Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
AQL Inspection Manual Dictionary: Acceptance Number
Transféré par
mehedy071Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
AQL Inspection Manual Dictionary: Acceptance Number
Transféré par
mehedy071Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
AQL Inspection Manual
Dictionary
Acceptance Number. The acceptance number is the maximum number of defects or
defective units in the sample that will permit acceptance lot or batch.
AQL has two different definitions due to standard changes.
MIL-STD-105E, ISO 2859-1 (1999)
Acceptable Quality Level. The acceptable level (AQL) is defined as the maximum
percent defective (or the maximum number of defects per hundred units) that, for
purpose of sampling inspection, can be considered satisfactory as a process average.
The sampling plans most frequently used by the department of Defense are based on
the AQL.
ANSI/ASQC Z1.4-2003
Acceptance Quality Limit. The AQL is the quality level that is the worst tolerable
process average when a continuing series of lots is submitted for acceptance sampling.
The following note on the meaning of AQL was introduced with the ANSI/ASQ Z1.4-
2003 revision.
The concept of AQL only applies when an acceptance sampling scheme with rules for
switching between normal, tightened and reduced inspection and discontinuance of
sampling inspection is used. These rules are designed to encourage suppliers to have
process averages consistently better than the AQL. If suppliers fail to do so, there is a
high probability of being switched from normal inspection to tightened inspection where
lot acceptance becomes more difficult. Once on tightened inspection, unless corrective
action is taken to improve product quality, it is very likely that the rule requiring
discontinuance of sampling inspection will be invoked.
Although individual lots with quality as bad as the AQL can be accepted with fairly high
probability, the designation of an AQL does not suggest that this is necessarily a
desirable quality level. The AQL is a parameter of the sampling scheme and should not
be confused with a process average which describes the operating level of a
manufacturing process. It is expected that the product quality level will be less than the
AQL to avoid excessive non accepted lots.
The AQL values are defined as percent nonconforming or defects or nonconformities
per hundred units.
Defects and Defectives. A defect is any nonconformance of the unit of product with the
specified requirements. A defective is a unit of product which contains one or more
defects. Failure to meet requirements with respect to quality characteristics are usually
described in terms of defects or defectives.
Critical - A critical defect is on that judgment and experience indicate is likely to:
a. result in hazardous or unsafe conditions for individuals using, maintaining, or
depending upon the products; or
b. prevent performance of the tactical function of a major end item. A critical
defective is a unit of product that contains one or more critical defects.
Major - A major defect is one, other than critical, that is likely to result in failure, or to
reduce materially the usability of the unit of product for its intended purpose. A major
defective is a unit of product that contains one or more major defects.
Minor - A minor defect is one that is not likely to reduce materially the usability of the
unit of product for its intended purpose, or is a departure from established standards
having little bearing on the effective use or operation of the unit of product. A Minor
defective is a unit of product that contains one or more defects.
Double Sampling Plan. A double sampling plan involves sampling inspection in which
the inspection of the first sample to a decision to accept, to reject or to take a second
sample. The inspection of a second sample, when required, lead to a decision to accept
or reject.
Drawing of Samples. Basic to sampling inspection is the assurance that the sample
selected from a quantity of units represents the quality of that quantity of units. Hence,
the procedure used to select units from a lot must be such that it assures a sample free
of bias.
Expression of Nonconformance. The extent of nonconformance of product shall be
expressed either in terms of percent defective or in terms of defects per hundred units
(DHU).
Defects per Hundred Units. The number of defects per hundred units of any given
quantity units of product is one hundred times the number of defects contained therein
(one or more defects being possible in any unit of product) divided by the total number
of units of product, i.e.:
number of defectives x 100
Defects per hundred units =
number of units inspected
Inspection. Inspection is the process of measuring, examining, testing, or otherwise
comparing the unit of product with the requirements.
Inspection by Attribute. Inspection by attributes is inspection where by either the unit
of product is classified simply as defective or non-defective, or the number of defects in
the unit of product is counted, with respect to a given requirement or set of
requirements.
Inspection Levels. The standards provides for three general inspection levels and four
special inspection levels. These seven levels permit the user to balance the cost of
inspection against the amount of protection required.
Lot or Batch. The term lot or batch shall mean "inspection lot" or "inspection batch" i.e.,
a collection of units of product from which a sample is to drawn and inspected to
determine conformance with the acceptance criteria, any may differ from a collection of
units designated as a lot or batch for other purposes (e.g., production, shipment, etc.).
Nonconformance. Nonconformance may be defined as the failure of a unit of product
to conform to specified requirements for any stated quality characteristic. The extent of
nonconformance of product to the required quality characteristics shall be expressed
either in terms of percent defective or in terms of defects per hundred units (DHU).
