Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Presentation As Guest 8857 130708 Service Quality 2 Others Misc PPT Power Point
Transféré par
Shreemant ShekharDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Presentation As Guest 8857 130708 Service Quality 2 Others Misc PPT Power Point
Transféré par
Shreemant ShekharDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
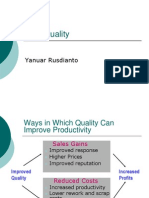
Service Quality 2 : Service Quality 2 Designing and Achieving Service Quality Objectives : Objectives After this session you
will be able to; Discuss the scope of service quality Illustrate methods applied to design quality in Services Describe tools used in achieving Service Quality Use a fishbone chart in a cause and effect analysis Scope of Service Quality : Scope of Service Quality Fitzsimmons proposes viewing quality from five perspectives Content Are standard procedures being followed? Process Is the sequence of events in the service process appropriate? Structure Are the physical facilities and organisational design adequate for the service? Outcome What change in status has the service effected? Impact What is the long range effect of the service on the consumer? Quality Service by Design : Quality Service by Design Incorporation of Quality in the Service Package Supporting facility Facilitating goods Explicit services Implicit services Table 10.4 (text pp 281) : Table 10.4 (text pp 281) Service Package Feature Attribute or Requirement Measurement Nonconformance Corrective action Definition of Quality : Definition of Quality By using a quality system to maintain conformance to the design requirements which definitional approach to quality is being used? Definition of Quality : Definition of Quality Crosby defines quality as conformance to requirementsThis means defining explicitly in measurable terms what constitutes conformance to requirements Quality is seen as an action-oriented activity requiring corrective measures when non-conformance occurs Quality Service by Design : Quality Service by Design Methods Taguchi methods Robust design to ensure proper functioning under adverse conditions Poka-yoke Checklists or devises that do not let the employee make a mistake Quality Function Deployment House of quality Central belief that products should be designed to reflect the customers desires and tastes thereby coordinating design, manufacturing and marketing Achieving Service Quality : Achieving Service Quality Cost of Quality Prevention Detection Internal failure External failure Prevention : Prevention Costs associated with operations or activities that keep failure from happening and minimise detection costs Examples Quality planning Recruitment and selection Training programmes Quality improvement projects Detection : Detection Costs incurred to ascertain the condition of a service to determine whether it conforms to quality standards Examples Periodic inspection Process control Collecting quality data Internal failure : Internal failure Costs incurred to correct nonconforming work before delivery to the customer Examples Scrapped reports and forms Rework Downtime External failure : External failure Costs incurred to correct nonconforming work after delivery to the customer or to correct work that did not satisfy a customers specified needs Examples Negative word of mouth Loss of future business Investigation time Slide 14: In manufacturing companies external and internal failure costs together accounted for 50% to 80% of the total cost of quality Juran suggests that $1 invested in prevention is worth $100 in detection costs and $10,000 in failure costs Tools for Achieving Service Quality : Tools for Achieving Service Quality Service Process Control Statistical Process Control
Service Process Control : Service Process Control The manufacturing based approach to quality focuses on conformance to internally developed specifications. The control of quality is viewed as a feedback control system comparing output with a standard The next overhead shows the basic control cycle as applied to service control process Service Process Control : Service Process Control Resources Identify reason for nonconformance Establish measure of performance Monitor conformance to requirements Take corrective action Service concept Customer input Customer output Service process Difficulties in implementation : Difficulties in implementation Defining service performance measures Intangibility of services Simultaneous production and consumption Customers are asked to evaluate the service after the factBy focusing on the delivery process itself these difficulties may be overcome statistical process control Statistical Process Control : Statistical Process Control What should happen if the process is not performing as expected? An investigation to identify the cause and to suggest corrective action Could the variance be a result of random occurrences and not a process failure? Is change necessary? Constructing and Using a Quality