Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Smart Conveyor Control
Transféré par
lolobobolDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Smart Conveyor Control
Transféré par
lolobobolDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
AN MEC COMPANY
UniDrive
Smart Conveyor Control (SCC) Guide to Installation and Use
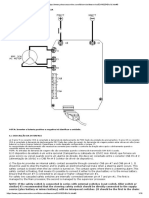
User Interface 1. Motor Connection 2. Smart Input/Output (I/O) 3. DC Power Input Connector 4. Blown Fuse Indicator 5. Replaceable 5A Fuse 6. Potentiometer for Speed Control 7. Diagnostic LEDS 8. Function Control Switches 9. Sensor Connector 10. Downstream Cable Connection Jack 11. Upstream Cable Connection Jack 12. Mounting Plate/Heat-sink 13. Cover
Organization This guide is organized in three sections. The first section is General Notes which apply regardless of the configuration of the conveyor. The numbers from 1 13 correspond to the features listed on the User Interface to the left and to the illustration above. The second section is the Quick Start Guide. The letters from A G provide specific instructions on how to set up the UniDrive Motor and SCC control board for applications commonly encountered in unit handling conveyor systems. The third section is Diagnostic and Troubleshooting Notes related to use of the indicator LEDs on the board for troubleshooting purposes. If you need additional assistance, call 931-537-3950.
www.AutomationControlsGroup.com 931-537-3950
Automation Controls Group, an MEC Company
Page 1 of 6 Rev 071204
AN MEC COMPANY
General Notes (Critical notes are marked with ! , important notes are marked with * ) 1. The Motor is provided with a pre-wired cable assembly. Do not disassemble. If the cable is damaged and on-site repairs are required, the wiring sequence is (from position 1 on the left through position 8 on the right): Green, Gray, Blue, Violet, Yellow, Brown, Red, Black. !Use of extension cables may cause permanent damage and will void the warranty. 2. Smart Inputs and Outputs (I/O) (4 position connector supplied) 2.1. Smart Inputs (Positions 1 & 2) can be either NPN or PNP based on Switch 2 (Second from the top) however all inputs to the board must be of the same type. 2.2. Smart Outputs (Positions 3 & 4) are PNP regardless of the condition of Switch 2. *If the smart I/O is not being used, leave the connector in place to avoid accidentally shorting the pins. 3. Power Connection 3.1. Position 1 (on the left) is for + DC between +22 and +28 VDC. While there is some polarity protection on the board it is not fool-proof, so it is important to make this connection correctly. *The function control switches are only read at power-up, so make the power connection after all other connections are in place. 3.2. Position 2 (on the right) is for the DC Ground. !This input is not fused. Connecting +DC to this position followed by shorting another pin to ground may cause catastrophic damage to the control. *When adjacent zones are operating from separate power supplies it is highly recommended that the DC grounds (only) be connected. 4. Blown Fuse Indicator see Diagnostic Notes. 5. Replaceable 5A fuse Replace with Littelfuse part number 0454 005. 6. Speed Control Potentiometer Fully clockwise the speed is limited to 275 RPM. Fully counterclockwise the speed will be approximately 55 RPM. Intermediate speeds can be selected by turning the pot appropriately. 7. Diagnostic LEDs see Diagnostic Notes. 8. Function Selector Switches Specific instructions for Switches 3 and 4 are included in the Quick Start Guide. Switches 1 and 2 always function as follow: 8.1. When Switch 1 is Off the motor rotates counterclockwise for forward motion. On sets the forward direction as clockwise. 8.2. When Switch 2 is Off the Smart Inputs and the Sensor Input must be NPN type connections. On will set the Smart Inputs and Sensor Input to function as PNP type. *The Smart Outputs are always NPN type. *Switches are read only at power-up, so if you need to change the functionality of a zone; disconnect power, set the switch and then reconnect power. *Off is to the left, On is to the right. 9. Sensor Connector (3 position plug provided) The first position (left-most) is the ground connection for the sensor, the second position is for the input from the sensor and the third position is the +VDC power to the sensor, fused for 0.2 Amps. !This fuse is not replaceable. Use of this output for any purpose that requires more than 0.2 Amps will blow the fuse and permanently disable this output. !If the sensor is mounted on non-conductive equipment, such as a plastic slide, be certain to ground the body of the sensor to provide for nondestructive discharge of static electricity. 10. Downstream Cable Connection Jack Install a 4wire or 6-wire modular phone cable (only the 4 center connections are used) for connection to an adjacent downstream SCC board. 11. Upstream Cable Connection Jack Plug the 4wire or 6-wire modular phone cable from the adjacent upstream SCC into this jack. 12. Mounting Plate For mounting the control assembly to the conveyor frame using two bolts. !If mounting on a curve use washers between the mounting plate and the conveyor frame to assure that the mounting plate is not distorted, causing damage to the enclosed printed circuit board assembly. 13. Cover This cover is designed to prevent incidental damage to the control by foreign objects. It is neither waterproof nor dustproof. *Removal of the cover will void the warranty.