Normal Inspection. Normal inspection is that which is used where there is no evidence
that the quality of product being submitted is better or poorer than the specified quality
level.
Percent Defective. The percent defective of any given quantity of units of product is
one hundred times the number of defective units of product contained therein divided by
the total number of units of product, i.e.: Percent defective = number of defectives
x100 / number of units inspected
Reduced Inspection. Reduced inspection under a sampling plan uses the same quality
level as for normal inspection, but requires a smaller sample for inspection.
Rejection Number. The rejection number is the minimum number of defects or
defective units in the sample that will cause rejection of the lot represented by the
sample.
Representative Sampling. When appropriate, the number of units in the sample shall
be selected in proportion to the size of sub-lots or sub-batches, or parts or the lot or
batch, identified by some rational criterion. When representative sampling is used, the
units from each part of the lot or batch shall be selected at random.
Resubmitted Lots or Batches. Lots or batches found unacceptable shall be
resubmitted for reinspection only after all units are re-examined or retested and all
defective units are removed or defects corrected. The responsible authority shall
determine whether normal or tightened inspection shall be used and whether
reinspection shall include all types or classes of defects or only the particular types or
classes of defects which caused initial rejection.
Sample. A sample consists of one or more units of product drawn from a lot or batch,
the units of the sample being selected at random without regard to their quality. The
number of product in the sample is the sample size.
Sampling Plans. A lot sampling plan is a statement of the sample size or sizes to be
used and the associated acceptance and rejection numbers.
Single Sample Plan. A single sampling plan is a type of sampling plan by which the
results of a single sample from an inspection lot are conclusive in determining
acceptability. The number of sample units inspected shall be equal to the sample size
given by the plan.
Severity of Inspection. The severity of inspection concerns the total amount, kind and
extent of inspection specified by the quality assurance provisions established for the
unit of product, or as dictated by quality history.
Unit of Production. The unit of product is the thing inspected in order to determine its
classification as defective or non-defective or to count the number of defects. It may be
a single article, a pair, a set, a length, an area, an operation, a volume, a component of
an end product, or the end product itself. The unit of product may or may not be the
same as the unit of purchase, supply, production, or shipment.
Tightened Inspection. Tightened inspection under a sampling procedure plan uses the
quality level as for normal inspection, but requires more stringent acceptance criteria.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Asq Z1.4 PDFDocument96 pagesAsq Z1.4 PDFj0% (1)
- Ansi Asq Z1 4-2003Document96 pagesAnsi Asq Z1 4-2003Hami KeserciPas encore d'évaluation
- Certified Quality Engineer Problem Bank 3Document34 pagesCertified Quality Engineer Problem Bank 3jackanddiane1100% (2)
- Inspection PDFDocument20 pagesInspection PDFSEGU PRATHEEK100% (1)
- First Article Inspection InstructionDocument21 pagesFirst Article Inspection Instructiongranburyjohnstevens100% (1)
- Certified Quality Auditor (ASQ Sample Exam Paper)Document24 pagesCertified Quality Auditor (ASQ Sample Exam Paper)Farhan Shariff86% (7)
- CERTIFIED Quality EngineerDocument16 pagesCERTIFIED Quality Engineeracadjournals. comPas encore d'évaluation
- Supplier Quality Requirements Manual AMWAYDocument22 pagesSupplier Quality Requirements Manual AMWAYlizmillosbtaPas encore d'évaluation
- CPGP CourseDocument7 pagesCPGP CourseantonygamalpharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Temario CQPA - Certified Quality Process AnalystDocument6 pagesTemario CQPA - Certified Quality Process AnalystAngel Cortez EspinozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Statical Sampling UpdatedDocument56 pagesStatical Sampling UpdatedPrashant PuriPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Prepare For Asq Cqe Exam?Document20 pagesHow To Prepare For Asq Cqe Exam?mchaumiPas encore d'évaluation
- AQL Inspection ManualDocument24 pagesAQL Inspection ManualFerdous Khan Rubel100% (3)