Control Chart : Constructing and Using a Quality Control Chart Decide on some measure of service system performance Collect representative historical data form which estimates of population mean and variance for the system performance can be made Decide on a sample size and calculate +/-3 standard deviation control limits Graph the control chart as a function of sample mean values versus time Constructing and Using a Quality Control Chart : Constructing and Using a Quality Control Chart Plot sample means collected at random on the chart Process in control (sample mean falls within control limits Process out of control (sample mean falls outside control limits, therefore; Evaluate the situation Take corrective action Check results of action Update the control chart and incorporate new data Control Charts : Control Charts Two types based on the type of performance measure Variable control charts record measurements that permit fractional values e.g. length, weight, time Attribute control charts record discrete data e.g. the number of errors as a percentage of the total Slide 23: Fishbone Chart Equipment Personnel Procedure Material Other Delayed Flight Departure Fishbone analysis (Ishikawa chart) : Fishbone analysis (Ishikawa chart) The analysis begins with the problem at the head and traces the major categories of causes along the spine Usual causes Personnel Procedure Equipment Material Other Fishbone Analysis : Fishbone Analysis Causes are eliminated through discussion and consensus and remaining causes targeted for additional data gathering See Midway example pp 293 in text Control Chart of Departure Delays : Control Chart of Departure Delays 1983 target 1983 lower limit 1982 1983 Flight Departure Delay Fishbone Chart : Flight Departure Delay Fishbone Chart Equipment Personnel Procedure Material Other Aircraft late to gate Late arrival Gate occupied Mechanical failures Late pushback tug Weather Air traffic Late food service Late fuel Late baggage to aircraft Gate agents cannot process passengers quickly enough Too few agents Agents undertrained Agents undermotivated Agents arrive at gate late Late cabin cleaners Late or unavailable cockpit crews Late or unavailable cabin crews Poor announcement of departures Weight an balance sheet late Delayed checkin procedure Confused seat selection Passengers bypass checkin counter Checking oversize baggage Issuance of boarding pass Acceptance of late passengers Cutoff too close to departure time Desire to protect late passengers Desire to help companys income Poor gate locations Delayed Flight Departure Pareto Analysis :
Pareto Analysis Data is arranged so that causes of a problem are ordered in descending frequency of occurrence 80/20 rule Apply the rule to the Midway example Pareto Analysis of Flight Departure Delay : Pareto Analysis of Flight Departure Delay All stations, except hub Newark Washington(national) Percentage Percentage Percentage of Cumulative of Cumulative of Cumulative incidences percentage incidences percentage incidences percentage Late 53.3 53.3 Late 23.1 23.1 Late 33.3 33.3 passengers passengers passengers Waiting for 15.0 68.3 Waiting for 23.1 46.2 Waiting for 33.3 66.6 pushback pushback pushback Waiting for 11.3 79.6 Waiting for 23.1 69.3 Late weight 19.0 85.6 fueling fueling and balance sheet Late weight 8.7 88.3 Cabin 15.4 84.7 Waiting for 9.5 95.1 and balance cleaning and fueling sheet supplies Summary : Summary In this session we Discussed the scope of service quality Illustrated methods applied to design quality in Services Described tools used in achieving Service Quality Used a fishbone chart in a cause and effect analysis Essay : Essay Customer loyalty is only due to the lack of a better alternativeDiscuss
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Operational Auditing Handbook: Auditing Business and IT ProcessesD'EverandThe Operational Auditing Handbook: Auditing Business and IT ProcessesÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (4)
- Controllership: The Work of the Managerial AccountantD'EverandControllership: The Work of the Managerial AccountantPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Analysis WSDDocument28 pagesProcess Analysis WSDAkhilesh ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- MDM TQMDocument5 pagesMDM TQMMuhammad Tayyab100% (1)
- Operations MGMT - AIMADocument549 pagesOperations MGMT - AIMATata SatishkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- SM IiiDocument11 pagesSM IiiAnonymous lZ0hmpoFPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost of QualityDocument10 pagesCost of QualityJagadish M Alokh GowdaPas encore d'évaluation
- Improving Service Quality and ProductivityDocument23 pagesImproving Service Quality and ProductivityUtsav MahendraPas encore d'évaluation
- Total Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key ElementsDocument35 pagesTotal Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key Elementsronski17Pas encore d'évaluation