www.AutomationControlsGroup.com 931-537-3950
Automation Controls Group, an MEC Company
Page 2 of 6 Rev 071204
AN MEC COMPANY
Quick Start Guide This section is organized with instructions for how to use the SCC and UniDrive Motor in the most common configurations. Connections and set up for the following operating modes are described below: Section A Standard Zero Pressure Accumulation (ZPA) Transport Zone. Section B Fast Zero Pressure Accumulation (ZIP) Transport Zone. Section C ZPA or ZIP Transport plus Slave Motor. Section D ZPA Entry Zone. Section E ZPA Exit Zone. Section F ZPA Entry and Exit Zone Section G Slave Motor or Remote Control. A. Standard ZPA Transport Zone installed between two other SCC controlled zones. This will cause the zones to transport the packages in standard ZPA mode with an empty zone between each package in transit and zones filling up at the output end of the conveyor. a. Mount the control in a location so that the motor reaches the connection position without putting strain on the cable or connector. b. Set the switches with Switch 1 and Switch 2 for the required direction of rotation and NPN or PNP inputs. Switch 3 must be Off and Switch 4 must be On. c. Connect the phone cables from Upstream on this board to Downstream on the adjacent upstream board and from Downstream on this board to Upstream on the adjacent downstream board. d. Connect the sensor located near the downstream end of this zone to the Sensor input. e. Do not connect anything to the 4 position I/O connector, but leave the connector in place. f. Plug the motor connector into the 8 pin header on the board, oriented as shown in the illustration. g. Connect the power leads to the two position connector with the correct polarity and when all the zones in the system are prepared, turn on the power. B. ZIP Transport Zone installed between two other SCC controlled zones. This will cause the zones to transport the packages in a true ZPA mode but with approximately double the throughput because the empty zones between the packages in transit are eliminated. This is not what is commonly referred to
www.AutomationControlsGroup.com 931-537-3950
as Slug release because of two important, patented1 control methods. The first difference is that the release of the package from each zone cannot occur until the downstream zone has begun the release of its package, so a small gap is maintained. The second difference is that upon release of the first of a group of accumulated zones, each subsequent upstream zone encounters a very brief (~0.1 sec) delay before releasing its load. This helps assure that the power supply does not encounter too great of a current surge and that suspended conveyors do not oscillate dangerously as a result of a large group of zones starting and stopping simultaneously. a. Mount the control in a location so that the motor reaches the connection position without putting strain on the cable or connector. b. Set the switches with Switch 1 and Switch 2 for the required direction of rotation and NPN or PNP inputs. Switch 3 and Switch 4 must both be On. This is the only difference between ZPA and ZIP setup. c. Connect the phone cables from Upstream on this board to Downstream on the adjacent upstream SCC and from Downstream on this board to Upstream on the adjacent downstream SCC board. d. Connect the sensor located near the downstream end of this zone to the Sensor input. e. Do not connect anything to the 4 position I/O connector, but leave the connector in place. f. Plug the motor connector into the 8 pin header on the board, oriented as shown in the illustration. g. Connect the power leads to the two position connector with the correct polarity and when all the zones in the system are prepared, turn on the power. C. ZPA or ZIP Transport plus Slave Motor Exactly the same as the two systems described in A and B above except that a second motor is include in the zone to provide additional force for, as an example, an inclined conveyor section. a. Mount the control in a location so that the motor reaches the connection position without putting strain on the cable or connector. b. Set the switches with Switch 1 and Switch 2 for the required direction of rotation and NPN or
1 US patents 6,244,421 and 6,253,906
Automation Controls Group, an MEC Company
Page 3 of 6 Rev 071204
AN MEC COMPANY
PNP inputs. Switch 3 and Switch 4 must both be On. For Standard Singulation set switch 3 Off and Switch 4 On. For Enhanced Singulation set both Switches 3 & 4 on. c. Connect the phone cables from Upstream on this board to Downstream on the adjacent upstream SCC and from Downstream on this board to Upstream on the adjacent downstream SCC board. d. Connect the sensor located near the downstream end of this zone to the Sensor input. e. Connect a single conductor wire from Smart Output 1 on this control (position 3 on the 4 position connector) to Smart Input 1 on the slave motor control (position 1 on its respective 4 position connector.) f. Plug the motor connector into the 8 pin header on the board, oriented as shown in the illustration. g. Connect the power leads to the two position connector with the correct polarity and when all the zones in the system are prepared, turn on the power. D. ZPA Entry Zone