- Acceptable Quality Level (AQL) - Issues and ResolutionDocument4 pagesAcceptable Quality Level (AQL) - Issues and Resolutionb-consultant960Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sampling Plan For Product InspectionDocument16 pagesSampling Plan For Product InspectionZaman ParvezPas encore d'évaluation
- DCMA Sampling GuidanceDocument4 pagesDCMA Sampling GuidanceAqueous CarlosPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality InspectionDocument60 pagesQuality InspectionAdina Claudia BesliuPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Acceptable Quality Level PDFDocument4 pagesWhat Is Acceptable Quality Level PDFمصطفى عبدالرحيمPas encore d'évaluation
- Sampling and InspectionDocument25 pagesSampling and InspectionAYUSHPas encore d'évaluation
- AQL TrainingDocument33 pagesAQL TrainingIrfan Khan100% (1)
- Acceptable Quality LevelDocument3 pagesAcceptable Quality LevelAmarech YigezuPas encore d'évaluation
- Acceptance SamplingDocument39 pagesAcceptance SamplingAhmedShabanPas encore d'évaluation
- AQLDocument6 pagesAQLarivaazhiPas encore d'évaluation
- AQL - What Is An Acceptable Quality LevelDocument5 pagesAQL - What Is An Acceptable Quality LevelpragantraPas encore d'évaluation
- AQL Calculator BetaDocument3 pagesAQL Calculator BetafitrahPas encore d'évaluation
- Ansi Asq - Z1.4 2003Document212 pagesAnsi Asq - Z1.4 2003mr.nguyenkPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Select AQL and Inspection LevelDocument67 pagesHow To Select AQL and Inspection LevelNavnath Tamhane100% (1)
- Quality in ManufacturingDocument3 pagesQuality in ManufacturingMahendar SdPas encore d'évaluation
- General Guidelines of SamplingDocument69 pagesGeneral Guidelines of Samplingpiyush64173Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Acceptance Sampling by MoinDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Acceptance Sampling by MoinChowdhury Jony MoinPas encore d'évaluation
- Acceptance Sampling InspectionDocument8 pagesAcceptance Sampling InspectionsachinPas encore d'évaluation
- AQL SamplingDocument4 pagesAQL SamplingBella WatiPas encore d'évaluation
- TQM1Document50 pagesTQM1mohsinmakkiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cqa PDFDocument39 pagesCqa PDFcasmith430% (1)
- Manual Sampling Guidelines 25-05-2016Document47 pagesManual Sampling Guidelines 25-05-2016Rajam SankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Tools WorkshopDocument45 pagesQuality Tools WorkshopAhmed Hassan ShehataPas encore d'évaluation
- CertifiedqualityengineerDocument10 pagesCertifiedqualityengineersriram100% (1)
- Overview PF CPGPDocument26 pagesOverview PF CPGPmmmmm0% (1)
- Lot Size: Acceptable Quality Level (AQL)Document1 pageLot Size: Acceptable Quality Level (AQL)Alberto ItzincabPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Manual: With Our Commitment, Comes Your Success With Your Success, Comes Our!Document26 pagesQuality Manual: With Our Commitment, Comes Your Success With Your Success, Comes Our!erreeteshPas encore d'évaluation
- Compare ISO 9001 AS9100c PDFDocument1 pageCompare ISO 9001 AS9100c PDFRamses SalazarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost of QualityDocument18 pagesCost of QualityMadhupam BansalPas encore d'évaluation
- Certified Quality Auditor Certification OverviewDocument10 pagesCertified Quality Auditor Certification OverviewStephen Deas50% (4)
- QM0012 Statistical Process Control & Process CapabilityDocument19 pagesQM0012 Statistical Process Control & Process CapabilityajayvmehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aql StandardDocument13 pagesAql StandardVaradhan Stylewiz-incPas encore d'évaluation
- Maxim Qa ManualDocument83 pagesMaxim Qa ManualRoselyn B. ManansalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Asq Certification Exam Pass RateDocument13 pagesAsq Certification Exam Pass RateEduPas encore d'évaluation
- Iso 17025Document3 pagesIso 17025Gowrisanthosh PalikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundementals of Torque CalibrationDocument137 pagesFundementals of Torque CalibrationMiguel Alfonso Ruiz MendezPas encore d'évaluation
- ANSI Z142008 - 2013 TabletsDocument96 pagesANSI Z142008 - 2013 Tabletsmegacity100% (3)
- Advanced Product Quality Planning A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionD'EverandAdvanced Product Quality Planning A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionPas encore d'évaluation
- MIL-STD-105E, ISO 2859-1 (1999) : Acceptance NumberDocument12 pagesMIL-STD-105E, ISO 2859-1 (1999) : Acceptance NumberShubham TilaraPas encore d'évaluation
- SQC: Three Broad CategoriesDocument12 pagesSQC: Three Broad CategoriesRohitPas encore d'évaluation
- Iqc Chapter 01 PDFDocument8 pagesIqc Chapter 01 PDFNaveen Kumar GunisettyPas encore d'évaluation
