Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
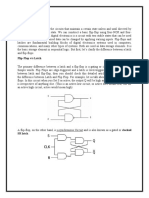
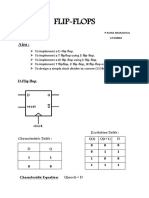
Flip Flop
Transféré par
sarrks007Description originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Flip Flop
Transféré par
sarrks007Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
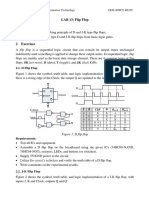
Class 13: Flip Flops
Topics: 1. TOC 2. Introduction 3. Types of Flip Flops 4. Types of Flip Flops 5. D Flip Flop Operation 6. D Flip Flop Master Circuit 7. D Flip Flop Circuit 8. Tri-State Inverter 9. Flip-Flop Ideas 10. Flip-Flop Ideas
Joseph A. Elias, PhD
Class 13: Flip Flops
Introduction (Martin c.7)
Flip Flops basics: Storage elements for synchronous circuits (what is synchronous?) Break up any race conditions or oscillations, i.e., feedback loops around a cyclic logic circuit Inputs: normally have 1 or 2 input signals and a clock Outputs: differential outputs Q and Q output latched or stored on rising/falling edge of clock output stable until next rising/falling edge of clock Can optionally have set and/or reset asynchronous inputs regardless of state of the clock, the outputs will either be set to a 1 or reset to a 0 Typical techniques master_slave edge_sensitive Typical configurations: SR (set_reset) D JK T (toggle) D FF is the most common for ICs SR flip flop symbol SR flip flop symbol changes on positive changes on negative going clock edge going clock edge
Joseph A. Elias, PhD
Class 13: Flip Flops
Types of Flip Flops (Martin c.7)
_____________________________________________________________________________________________ SR
_____________________________________________________________________________________________ JK
_____________________________________________________________________________________________ T realized by tying J and K together from a JK FF
Joseph A. Elias, PhD
Class 13: Flip Flops
Types of Flip Flops (Martin c.7)
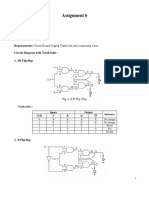
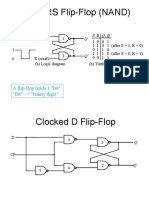
D cascade of two latches with opposite clock phases best choice (usually) for IC design after FF is clocked, output is equal to the D value just before the clock changed _____________________________________________________________________________________________ SR same as D FF if S=D and R=D can be set, reset, or remain in its previous state intedeterminate state exists if S=R=high when CLK=low major limitation is output can be affected by the input at any time the CLK is high, a.k.a., noise problem _____________________________________________________________________________________________ JK often used for synchronous machines or counters J=1, K=0 FF is set J=0, K=1 FF is reset J=0, K=0 No change J=1, K=1 FF state toggles (difference between JK and SR, but same noise limitation) _____________________________________________________________________________________________ T useful in counters
Joseph A. Elias, PhD
Class 13: Flip Flops
D Flip Flop Operation (Martin c.7)
Clk is 1, implies master active, slave latched B=D=1 since 1 or anything is 1 in c 1 1 0 (D) 0 0 Clk=0 D=0 Clk is 0, implies master latched, slave active Q=D=0 since 1 or anything is 1 in h 1 0 0 (D) 1 0 latched Q=D=0 0 (D) Q=D=1 0 0 latched
Joseph A. Elias, PhD
Clk is 1, implies master active, slave latched B=D=0 since 1 or anything is 1 in d Q 1 0 0 1 (D) 0 1 Q latched Clk is 0, implies master latched, slave active Q=D=0 since master disabled by a and b 0 0 0 (D) 1 Q=D=0 0 (D) Q=D=1 0 Q
1 0
1 (D)
Q latched
0 (D)
0 0
1 (D)
1 (D)
1 (D)
1 (D)
Class 13: Flip Flops
master
D Flip Flop Master Circuit (Martin c.7)
A
Q1
A
Q D Clk Q
B
D Clk
B
Joseph A. Elias, PhD
[Q + (D)(Clk)]
[Q + (D)(Clk)]
Class 13: Flip Flops
D Flip Flop Circuit (Martin c.7)
S = 1 : Q = 0 immediately, Q = S after inv delay R = 1 : Q = 1 immediately, Q = R after inv delay
Joseph A. Elias, PhD
Class 13: Flip Flops
Tristate Inverter (Weste c.2)
Cascade of a transmission gate with an inverter C=0 C=1: Z is tristated, i.e., A does not influence Z C=1 C=0: Z = A
Joseph A. Elias, PhD
Class 13: Flip Flops
Flip Flop Ideas (Martin c.7)