Installed at the upstream end of a series of SCC controlled zones. The smart inputs and outputs are used to communicate a request from an external device to the control to begin induction of a package from upstream and permission from the SCC to the external device to discharge the package into the zone. a. Mount the control in a location so that the motor reaches the connection position without putting strain on the cable or connector. b. Set the switches with Switch 1 and Switch 2 for the required direction of rotation and NPN or PNP inputs. Switch 3 must be On and Switch 4 must be Off. c. Connect only the Downstream cable to the adjacent Downstream SCC board. Connection of a cable to the Upstream position may cause undesirable results. d. Connect the sensor located near the downstream end of this zone to the Sensor input. e. Connect Smart I/O as follows: i. For a manually loaded conveyor install a second sensor at the upstream edge of the zone and connect the output of the sensor to Smart Input 2 (position 2 on the 4 position plug supplied.) This allows the zone to automatically start running to transport a
www.AutomationControlsGroup.com 931-537-3950
package to the downstream edge as soon as the zone is available. ii. For an automatically loaded conveyor install a single lead wire from the upstream device to Smart Input 2 (position 2 on the 4 position plug supplied) to present a request to the zone to allow transport into the zone. Also install a single lead wire from Smart Output 2 (position 4 on the 4 position plug supplied) to send permission via a PNP output to the external device. f. Plug the motor connector into the 8 pin header on the board, oriented as shown in the illustration. g. Connect the power leads to the two position connector with the correct polarity and when all the zones in the system are prepared, turn on the power. E. ZPA Exit Zone Installed at the downstream end of a series of SCC controlled zones. The smart inputs and outputs are used to communicate a request from the control to an external take-away and for the external device to respond with permission for the zone to discharge the package. a. Mount the control in a location so that the motor reaches the connection position without putting strain on the cable or connector. b. Set the switches with Switch 1 and Switch 2 for the required direction of rotation and NPN or PNP inputs. Switch 3 must be On and Switch 4 must be Off. c. Connect only the Upstream cable to the adjacent upstream SCC board. Connection of a cable to the Downstream position may cause undesirable results. d. Connect the sensor located near the downstream end of this zone to the Sensor input. e. Connect Smart I/O as follows: i. For a manually unloaded conveyor, simply remove the package at the end of the conveyor from the sensor and upstream packages will advance appropriately. ii. For an automatically unloaded conveyor install a single lead wire from the downstream device to Smart Input 1 (position 1 on the 4 position plug supplied) to present permission to the zone to allow discharge an accumulated package. Also install a single lead wire from Smart Output 1 (position 3 on the 4 po-
Automation Controls Group, an MEC Company
Page 4 of 6 Rev 071204
AN MEC COMPANY
sition plug supplied) to send a request via a PNP output to the external device. iii. Note that a manual switch or foot pedal or other simple dry contact device can be used to provide the permission signal with the appropriate polarity. f. Plug the motor connector into the 8 pin header on the board, oriented as shown in the illustration. g. Connect the power leads to the two position connector with the correct polarity and when all the zones in the system are prepared, turn on the power. F. ZPA Entry & Exit Zone This would most commonly be used in a situation where a single zone is installed between two non-SCC controlled conveyor sections, such as a lift gate or other similar device installed in a traditional line shaft or chain driven conveyor. a. Mount the control in a location so that the motor reaches the connection position without putting strain on the cable or connector. b. Set the switches with Switch 1 and Switch 2 for the required direction of rotation and NPN or PNP inputs. Switch 3 must be On and Switch 4 must be Off. c. Do not connect cables to either the Upstream or Downstream connector jacks. d. Connect the sensor located near the downstream end of this zone to the Sensor input. e. Connect Smart I/O as follows: i. For an automatically loaded conveyor install a single lead wire from the upstream device to Smart Input 2 (position 2 on the 4 position plug supplied) to present a request to the zone to allow transport into the zone. Also install a single lead wire from Smart Output 2 (position 4 on the 4 position plug supplied) to send permission via a PNP output to the external device. ii. For an automatically unloaded conveyor install a single lead wire from the downstream device to Smart Input 1 (position 1 on the 4 position plug supplied) to present permission to the zone to allow discharge an accumulated package. Also install a single lead wire from Smart Output 1 (position 3 on the 4 position plug supplied) to send a request via a PNP output to the external device.
