimahehe31323Pas encore d'évaluation
- Module 5 - Paper 3 Section A / Bahagian ADocument11 pagesModule 5 - Paper 3 Section A / Bahagian AmathseditPas encore d'évaluation
- F4 Physics Paper 3 Section B ExperimentsDocument7 pagesF4 Physics Paper 3 Section B Experimentsjajabeans80% (5)
- 1 A Student Carries Out An Experiment To Investigate The Relationship Between Current andDocument5 pages1 A Student Carries Out An Experiment To Investigate The Relationship Between Current andneoo1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Coimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Eaving Ertificate XaminationDocument12 pagesCoimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission: Eaving Ertificate Xaminationfrank mutalePas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Leaving Certifi Cate Examination, 2017 Triailscrúdú Na Hardteistiméireachta, 2017Document12 pagesPre-Leaving Certifi Cate Examination, 2017 Triailscrúdú Na Hardteistiméireachta, 2017Diaa SaberPas encore d'évaluation
- Co Sta Oimis Ate Ex Iún Na Xamin A Scrú Nation Úduith S Com He Stá Mmiss Áit SionDocument12 pagesCo Sta Oimis Ate Ex Iún Na Xamin A Scrú Nation Úduith S Com He Stá Mmiss Áit Sionfrank mutalePas encore d'évaluation
- Phys 1011 Worksheet IDocument9 pagesPhys 1011 Worksheet IAHMMED AHMMED100% (1)
- Science Revision KSSM C11Document5 pagesScience Revision KSSM C11Ziyi EngPas encore d'évaluation
- Centripetal Force and Circular Motion Lab CC NGSS Revision 2014Document2 pagesCentripetal Force and Circular Motion Lab CC NGSS Revision 2014pepe zimbaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Sem Form 5 (Paper 3)Document9 pages1st Sem Form 5 (Paper 3)pallz007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7Document6 pagesChapter 7Zainal Abidin MohammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre-Leaving Certifi Cate Examination, 2016 Triailscrúdú Na Hardteistiméireachta, 2016Document12 pagesPre-Leaving Certifi Cate Examination, 2016 Triailscrúdú Na Hardteistiméireachta, 2016Diaa SaberPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 6, ExerciseDocument2 pagesModule 6, ExerciseTeoh MilayPas encore d'évaluation
- General Physics 1 Laboratory ManualDocument61 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Laboratory Manualmintimai01Pas encore d'évaluation
- Centripetal Force and Circular Motion Lab CC NGSS Revision 2014Document2 pagesCentripetal Force and Circular Motion Lab CC NGSS Revision 2014bob sagetPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Paper 3 (Topic 4 - Heat P3)Document15 pagesQuestion Paper 3 (Topic 4 - Heat P3)Nur Syidah100% (1)
- Expt 1 - PHY400 - MeasurementDocument5 pagesExpt 1 - PHY400 - MeasurementMubarak Noor AzliPas encore d'évaluation
- Class XI Physics Target Paper: Ch#01 The Scope of Physics Short Q/A Long Q/A NumericalDocument3 pagesClass XI Physics Target Paper: Ch#01 The Scope of Physics Short Q/A Long Q/A Numericalkashif ibrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- PAPER 3 - SECTION B - PhysicsDocument21 pagesPAPER 3 - SECTION B - PhysicsLee Li JiePas encore d'évaluation
- Class-XI IMP Questions 2023-24Document3 pagesClass-XI IMP Questions 2023-24AbhishekPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet #1g: Hydrostatic Pressure & Archimedes' PrincipleDocument3 pagesWorksheet #1g: Hydrostatic Pressure & Archimedes' PrincipleLuke NancooPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 3 Part B Sms Alam ShahDocument10 pagesPaper 3 Part B Sms Alam ShahThalhah AliasPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 1 - Statistical Analysis LabDocument7 pagesLab 1 - Statistical Analysis Labdibia collinsPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample: 1 (A) Small Car AfterDocument1 pageSample: 1 (A) Small Car AfterSiti Hajar ZainuddinPas encore d'évaluation
- A Correlation Study of Methods of Matrix Structural Analysis: Report to the 14th Meeting, Structures and Materials Panel Advisory Group for Aeronautical Research and Development, NATO, Paris, France, July 6, 1962D'EverandA Correlation Study of Methods of Matrix Structural Analysis: Report to the 14th Meeting, Structures and Materials Panel Advisory Group for Aeronautical Research and Development, NATO, Paris, France, July 6, 1962Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Understanding Proof: Explanation, Examples and Solutions of Mathematical ProofD'EverandUnderstanding Proof: Explanation, Examples and Solutions of Mathematical ProofPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.2 Understanding Pressure in LiquidDocument16 pages3.2 Understanding Pressure in LiquidzoulezPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.10 Work, Energy, Power N EfficiencyDocument5 pages2.10 Work, Energy, Power N EfficiencyzoulezPas encore d'évaluation
