Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Transnational R
Transféré par
Rohit SharmaDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Transnational R
Transféré par
Rohit SharmaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Transnational R&D projects are managed more easily if the R&D network consists of competence centers such as is the
case for Roche or Schindler, giventhat complementary competencies are provided locally. With increasing comple-mentarity of resources, competencies, and knowledge bases, as well as the divi-sion of labor and specialization of work, synergy potential in R&D projects can beexploited. Productivity measurements of production or sales centers are difficult, but for R&D sites adequate monetary figures indicating management results can be im-plemented only indirectly and with much imperfection. Schindler chose a credit-point-based solution for bringing profit center thinking into R&D: For each pro-ject which is ordered by field operations, a contract is made. After R&D deliversthe new product, the field operations assign credit points for R&D performance.At the end of the year, corporate R&D management results are measured by howmuch the sum of all credit points exceeds the previously agreed R&D budget. Thisintroduces pressure to reduce cycle-times and increase first-pass-yield. Neverthe-less, this scheme has been found inappropriate as a factor in the decision to closedown entire R&D units. Schindler Advanced development, technology scanning & monitoring and development of software,cars, drives, safeties and system concepts, and corporate R&D in Ebikon (CH), Morristown(New Jersey, USA), Shanghai (P. R. China), and Sao Paulo (Brazil) Module development and market-driven development take place at the decentralized sites:landing doors in Melun (F), sheet metal components in Mulhouse (F), electronics in Locarno(CH), hydraulic systems in Stockholm (Sweden) and Morristown (USA), gears in Zaragoza(Spain) As of 2005, approx. 500 engineers in the R&D centers throughout the world Research and advanced development focus on intelligent traffic management, state-of-the-art control systems, and alternative drive technologies, as well as new safety and ride-comfort solutions for topspeed elevators. Environmental impacts - particularly the consumption of energy and materials - are taken into account when developing new products. Schindler Lifts (the worldwide leader in escalators and second in elevators)started to establish a competence-based R&D network in 1996. Schindlers rapidexpansion was based mainly on acquisitions. Its R&D was therefore dispersedover several units in Switzerland, France, Spain, Sweden, Brazil and USA. Inorder to avoid duplication and to realize synergy, its management identified andanalyzed core competencies in R&D. These core competencies and the changefrom a functional organization (i.e. software,
mechanics, electronics) to a module-oriented organization (i.e. drive, control, hoistway, car) were the basis for a major reorganization of R&D in 1998. In the new organization, R&D activities wereconducted in three areas: corporate R&D, manufacturing R&D and field opera-tions engineering. Each R&D area had its own mission; the efficient cooperationof these areas in a highly interdependent network was a prerequisite for the lowcycle-time development of advanced product systems (Fig. I.4.12).
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Standards For Parking DesignDocument21 pagesStandards For Parking DesignPoorvi SarepakaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Catalog Kleemannn 2019Document19 pagesCatalog Kleemannn 2019Gîlea ȘtefanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
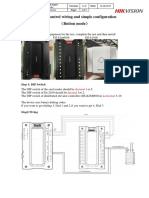
- Elevator Control Wiring and Simple Configuration: Button ModeDocument7 pagesElevator Control Wiring and Simple Configuration: Button ModeAgnelo FernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Five Star Hotel Space ProgramDocument22 pagesFive Star Hotel Space ProgramMark Gella Delfin77% (69)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Multilift Installation GuideDocument42 pagesMultilift Installation GuideMagtanggol Relucio100% (1)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Elevex ENDocument4 pagesElevex ENMirko Mejias SotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Saltation Velocity Calcuations PDFDocument8 pagesSaltation Velocity Calcuations PDFArun AppaduraiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cibes BrochureDocument32 pagesCibes Brochureapi-232605923Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- GDCR RudaDocument223 pagesGDCR RudaAshutosh Maru100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Cat Forklift Ep30k Service ManualDocument10 pagesCat Forklift Ep30k Service Manualsamanthamoyer170885csp100% (81)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Pit and Dump DesignDocument30 pagesPit and Dump DesignLucas GonzagaPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Bill of Quantity - BoilerDocument18 pagesBill of Quantity - BoilerVijay Raj100% (1)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- 03 Operating Manual Part 1 INDUPRESS General Part 2009 07 v1Document42 pages03 Operating Manual Part 1 INDUPRESS General Part 2009 07 v1Kokić Mirza100% (1)
- DHT - Latch-Les Wireline Coring SystemDocument33 pagesDHT - Latch-Les Wireline Coring SystemesandovalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pulley Lagging PDFDocument2 pagesPulley Lagging PDFSanatha AgungPas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- PDMS Fire Safety Reqmts For 2 Dec10Document26 pagesPDMS Fire Safety Reqmts For 2 Dec10usernaga84Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- 7 14 PDFDocument4 pages7 14 PDFJames MPas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- DOE-STD-1090-2007 Hoisting and Rigging Standard ToCDocument17 pagesDOE-STD-1090-2007 Hoisting and Rigging Standard ToCbenzfliegerPas encore d'évaluation
- Fire Protection of High Rise BuildingsDocument2 pagesFire Protection of High Rise Buildingsvenkateswara rao pothinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anderson Greenwood - Pentair Series 400 Modulating Datasheet PDFDocument4 pagesAnderson Greenwood - Pentair Series 400 Modulating Datasheet PDFSARATH KRISHNAKUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Sitdown Counterbalance sc4500 SpecDocument6 pagesSitdown Counterbalance sc4500 SpecCoque de LunaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1091)
- Transferring of ClientsDocument5 pagesTransferring of ClientsJaviePas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment of Lifting OperationDocument18 pagesAssessment of Lifting Operationafif atmajaPas encore d'évaluation
- AS 7 Wire Rope HoistDocument24 pagesAS 7 Wire Rope HoistDwiMaryantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Alaya BrochureDocument54 pagesAlaya BrochureGraze DPas encore d'évaluation
- Safe Job Procedures SJPDocument49 pagesSafe Job Procedures SJPapi-317342021Pas encore d'évaluation
- HTM 82-Health CareDocument39 pagesHTM 82-Health CareAbraham JyothimonPas encore d'évaluation
- Installation Manual PDFDocument64 pagesInstallation Manual PDFTharaka Kotambage100% (2)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Project Execution AND Quality Plan: Akr Sdn. BHDDocument32 pagesProject Execution AND Quality Plan: Akr Sdn. BHDShah KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Booklet 17: Installation Instructions For SpiritDocument112 pagesBooklet 17: Installation Instructions For SpiritJaime MarchantPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)