Biphase D FF asynchronous Set and Reset Inverter Based Biphase D FF transmission gates used NOR based
Joseph A. Elias, PhD
Class 13: Flip Flops
Flip Flop Ideas (Martin c.7)
Biphase JK FF transmission gates used Inverter based Design Assignment Biphase D FF (clk, clk) buffer the D input with a tristate inverter Inverter based Asynchronous Reset hint: can optimize the layout by rearranging ckt
Joseph A. Elias, PhD
10
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99D'EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99Pas encore d'évaluation
- Group 8 Adc Experiment 5-1Document17 pagesGroup 8 Adc Experiment 5-1ROHAN NAGRUTPas encore d'évaluation
- Latches and Flip Flops CharacteristicsDocument13 pagesLatches and Flip Flops CharacteristicsWeaam RaedPas encore d'évaluation
- American International University-Bangladesh: Title: Study of Different Flip-FlopsDocument7 pagesAmerican International University-Bangladesh: Title: Study of Different Flip-FlopsAbid ChowdhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- Flip FlopsDocument11 pagesFlip FlopsTi NaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sequence Detector DesignDocument2 pagesSequence Detector Designmaha8 balaPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 4: Study of FlipflopsDocument6 pagesExperiment 4: Study of FlipflopsAdi MohantyPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Flip-Flops: Experiment No. 12Document10 pagesIntroduction To Flip-Flops: Experiment No. 12Ramiz IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- F4 - Latches, Flip-Flops, Data Buses & Resolved Functions PDFDocument85 pagesF4 - Latches, Flip-Flops, Data Buses & Resolved Functions PDF陈晟音乐族--王子Pas encore d'évaluation
- State and Finite State Machines: Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2013Document61 pagesState and Finite State Machines: Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2013gorenganPas encore d'évaluation
- Harolds Discrete Math Flip Flops Cheat Sheet 2020Document6 pagesHarolds Discrete Math Flip Flops Cheat Sheet 2020Nandini JayakumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 12 DLDDocument4 pagesLab 12 DLDNoman KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 UpdatedDocument54 pagesChapter 5 UpdatedAttiq RehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 7Document27 pagesLecture 7rahulPas encore d'évaluation
- Flip FlopDocument29 pagesFlip FlopAndleeb juttiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch05-Part 1Document28 pagesCh05-Part 1hezzat964Pas encore d'évaluation
- Flipflops Latches 1Document20 pagesFlipflops Latches 1Varsha S LalapuraPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Logic Memory ElementsDocument20 pagesDigital Logic Memory ElementsPriyadharsini VPas encore d'évaluation
- L5: Simple Sequential Circuits and VerilogDocument11 pagesL5: Simple Sequential Circuits and Verilogbilal nagoriPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No: 08 Aim: Tool Used: TheoryDocument8 pagesExperiment No: 08 Aim: Tool Used: TheoryDeepanshGoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 4Document10 pagesExperiment 4Akshat AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- L2 FlipflopsDocument39 pagesL2 FlipflopsKogul ShiyamPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 13 2022 2Document2 pagesLab 13 2022 2CuongPas encore d'évaluation
- Name: Charan Tej Merugu Id:111-00-1840Document65 pagesName: Charan Tej Merugu Id:111-00-1840rinkeshpatel11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Multiplexors: Sequential Circuits and Finite State Machines Prof. Sin-Min LeeDocument62 pagesMultiplexors: Sequential Circuits and Finite State Machines Prof. Sin-Min LeeNanc JoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch.8 Flip-Flops and Related Devices: Latches, Edge-Triggered FFDocument84 pagesCh.8 Flip-Flops and Related Devices: Latches, Edge-Triggered FFDocbytePas encore d'évaluation
- DLC LAB - 06 - Student - ManualDocument8 pagesDLC LAB - 06 - Student - Manualrk refatPas encore d'évaluation