- DCMA Sampling GuidanceDocument4 pagesDCMA Sampling GuidanceGembong Van BeethovenPas encore d'évaluation
- AQL and AOQL-mandeep, Nishiket, Dhananjay, Nithil, ShubhamDocument8 pagesAQL and AOQL-mandeep, Nishiket, Dhananjay, Nithil, ShubhamNaina DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Sampling PlansDocument16 pagesSampling PlanssamadmsinPas encore d'évaluation
- The Course Is Designed To Provide Quality PractitionersDocument5 pagesThe Course Is Designed To Provide Quality PractitionersRabia ZulqarnainPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment-6 (Familiarization ofDocument3 pagesExperiment-6 (Familiarization ofacehabiniPas encore d'évaluation
- TextDocument2 pagesTextArron LuPas encore d'évaluation
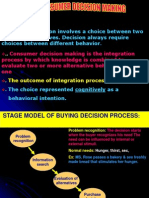
- Consumer Decision MakingDocument8 pagesConsumer Decision Making9986212378Pas encore d'évaluation
- Autodesk 2015 Products Direct Download LinksDocument2 pagesAutodesk 2015 Products Direct Download LinksALEXPas encore d'évaluation
- IOT Practical 2021-22Document25 pagesIOT Practical 2021-22Abhi AbhiPas encore d'évaluation
- J2018Sudarman-JPP-Development of Interactive Infographic Learning Multimedia - PDF InfografisDocument14 pagesJ2018Sudarman-JPP-Development of Interactive Infographic Learning Multimedia - PDF InfografissafiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Malhotra 01Document30 pagesMalhotra 01adiba10mktPas encore d'évaluation
- Hand Powered Drilling Tools and MachinesDocument70 pagesHand Powered Drilling Tools and Machinessmole79Pas encore d'évaluation
- Project Management FrameworkDocument30 pagesProject Management FrameworkbharathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Siemens - Sitrans Lr200Document192 pagesSiemens - Sitrans Lr200Jonathan Olivier Salgado NesbetPas encore d'évaluation
- F 3215 - 16Document4 pagesF 3215 - 16jose floresPas encore d'évaluation
- United States v. Juvenal Martinez Alvarado, 321 F.2d 336, 2d Cir. (1963)Document5 pagesUnited States v. Juvenal Martinez Alvarado, 321 F.2d 336, 2d Cir. (1963)Scribd Government DocsPas encore d'évaluation
- FIN350 Quiz 2 Monday First Name - Last Name - Version BDocument6 pagesFIN350 Quiz 2 Monday First Name - Last Name - Version BHella Mae RambunayPas encore d'évaluation
- Pearl and Dean (Phil.) Inc. v. Shoemart, Inc. and North Edsa Marketing Inc GR 148222, August 15, 2003Document13 pagesPearl and Dean (Phil.) Inc. v. Shoemart, Inc. and North Edsa Marketing Inc GR 148222, August 15, 2003Jeng Pion100% (1)
- SynopsysDocument27 pagesSynopsyssalmanPas encore d'évaluation
- MGT610-FinalTerm-By Rana Abubakar KhanDocument28 pagesMGT610-FinalTerm-By Rana Abubakar KhanAtif MubasharPas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm: Mathematics For Engineers (W2021)Document5 pagesMidterm: Mathematics For Engineers (W2021)spppppPas encore d'évaluation
- PDS Class Test 2: Let Us Establish The Pointer From Autumn Break To PDS!!!Document26 pagesPDS Class Test 2: Let Us Establish The Pointer From Autumn Break To PDS!!!Abhinaba SahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cis 252 Lab1Document4 pagesCis 252 Lab1Jack RyanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2012 Country Conference PamphletDocument8 pages2012 Country Conference PamphletNSW LaborPas encore d'évaluation
- A Smart Blind Stick For Aiding Visually Impaired PeopleDocument3 pagesA Smart Blind Stick For Aiding Visually Impaired PeopleInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S2213343717303950 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S2213343717303950 MainSeyram DavidPas encore d'évaluation
- PA-STARNet Overview and Fact SheetDocument2 pagesPA-STARNet Overview and Fact SheetDaryl JonesPas encore d'évaluation
- Preboard MsteDocument6 pagesPreboard MsteWinter DeenePas encore d'évaluation
- Stacie Adams: Professional Skills ProfileDocument1 pageStacie Adams: Professional Skills Profileapi-253574880Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fullsummary PDFDocument118 pagesFullsummary PDFEsa SulyPas encore d'évaluation
- 108-Article Text-409-3-10-20200211Document8 pages108-Article Text-409-3-10-20200211NadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Listing of SecuritiesDocument5 pagesListing of SecuritiesticktacktoePas encore d'évaluation
- 5 - GSR2014 - Full Report - Low Res PDFDocument216 pages5 - GSR2014 - Full Report - Low Res PDFPavel VicentiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Momentum Theory - A New Calculation of Blast Design and Assessment of Blast VibrationsDocument11 pagesMomentum Theory - A New Calculation of Blast Design and Assessment of Blast VibrationshectorPas encore d'évaluation