f. Plug the motor connector into the 8 pin header on the board, oriented as shown in the illustration. g. Connect the power leads to the two position connector with the correct polarity and when all the zones in the system are prepared, turn on the power. G. Slave Motor or Remote Control This dumb control simply runs or stops in response to one or two external signals. a. Mount the control in a location so that the motor reaches the connection position without putting strain on the cable or connector. b. Set the switches with Switch 1 for the required direction of rotation. i. If this unit is being operated as a Slave driven motor synchronized with the primary motor in the zone, Set Switch 2 in the Off position. ii. If this unit is being operated as a Remote Control drive, Set Switch 2 Off for NPN type Smart Inputs or On for PNP Smart Inputs. iii. Switch 3 and Switch 4 must both be Off. c. Do not connect cables to either the Upstream or Downstream connector jacks. d. Do not connect a sensor to the sensor input, but leave the 3 position plug in place to prevent accidentally shorting the connector pins. e. Connect Smart I/O as follows: i. If this unit is being operated as a Slave driven motor, connect the single lead from Smart Output 1 on the main control to Smart Input 1 on this control.(see Section C, subsection e, above.) *Do Not connect anything to Smart Input 2 on this control. ii. If this Unit is being operated as a Remote Control drive the two Smart inputs are used in combination to cause the motor to operate on demand in one of the following four modes: Run Forward (as defined by Switch 1) by connecting only Smart Input 1 to a signal with the correct NPN or PNP polarity. Run Reverse (as defined by Switch 1) by connecting only Smart Input 2 to a signal with the correct NPN or PNP polarity. Brake with Position Holding by leaving both Smart Input 1 and Smart Input 2 disconnected. Coast (no appreciable braking) by connecting both Smart Input 1 and Smart InPage 5 of 6 Rev 071204
www.AutomationControlsGroup.com 931-537-3950
Automation Controls Group, an MEC Company
AN MEC COMPANY
put 2 to appropriate NPN or PNP signals simultaneously. f. Plug the motor connector into the 8 pin header on the board, oriented as shown in the illustration. g. Connect the power leads to the two position connector with the correct polarity and when all the zones in the system are prepared, turn on the power.
Diagnostic & Troubleshooting Notes There are four LEDs on the board shown in the illustration as positions 4 and 7.1 7.3 that may be useful in diagnosing various wiring and connection problems. If power is connected there will always be at least one LED illuminated or flashing. No LEDs = no power. 4. Blown Fuse LED (Red) This will be illuminated constantly if the fuse (5) is blown and power is applied with the proper polarity. Replace the fuse with Littelfuse 0454 005. *Note that this fuse will not blow under normal circumstances. Inspect all wiring connections to assure that there are no short circuits. 7. Three LEDs are located directly over the speed control potentiometer. The LED on the far left will be referred to as 7.1 and then sequentially 7.2 and 7.3. 7.1. Fault LED (Red) This is off under normal circumstances but will provide one of 5 signals if a problem is detected. 7.1.1. 1 flash in 4 seconds = The board has a hardware problem. Return it to your supplier. 7.1.2. 2 flashes in 4 seconds = The input voltage is too high. Adjust voltage. 7.1.3. 3 flashes in 4 seconds = The input voltage is too low. Adjust voltage. 7.1.4. 4 flashes in 4 seconds = There is a problem with the motor cable or connection. Check to see that the cable is not damaged and that all of the wires are secure. If the cable has been cut or the wires disconnected refer to section 1 in the General Notes. 7.1.5. Constantly on = Either the motor is stalled or the sensor is continuously blocked. Check for mechanical obstructions. 7.2. Motor LED (Amber)
4 flashes in 4 seconds = Components on the board have overheated and the circuit is limiting the power to the motor to about of normal. This problem will correct itself when the board has cooled adequately. Check for mechanical obstructions. 7.2.2. Constantly on = Motor current is at the maximum allowed and is being electronically. Check for mechanical obstructions. 7.2.3. Flickering = If the motor starts under significant load, the current may be limited briefly causing the LED to flicker. This is not cause for concern and no corrective action is required. 7.3. Power LED (Green) should be constantly on when power is properly applied as long as the fuse is not blown.