- Senarai 4pdDocument1 pageSenarai 4pdzoulezPas encore d'évaluation
- Laporan Kereta SolarDocument24 pagesLaporan Kereta SolarzoulezPas encore d'évaluation
- Safety Features in CarDocument4 pagesSafety Features in CarzoulezPas encore d'évaluation
- Kerja Cuti Sains 5paDocument4 pagesKerja Cuti Sains 5pazoulezPas encore d'évaluation
- Ground PlaneDocument1 pageGround Planeaeronautical rajasPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz - Ionic EquilibriumDocument2 pagesQuiz - Ionic EquilibriumSiddPas encore d'évaluation
- An Infallible JusticeDocument7 pagesAn Infallible JusticeMani Gopal DasPas encore d'évaluation
- 1C09-08 Design For Seismic and Climate ChangesDocument31 pages1C09-08 Design For Seismic and Climate ChangesSanketWadgaonkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Squares and Square Roots Chapter Class ViiiDocument24 pagesSquares and Square Roots Chapter Class ViiiManas Hooda100% (1)
- Lesson 24 - Laminate Modeling - Rev C PDFDocument20 pagesLesson 24 - Laminate Modeling - Rev C PDFraduga_fbPas encore d'évaluation
- A General Strategy For The Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide-Based CompositesDocument8 pagesA General Strategy For The Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide-Based CompositesCristian Gonzáles OlórteguiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ingles y Español Unidad 7Document9 pagesIngles y Español Unidad 7Pier Jhoani Ñañez LlanosPas encore d'évaluation
- Maximum Influence at A Point Dueto A Series of Concentrated LoadsDocument12 pagesMaximum Influence at A Point Dueto A Series of Concentrated LoadsAyad SlabyPas encore d'évaluation
- MalachiteDocument2 pagesMalachiteAkhil KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- HYW-17 T5 S5: Industrial Range MobileDocument6 pagesHYW-17 T5 S5: Industrial Range MobileghostshotPas encore d'évaluation
- Glamour Secrets Prices For Products and ServicesDocument1 pageGlamour Secrets Prices For Products and ServiceslocalintheknowPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Kingdoms of OrganismsDocument13 pages5 Kingdoms of OrganismsChoirul Anam100% (2)
- DST Tmpm370fydfg-Tde en 21751Document498 pagesDST Tmpm370fydfg-Tde en 21751trân văn tuấnPas encore d'évaluation
- API 571 Quick ReviewDocument32 pagesAPI 571 Quick ReviewMahmoud Hagag100% (1)
- Seminar1final ReviewDocument19 pagesSeminar1final ReviewMounika ChPas encore d'évaluation
- Dragons and Winged SerpentsDocument5 pagesDragons and Winged SerpentsYuna Raven100% (1)
- Lecture2 v1Document69 pagesLecture2 v1c.ronaldo2012777Pas encore d'évaluation
- Notes StressDocument4 pagesNotes StressRohitKalraPas encore d'évaluation
- RA - Ducting WorksDocument6 pagesRA - Ducting WorksResearcherPas encore d'évaluation
- Company ProfileDocument36 pagesCompany ProfileShahzad Nasir SayyedPas encore d'évaluation
- Model A SOLUTIONSDocument8 pagesModel A SOLUTIONSasdfPas encore d'évaluation
- Nature 00869Document3 pagesNature 00869鍾宗霖Pas encore d'évaluation
- Course Specification Course Title: Basic Architectural DraftingDocument1 pageCourse Specification Course Title: Basic Architectural DraftingDinah Fe Tabaranza-OlitanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 13 Managerial AccountingDocument168 pagesChapter 13 Managerial AccountingChandler Schleifs100% (4)
- Ligamentele LargiDocument2 pagesLigamentele LargiIoana IonicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Eurolite Led TMH 7 PDFDocument2 pagesEurolite Led TMH 7 PDFSarahPas encore d'évaluation
- Reservoir Rock PropertiesDocument148 pagesReservoir Rock Propertiesiscribdusername100% (7)
- Time Series - Practical ExercisesDocument9 pagesTime Series - Practical ExercisesJobayer Islam TunanPas encore d'évaluation
- Recipes G.garvin Copy1 Scribd 5Document7 pagesRecipes G.garvin Copy1 Scribd 5Peggy Bracken StagnoPas encore d'évaluation