Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Blistering Dse Table
Transféré par
Dihas Aesthetics AntiagingDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Blistering Dse Table
Transféré par
Dihas Aesthetics AntiagingDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
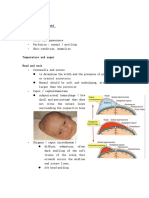
Skin lesions
Pemphigoid Vulgaris Flaccid bullae on Normal skin, erosions, crust, (+) nickolsky sign
Mucous Membra ne
Always involved
Distribution
Localized / generalized
Blister location/ histopathology
Suprabasal acatholysis
Immunopatho logy
IgG intracellular
serum
IgA intracellular epidermis Desmoglein 3 >> desmoglein 1
Treatment / Management
Prednisone: 23 mg/kg BW until
cessation of new blister formation & disappearance of Nikolsky sign
Immunosuppresive therapy given for glucocorticoidsparing effecr
Azathioprine : 2-3 mg/kg BW
until clearing 1mg/kg tapering dose
Methotrexate: 25 35 mg/week PO or IM Continued even
after cessation of glucocorticoid tx (months)
Plasmapharesi s Gold therapy (milder case)Initial dose
To reduce antibody titers
10mg IM 25 50mg gold sodium thiomalate IM every week to max. cumulative dose to 1g
Mycophenolate mofetil
1g BID (clinical studies still on going)
High dose intravenous immunoglobuli n (HIVIg)
2g/kg BW every 3 4 weeks Have glucocorticoid sparing effect
Bullous Pemphigoid
Tense bullae
mouth
Localized / generalized
Subepidermal blister
IgG & C3 linear at
IgG antibodies
Prednisone
50
(most common)
on Normal and/or erythematous skin, Urticarial plaques and papules Bullae rupture less than PV
basement membrane
to basement membrane. IIF directed to BPAG1e & BPAG2
100mg/day until clear. Used alone or in combination
Azathioprine
150mg/day for remission induction 50 -100mg for maintenance
Sulfones (dapsone)
for milder cases 100 150mg/day
Topical glucocorticoids
very mild cases
Tetracycline + nicotinamide
effective in some cases Patients often go to permanent remission, local recurrence controlled with glucocorticoids
Epidermolysis Bullosa
Tense / Flaccid, erosions, inflammatory
Severe, esophagus, oral, vagina
Traumatized regions
Subepidermal
Linear IgG at basement membrane
IgG antibodies
a)
EB Simplex Generalized (koebner) Localized (weber-cockayne) a) a) Epidermis or uppermost layer of skin cells (keratinocytes ) Lamina lucida within the basement membrane zone (layer lying between the epidermis and dermis) Lamina densa and upper dermis (deeper
No therapy for EB Management tailored to severity, extent of skin involvement
Supportive Systemic treatment for complications Wound management Nutrition Infection control Cool environment Soft well ventilated shoes Saline compress, topical antibiotics and steriods Surgical intervention on
b)
Junctional EB (Herlitz)
b)
c)
Dystropic EB
c)
layers of skin cells)
cutaneous infection Release of contractures IgG intracellular IgG antibodies desmoglein 1 only Antiendomysi al antibodies
Pemphigous Folliaceous Dermatits Herpetiformis (Gluten Sensitive)
Pemphigoid Gestationis
Crusted erosion / flaccid vesicles Grouped papules, vesicles, urticarial plaques, crust Tense bullae, urticarial plaques, papules, vesicles, erythematous , edematous
Rare
Exposed seborrheic regions or generalized Elbows, knees, gluteal, sacral and scapular areas
Acantholysis in granular layer Papillary, miscroabsces, subepidermal vesicles
None
Granular IgA on tips of papilla
Dapsone, sulfapyridine, gluten free diet Antihistamine, topical steroids, Prednisone 20
40mg/d tapered gradually during post partum
none
Pregnant & postpartum >> abdomen
Subepidermal
C3 in basement membrane IgG
IgG antibasal membrane antibodies HG factor
Cicatricial Pemphigoid
Skin lesions in only 30% of patients
Mouth, oropharynx
Ocular Unilateral or bilateral conjunctivitis & other ocular diseases
BPAG2, type VII collagen, integrin B4 M168 antigen Laminin 5
Dapsone + low dose prednisone Cyclophospha mide, azathioprine + steroids surgery
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1091)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Unit 5 Medical EnglishDocument7 pagesUnit 5 Medical EnglishJOSSUÉ ALEJANDRO TORRES GÓMEZPas encore d'évaluation
- Newborn AssessmentDocument6 pagesNewborn AssessmentAyuni Salleh100% (1)