- Service Quality Management & MeasurementDocument22 pagesService Quality Management & MeasurementKumen22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Supplier Audit ChecklistDocument16 pagesSupplier Audit Checklistvoigte0% (1)
- Cost of Quality PDFDocument29 pagesCost of Quality PDFSenthil KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Om 2Document80 pagesOm 2Mantasha AsadPas encore d'évaluation
- GAP AnalysisDocument85 pagesGAP AnalysisTenzin Tashi75% (4)
- Risk Assessment: Fig. 1 - Example of Failure Mode, Failure Cause, Task and MonitoringDocument10 pagesRisk Assessment: Fig. 1 - Example of Failure Mode, Failure Cause, Task and MonitoringGaneshrudPas encore d'évaluation
- Subjective CSQADocument46 pagesSubjective CSQAAdam TuckerPas encore d'évaluation
- COPQDocument8 pagesCOPQJocelyn Garcia100% (1)
- Production MangementDocument66 pagesProduction MangementHARSHIT KUMAR GUPTA 1923334Pas encore d'évaluation
- Airports Total Quality ManagementDocument87 pagesAirports Total Quality ManagementmuhamadmomtazPas encore d'évaluation
- Global Supplier Quality System AssessmentDocument11 pagesGlobal Supplier Quality System AssessmentPvinoth000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 1 6331Document4 pagesAssignment 1 6331ALIKNFPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk Assessment: Fig. 1 - Example of Failure Mode, Failure Cause, Task and MonitoringDocument11 pagesRisk Assessment: Fig. 1 - Example of Failure Mode, Failure Cause, Task and MonitoringGaneshrud100% (1)
- Project Quality ManagementDocument41 pagesProject Quality ManagementhaithamaePas encore d'évaluation
- APQP - in ProgressDocument19 pagesAPQP - in ProgressreshunkPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Five Quality Management and Control 5.1. Overview of Total Quality Management and Quality SpecificationDocument7 pagesChapter Five Quality Management and Control 5.1. Overview of Total Quality Management and Quality SpecificationGebrekiros ArayaPas encore d'évaluation
- G Sundar Pharmqa Compliance Services IndiaDocument26 pagesG Sundar Pharmqa Compliance Services IndiaTarikPas encore d'évaluation
- Project ControlDocument45 pagesProject ControlSanchit BatraPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost of Quality PDFDocument33 pagesCost of Quality PDFAlvin DimasacatPas encore d'évaluation
- COPQ AssessmentDocument4 pagesCOPQ Assessmentvidyut3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cost of Quality-PresentationDocument78 pagesCost of Quality-PresentationSweeetMimi100% (2)
- Chapter 4-: Statistical Process Control (SPC)Document80 pagesChapter 4-: Statistical Process Control (SPC)Dv DickosPas encore d'évaluation
- ProjectQuality-modified CompressedDocument60 pagesProjectQuality-modified CompressedAnupam BongalePas encore d'évaluation
- ISPE - Indo - Process & Product Review & CIDocument70 pagesISPE - Indo - Process & Product Review & CIike mayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality CostsDocument3 pagesQuality CostsNupur WalawalkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk Assessment: Level of Risk Description of RiskDocument10 pagesRisk Assessment: Level of Risk Description of RiskGaneshrudPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Management ProceduresDocument10 pagesQuality Management Proceduresselinasimpson1201Pas encore d'évaluation
- General RequirementsDocument8 pagesGeneral RequirementsRaviTejaMeganathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Costing - Cost AccountingDocument20 pagesQuality Costing - Cost AccountingMd. Ruhul- AminPas encore d'évaluation
- Intro Quality - TQMDocument62 pagesIntro Quality - TQMAgung GuskaPas encore d'évaluation
- Different Type of Quality CostDocument2 pagesDifferent Type of Quality CostKamardeen NazurudeenPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 13 Auditing and Assurance ServicesDocument26 pagesChapter 13 Auditing and Assurance ServicesEdwin Gunawan100% (2)
- 5 AuditsandAssessmentsDocument44 pages5 AuditsandAssessmentsChinh Lê Đình100% (1)
- 12 Steps To Implementing A Quality Management SystemDocument18 pages12 Steps To Implementing A Quality Management Systempatricia navasPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 - Quality CostDocument16 pagesChapter 5 - Quality CostDM RodPas encore d'évaluation
- Total Quality Management Assignment Section: Submitted To: Sir Mohsin RashidDocument12 pagesTotal Quality Management Assignment Section: Submitted To: Sir Mohsin RashidPari Aslam WPas encore d'évaluation
- PDCA in QMSDocument2 pagesPDCA in QMSHimanshu KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- CoqDocument7 pagesCoqbharathimanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Process For Control of Non-Conforming ProductDocument8 pagesProcess For Control of Non-Conforming ProductselvamuthukumarPas encore d'évaluation
- PMP Exam PREP - CONDENSED NOTES - Prepared by Cindy J, Bell, PMPDocument9 pagesPMP Exam PREP - CONDENSED NOTES - Prepared by Cindy J, Bell, PMPBeth SaadPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.0 Project Quality ManagementDocument5 pages8.0 Project Quality Managementasokanen100% (1)