7.2.1.
www.AutomationControlsGroup.com 931-537-3950
Automation Controls Group, an MEC Company
Page 6 of 6 Rev 071204
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2D'EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1D'EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Évaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (3)
- s1000 Voltage RegulatorDocument36 pagess1000 Voltage RegulatorAnonymous 7PtTlrPas encore d'évaluation
- Honeywell 4219 Install GuideDocument2 pagesHoneywell 4219 Install GuideAlarm Grid Home Security and Alarm MonitoringPas encore d'évaluation
- DYNA Power Control Manual For Plus 1, Plus 2, Plus 4 and Plus 6 Ft. Lb. SystemsDocument18 pagesDYNA Power Control Manual For Plus 1, Plus 2, Plus 4 and Plus 6 Ft. Lb. SystemsDavid Coronado100% (1)
- PASL MANUAL General System Description (English 060308)Document0 pagePASL MANUAL General System Description (English 060308)Emy ZaninkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dkg-329 Automatic Transfer Switch With Uninterrupted Transfer and Multiple Genset SupportDocument43 pagesDkg-329 Automatic Transfer Switch With Uninterrupted Transfer and Multiple Genset SupportLuis Fernando CuaspudPas encore d'évaluation
- Door Inverter NSFC01-02Document39 pagesDoor Inverter NSFC01-02HƯNG NGUYỄN THANHPas encore d'évaluation
- Dthoii 631355907Document22 pagesDthoii 631355907Nigel RamkhalawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen Auto XMDocument47 pagesGen Auto XMCameron Ledingham100% (1)
- D1 Swing Gate Control Board ManualDocument9 pagesD1 Swing Gate Control Board ManualjohnPas encore d'évaluation
- KEPCO Quick Start GuideDocument8 pagesKEPCO Quick Start Guideankara271828Pas encore d'évaluation
- 310MV InstructionsDocument29 pages310MV InstructionsMIGUELPas encore d'évaluation
- Remy TechnicalBulletin - July - WebDocument2 pagesRemy TechnicalBulletin - July - WebHenry CanalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Serie PL3000Document13 pagesManual Serie PL3000Anonymous j3b9ApBpPas encore d'évaluation
- Federal Signal Corporation Installation and Service InstructionDocument29 pagesFederal Signal Corporation Installation and Service InstructionTiagoPas encore d'évaluation
- Calibration ChokeDocument11 pagesCalibration ChokeAmar BadradinePas encore d'évaluation
- SP9100 Rev1.2 DirectionsDocument14 pagesSP9100 Rev1.2 Directionsscada.wupptclPas encore d'évaluation
- Dkg-307 Automatic Mains Failure and Remote Start UnitDocument29 pagesDkg-307 Automatic Mains Failure and Remote Start UnitSalmaan HaiderPas encore d'évaluation
- DYNS 30000 CalibratorDocument4 pagesDYNS 30000 Calibratorgolu201100% (2)
- EXD2010 EX200: Compact Ex D Electro-Hydraulic Positioning and Monitoring SystemDocument8 pagesEXD2010 EX200: Compact Ex D Electro-Hydraulic Positioning and Monitoring SystemKelvin Anthony OssaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Red - E: User ManualDocument11 pagesRed - E: User ManualihwissoPas encore d'évaluation
- SAUER DANFOSS Bln-96-0001-E PDFDocument8 pagesSAUER DANFOSS Bln-96-0001-E PDFEdu Hdez100% (1)
- General System DescriptionDocument20 pagesGeneral System DescriptionZahid KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.0 Diagrama de Conexão de EnergiaDocument16 pages6.0 Diagrama de Conexão de EnergiaclaitonPas encore d'évaluation
- ConditionDocument12 pagesConditionأمجد راضي هادي /A1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Parker SSD Drives 650 Series Quick Start GuideDocument2 pagesParker SSD Drives 650 Series Quick Start Guideeng_karamazabPas encore d'évaluation