- Exam Questions and Solutions For 2003: EP101 - Fundamentals of EpidemiologyDocument11 pagesExam Questions and Solutions For 2003: EP101 - Fundamentals of EpidemiologyAngellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aus Endod J April 2012-31-35 PDFDocument5 pagesAus Endod J April 2012-31-35 PDFlupusebastianPas encore d'évaluation
- Covid CertificateDocument1 pageCovid CertificatesrilaksvelacheryPas encore d'évaluation
- The Case of Mr. Mohammad With Pneumonia Pleural EffusionDocument6 pagesThe Case of Mr. Mohammad With Pneumonia Pleural EffusionjanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Challenges in The Functional Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules Before Surgery For TSH-producing Pituitary AdenomaDocument5 pagesChallenges in The Functional Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules Before Surgery For TSH-producing Pituitary AdenomaAthul IgnatiusPas encore d'évaluation
- 2012 ESMO Handbook of Clinical Pharmacology of Anti Cancer Agents Chapter 1Document8 pages2012 ESMO Handbook of Clinical Pharmacology of Anti Cancer Agents Chapter 1Md Yusuf AnsariPas encore d'évaluation
- La Moderna Psicocirugía: Un Nuevo Enfoque de La Neurocirugía en La Enfermedad PsiquiátricaDocument11 pagesLa Moderna Psicocirugía: Un Nuevo Enfoque de La Neurocirugía en La Enfermedad PsiquiátricaLaura De BrigardPas encore d'évaluation
- Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain Disorders I Mitochondrial DNADocument6 pagesMitochondrial Respiratory Chain Disorders I Mitochondrial DNAAngie CeronPas encore d'évaluation
- Desprendimiento de RetinaDocument8 pagesDesprendimiento de RetinaDiana Carolina RodríguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers-PowerpointDocument16 pagesAngiotensin II Receptor Blockers-PowerpointRoxanne Postrano De VeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Health Education About Infection ControlDocument8 pagesHealth Education About Infection ControlSiĦãm MỡPas encore d'évaluation
- Mud Therapy - by DR Nikhila HiremathDocument15 pagesMud Therapy - by DR Nikhila HiremathEkalaivanPas encore d'évaluation
- A. Matching Type: M: Atch The Terms in The Left Column With The Correct Descriptions in The Right ColumnDocument9 pagesA. Matching Type: M: Atch The Terms in The Left Column With The Correct Descriptions in The Right ColumnCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoPas encore d'évaluation
- Laporan Kasus OADocument34 pagesLaporan Kasus OARosmana PuteraPas encore d'évaluation
- Kingsley Emily ResumeDocument1 pageKingsley Emily Resumeapi-402315475Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quantec Vs Emami Discussion PostDocument1 pageQuantec Vs Emami Discussion Postapi-374655242Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Morningness Eveningness QuestionnaireDocument8 pagesA Morningness Eveningness QuestionnairebobbysingersyahooPas encore d'évaluation
- BacteDocument210 pagesBacteEricsson CarabbacanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf 2Document8 pagesVentriculoperitoneal Shunt - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf 2Erick DjuandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Addiction CaseDocument8 pagesAddiction CasePooja varmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Apllication of Biotechnology in MedicineDocument9 pagesApllication of Biotechnology in MedicineVirendra YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Surgical Periodontal TherapyDocument37 pagesSurgical Periodontal Therapyperiodontics07Pas encore d'évaluation
- H. Mole Case ScenarioDocument1 pageH. Mole Case ScenarioJR Rolf NeuqeletPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment # 1Document4 pagesAssignment # 1Abrar AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- General AnestheticsDocument4 pagesGeneral AnestheticstrentsuggsPas encore d'évaluation
- Maharashtra (PGA CET 2006)Document24 pagesMaharashtra (PGA CET 2006)DrHassan Ahmed ShaikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Terapi 2Document7 pagesTerapi 2emma sitahPas encore d'évaluation
- Seven Keys To Relapse PreventionDocument7 pagesSeven Keys To Relapse PreventionJoshuaSyaputraPas encore d'évaluation