- Cost of Quality Section ADocument46 pagesCost of Quality Section APranav ShandilPas encore d'évaluation
- Internal Audit ISO 9001-2008 Checklist 1-20-12Document43 pagesInternal Audit ISO 9001-2008 Checklist 1-20-12TravisPas encore d'évaluation
- Operation Management Chapter 12Document70 pagesOperation Management Chapter 12Ahmad Izzat HamzahPas encore d'évaluation
- Aqs 9000Document4 pagesAqs 9000sairam0504664l9887Pas encore d'évaluation
- CAPA Corrective and Preventive Action in PharmaceuticalDocument5 pagesCAPA Corrective and Preventive Action in PharmaceuticalRainMan75Pas encore d'évaluation
- Development of Quality System For Engine AssemblyDocument55 pagesDevelopment of Quality System For Engine AssemblysvrbchaudhariPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Integrity TemplateDocument4 pagesData Integrity Templategotty74Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cost of QualityDocument30 pagesCost of QualityrkshpanchalPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.measure of Index of Customer SatisfactionDocument5 pages1.measure of Index of Customer SatisfactionCam ChoudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Costs 1Document47 pagesQuality Costs 1ramakanta_mishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 1 PDFDocument14 pagesAssignment 1 PDFfaranimohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Enter Post Title HereDocument39 pagesEnter Post Title HerehPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Improvement Project: ToyotaDocument15 pagesProcess Improvement Project: ToyotaMuhammad Sajid Saeed100% (5)
- Calidad Grafica 1Document12 pagesCalidad Grafica 1wincu roPas encore d'évaluation
- Positioning of Company XDocument15 pagesPositioning of Company X2rohitjacob100% (1)
- Textile DocumentDocument28 pagesTextile DocumentKhandaker Sakib FarhadPas encore d'évaluation
- Ducab XLPEDocument44 pagesDucab XLPEZechPas encore d'évaluation
- Bus 200 Chapter 10Document32 pagesBus 200 Chapter 10Carlos Rodolfo Salcedo AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategies and Success Factors For Overcoming Challenges in TPM Implementation PDFDocument25 pagesStrategies and Success Factors For Overcoming Challenges in TPM Implementation PDFRahulKrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2017 Summer Model Answer PaperDocument34 pages2017 Summer Model Answer PaperMahesh LamkanePas encore d'évaluation
- Final Rpeort (Jakson)Document82 pagesFinal Rpeort (Jakson)Vikas SolankiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Quality Improvement ProcessDocument29 pagesThe Quality Improvement Processmadhuri_trivedi04Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ignou PapersDocument59 pagesIgnou PapersAshwani K Sharma100% (1)
- Essential Requirements of PPAPDocument4 pagesEssential Requirements of PPAPeditor_ijtelPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 - Introduction Into Operations ManagementDocument20 pagesModule 1 - Introduction Into Operations ManagementBharathKumarM87% (15)
- A Study On Honda - Operations ManagmentDocument11 pagesA Study On Honda - Operations Managmentwackyboi100% (1)
- 9993 CT 0901Document558 pages9993 CT 0901Sebastian IonutzPas encore d'évaluation
- Addressing Change in ISO 9001Document13 pagesAddressing Change in ISO 9001Abusaada2012Pas encore d'évaluation
- Front Page of JoonixDocument78 pagesFront Page of JoonixJyoti YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- CBC - Animation NC IIDocument52 pagesCBC - Animation NC IIMichael V. MagallanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Management of QualityDocument4 pagesManagement of QualityRoseanne Binayao LontianPas encore d'évaluation
- Gemba Kaizen: by Ismail ClementDocument30 pagesGemba Kaizen: by Ismail ClementArvind SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Training and Mentoring: Necessity For Orientation TrainingDocument6 pagesTraining and Mentoring: Necessity For Orientation TrainingBhosx KimPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Production and Operation Management: Chapter OutlineDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Production and Operation Management: Chapter OutlineJoginder GrewalPas encore d'évaluation
- ToR - Qaisar-Laman PDFDocument22 pagesToR - Qaisar-Laman PDFGolam MasudPas encore d'évaluation
- (L10) Managing International OperationsDocument34 pages(L10) Managing International OperationsMarvin YuPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Management GuidebookDocument18 pagesProject Management GuidebookStayce Gatison100% (1)
- Mba TQM Unit-5 Quality Systems Organizing and Implementation 2003Document30 pagesMba TQM Unit-5 Quality Systems Organizing and Implementation 2003KaviArasu100% (2)
- OM Critics On Journal Ind AssignDocument15 pagesOM Critics On Journal Ind AssignJeffrilim VkiatPas encore d'évaluation
- Iqa Training SlidesDocument126 pagesIqa Training SlidesAnkur100% (3)