- Flip Flops: Prof. Jagannadha Naidu KDocument14 pagesFlip Flops: Prof. Jagannadha Naidu KArvind kumar PrajapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Flip Flop ExperimentDocument5 pagesFlip Flop ExperimentDeepak KumbharPas encore d'évaluation
- L5: Simple Sequential Circuits and VerilogDocument25 pagesL5: Simple Sequential Circuits and VerilogKadal ChaitraPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 29 30Document50 pagesLecture 29 30amna sajjadPas encore d'évaluation
- LDICA Unit 5 PDFDocument80 pagesLDICA Unit 5 PDFbhanumanuPas encore d'évaluation
- attachment_1 (33)Document2 pagesattachment_1 (33)anthony.onyishi.242680Pas encore d'évaluation
- El G 3336 Digital ElectronicsDocument18 pagesEl G 3336 Digital ElectronicsWaterson MpilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Flip FlopsDocument6 pagesFlip FlopsRahul PendyalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analog and Digital Electronics Lab: Experiment - 7Document16 pagesAnalog and Digital Electronics Lab: Experiment - 7Ashutosh GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- DLD Exp 8 Student ManualDocument8 pagesDLD Exp 8 Student ManualS M AkashPas encore d'évaluation
- Flipflops AnswersDocument6 pagesFlipflops AnswersstudboyPas encore d'évaluation
- DICD Lecture 14 Ver2 Class RoomDocument35 pagesDICD Lecture 14 Ver2 Class Roomjanapaneni ramadeviPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Logic Design Lecture on Sequential CircuitsDocument25 pagesDigital Logic Design Lecture on Sequential CircuitsALEMU DEMIRACHEWPas encore d'évaluation
- Flip FlopsDocument53 pagesFlip FlopsmoretejhonadrianPas encore d'évaluation
- Flip FlopsDocument39 pagesFlip FlopsPradeep KuruvattiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - 05 - Sequential CircuitsDocument43 pagesChapter - 05 - Sequential CircuitsThanh Diện NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- Ex No: 7 Date: Design, Implementation and Verification of Flip FlopsDocument5 pagesEx No: 7 Date: Design, Implementation and Verification of Flip FlopsKARTHIK MPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 SequentialDocument25 pages3 SequentialABHI LIFEPas encore d'évaluation
- VHDL Models of Sequential CircuitsDocument8 pagesVHDL Models of Sequential CircuitsbilgefPas encore d'évaluation
- Sequence Detector PDFDocument9 pagesSequence Detector PDFRahul PendyalaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 SequentialDocument25 pages3 SequentialXXXPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 - Sequential Circuits: Logic and Computer Design FundamentalsDocument20 pagesChapter 5 - Sequential Circuits: Logic and Computer Design FundamentalsFarel IandiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Flip FlopsDocument14 pagesFlip FlopsAnurag ThotaPas encore d'évaluation
- FlipFlops Chapter 5Document27 pagesFlipFlops Chapter 5jenny khanPas encore d'évaluation
- FlipflopDocument20 pagesFlipflopSam BradshawPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic RS Flip-Flop (NAND)Document25 pagesBasic RS Flip-Flop (NAND)XXXPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Flip-FlopsDocument35 pagesUnderstanding Flip-FlopsKaustav MitraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch5 - 1 Latches and Flip FlopsDocument50 pagesCh5 - 1 Latches and Flip FlopsMariam ElnourPas encore d'évaluation
- ECE 545-Digital System Design With VHDL: Digital Logic Refresher Part B - Sequential Logic Building BlocksDocument20 pagesECE 545-Digital System Design With VHDL: Digital Logic Refresher Part B - Sequential Logic Building BlocksAli Mohamed EltemsahPas encore d'évaluation
- Esc201: Introducton To Electronics: Sequental CircuitsDocument34 pagesEsc201: Introducton To Electronics: Sequental CircuitssomeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 9 Areeba Sana 220610Document13 pagesLab 9 Areeba Sana 220610Bismah AsifPas encore d'évaluation
- Name:-Bharat Arora Section: - A Rollno: - 18 University Rollno: - 191500212Document6 pagesName:-Bharat Arora Section: - A Rollno: - 18 University Rollno: - 191500212Deepam AsnaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 9Document8 pagesLab 9Fakhar AbbasPas encore d'évaluation