- SolarImmersion QuickStart Installation UserManualDocument21 pagesSolarImmersion QuickStart Installation UserManualRelu IanoviciPas encore d'évaluation
- SpecificationsDocument3 pagesSpecificationsvenkat0236Pas encore d'évaluation
- Syncro Io2Document7 pagesSyncro Io2yulizardPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Document: 757-4002-097 CAD #D8478Document29 pagesEngineering Document: 757-4002-097 CAD #D8478Vasi ValiPas encore d'évaluation
- File 1620307458Document36 pagesFile 1620307458Paulo SergioPas encore d'évaluation
- DEYE SUN-3.6-5K-SG03LP1-EU-user-manual-Ver1.6-Deye PDFDocument36 pagesDEYE SUN-3.6-5K-SG03LP1-EU-user-manual-Ver1.6-Deye PDFspeedtouchbr9027Pas encore d'évaluation
- Yaskawa TM.J7.01Document96 pagesYaskawa TM.J7.01Salvador CrisantosPas encore d'évaluation
- 5A To 9A Stroker. Electronic Controller Conversion Guideline ManualDocument20 pages5A To 9A Stroker. Electronic Controller Conversion Guideline Manualabuzer1981Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1079 3Document5 pages1079 3Marco OlivettoPas encore d'évaluation
- DataKom 207 - USERDocument28 pagesDataKom 207 - USERKhaleel KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- VaraDocument8 pagesVaraCesar Alfonso Saldivar MontoyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cd34install EnglishDocument24 pagesCd34install EnglishZoltán VéberPas encore d'évaluation
- TenTec Owner's Manual Omni-A and D Transceiver and Model 280 Power Supply, 1980.Document91 pagesTenTec Owner's Manual Omni-A and D Transceiver and Model 280 Power Supply, 1980.Bob Laughlin, KWØRL100% (2)
- Wiring DiagramDocument28 pagesWiring DiagramAbdulSattarPas encore d'évaluation
- MID 039 - CID 1847 - FMI 09: Pantalla AnteriorDocument6 pagesMID 039 - CID 1847 - FMI 09: Pantalla AnteriorWalterPas encore d'évaluation
- Vacon Drive ManualDocument41 pagesVacon Drive ManualAliRouyou100% (1)
- SubMonitor ManualDocument20 pagesSubMonitor ManualfelipezambranoPas encore d'évaluation
- M 614 (I) PDFDocument60 pagesM 614 (I) PDFAntony MylvaganamPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Gp4303d A Gp4185d ADocument11 pagesManual Gp4303d A Gp4185d ADiego AsiconaPas encore d'évaluation
- Over Cureent and EfDocument7 pagesOver Cureent and EfBasudev Patra100% (1)
- MID 039 - CID 1846 - FMI 09: Pantalla AnteriorDocument6 pagesMID 039 - CID 1846 - FMI 09: Pantalla AnteriorWalterPas encore d'évaluation
- Inversor Abb 5kwDocument2 pagesInversor Abb 5kwapi-290643326Pas encore d'évaluation
- P 7132 BGM en A5Document32 pagesP 7132 BGM en A5Orlando Jose Romero ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Latching Relay ModuleDocument8 pagesLatching Relay ModuleJunior ElimeelogodavejuniorPas encore d'évaluation
- Honeywell 5800C2W Installation ManualDocument2 pagesHoneywell 5800C2W Installation ManualAlarm Grid Home Security and Alarm MonitoringPas encore d'évaluation
- Intelligent Elevator Rescue Device Controller: User'S ManualDocument5 pagesIntelligent Elevator Rescue Device Controller: User'S ManualelecompinnPas encore d'évaluation
- PCC2100 Instruction SheetDocument5 pagesPCC2100 Instruction SheetKhaled KamelPas encore d'évaluation
- Aspiro - 2RU 3200W Quick Install Guide BCG.00037 PDFDocument2 pagesAspiro - 2RU 3200W Quick Install Guide BCG.00037 PDFlitemenPas encore d'évaluation
- SubMonitor ManualDocument20 pagesSubMonitor ManualAdrian CantaragiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Tea Sensor de Velocidade 3Document7 pagesTea Sensor de Velocidade 3Valmaq Prestação Serviço LdaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dkg-329 User ManualDocument43 pagesDkg-329 User ManualKỹ Sư TđhPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuente Goldstar PDFDocument11 pagesFuente Goldstar PDFdirectPas encore d'évaluation
- Mercedes 06 - I01 High Voltage ComponentsGBDocument190 pagesMercedes 06 - I01 High Voltage ComponentsGBFunny/Football F&FPas encore d'évaluation
- Fiat Barchetta: Fault DiagnosisDocument31 pagesFiat Barchetta: Fault DiagnosisHallex OliveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Saab 900 Convertible Owners ManualDocument60 pagesSaab 900 Convertible Owners ManualScottPas encore d'évaluation
- Approved Switch Gear ListDocument10 pagesApproved Switch Gear ListprasannamohandasPas encore d'évaluation
- Alalalal LuaDocument53 pagesAlalalal Luarenato soportePas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - Relays & Contactors PDFDocument14 pages1 - Relays & Contactors PDFSallak IdrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Compressor: C20160-1790, Issue 1, January 2000Document26 pagesAir Compressor: C20160-1790, Issue 1, January 2000RomanCHubaPas encore d'évaluation
- Finder-70 11 8 230 2022-Datasheet PDFDocument10 pagesFinder-70 11 8 230 2022-Datasheet PDFovidiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Probe On-Wafer DiodesDocument3 pagesProbe On-Wafer DiodesAmador Garcia IIIPas encore d'évaluation
- Murano 2009Document138 pagesMurano 2009alexPas encore d'évaluation
- DOPPLER ONE Technical Specs EuropeDocument6 pagesDOPPLER ONE Technical Specs EuropeZlatko MPas encore d'évaluation
- Rectifiers and FiltersDocument15 pagesRectifiers and Filtersjovinchungath777Pas encore d'évaluation
- ON-Load-Switches GeneratorxgDocument9 pagesON-Load-Switches GeneratorxgSIVA NAGA SUDHEER SIDDANIPas encore d'évaluation
- High Bay 200w LedDocument3 pagesHigh Bay 200w LedEdizon Ramos OrtizPas encore d'évaluation
- Sirocco 1000w HTI: Versatile Lighting BalloonDocument2 pagesSirocco 1000w HTI: Versatile Lighting BalloonSiding BarroPas encore d'évaluation
- EPSS 627: DescriptionDocument2 pagesEPSS 627: DescriptionudayakumartPas encore d'évaluation
- Lintels AutoCad Files ListDocument6 pagesLintels AutoCad Files ListAngel MurrayPas encore d'évaluation
- GPC 3000 PDFDocument23 pagesGPC 3000 PDFmarceloo1993100% (1)
- 220 3PS Euy0 00001 - BDocument12 pages220 3PS Euy0 00001 - BfaradioPas encore d'évaluation
- Clark C50 60 70 80DDocument263 pagesClark C50 60 70 80DMarcio100% (5)
- ANN-RLY Relay Module Installation Instructions: Mounting in FACP Main Board ChassisDocument3 pagesANN-RLY Relay Module Installation Instructions: Mounting in FACP Main Board ChassisSergio Dal DossoPas encore d'évaluation
- Take Ac Generator Quiz To Test Your KnowledgeDocument5 pagesTake Ac Generator Quiz To Test Your KnowledgeRubab MalikPas encore d'évaluation
- 315 D CaterpillarDocument13 pages315 D CaterpillarJose nildo lobato Mendes MendesPas encore d'évaluation
- Specifications: I. General ProvisionsDocument4 pagesSpecifications: I. General Provisionsemem CatzPas encore d'évaluation
- (Estimation and Costing)Document26 pages(Estimation and Costing)Diksha GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Synchronous MotorDocument4 pagesSynchronous MotorLiviu DeaconuPas encore d'évaluation
- Tyco RelaysguideDocument11 pagesTyco Relaysguidejaysingh12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wag9hc CLWDocument93 pagesWag9hc CLWShrish ShankhdharPas encore d'évaluation
- Q21102-Dwg-Ii-2021-01 (Single Line Diagram)Document1 pageQ21102-Dwg-Ii-2021-01 (Single Line Diagram)Prayogo SetiawanPas encore d'évaluation
- LCD Module Repair Guide 240209Document21 pagesLCD Module Repair Guide 240209ledu035Pas encore d'évaluation